
A Thermochromic Ink Heater-cooler Color Change System for
Medical Blood Simulation
Mohammad Noorizadeh, Abdullah Alsalemi, Yahya Alhomsi, Faycal Bensaali and Nader Meskin
Department of Electrical Engineering, Qatar University, Doha, Qatar
Keywords: Simulation-based Training (SBT), Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO), Blood Oxygenation,
Thermochromism, High-fidelity Simulation, Temperature Control.
Abstract: Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is a modified form of CPB that supports intensive care
patients’ vital functions during recovery from cardiac or pulmonary trauma. ECMO, although lifesaving, is
vulnerable to a plethora of mechanical complications which can cause mortality. This is why developing
advanced training systems is of crucial importance. In this paper, as part of an ECMO simulator for training
management, a novel thermochromic heater-cooler system is presented. The need of such contribution arises
from the lack of high-realism blood simulation methodologies Hence, developed upon thermochromic ink,
cost-effective blood simulation is achieved by temperature adjustment, simulating oxygenation and
hypoxemia. The system has been developed as a prototype with successful and reversible transitions between
dark and bright red blood color. After addressing the limitations, the heater-cooler will be integrated with the
ECMO simulator, allowing unpreceded cost-efficient simulation possibilities.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is technique that is
employed to take over a patient’s blood circulation
and oxygenation functions, and is commonly used
during open-heart surgery; allowing surgeons to
easily operate on a beat-less heart (What Is
Cardiopulmonary Bypass?, 2004). Extracorporeal
membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is a modified form
of CPB that supports intensive care patients’ vital
functions during recovery from cardiac or pulmonary
trauma (What Is Cardiopulmonary Bypass?, 2004).
Patients are connected to ECMO via cannula and
tubes and their deoxygenated blood is drained and
pushed through an oxygenation membrane using a
pump (“What Is ECMO?,” 2016). The membrane
facilitates blood oxygenation, and the pump draws
and returns the blood to the patient; replacing the
patient’s lung and/or heart function (“What Is
ECMO?,” 2016).
Recent technological advancements in ECMO
have made it a simpler and safer procedure; boosting
survival rates up to 70%, across age groups and
making ECMO an increasingly adopted technique
(MacLaren et al., 2012; Nichani, 2011).
Consequently, the demand for highly trained
individuals that can operate the machine has
increased. ECMO, although lifesaving, is vulnerable
to a plethora of mechanical complications which can
cause mortality. Common ECMO complications on
the machine side are air entrainment, oxygenator
failure, pump failure, and blood clots (Lafçı et al.,
2014). Such high risk emergencies require ECMO
staff to process critical problem identification skills,
make quick interventions, have common behavioral
patterns to work as an effective team, and good
communication skills to decrease ECMO support
suspension; hence avoiding mortality (Peets & Ayas,
2013).
ECMO educators have used simulation modalities
to create realistic and high risk scenarios to instill
positive technical and behavioral patterns in their
trainees (Brazzi et al., 2012; Chan et al., 2013).
However, due to lack of support, ECMO simulation
methods are still relatively primitive. They consist of
modifying a mannequin to enable circulation,
connecting the mannequin to a colored water filled
ECMO circuit, and using workarounds like manually
injecting air into the circuit to trigger alarms and
initiate the simulated emergency (Anderson et al.,
2006; Ng et al., 2016). Current ECMO simulation
practices suffer from high initial and reoccurring
costs due to the use of medical equipment and
Noorizadeh, M., Alsalemi, A., Alhomsi, Y., Bensaali, F. and Meskin, N.
A Thermochromic Ink Heater-cooler Color Change System for Medical Blood Simulation.
DOI: 10.5220/0010264001070113
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2021) - Volume 1: BIODEVICES, pages 107-113
ISBN: 978-989-758-490-9
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
107
expensive circuit consumables such as the
oxygenation membrane. It also offers little fidelity
and interactivity relative to the cost; the circuit does
not visually simulate blood oxygenation color
differentials unless they use real blood and
deoxygenate the it with carbon dioxide (CO
2
)
through a modified circuit, but the display of custom
information on the ECMO console often remains a
challenge.
Thermochromic ink is a special ink with a
chemical composition that reacts to temperature by
changing its hue (Abdullah Alsalemi, Aldisi, et al.,
2017). The ink can be customized to switch between
two colors at a set temperature; for example, going
from red to invisible when a pizza box is under 40°C.
On the other hand, the blood oxygenation process is
where the lung (or ECMO oxygenator) exchanges
blood CO
2
for oxygen (O
2
). The oxygenation process
is visually represented with a clear blood color
differential; blood changes from dark red to red as it
loses CO
2
and gains O
2
. Blood color differentials
serve as an important diagnostic tool for ECMO staff;
indicating lack of oxygen in the circuit.
Thermochromic can be used to simulate blood
oxygenation by customizing it to shift between dark
red and red and placing it within a system that
continuously manipulates its temperature above and
below a defined threshold. Incorporating
thermochromic ink into current ECMO simulation
practice means increased fidelity; by introducing the
oxygenation visual effect, and reduced cost; by
getting rid of expensive consumables that do not
introduce any actual functionalities to the simulation
environment.
In order to operate thermochromic ink in ECMO
simulations, a temperature control system is needed.
It also needs to be compact, efficient, and
controllable. In this paper, we are presenting a novel
heater-cooler system for thermochromic ink control,
where oxygenation and deoxygenation can be
simulated.
The remainder of this paper is organized is
follows. Section 2 describes the overall simulation
system. Section 3 elaborates on the design of the
heater-cooler system. Section 4 presents and
discusses preliminary results of the first prototype.
The paper is concluded with future work in Section 5.
2 OVERVIEW OF THE
MODULAR ECMO
SIMULATOR
This section describes the research and development
processes behind the proposed ECMO training system.
The training system is focused on practically training
practitioners for ECMO on adult patients (A. Alsalemi,
Al Disi, et al., 2017). The system is expected to be used
alongside a strong theoretical course to develop a solid
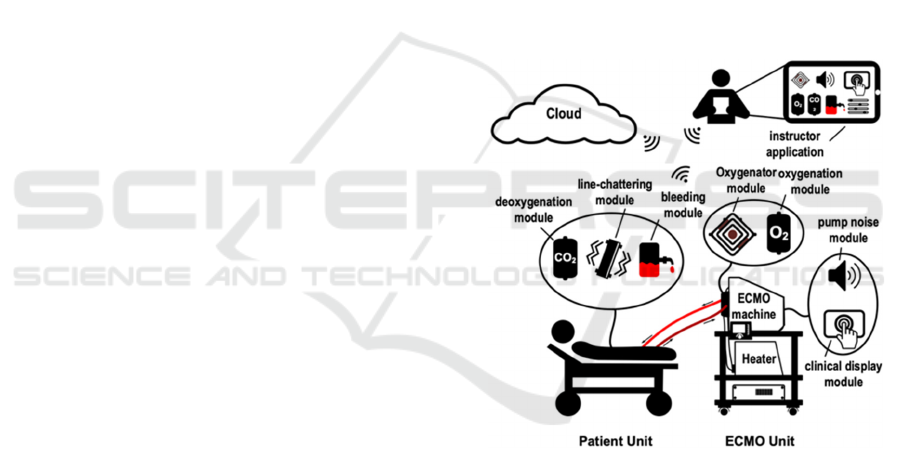
foundation. Figure 1 depicts the proposed system’s
block diagram comprising three physical subsystems:
the patient unit, the ECMO unit, and the oxygenator all
centered around the thermochromic loop. Each unit
includes simulation modules as shown in the diagram.
To control the operation of those modules, a
communications system is developed, and connected
to a tablet application for instructors to steer the
training experience for a smooth learning experience.
Figure 1: Overview of proposed training system.
The thermochromic loop is a system designed
around using thermochromic ink to simulate basic
ECMO functionalities; circulation and oxygenation.
The patient unit contains a tank that houses a
thermochromic ink mixture diluted in water and
includes red and black. The black ink can be
deactivated and activated above and below 30°C
respectively. The thermochromic mixture is pushed
through the circuit using a brushless DC pump. It
goes out of the patient unit and heads towards a mock
oxygenator which bypasses it to the heater unit below.
The heater unit heats the mixture causing it to lose its
dark color; simulating oxygenation. The mixture then
returns to the patient station where it is cooled down;
BIODEVICES 2021 - 14th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
108
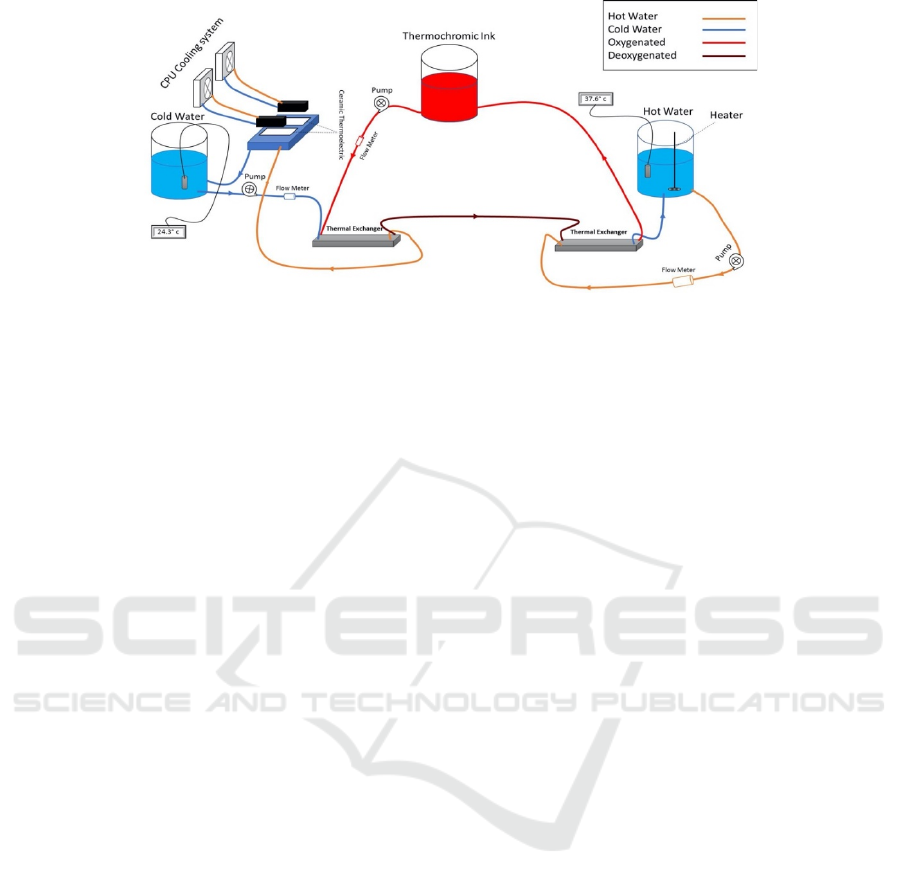
Figure 2: Block diagram of the thermochromic heater-cooler system.
gaining its dark color back and simulating
deoxygenation.
The loop function relies on continuously adding
and removing heat in and out of the mixture; making
the appropriate design of the heat exchange process
of utmost importance.
The proposed system is constituted of the primary
and secondary loop. The primary loop is where the
thermochromic mixture flows; it includes two heat
exchangers (one with a cold-water stream and another
with a hot-water stream), a pump, and a reservoir tank
placed inside the patient unit. The secondary loop is
between the source of the water streams and the heat
exchangers (Al Disi et al., 2018).
In addition, the simulator contains a variety of
simulation modules, each specially designed to
physically, audibly, or haptically imitate a certain
ECMO phenomena. Examples include line breakage,
patient bleeding, head pump noise, among others (Al
Disi et al., 2017).
Moreover, the simulator system has been
holistically thought out in the point of views of both
the learner and the instructor (Alhomsi et al., 2018;
Abdullah Alsalemi et al., 2018; Abdullah Alsalemi,
Homsi, et al., 2017). The teaching aspect has been
supported by the development of two innovative
software components: the instructor tablet application.
The application is comprised of two parts: the scenario
designer and the live control panel, both connected to
a CouchDB cloud server for parameter and wireless
scenario transmission (Al Disi et al., 2019).
3 METHODS
3.1 Thermoelectric Module
The fundamental underlying operation of the
thermochromic loop is heat exchange;
increasing/decreasing temperature to above/below
the ink’s specific deactivation temperature. The ink
mixture used is a combination of black and red, with
deactivation temperatures of 31°C and 47°C
respectively. In this case, the ink used has a
transitional region between 27℃ to 32℃; where the
liquid color moves between light and dark red. Thus,
the heat exchange process is required to cool/heat the
liquid below/above the transitional region.
A thermoelectric module is a transducer that can
generate electricity by applying heat and vice versa
(i.e. the Peltier effect). Indeed, by injecting current to
the thermoelectric module, heat can be produced.
Therefore, when the current is fed to thermoelectric
module, it flows through two different semi-
conductors, and consequently, the heat or the cold
will be generated. In the other words, a thermoelectric
module has two faces, once one of them gets cold, the
other face become hot. Furthermore, the performance
of cooling side is directly related to the heating face,
which means that, by decreasing the temperature of
the heating side, the performance of cooling side will
increase significantly.
3.2 System Design
In order to demonstrate the visual effect of blood
color change, the color of thermochromic ink in the
simulator needs to simulate the different states of
human blood. Thus, the heater-cooler prototype has
been designed and developed in order to satisfy the
simulator’s needs.
Therefore, the prototype is split into three main
subcomponents: A) main tank for supplying blood, B)
the cooling unit, and C) the heating unit.
3.2.1 Main Tank
In this stage, blood is transmitted into the next stage
(the cooling unit) by a controllable pump, and
eventually, passed to the last stage (the heating unit)
when returning back to the same tank.
A Thermochromic Ink Heater-cooler Color Change System for Medical Blood Simulation
109

3.2.2 Cooling Unit
As illustrated in Figure 2, the cooling unit consists of
the following components.
• Thermal exchanger
• Ceramic thermoelectric
• CPU cooling module
• Tank (Koolance BDY-TK120X70) and
pipes
• Water or coolant
• Aluminum water/coolant cooling block
• Pump (Koolance PMP-300)
• Flow Meter (Koolance INS-FM14)
• Temperature sensor
As shown in Figure 2, the thermal exchanger has
4 ports: IN1, IN2, OU1, and OUT2. Accordingly, the
blood is delivered to IN1, and goes out from OUT1.
Meanwhile, the cooling unit affects the blood
entering to IN2, and then goes out from OUT2.
Indeed, by placing two thermoelectric modules on the
aluminum water/coolant cooling block, the
temperature of the water/coolant inside this block will
decrease. It will also circulate, by a controllable
pump, between the cooling tank and the thermal
exchanger unit. In the other hand, two CPU cooling
modules decrease the temperature of the heating side
of the thermoelectric module. The unit components
have been selected from the same manufacturer to
ensure compatibility and fitting.
Moreover, due to the considerable effect of
flowrate on the cooling performance, several flowrate
meters have been implemented in the circuit after
each pump. In the other words, by increasing the
flowrate, the cooling effect dramatically decreases for
the cooling unit. However, flowrate is a significant
key factor in this prototype, and it is not negligible.
Therefore, by finding the trade-off between the
flowrate and appropriate temperature, the overall
performance can be optimized.
3.2.3 Heating Unit
As illustrated in Figure 2, a heating unit consists of
the following components:
• Tank (Koolance BDY-TK120X70) and pipes
• Pump (Koolance PMP-500)
• Heater module
• Flow meter (Koolance INS-FM14)
• Thermal exchanger (Koolance HXP-193)
• Water
The heating unit includes almost the same cyclic
process as the cooling unit. However, in order to heat
up the tank’s water, a heating element is used. Indeed,
in order to optimize the performance in the compact
size, the 3D printer’s hot-end heater has been
employed in this prototype. Hence, by placing the
heater inside the water tank, water’s temperature will
increase. Likewise, the unit components have been
selected from the same manufacturer to ensure
compatibility.
The tanks are: the thermochromic ink’s tank, cold
water’s tank, and hot water’s tank. Furthermore, three
pumps correspond to each tank. Indeed, the
thermochromic ink’s tank contains the bright ink all
the time. Therefore, by injecting ink to the cooling
unit, the ink’s color will turn to dark red.
At this point, the ink will transfer to the heater unit
to turn the color back to light red. The entire liquid
flow is circulating via those three pumps explained
earlier. Due to the proportional effect of flow and the
performance of the heater/cooler, three flowrate
meters have been implemented in the circuit in order
to control flowrate, and eventually, improve the entire
process to operate autonomously.
In addition, power supply is also provided in order
to supply power to pumps, CPU cooling systems,
heater, flowrate meters, and the thermoelectric
modules. Moreover, the flowrate of motors can be
controlled by voltage adjustment.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this section, light is shed on preliminary results of
the prototype thermochromic heater-cooler system.
The prototype was developed at Qatar University. It
is worth noting that, in this initial version,
thermoelectric modules were used in both the cooling
and heating units. Also, the system has been initially
tested with successful color transformation of blood
color from dark bright (cold) to bright red (hot). This
is shown in Figure 3. More specifically, bright red
simulated blood refers to oxygenation, which is the
normal and healthy state for human organ function.
On the other hand, simulating dark red refers to
deoxygenation, which is a hypoxemic, unhealthy
state. To achieve the oxygenation state, the fluid
temperature has to exceed 35°C, conversely,
hypoxemia can be simulated when cooling the fluid
to under 25°C.
BIODEVICES 2021 - 14th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
110
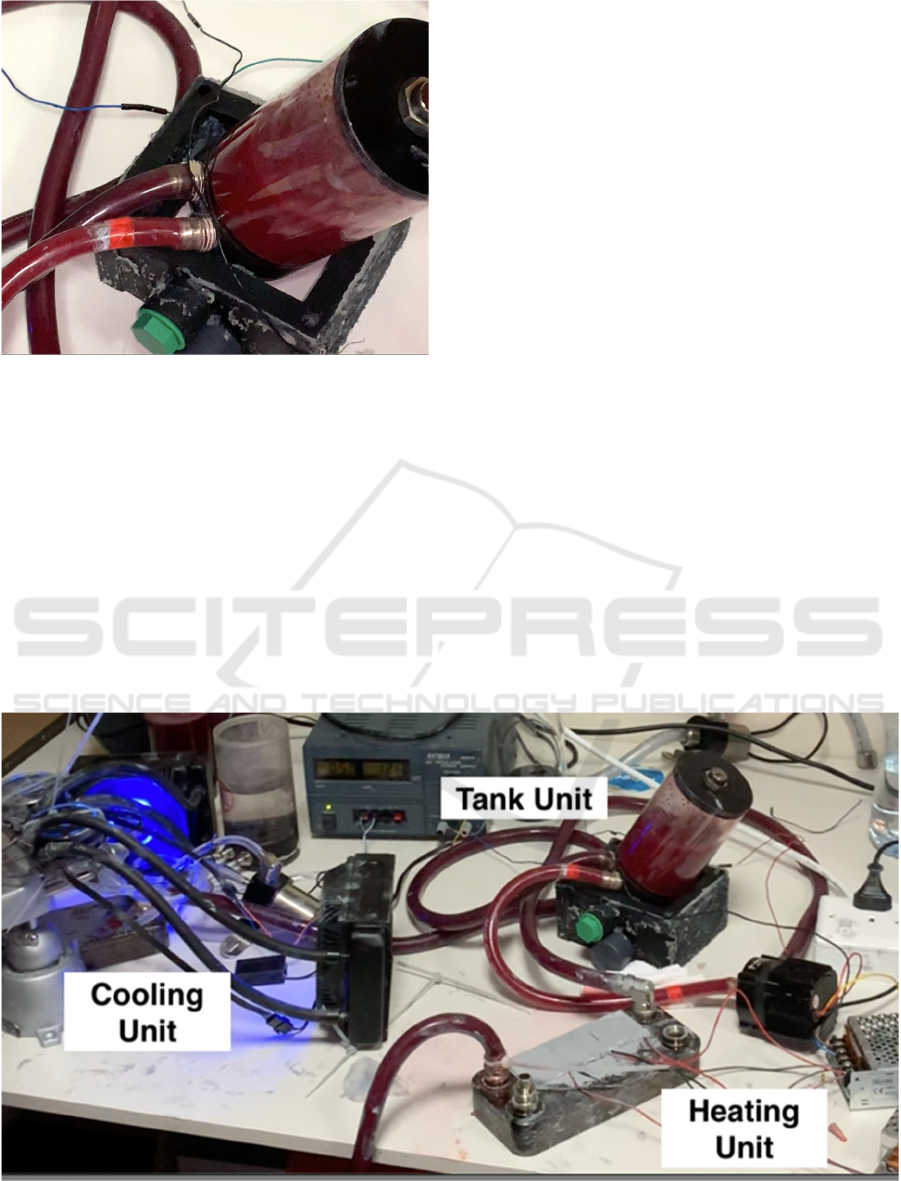
Figure 3: Color change effect achieved by heater-cooler
system prototype.
With several tests undertaken on the cooling unit,
the following results are attained. By increasing the
flow rate to approximately 5 L/min, and raising the
temperature to 35°C degrees, it is evident that color
of the thermochromic ink turns to bright red. On the
flip side, by dropping the flow rate to approximately
3 L/min or less, the temperature can drop readily to
below the temperature to 25°C degrees, showing dark
red simulated blood. We have observed an inverse
relation between flow rate and cooling efficiency, i.e.,
the lower the flow rate, the faster the fluid cools
down, achieving simulated hypoxemia.
Figure 4 shows the current prototype of the
thermochromic heater-cooler system. For simplified
analysis the system has been minimized to a single,
closed loop. It is also worth noting that the tests
conducted proved that the two color states are
reversible, with average transition time of 25 sec.
The system includes a number of limitations.
First, a single, closed loop was deployed, however,
higher heating and cooling efficiencies can be
achieved by separating the units, enabling
independent heating and cooling functionalities.
Second, proper more effective heating modules
should be used to significantly increase the heating
efficiency. Third, an automated control system is to
be developed to enabled dynamic adjustment of flow
rate to achieve the desired effect without human
intervention.
From a cost-effectiveness standpoint, the current
prototype can be developed with an equipment cost
of less than 500 USD. Compared to using an actual
ECMO machine with real blood (i.e. more than
100,000 USD depending on the machine brand), the
proposed solution is a powerful alternative for
simulations.
In the next prototype of the system, the heater-
cooler will be integrated with the simulator’s patient
unit, allowing it to be controlled by the instructor
tablet application. Also, the aforementioned
limitations are to be addressed as well as packaging
the system as a compact module for increase
portability.
Figure 4: Current prototype of thermochromic heater-cooler system.
A Thermochromic Ink Heater-cooler Color Change System for Medical Blood Simulation
111

5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, a novel thermochromic heater-cooler
system is presented as part of the modular ECMO
simulator. Developed upon thermochromic ink, cost-
effective blood simulation is achieved by temperature
adjustment, simulating oxygenation and hypoxemia.
The system has been developed as a prototype with
successful and reversible transitions between dark
and bright red blood color. After addressing the
limitations, the heater-cooler will be integrated with
the ECMO simulator, allowing unpreceded cost-
efficient simulation possibilities.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This paper was supported by Qatar University Internal
Grant No. M-CTP-CENG-2020-1. The findings
achieved herein are solely the responsibility of the
authors.
REFERENCES
Al Disi, M., Alsalemi, A., Alhomsi, Y., Bensaali, F., Amira,
A., & Alinier, G. (2017). Revolutionizing ECMO
simulation with affordable yet high-Fidelity
technology. The American Journal of Emergency
Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2017.11.036
Al Disi, M., Alsalemi, A., Alhomsi, Y., Bensaali, F., Amira,
A., & Alinier, G. (2018). Using thermochromism to
simulate blood oxygenation in extracorporeal
membrane oxygenation. Perfusion,
0267659118798140.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0267659118798140
Al Disi, M., Alsalemi, A., Alhomsi, Y., Bensaali, F., Amira,
A., & Alinier, G. (2019). Extracorporeal membrane
oxygenation simulation-based training: Methods,
drawbacks and a novel solution. Perfusion, 34(3), 183–
194. https://doi.org/10.1177/0267659118802749
Alhomsi, Y., Alsalemi, A., Al Disi, M., Bensaali, F., Amira,
A., & Alinier, G. (2018). CouchDB Based Real-Time
Wireless Communication System for Clinical
Simulation. 2018 IEEE 20th International Conference
on High Performance Computing and
Communications; IEEE 16th International Conference
on Smart City; IEEE 4th International Conference on
Data Science and Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS),
1094–1098.
https://doi.org/10.1109/HPCC/SmartCity/DSS.2018.0
0182
Alsalemi, A., Al Disi, M., Ahmed, I., Alhomsi, Y.,
Bensaali, F., Amira, A., & Alinier, G. (2017).
Developing cost-effective simulators for patient
management: A modular approach. 1–4.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ICABME.2017.8167552
Alsalemi, Abdullah, Aldisi, M., Alhomsi, Y., Ahmed, I.,
Bensaali, F., Alinier, G., & Amira, A. (2017). Using
thermochromic ink for medical simulations. Qatar
Medical Journal, 2017, 63.
https://doi.org/10.5339/qmj.2017.swacelso.63
Alsalemi, Abdullah, Disi, M. A., Alhomsi, Y., Bensaali, F.,
Amira, A., & Alinier, G. (2018). Enhancing Clinical
Learning Through an Innovative Instructor Application
for ECMO Patient Simulators. Simulation & Gaming,
49(5), 497–514.
https://doi.org/10.1177/1046878118794984
Alsalemi, Abdullah, Homsi, Y. A., Disi, M. A., Ahmed, I.,
Bensaali, F., Amira, A., & Alinier, G. (2017). Real-
Time Communication Network Using Firebase Cloud
IoT Platform for ECMO Simulation. 2017 IEEE
International Conference on Internet of Things
(IThings) and IEEE Green Computing and
Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber,
Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) and IEEE
Smart Data (SmartData), 178–182.
https://doi.org/10.1109/iThings-GreenCom-CPSCom-
SmartData.2017.31
Anderson, J. M., Boyle, K. B., Murphy, A. A., Yaeger, K.
A., LeFlore, J., & Halamek, L. P. (2006). Simulating
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Emergencies
to Improve Human Performance. Part I: Methodologic
and Technologic Innovations: Simulation In
Healthcare: The Journal of the Society for Simulation
in Healthcare, 1(4), 220–227.
https://doi.org/10.1097/01.SIH.0000243550.24391.ce
Brazzi, L., Lissoni, A., Panigada, M., Bottino, N., Patroniti,
N., Pappalardo, F., & Gattinoni, L. (2012). Simulation-
Based Training of Extracorporeal Membrane
Oxygenation During H1N1 Influenza Pandemic: The
Italian Experience. Simulation in Healthcare: The
Journal of the Society for Simulation in Healthcare,
7(1), 32–34.
https://doi.org/10.1097/SIH.0b013e31823ebccb
Chan, S.-Y., Figueroa, M., Spentzas, T., Powell, A.,
Holloway, R., & Shah, S. (2013). Prospective
Assessment of Novice Learners in a Simulation-Based
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO)
Education Program. Pediatric Cardiology, 34(3), 543–
552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-012-0490-6
Lafçı, G., Budak, A. B., Yener, A. Ü., & Cicek, O. F.
(2014). Use of Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation
in Adults. Heart, Lung and Circulation, 23(1), 10–23.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hlc.2013.08.009
MacLaren, G., Combes, A., & Bartlett, R. H. (2012).
Contemporary extracorporeal membrane oxygenation
for adult respiratory failure: Life support in the new era.
Intensive Care Medicine, 38(2), 210–220.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-011-2439-2
Ng, G. W. Y., So, E. H. K., & Ho, L. Y. (2016). Simulation
Training on Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation. In
M. S. Firstenberg (Ed.), Extracorporeal Membrane
Oxygenation: Advances in Therapy. InTech.
http://www.intechopen.com/books/extracorporeal-
BIODEVICES 2021 - 14th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
112

membrane-oxygenation-advances-in-
therapy/simulation-training-on-extracorporeal-
membrane-oxygenation
Nichani, S. (2011). An overview of extracorporeal
membrane oxygenation (ECMO). Paediatrics and
Child Health, 21(4), 170–176.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paed.2010.09.006
Peets, A. D., & Ayas, N. T. (2013). Simulation in
Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine. In A. I. Levine,
S. DeMaria, A. D. Schwartz, & A. J. Sim (Eds.), The
Comprehensive Textbook of Healthcare Simulation (pp.
525–536). Springer New York.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5993-4_37
What is Cardiopulmonary Bypass? (2004, September 1).
Perfusion.Com. http://www.perfusion.com/cgi-
bin/absolutenm/templates/articledisplay.asp?articleid=
1549#.WK09dRDmQ_U
What is ECMO? (2016). American Journal of Respiratory
and Critical Care Medicine, 193(6), P9–P10.
https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.1936P9.
A Thermochromic Ink Heater-cooler Color Change System for Medical Blood Simulation
113
