
PIACAN: Pathway Integration and Analysis of Cancer Networks
Adrian Quintana
1a
, Vinh Nguyen
2b
, Tommy Dang
2c
and Chiquito Crasto
1d
1
Center for Biotechnology and Genomics, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, Texas, U.S.A.
2
Department of Computer Science, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, Texas, U.S.A.
Keywords: Cancer Biological Pathways, Merged Networks, Cytoscape, Javascript, Web Resource, PIACAN.
Abstract: We developed a web-based software tool, Pathway Integration and Analysis of Cancer Networks (PIACAN),
to identify key cancer genes, pathways and sub-pathways that are implicated in more than one type of cancer.
PIACAN is the result of merging biological pathways associated with 15 different human cancer types mined
from the Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). The Cytoscape software was used to port the
mined information for pathway merging and subsequent analysis. Web-determined visualization of the
merged networks was achieved by programming using the JavaScript library Data-Drive-Documents (D3).
The results of PIACAN allow us a mechanistic glimpse into the potential development of secondary cancers
spreading to distant tissues, following the primary tumour-localization in a specific tissue, via traversal of the
blood-brain barrier. Given the similarities in biological networks between different cancers, PIACAN allows
us a glimpse into the similarities in cancer development in remote tissues. PIACAN is a free, public, web-
accessible resource (https://adrquint.github.io/integrated-cancer-networks/), where users can identify how and
where biological pathways and/or sub-pathways, depending on the cancer type. A video-demonstration of the
preliminary work can be found at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tOJ-EOY33fU. PIACAN is also
developed as a knowledge- dissemination tool. In its current iteration, for each gene in the pathway, the system
links to cancer gene information in KEGG, GeneCards, Gene Ontology, NCBI AceView, and Ensembl.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cancer is the second leading cause of death in the
United States (US) accounting for approximately, a
million and a half diagnoses and six hundred thousand
deaths per year (Siegel, Miller, Fedewa, et al., 2017).
Targeting the local cancer tissue for one or more of
several specialized treatment modalities is crucial for
the remission of the cancer and an increase in patient
survival rate. If diagnosed early, survival-rates are
highest because the cancer cells are localized to a
specific tissue or organ (ACS, 2016). Breast cancer,
which is a leading cause of death in women, has a 99-
percent five-year survival rate when treatment begins
during the (tumour) localized stage. If left untreated,
and if distant tumour-formations occur, survival-rates
decrease to 26-percent (Wingo, Cardinez, Landis, et
al., 2003). Efforts to cure cancer have been underway
and have evolved over several decades. Though
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8257-7038
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1300-3943
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8322-0014
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2083-5366
survival rates have increased as treatment modalities
have improved, the overall morbidities associated with
cancer have not significantly decreased (Murphy,
Kocanel, Xu and Heron, 2015).
In the primary stages of cancer (stages I-II),
granular tumours are often small. It is recommended
that tumours discovered at initial stages be surgically
removed to deter the progression of the cancerous
tissue onto adjacent tissue. A serious health concern
is the metastasis of the cancer tissue, otherwise
characterized by Stage IV cancer. At this stage, the
cancer begins its progression to tissue that surrounds
the primary tumour (ACS, 2015). In an ideal world,
treatment would begin as soon as the patient began to
exhibit symptoms. Diagnosis and disease progression
is difficult to pinpoint however, due to the unknown
progression patterns exhibited by certain cancers.
(Nichols, Richmond & Daniels, 2017) Further
treatment complications occur when the cancer
246
Quintana, A., Nguyen, V., Dang, T. and Crasto, C.
PIACAN: Pathway Integration and Analysis of Cancer Networks.
DOI: 10.5220/0009185902460252
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2020) - Volume 3: BIOINFORMATICS, pages 246-252
ISBN: 978-989-758-398-8; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

progresses into the meninges of the brain in the form
of brain tumours. At this phase, the cancer has free
access to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) (Fidler
& Ellism 1994). Consequently, the survival rate at
this stage decreases dramatically due to the inability
for modern drug treatments to effectively penetrate
the BBB (Nieder, Spanne, Mehta, et al., 2011;
Marchesi, 2013).
Ongoing research suggests that signalling
pathways associated with cancer progression are
interconnected (Andrew, 2008). Autophagy, which is
the programmed degradation of a cell and its proteins,
is initiated at the preliminary stages of cancer. It is
believed that certain chemical triggers resulting from
adjacent chemical signalling reactions activate this
process of degradation. These adjacent pathways
have been theorized to be part of p53 signalling and
the mTOR sub-network. More importantly, one
observes connections in certain cancer networks,
which contain in them sub-networks or through
specific nodes in the networks, progress to adjacent
networks. Studies suggest that the p53 signalling
pathway transcends through the mTOR sub-network
via the gene AMPK; it then exits the mTOR sub-
network via the gene FIP200, thereby resulting in the
activation of autophagy-related processes of (Ganley,
Lam, Wang, et al., 2009). The importance of targeting
certain signalling pathways for inhibition is further
complicated by the realization that if a part of a
pathway is altered this could lead to unwanted effects
downstream (Liu, Mou, Yu, et al., 2011).
In recent years, the development of bioinformatics
tools has allowed for the visualization of signalling
pathways via web resources. One such comprehensive
resource is the Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and
Genomes (KEGG), created and constantly updated
since 2000 (Kanehisa & Goto, 2000). This resource
and others like it have propelled the study of genomic
pathways and their overall transcriptional effects
within different organisms (Arlt, Casper, Glover, et al.,
2003). In this study, we focused on libraries that
represent research related to cancer pathways and their
genomic interactions within humans.
In studying the pathways and genomic products
that are associated each independent cancer, different
notions of treatment can be considered (Krogan,
Lippman, Agard, et al., 2015). The segregation and
independent study of the most common genes found
in distinct cancers has led to the development of
diagnostic testing that is specialized in detecting the
abnormal transcription of one gene in a series of
pathways involved in one type of signalling.
The merging of different signalling pathways to
assess functional relatedness has allowed for the
analysis of once thought to be independent signalling
events. In merging pathway networks, one can begin
to track the differential centres found in the merged
networks. Key results of this process are the advances
in the research of personalized (now called) precision
medicine (Iyengar, Zhao, Chung, et al., 2012). Thus,
pharmacological applications can be specialized to
target the multiple genomic and epigenomic
signatures for a patient by targeting common centres
for pathways that are activated in a downstream or
upstream process. In this form of treatment plan, a
patient is treated not by their overall symptoms for a
disease but by their own distinct genomic markers
exhibited during disease progression.
The study of cancer pathway networks has
revealed that many of the genes and gene products
involved in each cancer are not unique to just one
cancer in general but are in fact in multiple cancer
pathways (Edelman, Guinney, Chi, et al., 2008)
Although previous research suggests that the
correlation between one specific cancer and the
development of a subsequent different cancers are
strong (Khatri, Sirota, Butte, et al., 2012), research
conducted to substantiate thise has been insufficient,
especially, in a way that allows one to visualize these
interactions.
Our systematic approach could lead to an
innovative targeting of cancers at key locations before
they metastasize and form secondary cancers. Our
research focuses on better understanding these
cancer-related gene interconnections by utilizing
available bioinformatics tools and online genomic
libraries to visually link networks at common gene
points—referred to as nodes—and document the
overlaps in the pathway-networks for 15 typically
identified cancers in humans.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
PIACAN—a meta-network system that allows users
to visualize commonalities in cancer-related
biological pathways is the first of its kind. We
anticipate that users: clinicians, biomedical
researchers and students will be able to easily access
through this resources, knowledge related to the
literature, clinical trials, drug-gene interactions, Big
Data and genomic data-driven mapping onto cancer
pathways. Novel discoveries and testable hypothesis
will be possible from the identification commonality
in genes and sub pathways among different cancer-
types.
PIACAN: Pathway Integration and Analysis of Cancer Networks
247

2.1 Data Processing
All the preliminary computational work and data
analysis conducted in this study was performed on an
Apple MacBook Pro (late 2013 model) running
MacOS version 10.12.3. The information used to
populate the studied cancer networks was obtained
from the KEGG online library via customized Python
script (section 2.2). The script was created using
Python version 2.7.11 and was executed in Python’s
Integrated Development and Learning Environment
(IDLE) version 2.7.11. Any additional code utilized
in the creation or updating of the networks can be
found in the attached appendix.
2.2 Network Design and Integration
The cumulative network containing all 15 cancer
networks was created using Cytoscape (Shannon,
Markiel, Ozier, et al., 2003) version 3.4.0 in
conjunction with Java version 1.8.0_111. Each cancer
network was imported individually into Cytoscape
(www.cytoscape.org) via the Cytoscape application
KEGGParser (Nersisyan, Samsonyan, Arakelyan,
2014) version 1.7.11. Importing each sub-network
individually allowed for the verification of the data,
especially comment tagging, assuring its
completeness before the cumulative merge was
initiated. The specific composition of each sub-
network was used by Cytoscape to determine which
nodes and edges would be fused in the cumulative
network. During the merging process, each network
element was analysed by Cytoscape to determine
whether it was common in the adjoining network;
and, if the match was found, it would lead to the
accumulation of comment tags. Cytoscape network
merge tools were used to integrate the 15 sub-
networks into a cumulative network.
Customized Python scripts requested the pathway
information for each cancer network by leveraging
the KEGG API. The script searched for the organism
Homo sapiens (code in KEGG for human: hsa) and
output all available files matching the specified
protocols. The files were all saved separately in the
eXtensible Markup Language (.xml) format.
2.3 Network Information Formatting
Cytoscape export controls were used to export the
background information of the cumulative network in
the Cytoscape.js (.cyjs) format.
The data contained in the exported file were first
reformatted into the JavaScript Object Notation
(JSON, .json) format by using Regular Expression
(regex) patterns thereby creating the required JSON
file. The data contained in the JSON file were further
adjusted to include a community object and to
account for the additional genomic libraries appended
to each individual node in the form of image
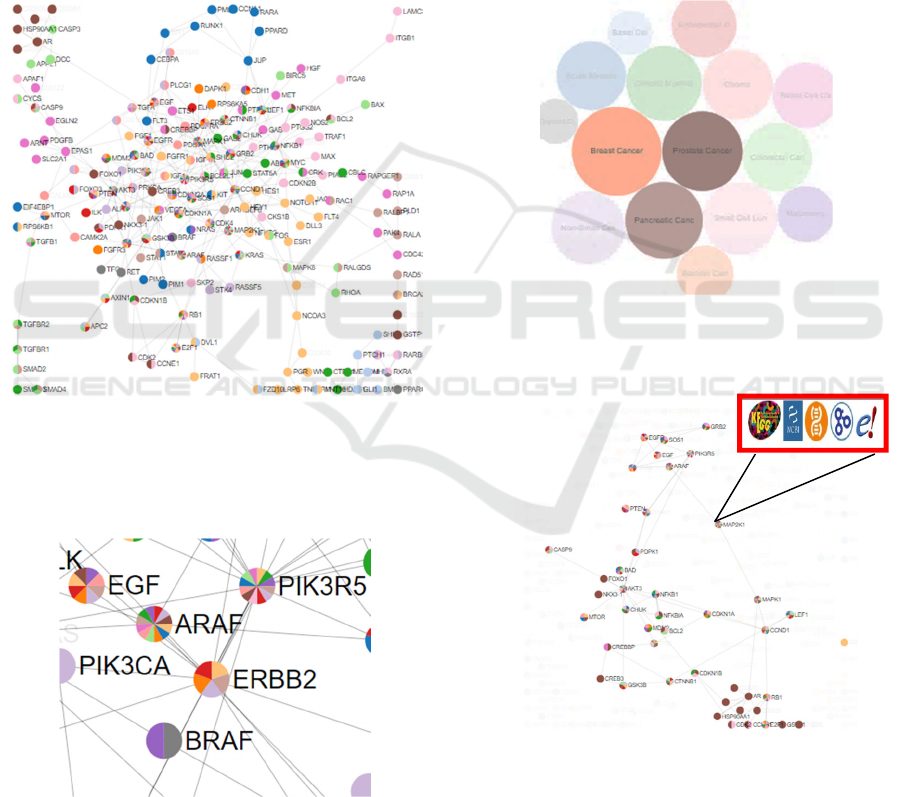
hyperlink objects (Figure 1).
Figure 1: The preliminary merging of 15 cancer-type
biological pathways from the KEGG resources by the
Cytoscape network analysis software. Green rectangular
nodes represent genes. Smaller circular nodes represent
chemical compounds. Each edge represents an individual
interaction within a pathway. 302 edges and 256 nodes are
represented in the merged pathways system.
Each image hyperlink object serves the purpose of
affixing a path that when clicked would redirect the
web browser to supplementary genomic content
stored in KEGG, NCBI AceView, GeneCards, Gene
Ontology, and Ensemble (depending on which icon is
selected) as will be illustrated in Figure 5b. The
community object includes information regarding
background pathway information of each individual
gene and compound node. The community object
serves two primary purposes: first, it allows for
further characterization of the node information
detailing the specific biological pathway(s) that
contains that node; and, second, it allows for future
implementation of features which will allow for the
visualization of each independent sub-pathway
contained in each of the 15 cancer sub-networks.
The final cumulative network was migrated to a
freely accessible webpage located on GitHub
(https://adrquint.github.io/integrated-cancer-
networks/). The migration of the cumulative network
allowed for final visualization of the cumulative
network as well as the implementation of JavaScript
applications. Network visualization was accomplished
by using the “Force Directed” Layout found on the
Data-Drive Documents JavaScript library (D3.js)
(https://d3js.org/). A selection colour palette was added
on the left side of the page, Figure 2).
BIOINFORMATICS 2020 - 11th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
248
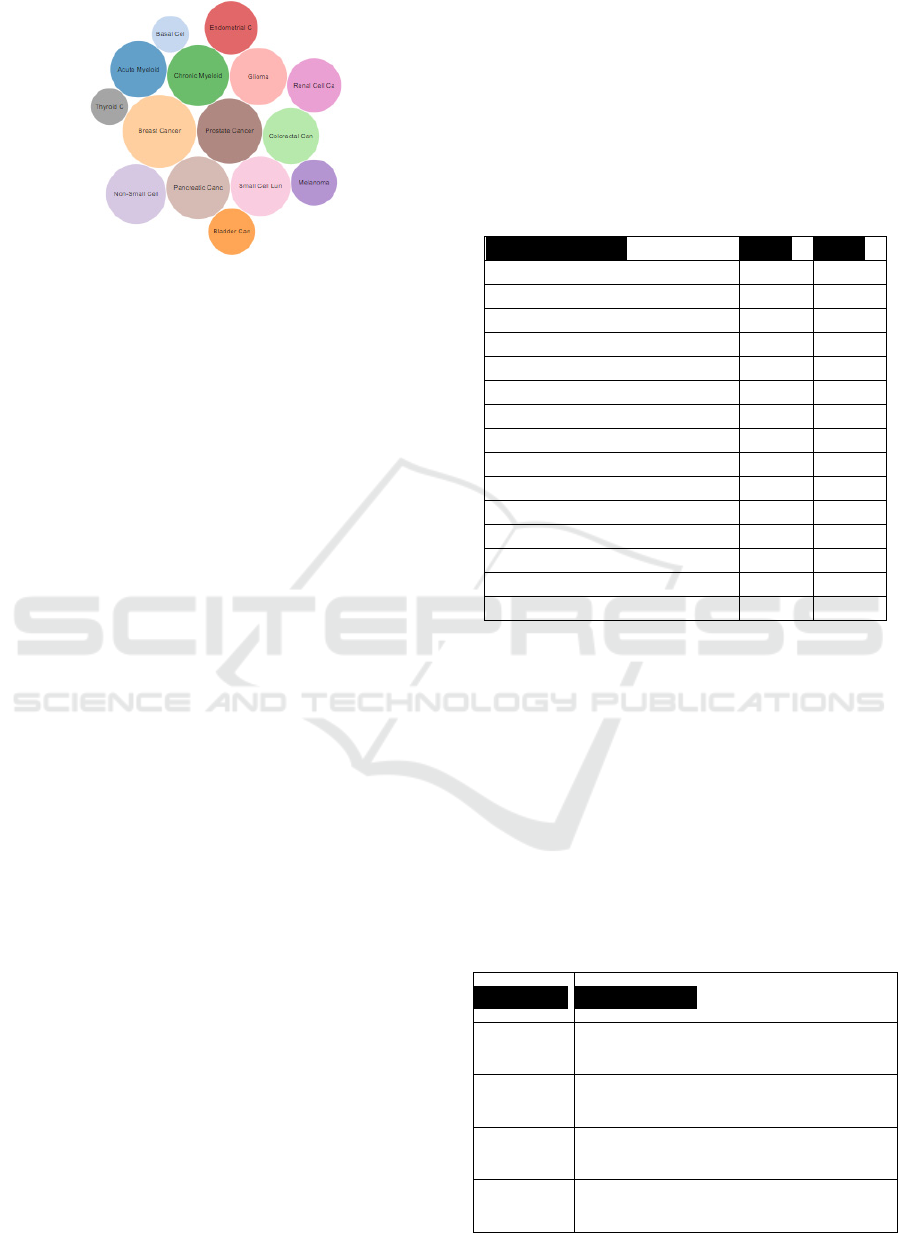
Figure 2: The fifteen cancer networks represented as circles
with specific colour codes. The size of the circles are
illustrative of the number of genes involved in each cancer
network.
This allowed for a specific cancer sub-network to
be selected and the background to become semi-
transparent; this visual aid identifies the network
being considered in the context of the overall merge-
system. The selection for each individual sub-
network grants the user the ability to visualize one
network at a time. By selecting multiple networks,
this process can be additive to form merged networks
which are strictly common to only those cancer types.
The palette also serves the purpose of associating the
node (gene product) with specific cancer networks. A
drop-down menu was incorporated to allow the user
to directly view and select the genes present after the
selection of one or several sub-networks.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Figure 1 represents the results of work that involved
auto-downloading, merging and developing a
cumulative network containing 15 human cancer-
sub-networks.
The green rectangles are nodes that represent gene
products. Chemical compounds contained in a
pathway are represented by smaller circular nodes
(possibly too small to visualize). The edges that
connect the genes represent an individual type of
interaction in the pathway. The networks for
specifically chosen types of cancers represent 265
nodes and 302 edges.
Table 1 represents the number of nodes and edges
identified for each of the 15 types of cancers studied.
Breast cancer is significantly overrepresented in the
table.
The primary aim of this paper is to illustrate the
merging of cancer networks. The methodologies
described in the previous section demonstrated how
the position of the node in the network is transferred
from the cancer biological pathway name to the gene.
Table 2 represents a truncated list of sub-pathways
and networks that are associated with common genes.
The full Excel spreadsheet is available upon request
from the corresponding author of the paper (CJC).
Table 1: The Table shows the total number of nodes (genes)
involved in the pathways and the total edges (interactions)
for each cancer-type.
Cancer Network Nodes Edges
Breast 119 104
Glioma 78 73
Renal Cell Carcinoma 64 34
Pancreatic 57 45
Prostate 57 47
Colorectal 55 32
Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia 54 42
N
on-small Lung 54 47
Small Lung 47 34
Acute Myeloid Leukaemia 44 40
Endometrial 43 25
Bladder 39 17
Melanoma 34 23
Basal Cell Carcinoma 27 11
Thyroid 26 14
Cytoscape is a powerful network design and
analysis software. It can be used for different
networks—not necessarily for biological pathways.
One of the drawbacks of using the Cytoscape network
analysis software however, is in the area of universal
knowledge dissemination. This standalone software
has to be downloaded to one’s computer (free). In
order to make the merged-network resource,
PIACAN, accessible over the Internet, the web
resources were developed as described in Section 2.3.
Table 2: The table shows which genes are common to the
four pathways that contain the most number of common
genes.
Gene Node Sub-Networks
ARAF
ENDO, nSCLC, PROS, BRCA, AMLE, BLAD, COLO, GLIO,
RENA, PANC, CMLE, MELA
MAP2K1
ENDO, nSCLC, COLO, PROS, BRCA, AMLE, BLAD, GLIO,
THYR, RENA, PANC, CMLE, MELA
MAPK1
ENDO, nSCLC, COLO, BRCA, PROS, AMLE, GLIO, BLAD,
THYR, PANC, RENA, CMLE. MELA
PIK3R5
BRCA, CMLE, MELA, PANC, nSCLC, ENDO, SCLC, PROS,
GLIO, AMLE, COLO, RENA
PIACAN: Pathway Integration and Analysis of Cancer Networks
249
When the user accesses the PIACAN web-
resource (https://adrquint.github.io/integrated-
cancer-networks), the web page dynamically opens
into a two-panel arrangement. The first panel (Figure
2) indicates the 15 cancers in colour-coded circles.
The size of the circles represent the number of
pathways associated with that specific cancer type.
Each gene in figure 3 is represented only once in
the merged pathway system. Each of these genes is
colour coded. Most have multiple colours. The
colours allow the user at a glance to see which cancer
pathways contain that gene. Figure 4 is a close-up of
a portion of Figure 2.
Figure 3: The figure shows all the merged cancer networks
for all cancer types. The gene-nodes in this merged pathway
are represented by circles. Each gene is represented by
colours depending on the number of pathways of cancer
types they represent.
Figure 4: Close-up of a region of the merged cancer
networks that show colours for each gene representing
cancer types with which they are associated.
In figure 4, (a zoomed-in area of the merged
network represented in Figure 3), one can see, for
example, that two colours represent the BRAF gene:
purple and dark gray. The colours can be matched by
the cancer type in figure 2a which shows that BRAF
gene can be found in Thyroid Cancer (dark gray) and
Melanoma (purple). One can also see that the ARAF
and PIK3R5 genes are present in many of the cancers
whose pathways are represented here.
The web resource also helps users dynamically
assess genes, pathways and cancer types. Users can
click multiple cancer types and only those nodal-
genes implicated in selected cancers and their
associated networks and sub-networks become
visible (Figure 5 and 6).
Figure 5: Figure shows a use-case where the user has
selected three cancer-types. The other cancer-types faded
for additional clarity.
Figure 6: When specific cancers are selected, only the
merged pathways related to those cancers are illustrated
from the complete pathway show in Figure 3. The red-
bordered inset shows how when a mouse is placed over a
gene, dynamic links are created (via icons) for more
information about that gene at KEGG, AceView, NCBI,
Gene Ontology, Gene Cards and Ensemble.
BIOINFORMATICS 2020 - 11th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
250

Circles representing the other cancers are
rendered faded. In the right panel only the nodes that
are common to breast and prostate cancer are
rendered—the rest of the meta-network is faded. The
colour codes on the genes that are common to cancer-
types to which they belong.
4 DISCUSSION
PIACAN allows the direct and dynamic comparison
each of the 15 cancer networks against each other in
terms of gene content. In this study, we have changed
the paradigm of the assessment of gene- networks
from the “network name” to the “gene”. The latter
now becomes the pivotal node around which the
merged networks are illustrated.
The comparative analyses resulted in the
conclusion that a common set of genes initiated
several cancer progression origin sites. Furthermore,
this information can be utilized to actively monitor
the organism’s evolutionary developments and how
this process affects cancer progression. To illustrate
this, we assessed the merged pathways and coinciding
sub-networks for three cancers: breast and
endometrial cancers, breast and prostate cancers, and
endometrial and prostate cancers. The rationale
behind the selection of these pair-wise comparisons
was due to these groups having the closest alignments
in regard to the number of genes they had in common.
Breast and Endometrial Cancer. The comparison of
the breast and endometrial cancer groups yielded 20
common genes between the two groups. This
comparison produced the highest number of common
genes of all the three groups compared. Out of the 20
common genes, eight of these are found in the 10
genes most commonly found in all 15 networks. The
only two that weren’t found in the 20, were RB1 and
E2F1. Although, drawing connections between
pathways in terms of a mechanism of the progression
of cancer from a primary to a secondary tissue is
premature, it is noteworthy that the overlap between
the breast cancer and endometrial cancer networks is
significant. One can make the case the genomic
relatedness of these two cancers can be attributed to
the fact that both tissues are anatomically present
primarily in females and thus the possibility that they
both are active is much higher than in a study
comparing differences in cancer that primarily affect
one sex over the other. The connection between breast
and endometrial tissues can be attributed to the stages
of embryonic development. In these processes, the
tissues differentiating the male and female sexes
develop resulting in distinctive developmental
processes uniquely found in one sex and not the other.
In females,
Breast and Prostate Cancer. In our second group, we
compared the levels of overlap in gene contents of
breast and prostate cancers. This group contained 19
common genes which were found to be active in both
cancers. Out of 19 common genes, nine of which were
found in the list of the top most commonly found
genes among the networks processed. The only one
that wasn’t was TP53. Generally, cancers affecting
primarily one sex have a much higher percentage of
cases reported within that sex. Cases of occurrences
in the opposite sex however, are also common. Breast
cancer is predominately present in females; however,
cases in males have been reported.
Endometrial and Prostate Cancer. In the third group,
we compared the gene contents of endometrial and
prostate cancers. This group contained 18 common
genes involved in both cancer networks. Out of the 18
common genes in this group, seven of these were
found in our top 10 common genes in all of our
networks.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The merging of the cancer networks demonstrated
that the gene products found within certain cancer
networks are not unique. They are found in many
other mapped networks. PIACAN leverages on-line
resources of cancer-pathways, already available
network merging pathways as well as web-
development for universal free access. Although this
is a valid step forward and provides many
opportunities for discovery, more work remains to be
done. Integrating more data from addition resource
into our dynamic networks would be highly beneficial
to visually expressing the similarities found between
different cancers.
The information contained within KEGG is vast
and diverse; it is not however, the only online
resource that can be incorporated into our research.
What was demonstrated in this report is a pilot
system. To make this a truly comprehensive system,
future work will involve the incorporation of
information of online libraries including PubMed,
PubChem, and the Protein Data Bank (PDB). The
resources for gene-product information which
PIACAN can currently access are those where the
gene product name can be directly incorporated into
a URL link. If we were to create additional links to
resources where gene information is mapped onto
alphanumeric IDs, the one would have to dedicate
effort to translating these IDs into gene names.
PIACAN: Pathway Integration and Analysis of Cancer Networks
251

With the array of other online bioinformatics
libraries, which are freely accessible, it possible to
begin to make conjectures and generate hypotheses as
to how diseases, in this case cancer, are related and
how they interact with each other. This systematic
approach could lead to an innovative targeting of
cancers at key locations before they metastasize and
form secondary cancers, which is a significant health
concern.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors wish to thank the Interactive Data
Visualization Lab (iDVL), from the Department of
Computer Science and the Center for Biotechnology
and Genomics at Texas Tech University where the
development of this resource was conducted.
REFERENCES
American Cancer Society, 2015. Secondary cancers after
melanoma cancer. Retrieved: November 15, 2019, from
http://www.cancer.org/cancer/skincancermelanoma/deta
iledguide/melanoma-skin-cancer-after-second-cancers
American Cancer Society, 2016. Cancer Facts & Figures
2016. Atlanta: American Cancer
Society. Retrieved: November 15, 2019, from
http://www.cancer.org/research/cancerfactsstatistics/ca
ncerfactsfigures2016/index.
Andrew, T., 2008. Apoptosis and autophagy: regulatory
connections between two supposedly different
processes. Apoptosis, 13, pp. 1–9.
Arlt, M. F., Casper, A. M., Glover, T. W., 2003. Common
fragile sites. Cytogenet Genome Res. 100, pp.92–100.
Edelman, E. J., Guinney, J., Chi, J. T., Febbo, P. G.,
Mukherjee, S., 2008. Modeling Cancer Progression via
Pathway Dependencies. PLoS Comput Biol. 4(2): e28.
Fidler, I., Ellis, L. M., 1994. The implications of
angiogenesis for the biology and therapy of cancer
metastasis. Cell 79: 185-188.
Ganley, I. G., Lam, D. H., Wang, J., Ding, X., Chen, S.,
Jiang, X. 2009. ULK1.ATG13.FIP200 complex
mediates mTOR signaling and is essential for
autophagy. J Biol Chem, 284, pp. 12297–12305.
Iyengar, R., Zhao, S., Chung, S-W., Mager, D. E., Gallo, J.
M., 2012. Merging Systems Biology with
Pharmacodynamics. Science Translational Medicine.
4(126):126.
Kanehisa, M., Goto, S. 2000. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia
of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 27-30.
Khatri, P., Sirota, M., Butte, A. J., 2012. Ten years of
pathway analysis: current approaches and outstanding
challenges. PLoS Comput Biol. 8(2):e1002375.
Krogan, N. J., Lippman, S., Agard, D. A., Ashworth,
A., Ideker, T. 2015. The Cancer CellMap Initiative:
Defining the Hallmark Networks of Cancer. Molecular
Cell. 58 (4), pp. 690-698.
Lui, J. J., Mou, L., Yu, J. Y., Liu, B., Bao, J. K., 2011.
Targeting apoptotic and autophagic pathways for
cancer therapeutics. Cancer Lett, 300, pp. 105–114.
Marchesi, V., 2013. CNS cancer: metabolic changes in
brain tumors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 10: 607.
Murphy, S. L., Kochanek, K. D., Xu, J., Heron, M., 2015.
Deaths: Final Data for 2012. National Vital Statistics
Reports. Vol 63. No. 9. Hyattsville, MD: National
Center for Health Statistics.
Nersisyan, L., Samsonyan, R., Arakelyan, A., 2014.
CyKEGGParser: tailoring KEGG pathways to fit into
systems biology analysis. F1000Research. 3:145.
Nichols, E. E., Richmond, A., Daniels, A. B., Erin E. 2017,
Micrometastatic Dormancy in Uveal Melanoma,
International Ophthalmology Clinics. 57, 1, 1.
Nieder, C., Spanne, O., Mehta, M. P., Grosu, A. L., Geinitz,
H., 2011. Presentation, patterns of care, and survival in
patients with brain metastases: what has changed in the
last 20 years? Cancer 117: 2505-2512.
Rebecca, L., Siegel, K. D., Fedewa, S. A., Ahnen, D. J.,
Reinier, G. S., Meester, R. G. S., Barzi, A., Jemal, A.,
2017. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017, CA: A Cancer
Journal for Clinicians.
Shannon, P., Markiel, A., Ozier, O., Baliga, N. S., Wang, J.
T., Ramage, D., Amin, N., Schwikowski, B., Ideker, T.,
2003. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated
models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome
Research. 13(11): 2498-50.
Wingo, P. A., Cardinez, C. J., Landis, S. H., 2003. Long-
term trends in cancer mortality in the United States,
1930-1998. Cancer. 97(suppl 12):3133-3275
BIOINFORMATICS 2020 - 11th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms
252
