
3D Printing Materials for Physical Breast Phantoms:
Monte Carlo Assessment and Experimental Validation
R. M. Tucciariello
1a
, P. Barca
1
, D. Caramella
4
, R. Lamastra
1
, A. Retico
3
, A. Traino
2b
and M. E. Fantacci
1,3 c
1
Department of Physics, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy
2
Unit of Medical Physics, Pisa University Hospital “Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Pisana”, Pisa, Italy
3
INFN, Pisa Section, Pisa, Italy
4
Department of Radiology, Pisa University Hospital “Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Pisana”, Pisa, Italy
alessandra.retico@pi.infn.it, c.traino@ao-pisa.toscana.it, maria.evelina.fantacci@unipi.it
Keywords: 3D-printing Materials, Breast Phantoms, Digital Mammography, Monte Carlo Simulations, Dosimetry,
GEANT4, Radiochromic Films, XR-QA2, RADIOMA.
Abstract: The aim of this work is to characterize 3D-printing materials to be used for breast physical phantoms in
mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis QA procedures or research. Our approach involves both Monte
Carlo (MC) calculations and experimental measurements. Using a GEANT4-based application, MC
simulations are involved in order to compare transmission properties of the digital “standard breast”, which is
composed by the external skin layer and the breast tissue inside, with those of typical printable materials.
Substitute materials for skin layer and breast tissue have been identified and a 3D-printed physical breast
phantom has been derived. Finally, a comparison between MC results and experimental measurements has been
performed with the Hologic Selenia® Dimensions® mammography unit using XR-QA2 radiochromic films.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the last decades breast cancer screening programs
have been introduced by public health services of
many countries, highlighting an increasing
involvement on early detection of breast masses.
Indeed, breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer
deaths in female subjects and tumour detection in an
early stage ensures greater possibilities of treatment
cures. Early detection and accurate diagnosis are
carried out, in the last decades, with Digital
Mammography (DM) and, in the last few years, with
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT), a new pseudo-
3D imaging modality (Sechopoulos 2013a, 2013b).
X-ray mammography and breast tomosynthesis
provide radiographic images of the compressed
breast. In the first case two images for each breast are
acquired (cranio-caudal and medio-lateral-oblique
views), while in DBT the X-ray tube moves in an arc
over the compressed breast and multiple projections
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9600-4177
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3521-6293
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2130-4372
are acquired and then reconstructed by a computer,
forming pseudo-three-dimensional images. The
purpose of screening programs is to reduce breast
cancer mortality by ensuring high quality services and
optimized X-ray mammography units. This can be
reached first of all with quality assurance (QA)
protocols, which guarantee optimized equipment, and
with training and research activities. Since both
investigations use ionizing radiation, dosimetry
assessment is mandatory.
Breast physical phantoms, which are test objects,
represent fundamental tools used to perform quality
assurance (QA) procedures and allow the calculation
of useful parameters for imaging and radiation
dosimetry. QA procedures and research are usually
performed using polymethyl-metacrilate phantoms
(PMMA), or other tissues simulating breast
composition, which generally include objects
representing mammographic lesions (tumour masses,
fibers, microcalcifications), resolution patterns and
254
Tucciariello, R., Barca, P., Caramella, D., Lamastra, R., Retico, A., Traino, A. and Fantacci, M.
3D Printing Materials for Physical Breast Phantoms: Monte Carlo Assessment and Experimental Validation.
DOI: 10.5220/0009162302540262
In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2020) - Volume 1: BIODEVICES, pages 254-262
ISBN: 978-989-758-398-8; ISSN: 2184-4305
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

step wedges for assessing spatial resolution and
contrast for the image quality assessment (Barca et al.
2019a; Barca et al. 2019b). The most used
commercially physical phantoms for QA procedures
are TORMAM (www.leedstestobjects.com) CDMAM
(www.artinis.com), ACR (www.cirsinc.com). It is
commonly assumed that a uniform PMMA block 45
mm thick is equivalent in absorption to a standard
breast, which is a 5 cm thick compressed breast. It
consists in a 40 mm thick central region comprising a
certain mixture by weight of adipose tissue and
glandular tissue (dependent on compressed breast
thickness and age) surrounded by a 5 mm thick
superficial layer of adipose tissue, simulating skin
absorption (Perry et al. 2008).
Since breast glandularity
1
can vary from 0 to
100% and it strongly affects MGD, there is the need
to consider this variable in physical phantoms, as well
as in the MC simulations. Nevertheless, skin layer,
not included in commercial phantoms, influences
MGD and attenuation properties (Massera and Tomal
2018, Tucciariello et al. 2019).
The spread of the 3D-printing technology in the
last years and the relatively inexpensive materials
have led research groups to include printing materials
in the context of medical physics and radiotherapy,
for research, QA procedures and patient treatments
(Ferreira et al. 2010; Madamesila et al. 2016).
Nevertheless, 3D-printing is challenging due to
variability of materials and printing methods, and an
accurate characterization of printing materials is
needed. Ivanov and colleagues (2018) explored 3D-
printing materials exposing step-wedge phantoms
with monochromatic beams at ESRF in Grenoble, in
order to characterize attenuation coefficients.
The purpose of this study is to explore different
3D-printing materials which could be employed in the
creation of new physical phantoms for DM and DBT
which better represent both breast anatomy and X-ray
attenuation properties. We propose the method used
by our research group to define X-ray transmission
properties of different materials using a DM X-ray
source, widespread in clinics, and we introduce an
experimental 3D-printed physical phantom. We made
use of Monte Carlo (MC) simulations
2
and validated
our method with experimental measurements using
GAFchromic™ films.
1
The term glandularity means the percentage of glandular tissue
respect to the adipose tissue.
2
The Monte Carlo method refers to a set of computational methods
based on the use of artificially generated random numbers for
solving phenomenon under investigation. In this case, photons
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
Best practice in dosimetry purposes is to consider
glandular tissue (a complex system of branched ducts
that develop from the inside of the breast to the
nipple) as the radiosensitive tissue in the breast. Thus,
Mean Glandular Dose (MGD) is the parameter used
to assess dose delivered to the glandular tissue. Since
MGD is not a physical quantity, radiation dosimetry
is performed using MC simulations thanks to the
ability to estimate quantities that are challenging to
measure empirically. This kind of approach makes
use of certain geometry assumptions that depend on
breast characteristics and allows to digitally
reproduce a breast phantom model.
We investigated 3D-printing materials for
physical breast phantoms, using the geometry
assumptions followed by research groups whose
works have been milestones for international
dosimetry protocols (Boone 1999; Dance 1990;
Dance, Young, and Van Engen 2011). Our approach
involves both MC simulations as well as experimental
measurements to validate our method.
2.1 Monte Carlo Model
Using the GEANT4 toolkit
3
, which is a C++ object-
oriented toolkit for the simulation of particle through
matter, we developed a MC code (Tucciariello et al.
2019) that reproduces mammographic and
tomosynthesis investigations, with the same
geometry assumptions (Figure 1) used for validation
purposes (AAPM Task Group 2015). According to
the prescriptions provided by the report of AAPM, the
Option4 PhysicsList was used in GEANT4, for the
constructors and instances, designed for high
accuracy in low-energy physics processes.
In MC models, breast digital phantom is modelled
as a semi-cylinder with an outer layer of skin made
by adipose tissue while the inner part is a
homogeneous mixture of adipose and glandular
tissues. Hammerstein et al. (1979) derived weight
fraction of elements and total tissue density of both
tissues (Table 1). Glandularities ranging from 0 to
100% are composed by mixing properly glandular
and adipose tissues.
Polychromatic X-ray source has been
implemented referring to the Hologic Selenia®
Dimensions® mammography unit, with which
emitted by the X-ray source and interacting with the breast tissue
are traced and all the interactions and dose deposits are registered.
3
https://geant4.web.cern.ch/
3D Printing Materials for Physical Breast Phantoms: Monte Carlo Assessment and Experimental Validation
255

experimental measurements have been executed. An
algorithm for tungsten anode spectral model has been
involved, dubbed TASMIP
M
(Boone, Fewell, and
Jennings 1997), based on experimental measurements
of mammography-energy X-ray spectra.
Figure 1: Schematic drawing of the (a) acquisition
geometry for the cranio-caudal view in DM, and (b) breast
phantom geometry adopted.
Table 1: Elemental composition and density of the two
main constituents of the breast tissue.
Tissue H C N O P density
(g/cm
3
)
glandular 0.102 0.184 0.032 0.677 0.005 1.04
adipose 0.112 0.619 0.017 0.251 0.001 0.93
Since X-ray imaging is a transmission-based
technique, X-ray transmission properties have been
investigated involving Air Kerma (K) estimates. K can
be easily defined in both experimental measurements,
using e.g. an ionization chamber or radiochromic films,
and in MC simulations. Air Kerma is the reference
physical quantity for MGD evaluation purpose.
Indeed, glandular dose estimates start from incident air
kerma and then multiplying it for dedicated conversion
factor from K to MGD, with the surface S for air kerma
scoring placed under the compression paddle and on
the upper surface of the breast. This formalism has
been well defined in literature (Sarno et al. 2019) and
is not the intend of this work.
For air kerma scoring, in our code we use the
formalism provided by Sarno and colleagues (Sarno,
Mettivier, and Russo 2017) using
K
E
μ
ρ
E
Scos
(1)
where E
is the energy of the ith incident photon
passes through the scoring surface S,
is
the air mass energy absorption coefficient at the
4
www.3ntr.net
energy E
(Hubbell and Seltzer 1995) and
is the
angle between the photon direction and the direction
perpendicular to S.
In MC code, in order to define transmission
properties of different materials, we simply place the
air kerma scoring surface S inside a reference
phantom 5 cm thick under the skin layer, or under the
whole phantom, respectively to evaluate the influence
of a certain material, e.g. skin layer or breast tissue.
Data will be provided in terms of mGy per event, for
both monoenergetic and polychromatic
investigations.
In order to compare MC simulations results with
experimental ones, we need to normalize both for a
reference measurement that is the air kerma incident
on the top of the phantom. The ratios in eq. (2) will
be compared
,
,
≅
,
,
(2)
which provides the transmission factors using MC
simulations and GAFchromic films, where
,
is the air kerma at a given depth d in the medium m,
and
,
is the incident air kerma on the upper
side. In the paragraph 2.3 the formalism for obtaining
will be presented.
Since MC results uncertainties are evaluated
following Sempau et al. (2001), air kerma estimations
are performed for monochromatic beams with 10
7
incident photons, while for polychromatic beams 10
8
primary photons are involved. These numbers let to
obtain uncertainty on air kerma respectively tree and
four orders of magnitude less. Uncertainties have not
been introduced in all figures because they would not
be visible.
2.2 3D-printing Materials
Breast tissue substitutes have been searched from few
commercial low-cost 3D-printing materials. PLA,
PET-G, ABS, PCABS, CARBON PA, GLASS PA,
ASA have been investigated.
Since MC code needs for each material both
elemental composition and density, using a A2v4 3D-
printer
4
we printed test objects for each one in order
to define the printing precision and density
5
.
We used two simple parallelepiped solids of
10580 mm
3
and 40405 mm
3
, and for each of
them three copies were printed. Solids dimensions
and weights were then measured and densities
5
Is commonly known that after 3D-printing phase material density
can change due to the extrusion printing procedure.
BIODEVICES 2020 - 13th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
256

estimated. Due to the low printing reliability,
CARBON PA and GLASS PA were rejected, while
ASA material, despite the good printing quality, was
avoided since it is a copolymer and its chemical
formula can be different depending on the modality
the three monomers repeat on the structure (Liu et al.
2011). A separate evaluation has been achieved for
PCABS; because of not negligible variations in the
test objects, we used a bigger test object to assess
material density.
Elemental compositions of PLA, ABS, and PET-
G have been taken from Alssabbagh et al. (2017),
while for PCABS, polycarbonate composition is
available on GEANT4 database (Table 2)
6
.
Composition and density obtained were involved in
MC simulations for evaluating transmission
properties.
In the subsequent chapter the results that led to
choose materials for the final physical phantom will
be presented.
Table 2: Percentage elemental compositions of 3D-printing
materials evaluated in our work.
Tissue H C
N
O S K
PLA 0.053 0.519 - 0.426 0.001 0.001
ABS 0.075 0.855 0.053 0.016 0.001 -
PET‐G
0.075 0.652 - 0.271 0.002 -
Poly‐
carbonate
0.055 0.756 0 0.189 0 -
PCABS
80 % polycarbonate, 20% ABS
2.3 Experimental Verification
Experimental verification of transmission properties
for the 3D-printed materials was executed using
GAFchromic
TM
XR-QA2 films. Radiochromic films
are well suited for radiographic QA tests and research
in dosimetry, thanks to the self-developing of the
response after the irradiation process. XR-QA2 are
designed for energies ranging in radiology, with
anode tube potential ranging from 20 to 200 kVp.
XR-QA2 films are sensitive in the dose range 1-
200 mGy and an increasing change in optical
reflectance occurs with increasing doses.
2.3.1 Film Calibration and Digitization
Response of radiochromic films must be assessed
with an accurate calibration in order to obtain a
calibration curve, expressed in terms of air kerma
versus reflectance change R. Since Di Lillo et al.
6
PCABS is composed by polycarbonate and ABS. The percentage
of ABS can be different depending on manufactures.
7
Scans for irradiated samples have been executed 24h after the
exposition.
(2016) showed energy dependant dose-response
curves for XR-QA2 using synchrotron radiation, we
proceeded to realize three calibration curves for 25,
30 and 35 kVp with the Hologic Selenia Dimensions
in mammography modality. For each calibration
curve 12 points were used, each of them is from the
average value of 3 different radiochromic samples.
Since X-ray mammography units permits low-
doses irradiations, in order to observe XR-QA2 dose
range, a Radcal 20X6-60E ionisation chamber
coupled with the 2026C dosimeter was used to choose
correct mAs tube loading values and air kerma
exposures, chosen in an optimal range from about 1
mGy to a maximum value depending on the
kilovoltage applied.
The formalism defined by Tomic et al. (2010) and
Di Lillo et al. (2016) was used and discussed above.
From original XR-QA2 1012'' sheets, samples of
33 cm
2
have been cut to be used for calibrations and
measurements. For calibration, 5 samples were used
as “control films” to quantify background radiation
and 36 samples for each calibration curve.
Using a flatbed scanner (Epson Expression
10000XL), samples were scanned before and after
7
the exposition, in 48-bit RGB mode, at 150 dpi, in the
same position of the scanner surface and saved as
TIFF image file format. Multiple scans for each
sample were executed. Raw images have been
analysed with the open software ImageJ
8
. Formalism
provides the film response in terms of reflectance
change R
using the 16-bit red channel in a
ROI of 11 cm
2
in the center of each sample (Figure
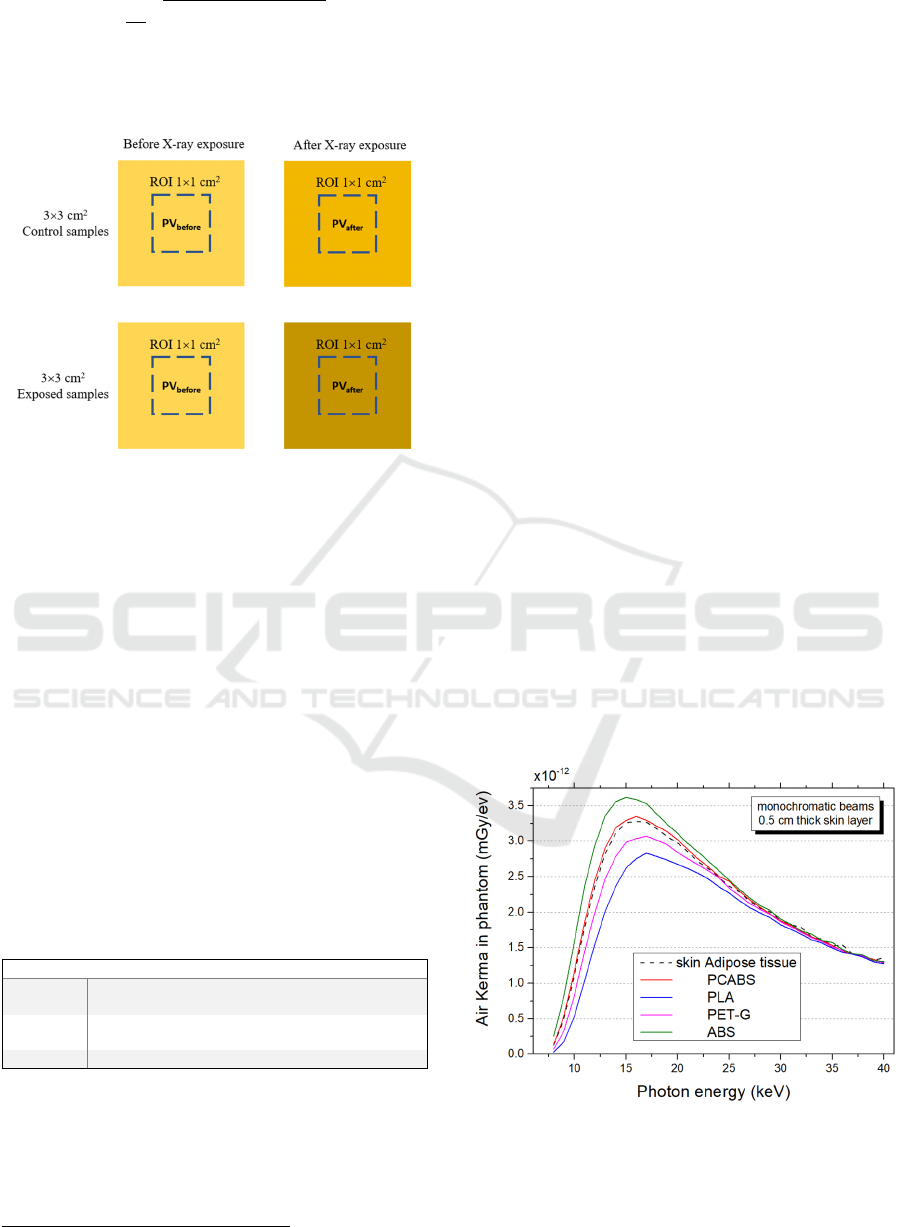
2).
R
1
2
(3)
1
2
(4)
where
and
are the mean pixel value
of samples respectively before and after the X-ray
exposition, and
and
the standard
deviations.
Statistical uncertainty due to scanner response in
multiple scans is included in
. The final value
is considered
net
R
R
R
(5)
with the relative uncertainty
8
https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/
3D Printing Materials for Physical Breast Phantoms: Monte Carlo Assessment and Experimental Validation
257
R
R
.
(6)
Calibration data points have been fitted using the
commercial analysis software Origin 9
9
and using the
exponential function ∙∙
.
Figure 2: Scheme of radiochromic samples before and after
the exposure, and ROI used for the pixel values estimation.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Density Assessment
Our first purpose was to evaluate the change in
density for different materials from the coil nominal
density value to the post-printed value. Test objects
reported variation between -9% and -14% and
reported in Table 3. PCABS final density has been
evaluated with a bigger test object which presented a
different value in density respect to the smaller
objects, suggesting a “form factor” influencing
printed objects density depending on dimensions.
Table 3: Change in density for the materials under
investigation. The uncertainty on the estimated density is
0.01 g/cm
3
.
[g/cm
3
] PLA ABS PET‐G PCABS ASA
Nominal
density
1.24 1.05 1.27 1.13 1.07
Estimated
density
1.12 0.92 1.09 0.99 0.97
variation
-10% -12% -14% -12% -9%
3.2 MC Assessment
Data provided in tables 1-3 were used in MC
simulations in order to compare transmission
9
www.originlab.com
properties of adipose skin layer and breast tissue with
those of 3D-printing material.
3.2.1 Skin Layer
Using the simulation setup shown in Figure 1, a
reference phantom 5 cm thick, 50% glandular, and a
skin thickness of 5 mm made by adipose tissue has
been adopted. We placed a scoring surface below the
skin and evaluated the air kerma transmission curve
through the skin due to monoenergetic X-ray beams,
from 8 to 40 keV at 1 keV steps. Using this approach,
we replaced adipose tissue composing the skin layer
with 3D-printing materials with density correction.
MC simulations were performed with 10
7
incident
photons for each energy beam. Results are shown in
Figure 3. At lower photon energies, the skin “shields”
the breast tissue and air kerma values are low; with
increasing photon energies X-ray beam penetrates the
skin layer up to a maximum value after which K
decreases due to the decreasing energy absorption
coefficient. Simulations suggest a better behaviour by
PCABS as skin layer respect to the other material, for
both low- and high-energies.
Since DM and DBT use polychromatic X-ray
source, we investigated polyenergetic X-ray beams @
27, 31 and 35 kV, in W/Rh anode/filter combination.
In Figure 4 is shown air kerma transmission through
the skin layer using polychromatic beams. MC
simulations were performed using 10
8
incident
photons. Air kerma values percentage variations,
respect to the adipose skin layer, suggest also in this
case that PCABS is a well substitute as skin layer.
Figure 3: Air kerma transmission through the skin layer due
to monoenergetic beams.
BIODEVICES 2020 - 13th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
258
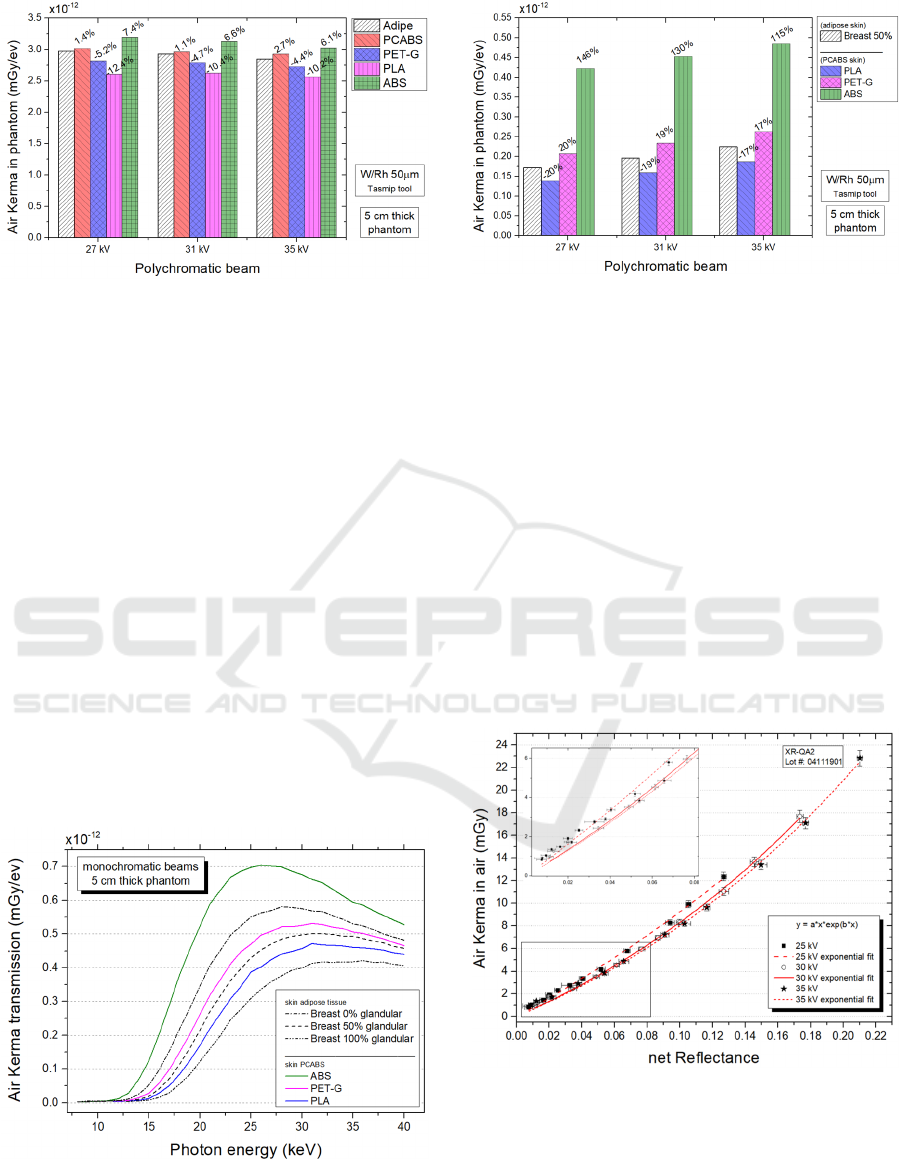
Figure 4: Air Kerma transmission through the skin layer
due to polychromatic beams. Percentage values in figure
refer to the variation respect to the adipose tissue.
3.2.2 Breast Tissue
Using the same approach of the previous paragraph,
we investigated 3D-printing materials for the inner
part of the breast phantom assuming PCABS as the
preferred skin layer material. We used, as usual, the
reference breast phantom cited previously. Figure 5
shows that both PLA and PETG can be used for the
inner part of the breast phantom, coupled with 5 mm
thick PCABS skin layer.
Since in literature there are studies involving the
amount of glandular fraction of women breast, we
noted a publication of Yaffe et al. (2009) whose work
found that, out of 2831 women, 95% were below the
45% glandularity. We show 0% glandularity
transmission curve in order to define the “range” of
transmission which 3D-materials have to follow.
Polychromatic beams have been investigated and
results are reported in Figure 6.
Figure 5: Air kerma transmission through the whole
phantom for monochromatic beams.
Figure 6: Air kerma transmission through the whole
phantom for polychromatic beams. Percentage values in
figure refer to the variation respect to the breast 50%
glandular.
3.2.3 Film Calibration Curves
Results from calibration procedure of GAFchromic
films XR-QA2 free-in-air are shown in Figure 7.
Energy dependant response curve is slightly marked,
where the beam mean energy is for 25, 30 and 35 kV
respectively 18.4, 19.1 and 20.0 keV. Points in the
graph are scattered from about 1 to 2 mGy and follow
the fit curve for doses higher than 2 mGy.
Even if digital mammography is a low-exposure
procedure, it is worth noting that high milliamperages
have been used in order to have a major statistic in the
calibration curves, which otherwise would be affected
too much by the low exposure fluctuations.
Figure 7: Calibration curves @ 25, 30 and 35 kV. In figure
is shown a magnification for low-doses exposures.
3D Printing Materials for Physical Breast Phantoms: Monte Carlo Assessment and Experimental Validation
259

3.3 3D-printed Phantom Dosimetry
Assessment
Results from the previous investigations led to create
a breast phantom with an outer layer made by PCABS
material and an inner part of PLA material.
Despite of PETG curve is between those of
glandularities 0% and 50% (Figure 5), we decide to
characterize experimentally PLA because during the
3D-printing phase, density can be further changed
with the infill option, that is the percentage of air
filling (Madamesila et al. 2016). This can cause a
major X-ray transmission depending on the infill
percentage. Using this approach, a greater number of
glandularities can be explored, from more than 50%
to 0%, incrementing the infill option. Infill option has
not been investigated yet, and our purpose is first of
all to evaluate experimentally our method and
PCABS+PLA physical phantom.
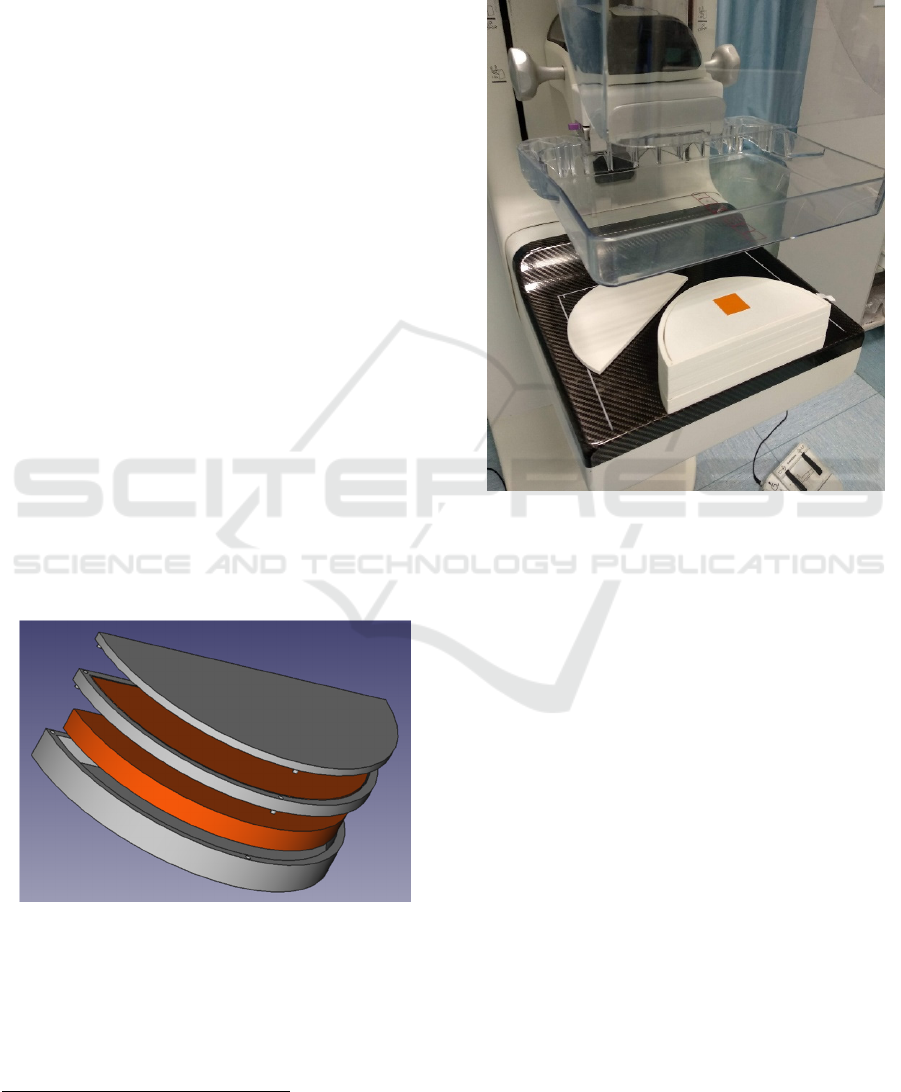
Using the open software FreeCAD
10
, we
developed a modular 3D phantom made by few slices
in order to compose different breast phantom
thicknesses. Each component of the phantom is
exported in STL file format used by the 3D printer.
Phantom is composed by external layers (in grey,
Figure 8) printed in PCABS, and PLA inner
components (in orange). As reported in Figure 1,
radius semi-cylinder is 10 cm, while thickness is
variable depending on how many slices are used.
Slices let to perform dosimetry with radiochromic
films by inserting below each layer a 33 cm
2
GAFchromic sample (Figure 9).
Figure 8: 3D project of the modular phantom created.
In order to demonstrate the agreement with
transmission properties of the physical phantom with
the expected values from MC simulations, a
comparison has been performed. Following equation
(2), experimental measurements have been performed
10
https://www.freecadweb.org/
@ 35 kV by inserting radiochromic film samples
under each slice of the phantom for obtaining
,
at a given depth , normalized by
,
obtained placing samples between the phantom
surface and the compression paddle.
Figure 9: Example of positioning of radiochromic sample
inside the phantom. The photograph refers to the
,
0.5 value obtained under the upper PCABS skin
layer which has been temporary removed for placing the
sample.
MC simulations refer to air kerma estimates at the
same depth in the phantom. Results in Table 4 show
a good agreement in transmission properties of the
skin layer (depth 0.5 mm) and the firsts two PLA
layers (depth 1.3 and 2.1 mm); in the last layers the
discrepancy is greater, because of the low doses
reached. Indeed, air kerma estimates derived from the
fitting curve show values from about 2 mGy to 0.8
mGy, not considered reliable. This is a limitation due
to characterizing low dose in mammography,
especially in the phantom lower layers, with
subsequent low dose exposures in radiochromic
films. This does not allow to complete the percentage
depth dose curve.
BIODEVICES 2020 - 13th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
260

Table 4: Comparison between experimental data with MC
simulations. Variations in the last column have been
obtained using equation 2. The first row (in grey) represents
the transmission due to the 5 mm thick PCABS layer, while
the other (orange) rows the transmission due to the 8 mm
thick PLA layers composing the phantom inner part.
Depth
d(mm)
net
R
(mGy)
(mGy/ev)
variation
In
c
0.1461 13.22
3.78 E-12
-
0.5
0.1205 10.19
2.98 E-12
-2.5%
1.3
0.0806 6.14
1.77 E-12
-1.1%
2.1
0.0530 3.75
1.09 E-12
-1.7%
2.9
0.0329 2.15
6.73 E-12
-9.7%
3.7
0.0207 1.35
4.23 E-12
-9.9%
4.5
0.0132 0.84
2.74 E-12
-14.4%
4 DISCUSSION
We presented the method used by our research group
to characterize 3D-printing materials to be used for
the creation of breast physical phantoms, having the
same transmission properties of the digital breast
phantoms used in MC breast dosimetry, whose have
dedicated elemental compositions for adipose and
glandular tissues. The approach of involving physical
phantoms with dedicated materials for the skin and
the for the breast tissue could be useful in research or
QA procedures for DM and DBT investigations,
where, until now, polymethyl-metacrilate
homogeneous phantoms are used. We involved MC
simulations to investigate transmission properties of
some 3D-printing materials, whose densities have
been corrected in the MC code, since the final density
of the printed object can vary during the printing
phase. Based on the MC results, performed over
monoenergetic and polyenergetic beams, a physical
breast phantom has been created. Results deriving
from densities estimation and MC simulations led to
consider PCABS material as a well substitute for the
5 mm thick skin layer and PLA material as substitute
for the inner breast tissue.
In order to validate our test phantom,
experimental measurements with GAFchromic XR-
QA2 films were performed, which results confirmed
an agreement with transmission estimations in MC
results for both PCABS layer and for the inner PLA
material, supporting our method, which uses
relatively low-cost equipment and procedures.
Since it is known that mostly of women breast
glandularities ranging from 0% to about 50%, we
decided to adopt PLA material, to support our next
step, which will be to characterize the infill option
that allows to decrease voluntarily the material
density during the printing phase. With this approach
various breast glandularities from 0 to about 50% can
be reached in synthetic phantoms, leading to perform
the image quality assessment for different synthetic
breast anatomies.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The presented work is part of the RADIOMA project
which is partially funded by "Fondazione Pisa",
Technological and Scientific Research Sector, Via
Pietro Toselli 29, Pisa (Italy). The authors would like
to thank Fondazione Pisa for giving the opportunity
to start this study.
REFERENCES
Alssabbagh, M., Tajuddin, A. A., Abdulmanap, M. and
Zainon, R., 2017. Evaluation of 3D Printing Materials
for Fabrication of a Novel Multi-Functional 3D
Thyroid Phantom for Medical Dosimetry and Image
Quality. Radiation Physics and Chemistry 135: 106–12.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2017.02.009.
Barca, P. et al. 2019. Image Quality Comparison between
Digital and Synthetic 2D Mammograms: A Qualitative
and Quantitative Phantom Study. BIOIMAGING 2019
- 6th International Conference on Bioimaging,
Proceedings; Part of 12th International Joint
Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and
Technologies, BIOSTEC 2019: 129–36.
Barca, P., et al. 2019. Comprehensive Assessment of Image
Quality in Synthetic and Digital Mammography : A
Quantitative Comparison. Australasian Physical &
Engineering Sciences in Medicine (Cd).
Boone, J. M., 1999. Glandular Breast Dose for
Monoenergetic and High-Energy x-Ray Beams: Monte
Carlo Assessment. Radiology 213(1): 23–37.
Boone, J. M., Fewell, T. R. and Jennings, R. J., 1997.
Molybdenum, Rhodium, and Tungsten Anode Spectral
Models Using Interpolating Polynomials with
Application to Mammography. Medical Physics 24(12):
1863–74.
Dance, D. R., 1990. Monte-Carlo Calculation of
Conversion Factors for the Estimation of Mean
Glandular Breast Dose. Physics in Medicine and
Biology 35(9): 1211–19.
Dance, D. R., Young, K. C. and Van Engen, R. E., 2011.
Estimation of Mean Glandular Dose for Breast
Tomosynthesis: Factors for Use with the UK, European
and IAEA Breast Dosimetry Protocols. Physics in
Medicine and Biology 56(2): 453–71.
Ferreira, C. C. et al., 2010. Evaluation of Tissue-Equivalent
Materials to Be Used as Human Brain Tissue Substitute
in Dosimetry for Diagnostic Radiology. Nuclear
Instruments and Methods in Physics Research, Section
B: Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms
3D Printing Materials for Physical Breast Phantoms: Monte Carlo Assessment and Experimental Validation
261

268(16): 2515–21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.
2010.05.051.
Hammerstein, G. R. et al., 1979. Absorbed Radiation Dose
in Mammography. Radiology 130(2): 485–91.
Hubbell, J. H., and Seltzer, S. M., 1995. Tables of X-Ray
Mass Attenuation Coefficients and Mass Energy-
Absorption Coefficients 1 KeV to 20 MeV for Elements
Z=1 to 92 and 48 Additional Substances of Dosimetric
Interest. Http://Physics.Nist.Gov/Xaamdi 5632.
http://www.nist.gov/pml/data/xraycoef/index.cfm.
Ivanov, D. et al., 2018. Suitability of Low Density Materials
for 3D Printing of Physical Breast Phantoms. Physics
in Medicine and Biology 63(17): aad315.
https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/aad315.
Di Lillo, F. et al., 2016. Energy Dependent Calibration of
XR-QA2 Radiochromic Film with Monochromatic and
Polychromatic x-Ray Beams. Medical Physics 43(1):
583–88.
Liu, S. et al., 2011. Reactive Compatibilization of Poly
(Butylene Terephthalate)/Acrylonitrile- Styrene-
Acrylate Blends by Epoxy Resin: Morphology and
Mechanical Properties. Journal of Macromolecular
Science, Part B: Physics 50(9): 1780–90.
Madamesila, J., McGeachy P., J. Barajas, E. J. and Khan,
R., 2016. Characterizing 3D Printing in the
Fabrication of Variable Density Phantoms for Quality
Assurance of Radiotherapy. Physica Medica 32(1):
242–47. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2015.09.013.
Massera, R. T. and Tomal, A., 2018. Skin Models and Their
Impact on Mean Glandular Dose in Mammography.
Physica Medica 51: 38-47.
Perry, N. et al., 2008. European Guidelines for Quality
Assurance in Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis.
Fourth Edition - Summary Document. Annals of
Oncology 19(4): 614–22. http://europa.eu.int/comm/
dgs/health_consumer/index_en.htm.
Sarno, A. et al., 2019. Monte Carlo Calculation of
Monoenergetic and Polyenergetic DgN Coefficients for
Mean Glandular Dose Estimates in Mammography
Using a Homogeneous Breast Model. Physics in
medicine and biology 64(12): 125012.
Sarno, A., Mettivier, G. and Russo, P., 2017. Air Kerma
Calculation in Monte Carlo Simulations for Deriving
Normalized Glandular Dose Coefficients in
Mammography. Physics in Medicine and Biology.
Sechopoulos, I., 2013a. A Review of Breast Tomosynthesis.
Part I. The Image Acquisition Process. Medical
Physics.
———. 2013b. A Review of Breast Tomosynthesis. Part II.
Image Reconstruction, Processing and Analysis, and
Advanced Applications. Medical Physics.
Sempau, J. et al., 2001. Monte Carlo Simulation of Electron
Beams from an Accelerator Head Using PENELOPE.
Physics in Medicine and Biology 46(4): 1163–86.
Task Group, Aapm. 2015. Monte Carlo Reference Data
Sets for Imaging Research. Medical Physics 42.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1118/1.4928676.
Tomic, N., Devic, S., Deblois, F. and Seuntjens, J., 2010.
Reference Radiochromic Film Dosimetry in
Kilovoltage Photon Beams during CBCT Image
Acquisition. Medical Physics 37(3): 1083–92.
Tucciariello, R. M. et al., 2019. Monte Carlo Methods for
Assessment of the Mean Glandular Dose in
Mammography: Simulations in Homogeneous
Phantoms. BIOINFORMATICS 2019 - 10th
International Conference on Bioinformatics Models,
Methods and Algorithms, Proceedings; Part of 12th
International Joint Conference on Biomedical
Engineering Systems and Technologies, BIOSTEC
2019: 242–49.
Yaffe, M. J. et al., 2009. The Myth of the 50-50 Breast.
Medical Physics 36(12): 5437–43.
BIODEVICES 2020 - 13th International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
262
