
Application of the Technique of Magnetic Resonance Voxel-based
Morphometry in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis before and after
using High-dose Immunosuppressive Therapy with Autologous
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Preliminary Results
E. A. Gorbunova
1
, G. N. Bisaga
2
, A. G. Trufanov
3
, M. P. Topuzova
2
, A. V. Fokin
1
, A. G. Levchuk
1
,
A. A. Medenikov
1
, E. D. Vyshedkevich
1
, T. A. Bukkieva
1
, A. Yu.
Efimtsev
1
and I. A. Mashchenko
1
1
MRI Department, Almazov National Medical Research Centre, Akkuratova str., 2, Saint-Petersburg, Russian Federation
2
Neurology Department, Almazov National Medical Research Centre, Akkuratova str., 2, Saint-Petersburg,
Russian Federation
3
Neurology Department, Military Medical Academy n.a. S. M. Kirov, Lebedeva str., 6, Saint-Petersburg,
Russian Federation
Keywords: Multiple Sclerosis, Morphometry, Voxel-based Morphometry, Autologous Haematopoietic Stem Cell
Transplantation.
Abstract: Correlation analysis of magnetic resonance voxel-based morphometric parameters of patients with multiple
sclerosis before and after high-dose immunosuppressive therapy with transplantation of autologous
hematopoietic stem cells (HDIT + AHSCT). The use of MR-morphometry methods makes it possible to
quantitatively and objectively changes of the volume and size of the structures of the brain and cerebellum in
patients with MS. We observed 10 patients with MS (3 men, 7 women) who underwent HDIT + AHSCT, and
MRI studies were performed before and after transplantation. After postprocessing of MRI data and statistic
analyses of morphometry parameters some changes were accrued: some patients showed negative dynamics
in white and grey mater volumes and decrease of the absolute volume of the thalamus. Also, study showed
positive dynamics in reducing the number of new MS lesions. These results can be associated with the result
of treatment, with a local decrease in edema and inflammation. Study showed the need for dynamic MR
control of the grey and white matter of the brain and subcortical structures with the help of MR morphometry.
ABBREVIATIONS
MS – multiple sclerosis
VBM – voxel-based morphometry
GM – grey matter
WM – white matter
HDIT – high-dose immunosuppressive therapy
AHSCT – autologous stem cell transplantation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease of
the central nervous system characterized by frequent
episodes of inflammation with demyelination and
neurodegeneration (Lipp, 2018). MS usually begins
at a young age (20–40 years) and is more common in
women. (Lublin, 2014). MS is characterized by an
immune attack on the myelin surrounding the axons
of neurons. This inflammation can damage the axons.
Evidence of neurodegeneration that extends beyond
inflammatory foci is the primary neurodegenerative
component of MS followed by secondary
inflammation (Lipp, 2018; Trapp, 2008; Stys 2012).
Traditionally lesions in multiple sclerosis are the
focus of diagnosis, prognosis and evaluation for
treatment. More recently, studies in multiple sclerosis
have focused on abnormalities in a brain and brain
volume loss, not only as predictors, but also as a result
of clinical trials evaluating the effectiveness of the
treatment (Lipp, 2018).
According to statistics, the prevalence of MS is
50–100 cases per 100 thousand population. There are
more than 2 million patients with multiple sclerosis in
the world. In addition, the average age of patients
Gorbunova, E., Bisaga, G., Trufanov, A., Topuzova, M., Fokin, A., Levchuk, A., Medenikov, A., Vyshedkevich, E., Bukkieva, T., Efimtsev, A. and Mashchenko, I.
Application of the Technique of Magnetic Resonance Voxel-based Morphometry in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis before and after using High-dose Immunosuppressive Therapy with
Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Preliminary Results.
DOI: 10.5220/0010389902430248
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2021) - Volume 1: BIODEVICES, pages 243-248
ISBN: 978-989-758-490-9
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
243

with this disease has dropped significantly and the
disease usually affects the working-age population.
There are different types of MS: a type with
repeated exacerbations and periods of remission, the
so-called "relapsing-remitting type", which can later
develop into a "secondary progressive type" or may
also have persistent progression from the onset of the
disease with no relapses or remissions - "primary
progressive type" (Silva, 2018; Lublin, 2014).
MS is characterized by a progressive course.
Current disease-modifying therapy inevitably leads to
disability, loss of the ability to provide self-care and
loss of cognitive functions.
Today, different neuroimaging techniques such as
magnetic resonance spectroscopy - quantitative
determination of metabolites in tissues, diffuse tensor
MRI (DTI) (Ontaneda, 2017; Das, 2019), magnetic
resonance morphometry have the potential to reveal
the pathogenic mechanisms of the disease and
determine the markers of the neurodegenerative and
atrophic process in multiple sclerosis (Bogachev,
2014).
The method of high-dose immunosuppressive
therapy with transplantation of autologous
hematopoietic stem cells (HDIT + AHSCT) is
intended to provide specialized medical care to
patients with MS. HDIT + AHSCT is considered by
the American Society for Blood and Bone Marrow
Transplantation (ASBMT) as the “standard”
treatment for MS in the nearest future, because this
course of treatment can possibly regenerate the cells
of immune system repertoire and enhance the
immune tolerance (Cohen 2019; Mancardi, 2017,
Gholamzad, 2018). This method of treatment has a
long-term immunomodulation effect, as a result of
which 85% of patients after AHSCT maintain a stable
remission from 5 years and more. This method is
relatively safe, but unfortunately, it is expensive and
is not included in the standards of care for MS
patients.
Atrophy of the grey (GM) and white matter (WM)
of the brain and subcortical structures is manifested
in the early stages of the disease, and its degree
correlates with physical and cognitive impairment.
The effect of treatment on cerebral atrophy predicts
further disability (Ontaneda, 2017; Righart, 2017;
Ghione, 2018). The annual decrease of brain volume
occurs 4 times more often in patients with
apolipoprotein E-e4 in the genotype, than in patients
without it. However, according to other studies, the
genotype with the presence of apolipoprotein E-e4
does not affect the degree of atrophy (Fernandez,
2015). Initially, the presence of cerebral atrophy in
patients with MS was qualitatively identified like an
expansion of the cerebral ventricles and subarachnoid
spaces and a decrease in the volume of brain matter.
The next step was the automatic quantitative
assessment of brain atrophy using voxel magnetic
resonance morphometry (Krotenkova, 2014).
Magnetic resonance morphometry is an accurate
quantitative technique that allows to study changes in
volumetric parameters of brain structures in different
diseases, including those with MS. In addition, MR-
morphometry can be informative in assessing the
treatment and dynamics of the disease development.
2 PURPOSE
To establish significant changes in the structures of
the brain of the patients with MS as a result HDIT +
AHSCT treatment using magnetic resonance voxel-
based morphometry.
3 MATERIALS AND METHODS
3.1 Study Population
An open, single-center, uncontrolled study of the
results of magnetic resonance voxel-based
morphometry of patients with MS before and after
HDIT + AHSCT (at two time points with an interval
of about 12 months).
The HDIT + AHSCT is conducted in several
stages, which occurred sequentially and included
mobilization and procurement of hematopoietic stem
cells (HSC), cryopreservation of HSC,
immunosuppression state by therapy with doses of
cyclophosphamide and rituximab, and transplantation
of HSC with subsequent support therapy with post-
transplant rehabilitation and assessment of
effectiveness.
The mobilization and procurement of HSC was
carried out in two stages:
1) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-
CSF) - dose 10 μg / kg / day (4 days)
2) Leukocytapharesis (5th day) when the total
number of leukocytes reaches more than 10x10 ^ 9 /
The number of CD34 + cells in leukopheresis
products should be 2-4x106 / kg of body weight.
Cryopreservation of the HSC was carried out with
10% dimethyl sulfoxide, followed by its storage at
-180°C in liquid nitrogen until transplantation.
Conditioning was carried out using high-dose
immunosuppressive therapy with cyclophosphamide
(50-200 mg/kg) with rituximab (500 mg/m^2).
NDNSNT 2021 - Special Session on Non-invasive Diagnosis and Neuro-stimulation in Neurorehabilitation Tasks
244

AHSCT was performed after thawing the frozen
graft in a water bath at a temperature of 37°C. The
transplantation of AHSC was carried out through a
central venous catheter.
Support therapy was aimed at symptomatic
treatment and treatment of AHSCT complications.
We observed 10 patients with MS (3 men, 7
women) who underwent HDIT + AHSCT, and MRI
studies were performed in 2 time points: before and
after transplantation. In this study, the small sample
of patients is due to the small number of patients who
underwent transplantation. The average age of the
patients was 41.6 ± 8.9 years.
The inclusion criteria of the patients for HDIT +
AHSCT were:
1. Age 18-65 years; verified diagnosis of MS;
EDSS 1.0-6.5;
2. The presence of confirmed progression of the
disease against the background of standard therapy;
3. Deterioration in EDSS by 1 point or more at
baseline level <5 points, deterioration in EDSS by 0.5
point or more at baseline level> 5 points;
4. The emergence of new (including Gd +) MS
lesions;
5. Absence of severe concomitant pathology; no
treatment with interferon drugs and
immunosuppressants in the last 3 months.
3.2 MR Imaging Protocol
MRI studies were carried out on a high-field magnetic
resonance imager "Siemens Magnetom Symphony"
with a magnetic field induction of 1.5 T using a head
coil.
All patients underwent structural MRI with
obtaining T1 and T2 weighted images and FLAIR
(Fluid attenuated inversion). Pulse sequence data of a
T1-weighted gradient echo (MP-RAGE -
Magnetization Prepared Rapid Acquired Gradient
Echoes) was collected to combine MRI data of
anatomical structures of the brain, (slice thickness -
4.5 mm, number of slices - 29, the number of
repetitions - 120, scan time - 6 minutes). This
sequence has high resolution with 0.8 mm isotropic
voxeles.
3.3 Image Analyses
At present, mathematical models have been
developed, with the help of which we can analyse
“thin” (not visible on MRI tomograms)
morphological changes, including secondary atrophic
changes in MS, which can be quantified and
presented topographically. One of the new and very
promising methods used to quantify GM, WM and
lesion volume is voxel-based morphometry (VBM).
The VBM workflow includes three main
preprocessing steps:
(1) Tissue classification, which is based on
intensity values and mainly serves to segment the
brain into grey matter, white matter, cerebrospinal
fluid after "removal" of the skull bones and other
structures of the head.
(2) Spatial normalization (linear and non-linear) -
needed to provide matching across brain voxels, in
accordance with the individual brain anatomy of each
person.
(3) Spatial smoothing, followed by statistical
analysis. Smoothing, since spatial normalization is
not ideal and small individual differences in the
anatomy of the brain remain. Spatial smoothing takes
into account these residual differences in local
anatomy. Therefore, after smoothing, each voxel is a
sphere, which is similar to the smoothing kernel, or,
in other words, the weighted average of the values
and values of adjacent voxels (Kurth, 2015; Gaser,
2016).
For morphometric evaluation, T1-WI images
were converted from the standard digital imaging and
communication (DICOM) format (.dcm) to the
Neuroimaging Informatics Technology Initiative
(NIfTI) (.nii) format suitable for analysis and post-
processing using the SPM12 - CAT extension.
Volumetric analysis using CAT allows to accurately
assess the structure of the brain and to avoid operator
errors when carrying out "manual" segmentations.
3.4 Data Analysis
Longitudinal evaluation of the results of
neuroimaging studies of each patient individually, as
well as their group totality (analysis of morphometry
volumetric data) were carried out.
Correlations between results of MR-morphometry
in 2 time points (before and after stem cell
transplantation) were established. Statistical
processing of the received data were carried out using
the package Statistica by StatSoft, (Mann- Whitney
test). Differences were considered significant at p
<0.005. Correlations were calculated using
Spearman's test.
3.5 Results
When assessing the dynamics of morphometric
indicators of the same patients at two time points
(before and after HDIT + AHSCT), 70% of patients
showed negative dynamics in white matter atrophy,
Application of the Technique of Magnetic Resonance Voxel-based Morphometry in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis before and after using
High-dose Immunosuppressive Therapy with Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Preliminary Results
245
while other 20% showed positive dynamics
(increased white matter volume), 10% showed no
change). Besides, 70% of patients have had negative
dynamics in grey matter atrophy (other 30% ща
patients showed positive dynamics in grey matter
atrophy).
Average
GM volume
(cm
3
/%)
Average
WM volume
(cm
3
/%)
Before HDIT+
AHSCT
735,150
±72,379
487,896
±91,716
After HDIT+
AHSCT
720,432
±54,347
459,019
±90,089
In addition, 62.5% of patients showed positive
dynamics in reducing the number of new MS lesions,
which also can be associated with the result of
treatment, with a local decrease in edema and
inflammation.
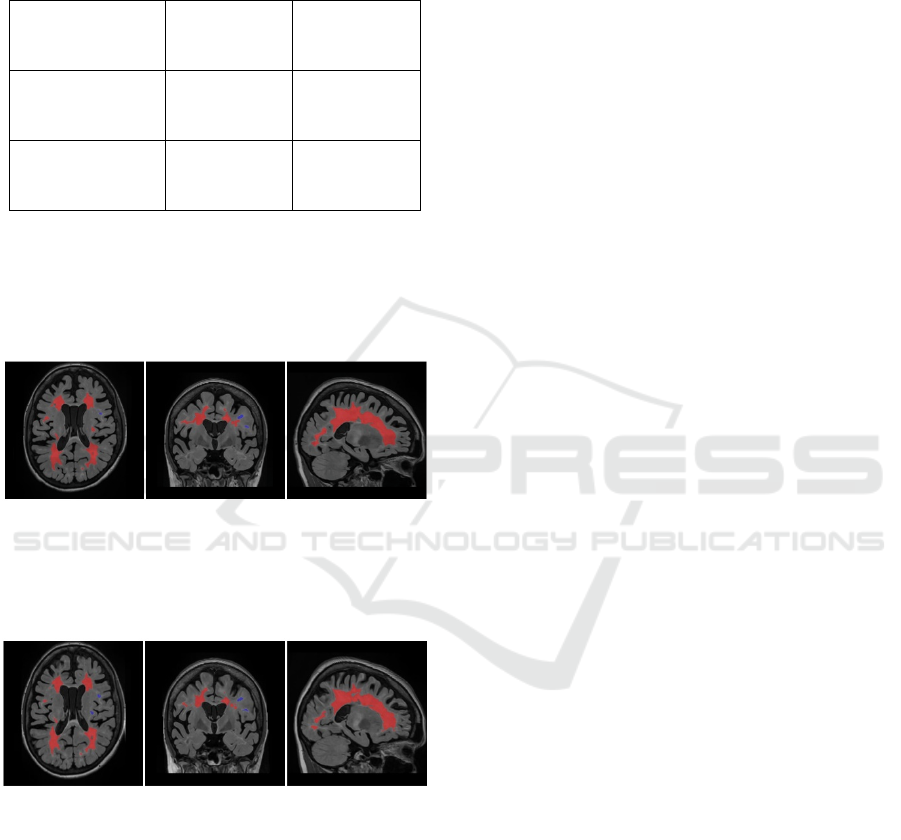
a b c
Figure 1: (a - axial, b - coronal, c - sagittal coronal). The
results of MRI morphometry of the lesions of 42 y.o. female
patient before HDIT + AHSCT. Red colour indicates MS
lesions.
a b c
Figure 2: (a - axial, b - coronal, c - sagittal coronal).The
results of MRI morphometry of the lesions of 42 y.o. female
patient after HDIT + AHSCT. Red colour indicates MS
lesions.
In 84% of the cases, there is a decrease of the
absolute volume of the thalamus (in cm ^ 3/%), while
in 50% of the cases the decrease was below the
average age norm. All these patients had a secondary
progressive type of MS, while statistically the
decrease of the volume of thalamus was not
associated with the duration of the disease or EDSS
score.
When discussing central nervous system atrophy
and MRI morphometry data in MS, it should be
mentioned that, in addition to the gradually increasing
loss of brain matter in MS, short-term brain volume
fluctuations may also occur. Inflammation and edema
as a result of the formation of new lesions lead to a
temporary increase of the brain volume, and vice
versa, for example, taking corticosteroids leads to a
short-term decrease of it - pseudoatrophy. The
mechanism of this process is not entirely clear, but it
is believed that this occurs as a result of a decrease in
inflammation in the central nervous system and
associated edema (Krotenkova, 2014). As a
rconsequence of the ongoing treatment of
HDIT+AHSCT and the anticipated results of this
treatment, it is expected that the decrease in the
absolute volumes of GM and WM is associated with
a decrease of edema and inflammation of the brain.
However, further dynamic observation is necessary,
due to the likelihood of an incorrect interpretation of
the results, since a decrease of brain volumes may be
associated with the ongoing process of
neurodegeneration. It is well known, that cerebral
atrophy occurs at all stages of MS, since at the
preclinical stages of the disease, and progresses
throughout the disease at a faster rate than during the
normal aging process (Inglese, 2018; Fox, 2016).
A. Cifelli et al. It was shown that, compared with
the control group, of patients with a secondary
progressive type of the disease, the volume of the
thalamus decreased by 17%, and the transverse size
of the third ventricle doubled, and a clear inverse
relationship between their volumes was revealed. The
above MRI data are confirmed by histological
studies: a decrease of the number of neurons in the
medial posterior thalamic nucleus and a decrease of
the total volume of the thalamus by 22% was revealed
(Cifelli, 2002). It has also been proven that the reduce
of thalamus volume annually increases by -0.71% per
year (Azevedo, 2018).
4 CONCLUSIONS
The use of MR-morphometry methods makes it
possible to quantitatively and objectively detect
changes of the volume and size of the structures of the
brain and cerebellum in patients with MS. The most
significant results were obtained for the amount of
WM atrophy in patients with MS. The changes
identified in our study correspond to the data of some
other studies: the process of neurodegeneration can
NDNSNT 2021 - Special Session on Non-invasive Diagnosis and Neuro-stimulation in Neurorehabilitation Tasks
246

last up to 1-2 years after the start of therapy with HSC.
This indicates the need for dynamic MR control of the
grey and white matter of the brain and subcortical
structures using MR morphometry to assess the
effectiveness of treatment and the patient’s life
prognosis. Besides, these results can be used for
assessing the prediction of the further course of
multiple sclerosis for patients who underwent
HDIT+AHSCT.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no conflict of interest
REFERENCES
Silva, B. A., Ferrari, C. C. Cortical and meningeal
pathology in progressive multiple sclerosis: a new
therapeutic target? Reviews in the Neurosciences.
2018; 0 (0). DOI:10.1515/revneuro-2018-0017
Ontaneda, D., Thompson, A. J., Fox, R. J., & Cohen, J. A.
Progressive multiple sclerosis: prospects for disease
therapy, repair, and restoration of function. The Lancet.
2017; 389 (10076): 1357–1366. DOI:10.1016/s0140-
6736(16)31320-4
Kurth, F., Luders, E., & Gaser, C. Voxel-Based
Morphometry. Brain Mapping. 2015; 345–349.
DOI:10.1016/b978-0-12-397025-1.00304-3
Righart, R., Schmidt, P., Dahnke, R., Biberacher, V., Beer,
A., Buck, D., Mühlau, M. Volume versus surface-based
cortical thickness measurements: A comparative study
with healthy controls and multiple sclerosis patients.
PLOS ONE. 2017; 12 (7), 0179590. DOI:10.1371/
journal.pone.0179590
Krotenkova, I.A., Brukhov, V.V., Peresedova, M.V.,
Krotenkova, M.V. Atrophy of the central nervous
system in multiple sclerosis: MRI-morphometry
results. Neurology and Psychiatry journal. 2014; 10 (2)
(in Russian).
Cifelli, A., Arridge, M., Jezzard, P., Esiri, M.M., Palace, J.,
Matthews, P.M. Thalamic neurodegeneration in
multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2002; 52: 5:
650—653.
Gaser, C. Structural MRI: Morphometry. Studies in
Neuroscience, Psychology and Behavioral Economics.
2016; 399–409. DOI:10.1007/978-3-642-35923-1_21
Inglese, M., & Petracca, M. MRI in multiple sclerosis.
Current Opinion in Neurology. 2018.
DOI:10.1097/wco.0000000000000559
Fox, J., Kraemer, M., Schormann, T., Dabringhaus, A.,
Hirsch, J., Eisele, P., Gass, A. Individual Assessment
of Brain Tissue Changes in MS and the Effect of Focal
Lesions on Short-Term Focal Atrophy Development in
MS: A Voxel-Guided Morphometry Study.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17
(4), 489. DOI:10.3390/ijms17040489
Cohen, J. A., Baldassari, L. E., Atkins, H. L., Bowen, J. D.,
Bredeson, C., Carpenter, P. A., Georges, G. E.
Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for
TreatmentRefractory Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis:
Position Statement from the American Society for
Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biology of Blood
and Marrow Transplantation. 2019. DOI:10.1016/
j.bbmt.2019.02.014
Das, J., Sharrack, B., Snowden, J.A. Autologous
Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Multiple
Sclerosis: a Review of Current Literature and Future
Directions for Transplant Haematologists and
Oncologists. Current Hematologic Malignancy
Reports. 2019; 14: 127–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/
s11899-019-00505-z
Bogachev, Yu. V., Cherdakov, O. A., Fokin V.A. Magnetic
resonance imaging in the diagnostics of multiple
sclerosis. Izvestia ETU "LETI". 2014; 3: 7-15. (In
Russian)
Mancardi, G., Sormani, M. P., Muraro, P. A., Boffa, G.,
Saccardi, R. Intense immunosuppression followed by
autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation as
a therapeutic strategy in aggressive forms of multiple
sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis Journal. 2017; 24 (3): 245–
255. DOI:10.1177/1352458517742532
Lipp, I., Muhlert, N., Tomassini, V. Brain Morphometry in
Multiple Sclerosis. Brain Morphometry. 2018; 279–
300. DOI:10.1007/978-1-4939-7647-8_17
Haider, L., Zrzavy, T., Hametner, S., Höftberger, R.,
Bagnato, F., Grabner, G., Lassmann, H. The topograpy
of demyelination and neurodegeneration in the multiple
sclerosis brain. Brain. 2016; 139 (3): 807–815.
DOI:10.1093/brain/awv398
Lublin, F. D., Reingold, S. C., Cohen, J. A., Cutter, G. R.,
Sorensen, P. S., Thompson, A. J., Polman, C. H.
Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: The
2013 revisions. Neurology. 2014; 83 (3): 278–286.
DOI:10.1212/wnl.0000000000000560
Trapp, B. D., Nave, K.-A. Multiple Sclerosis: An Immune
or Neurodegenerative Disorder? Annual Review of
Neuroscience. 2008; 31(1): 247–269.
DOI:10.1146/annurev.neuro.30.051606.094313
Stys, P. K., Zamponi, G. W., van Minnen, J., Geurts, J. J.
G. Will the real multiple sclerosis please stand up?
Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2012; 13 (7): 507–514.
DOI:10.1038/nrn3275
Fernandez, O., Alvarez-Cermeno, J.C., Arroyo-Gonzalez,
R., Brieva, L., CallesHernandez, M.C., Casanova-
Estruch, B. et al. Review of the novelties presented at
the 27th Congress of the European Committee for
Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis
(ECTRIMS) (I). Revista de Neurologia. 2012; 54: 11:
677—691.
Ghione, E., Bergsland, N., Dwyer, M. G., Hagemeier, J.,
Jakimovski, D., Paunkoski, I., Zivadinov, R. Brain
Atrophy Is Associated with Disability Progression in
Patients with MS followed in a Clinical Routine.
Application of the Technique of Magnetic Resonance Voxel-based Morphometry in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis before and after using
High-dose Immunosuppressive Therapy with Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Preliminary Results
247

American Journal of Neuroradiology. 2018; 39: 2237–
42. DOI:10.3174/ajnr.a5876
Azevedo, C. J., Cen, S. Y., Khadka, S., Liu, S., Kornak, J.,
Shi, Y., Pelletier, D. Thalamic atrophy in multiple
sclerosis: A magnetic resonance imaging marker of
neurodegeneration throughout disease. Annals of
Neurology. 2018; 83 (2): 223–234. DOI:10.1002/
ana.25150
Gholamzad, M., Ebtekar, M., Ardestani, M. S., Azimi, M.,
Mahmodi, Z., Mousavi, M. J., Aslani, S. A.
Comprehensive review on the treatment approaches of
multiple sclerosis: currently and in the future.
Inflammation Research. 2018. DOI:10.1007/s00011-
018-1185-0
Iskhakova, E.V., Lepekhina, A.S., Batozhargalova, Ya.B.,
Komlichenko, E.E., Fokin, V.A., Trufanov, A.G.,
Yurin, A.A., Potemkina, E.G. Features of the atrophic
process in progressive supranuclear paralysis according
to magnetic resonance morphometry (2020) Russian
Electronic Journal of Radiology, 10 (1), pp. 43-49.
DOI: 10.21569/2222-7415-2020-10-1-43-49
Sokolov, A.V., Vorobyev, S.V., Efimtcev, A.Y., Dekan,
V.S., Trufanov, G.E., Lobzin, V.Y., Fokin, V.A. fMRI
and voxel-based morphometry in detection of early
stages of Alzheimer's disease (2017) BIOIMAGING
2017 - 4th International Conference on Bioimaging,
Proceedings; Part of 10th International Joint
Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and
Technologies, BIOSTEC 2017, 2017-January, pp. 67-
71. DOI: 10.5220/0006109600670071
NDNSNT 2021 - Special Session on Non-invasive Diagnosis and Neuro-stimulation in Neurorehabilitation Tasks
248
