
Motor Speed Control toward Wall Surface Angle based on HC-SR04
Ultrasonic Sensor
Peri Turnip
1
, Erwin Sitompul
2
, Bambang Mukti Wibawa
3
, Agus Trisanto
3
, and Arjon Turnip
3*
1
Computer Engineering, Politeknik Pajajaran, Bandung,Indonesia
2
Study Program of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, President University, Indonesia
3
Department of Electrical Engineering,Universitas Padjajaran, Bandung, Indonesia
Keywords: Brain-Controlled Wheelchair, Control Motor DC with PWM.
Abstract: Brain-controlled wheelchair is an assisting device for patients with motor disabilities controlled by brain
waves. The convenience and security of users is the focus of the development of brain-controlled
wheelchairs. In this final task was designed dc motor speed control system using pulse width modulation
(PWM) method on a different surface slope using ultrasonic sensors. With this method it is expected that the
wheelchair can move at different speeds under certain surface conditions. This way the concept of security
of the user will be fulfilled for the future. The detection distance of the obstacle object is influenced by the
intensity of humidity, namely the drier the place gives more accurate results in its measurement. Research
on motor speed controllers can use other control methods to ensure that motor speed is stable on flat and
sloping surfaces, and to improve processing speed and object detection accuracy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Wheelchairs are usually used to help move people
with partial or total paralysis. Conventional or joistic
wheelchairs whose movements must be assisted by
other people or hand movements have not been able
to help people who are completely paralyzed to
move or move independently. Thus, for people with
total paralysis, a wheelchair that can be moved
through the mind is needed. The majority of people
with total paralysis can still think well. This brain
signal activity will then be used to move the motor
instead of joistic. The development of this
technology is supported by the development of
biosignal science which is able to identify and
classify brain signals for specific functions.
The ability to move freely is the desire and need
of each individual. Especially for people with
disabilities who have limited space. Not all persons
with disabilities can use their own wheelchair to
travel, therefore with the help of technology a Smart
Wheelchair or Electric Wheelchair is developed
based on control using physiological brain waves.
Physiological brain waves can be used to control
wheelchair movement (such as forward, stop, turn
right, or turn left) by recording and analyzing brain
biosignals. Electroencephalogram (EEG) is used to
record biosignals from the brain which can then be
used to run a wheelchair. In this case, control is
carried out of the user's brain signal activity
supported by several instruments such as sensors.
EEG is a device that captures the activity of
bioelectrical signals recorded from electrodes on the
scalp. In medicine, EEG is used to diagnose diseases
such as Alzheimer's and epilepsy. In this case, EEG
can be used as a controller that utilizes these
bioelectrical signals. The processing of data obtained
from the EEG makes it possible to group one's
thoughts in the form of waves. This can be used as
information for controllers, by adjusting the data that
has been trained to control wheelchair movement.
This wheelchair with EEG system cannot reduce
and increase the motor speed. EEG based signals can
only be used for certain movements such as forward,
backward, turn, stop. Therefore, in developing the
Brain-Controlled Wheelchair system, several
additional sensors are needed to obtain certain
information such as detecting obstacles, road slopes,
and others. Several studies related to brain-
wheelchair development have been carried out
[Turnip, A et al 2015; Turnip, M et al 2015].
In a previous study on smart wheelchairs,
entitled Ultrasonic Tethering to Enable Side-by-Side
Following for Powered Wheelchairs, tested and built
630
Turnip, P., Sitompul, E., Wibawa, B., Trisanto, A. and Turnip, A.
Motor Speed Control toward Wall Surface Angle based on HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor.
DOI: 10.5220/0010370900003051
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies (CESIT 2020), pages 630-637
ISBN: 978-989-758-501-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

a system using an ultrasonic sensor where a
wheelchair can detect someone to be used as a guide
in moving (Pingali et al., 2019) ). Another study
using ultrasonic sensors in wheelchairs is "Low cost
sensor network for obstacle avoidance in share-
controlled smart wheelchairs under daily scenarios"
by (Pu et al., 2018). In this journal, four cheap
ultrasonic sensors are used on the underside of the
front of the wheelchair to detect obstacles in front of
and below the wheelchair. A fuzzy logic navigation
controller implemented in hardware for an electric
wheelchair by (Rojas et al., 2018; Turnip et al, 2015;
Turnip et al, 2015) uses ultrasonic sensors with the
help of a fuzzy logic algorithm in determining
direction decisions on wheelchair movement. Smart
Navigation and Control System for Electric
Wheelchair” by (Dakhilallah et al., 2019) also uses
ultrasonic sensors as an aid in navigation. In the
paper, it is explained that in addition to ultrasoic
sensors, a controller using a joystick is also built as a
navigation aid. Smart Autonomous Wheelchair
Controlled by Voice Commands-Aided by Tracking
System explains how to control a wheelchair using
voice commands and also uses a tracking system to
find out the position of the wheelchair itself
(Alkhalid & Oleiwi, 2019). Autonomous Wheelchair
with a Smart Driving Mode and a Wi-Fi Positioning
System discusses the integration design using GPS
and wifi as a navigation tool while security uses
ultrasonic sensors and IR sensors (Manjunath, 2018;
Turnip et al, 2015).
Controlled Wheelchair System Based on
Gyroscope Sensor for Disabled Patients examines an
electric wheelchair that is controlled using motion
using an ultrasonic sensor as a safety device from
obstacles (Al-Neami & Ahmed, 2018). In this study,
it was also explained that the head movement data
used were obtained from a gyroscope sensor
mounted on the user's head. Voice Recognition
based on Intelligent Wheelchair and GPS Tracking
System explains that a wheelchair can be operated
by voice command by using firebase to control the
direction of the wheelchair for both forward and
backward (Aktar et al., 2019). Autonomous
wheelchair under a predefined environment
implements an electric wheelchair operating system
by using a keypad as a controller in movement and
using an IR sensor and also an Ultrasonic sensor as
an obstacle detection system (Roslan et al., 2017).
Smart Wheelchairs: Using Robotics to Bridge the
Gap between Prototypes and Cost-effective Set-ups
designed a wheelchair with automatic and manual
control, where manual control uses a joystick as the
controller and also uses an Ultrasonic Sensor as a
detecting obstacle and obstacle course (Aquilina et
al. al., 2019).
From all the journals that have been mentioned
above, there are many studies taking references on
how best ultrasonic sensors can work properly by
combining them with several other sensor devices.
However, in this study the ultrasonic sensor is used
in a different way, namely to measure the angle of
the wall surface or other obstacle. Furthermore, the
tilt information will be used to adjust the motor
rotation speed. Ultrasonic sensor (HC-SR04) is used
as a tool to calculate the slope angle to support the
brainsignal-based wheelchair motor controller from
the EEG system.
A motor speed control system with a pulse width
modulation (PWM) method on a different surface
slope using an ultrasonic sensor is designed. With
this method, it is expected that wheelchairs can
move at different speeds in certain surface
conditions. However, this system still has limitations
where the measurement results obtained are still less
precise.
2 THEORY
2.1 Brain-controlled Wheelchair
Brain-Controlled Wheelchair is a technology that
combines a wheelchair with a Brain-Computer
Interface (BCI) with the aim of helping wheelchair
control to make it easier for people with motor
disorders. BCI can communicate directly between
the computer and the brain. This allows wheelchair
surgery to use commands from the brain's
physiological signals while thinking. BCI is able to
represent the user's thoughts into controlling
wheelchair movement according to the user's wishes.
2.2 Ultrasonic Sensor HC-SR04
Ultrasonic sensor HC-SR04 is a sensor measuring
distance based on ultrasonic waves with a working
principle: the emitted ultrasonic waves are then
received back by the sensor receiver itself, then
detects any object in front of it in the form of a solid
object or a barrier. The detection range is 2-500cm,
the detection angle is 15 degrees, and can be
connected directly to the Arduino microcontroller
input / output (Saputra, 2013). The HC-SR04 has
two main components as a constituent in the form of
a transmitter emitting ultrasonic waves with a
frequency of 40 KHz and the receiver capturing the
Motor Speed Control toward Wall Surface Angle based on HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
631
results of ultrasonic wave reflections (Setyawan et
al., 2018).
2.3 Arduino UNO R3
Arduino UNO R3 is a microcontroller development
board based on the ATmega328P chip. Arduino
UNO has 14 gigital pins input / output pins (I / O, of
which 14 pins can be used as Pulse Wiidth
Modulation (PWM) output, including pins 0 to 13),
6 analog input pins, using a 16 Mhz crystal,
including pin A0 to A5, USB connection, power
jack, ICSP header and reset button. All of these pins
are required to support a microcontroller circuit. The
worst possibility is just damage to the ATMega328
chip, but it can be replaced easily and relatively
cheaply. Since the initial launch until now, Uno has
developed into a Revised 3 version or commonly
written as REV 3 or R3. Arduino IDE software,
which can be installed on Windows as well as Mac
and Linux, functions as a software that helps you
enter (upload) programs to the ATMega328 chip
easily (Hasriyani & H, 2018).
Integrated Development Environment (IDE) is a
software used to develop microcontroller
applications starting from writing source programs,
compiling, uploading compilation results and testing
in serial terminals. Arduino can be run on computers
with various platforms because it is supported or
based on Java. The source program for
microcontroller applications is C / C ++ and can be
combined with assembly.
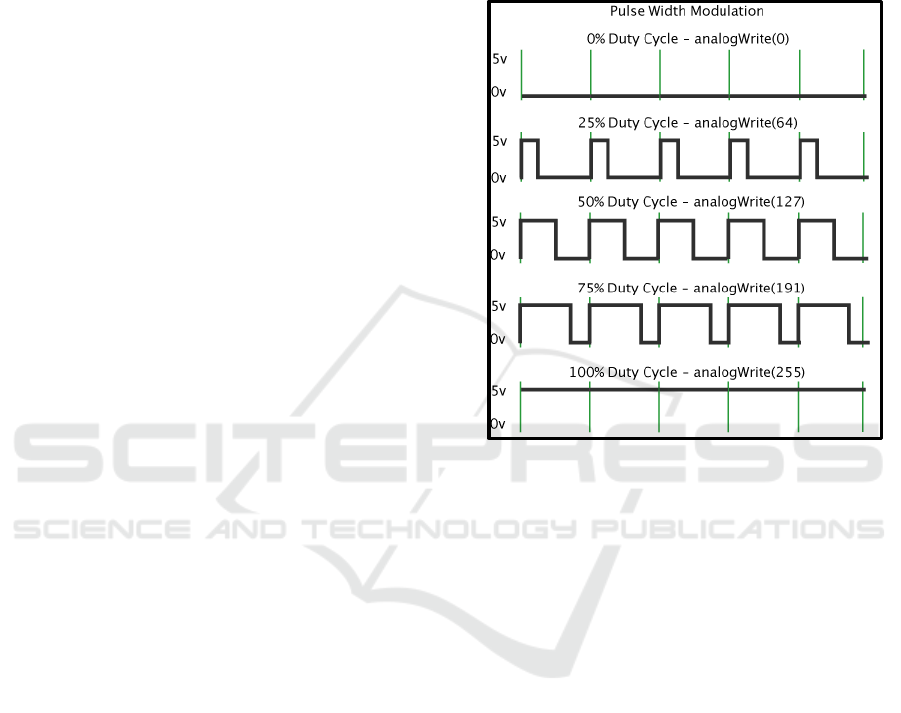
2.4 Pulse with Modulation
One way to adjust the rotational speed of a dc motor
is by means of pulse width modulation (PWM).
Pulse width modulation (PWM) is a way of
manipulating the pulse width in one. PWM signals
generally have a fixed basic amplitude and
frequency, but have varying pulse widths. The PWM
Pulse Width is directly proportional to the amplitude
of the original unmodulated signal. This means that
the PWM signal has a fixed wave frequency but the
duty cycle varies (from 0% to 100%) (Hasriyani &
H, 2018). Duty cycle is the percentage of high pulse
length in one signal period. When the duty cycle is
0% or the signal is fully low, the value of the voltage
output is 0V. When the duty cycle is 100% or the
signal high is full, the voltage output is 5V.
The PWM that can be generated by Arduino has
a data allocation of 8bit, or has a variation of
parameter value changes ranging from 0 - 255, a
change in value that represents the duty cycle of 0 -
100% of the PWM output. To set the duty cycle
value on Arduino, use the analogWrite function
([Pin number], [value]). If the duty cycle is to 0%
and 100%, then set the parameter values to be 0 and
255, respectively. So the duty cycle is 50%, meaning
that the parameter value that must be set is 127.
PWM graph can be seen as in Figure 1.
Figure 1: PWM graph.
3 DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT
Ultrasonic sensor signal processing aims to
determine the accurate distance between a
wheelchair and a wall in an inclined or non-vertical
position. The signal that is obtained is data from the
sensor on objects that are obstructions in front, side
and back of the wheelchair. The design of a speed
control system for the wall surface slope using an
Ultrasonic sensor is illustrated in Figure 2. The
system workflow starts from reading the distance
data on the Ultrasonic sensor. The distance data
from the two sensors as a reference for flat and tilted
surfaces is processed by Arduino UNO R3.
Furthermore, Arduino will be given a program with
an if condition, if sensor a is the same as sensor b
then it is assumed that the sensor detects a flat
surface, otherwise if one of the sensors reads the
distance is less then it will be detected as a sloping
surface. PWM control provides control action on the
motor based on the distance obtained where if the
surface detected is flat, the motor will reduce the
speed according to the predetermined speed,
conversely if the surface is detected is tilt, the motor
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
632

speed will be lowered according to the angular
conditions obtained in the calculation by the system.
Figure 2: Sheme of velocity control system for wall
surface slope using Ultrasonic sensor.
3.1 Motor Speed Control Design
The ultrasonic sensor added to the wheelchair
system is a device used to read the distance of an
object or object surface that will be traversed by a
brain-controlled wheelchair. Furthermore, the
motion controller is used to determine the precision
of an instrumentation system with the characteristics
due to good feedback on the system. Motion
Controller is used as a speed controller by providing
control action on the DC motor based on the
distance value obtained. Furthermore, the DC motor
will provide a speed value that is close to the desired
value in the form of a Set Point value.
3.2 Obstacle Detection System Design
Motion Control usually refers to a system with
accurate position, speed, torque capability that
operates in open or closed loop mode. The open-
loop drive sends a Movement command to the DC
motor, but receives no information about the result.
The closed loop system has a feedback device on the
motor shaft to verify or adjust the resulting motion.
The initial stage begins with data acquisition
from TrigPin by ultrasonic sensors (Figure 3). The
calculation process is carried out at the recorded
wavelength and the system will divide the wave
according to the equation used to convert the
wavelength into a measurable distance. In
processing signals from ultrasonic sensors, the
concept of median-filter is used as a reference so
that the data obtained has less noise and good
quality. The Median-Filter has a characteristic: it
only uses some of the data obtained previously and
is then processed to produce an accurate value by
taking the middle value of some of the data collected
and has sufficient accuracy because it always
performs calculations when the sensor reads new
data. The filter aims to minimize reading errors from
the ultrasonic sensor. The process of measuring
angles is obtained with several conditions that must
be met in order to obtain accurate and consistent
results. The calculation of angles and distances is
obtained from equations (1) and (2). The calculation
process is expressed in Figure 4. The wheelchair
kinematic model is used as a reference in
calculations to determine the wheel speed whether
the wheel rotates more to the left or right.
Figure 3: Recording and division process of recorded
wavelengths to get the closest wheelchair distance with the
wall.
𝜃tan
𝑎𝑏
𝐿𝑢
(1)
where, θ is the angle formed from the results of
calculations that have been done, Lu is the distance
between the ultrasonic sensor a and the ultrasonic
sensor b, a is the distance between the ultrasonic
sensor a and the wall, and b is the distance between
the ultrasonic sensor b and the wall.
ℎ
𝑎𝑏
2
cos𝜃
(2)
Motor Speed Control toward Wall Surface Angle based on HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
633
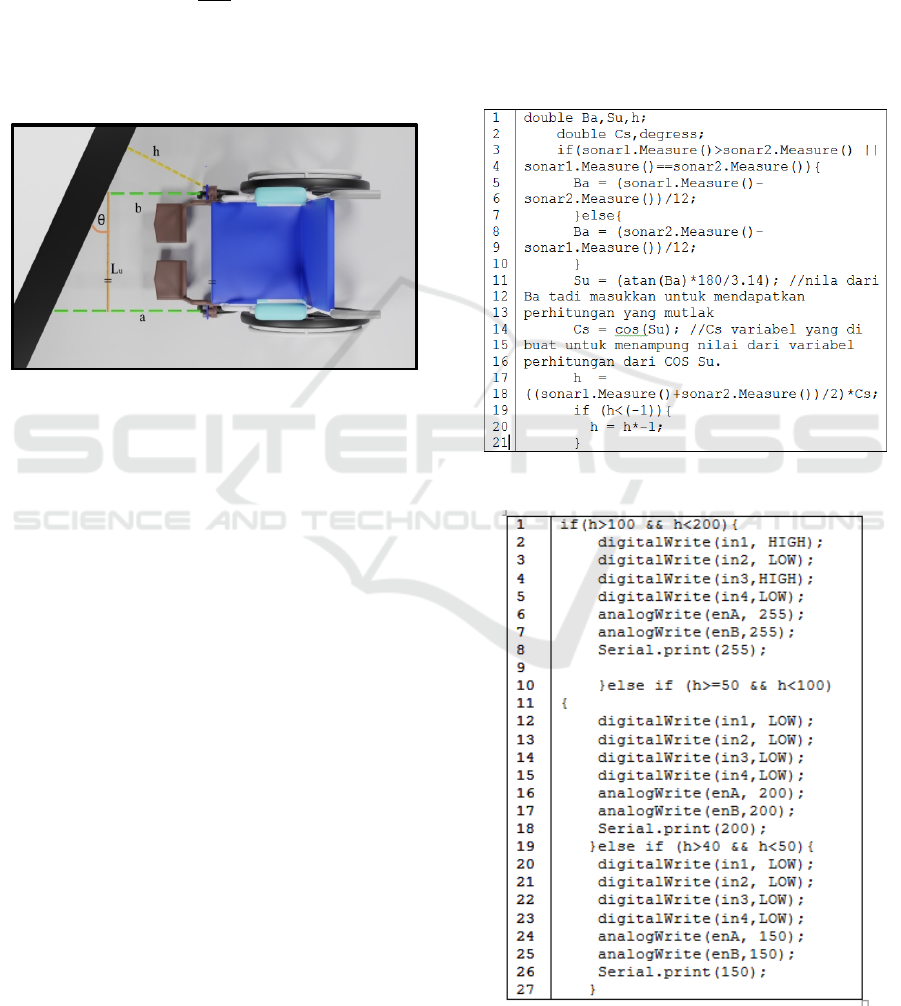
where θ is the angle formed from the results of
the calculations that have been done, h is the actual
distance between the wheelchair and the wall.
The following equation (3) is used to convert the
angle value into radians so that it can be recognized
by Arduino;
𝑛𝑁
𝜋
1
80
(3)
where, n is the value of the angle of the degree you
want to find, N is the radian value that we know
beforehand, and is a value that contains 3.14.
Figure 4: Calculation of the distance of a wheelchair to a
sloping wall.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Tool testing is carried out on hardware by obtaining
data using the serial monitor from the Arduino IDE.
The data obtained include: distance data read by the
ultrasonic sensor by testing the distance, angle and
velocity. The actual distance was measured as
comparative data for the results from the system.
Ultrasonic sensor test data aims to determine how
much influence the distance between the object and
the rotation speed of the DC motor wheel.
The waves from the ultrasonic sensor are sent by
setting the pin in the input state or as output on the
microcontroller. The distance was obtained by
calculating the speed of propagation of the wave
against the time difference between the transmitter
of the wave by the transmitter and the time when the
reflected wave is received by the receiver. The
received distance is processed again to get the
results from the calculations between several sensors
installed. The data is processed to obtain accurate
angles and distance calculations. The following is a
snippet of program code for the change process from
the distance received by the sensor to be converted
into the desired distance (Figure 4). Ba is a variable
that is made to accommodate the value of the
reduction between sensors a and b then it is divided
by the distance between the two sensors. Su is a
variable created to accommodate the tan-1 value of
Ba; Cs is a variable created to accommodate the cos
value of Su; h is the ideal distance that you are
looking for or you can also call it the setpoint. After
fulfilling the conditions described in the program
code, then the wheelchair speed is from the distance
that has been obtained. Figures 5 and 6 are the
program code for distance and the speed control of a
dc motor.
Figure 5: Program code snippets for distance calculation.
Figure 6: Code for setting motor speed.
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
634
Object detection testing using two ultrasonic
sensors was carried out to determine the success in
the detection of angles and distances with the
processing process that had been designed. The
simulation calculation results to get the closest
distance to the wheelchair and the change in the
motor rotation speed to the change in angle can be
seen as in Table 1 where
is the change in angle, a
and b are the distance of each sensor on the wall
(cm), h is the calculated closest distance v is the
rotational speed of the motor due to the change in
distance h, and Lu is the constant distance between
sensors.
Table 1: Calcualtion resuts on simulation with disferent
angels.
a b h v Lu
75 50 5 7.1 0 12
70 50 17 11.45 0 12
65 50 25 16.22 0 12
60 50 29 20 0 12
55 50 33 24 0 12
50 50 36 28 32 12
45 50 38 31 32 12
40 50 40 35 32 12
35 50 41.5 37 40 12
30 50 43 40 40 12
25 50 44.5 42 50 12
The results of manual calculations in Table 1
show that when the h value is less than 28 cm, the v
value automatically becomes zero, which means that
the wheel rotation stops. In this case the wheelchair
will wait for information from other sensors such as
cameras or brain signals to decide whether to stop or
turn (left or right) or reverse. When the distance or h
value is greater than or equal to 28 cm, the wheel
rotation becomes 28 rad / s and will continue to
increase as the h value is greater. If the wheelchair
moves towards the wall at a certain angle, the sensor
will calculate the closest distance before the
wheelchair hits the wall. Because the angle
is less
than 90 degrees, the distance between the wheelchair
and the wall will differ between sensors, so it is
necessary to estimate it.
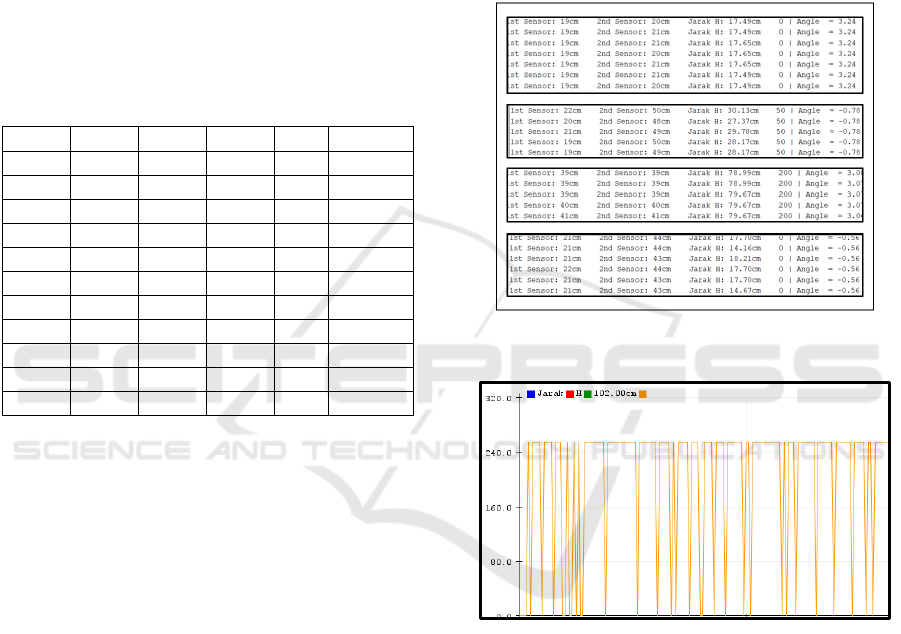
Figure 7 shows the test results displayed using a
serial monitor in realtime where the distance and
speed generated on the monitor screen work in
accordance with the conditions obtained. Figure 8 is
the print result of the serial plotter where it can be
seen that the ultrasonic sensor distance changes
quickly. These changes occur because of the
disconnection of sensors in detecting objects. With
the help of filters and averaging this problem can be
solved. If this result is used directly to the motor
rotation it will result in unstable wheelchair
movement. Further development related to this
problem needs to be done, namely by increasing the
ability of filters and estimators. In this experiment,
the results of this problem can still be resolved
considering that testing is still limited. However, if
applied with a wheelchair on a varied track, it is
assumed that the stability will decrease.
Figure 7: Realtime Test Using Serial Monitor.
Figure 8: Serial plotter display.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The object detection system based on the ultrasonic
sensor with a direction at a certain slope is able to
recognize obstacles in the form of walls in realtime.
A filtering system to minimize unwanted values due
to sensor limitations as well as changes in
wheelchair direction has been developed with
accurate results. The detection distance of the
obstacle object is influenced by the intensity of
humidity, namely the drier the place gives more
accurate results. Research on motor speed
Motor Speed Control toward Wall Surface Angle based on HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
635

controllers can use other control methods to ensure
that motor speed is stable on flat and sloping
surfaces, and to improve processing speed and
object detection accuracy. The offline and realtime
test results show fairly accurate results where a
wheelchair is able to detect objects in the form of
walls at an angle of less than 90 degrees.
Incorporation of additional sensors such as an
ultrasonic sensor to detect paths before the IMU
sensor detects surface slope is necessary. The motor
used must be equipped with a speed reading so that
the accuracy of the speed reading can be better.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by Technical
Implementation Unit for Instrumentation
Development, Indonesian Institute of Sciences,
Department of Electrical Engineering, Universitas
Padjadjaran, and Toba Research Center, Indonesia.
REFERENCES
Aktar, N., Jaharr, I., & Lala, B., 2019. Voice Recognition
based intelligent Wheelchair and GPS Tracking
System. 2nd International Conference on Electrical,
Computer and Communication Engineering, ECCE
2019, February.
https://doi.org/10.1109/ECACE.2019.8679163.
Al-Neami, A. Q. H., & Ahmed, S. M., 2018. Controlled
Wheelchair System Based on Gyroscope Sensor for
Disabled Patients. Biosciences Biotechnology
Research Asia, 15(4), 921–927.
https://doi.org/10.13005/bbra/2703.
Alkhalid, F. F., & Oleiwi, B. K., 2019. Smart Autonomous
Wheelchair Controlled by Voice Commands-Aided by
Tracking System. Iraqi Journal of Computer,
Communication, Control and System Engineering, 82–
87. https://doi.org/10.33103/uot.ijccce.19.1.10
Aquilina, M., Bugeja, M. K., & Fabri, S. G., 2019. Smart
wheelchairs: Using robotics to bridge the gap between
prototypes and cost-effective set-ups. ICINCO 2019 -
Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on
Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics,
2(Icinco), 181–189.
https://doi.org/10.5220/0007796801810189.
Dakhilallah, B., Alrashdi, S., Rao, K. P., & Alotaibi, N.
D., 2019. Smart Navigation and Control System for
Electric Wheelchair American Journal of Engineering
Research (AJER). 4, 90–94.
Hasriyani, & H., 2018. Bab II tinjauan pustaka BBLR. 5,
1–40. http://eprints.undip.ac.id/62287/4/BAB_II.pdf
Ii, B. A. B., 2001. Universitas Sumatera Utara 6. 1(2), 6–
38.
Manjunath, G., 2018. Autonomous Wheelchair with a
Smart Driving Mode and a Wi-Fi Positioning System.
April.
Pingali, T. R., Lemaire, E. D., & Baddour, N., 2019.
Ultrasonic tethering to enable side-by-side following
for powered wheelchairs. Sensors (Switzerland),
19(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/s19010109
Pu, J., Jiang, Y., Xie, X., Chen, X., Liu, M., & Xu, S.,
2018. Low cost sensor network for obstacle avoidance
in share-controlled smart wheelchairs under daily
scenarios. Microelectronics Reliability, 83(March),
180–186.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microrel.2018.03.003
Rojas, M., Ponce, P., & Molina, A., 2018. A fuzzy logic
navigation controller implemented in hardware for an
electric wheelchair. International Journal of Advanced
Robotic Systems, 15(1), 1–12.
https://doi.org/10.1177/1729881418755768
Roslan, M., Yahya, M., Ahmad, Z., Hani, A., & Mokhtar,
I., 2017. International Journal of Advanced and
Applied Sciences. Order, 14(4), 18.
Saputra, D. A., 2013. Simulasi Pemrograman Sistem
Pengendali Kecepatan Pada Rancang Bangun Mobil
Remote Kontrol Menggunakan PWM Berbasis Sensor
Ultrasonik HC-SR04 dan Mikrokontroler Arduino.
Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta.
https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
Setyawan, B., Andryana, S., & Winarsih, W., 2018.
Sistem Deteksi Menggunakan Sensor Ultrasonik
berbasis Arduino mega 2560 dan Processing untuk
Sistem Keamanan Rumah. J I M P - Jurnal
Informatika Merdeka Pasuruan, 3(3), 15–20.
https://doi.org/10.37438/jimp.v3i3.183
Subroto, T., & Sholihah, W., 2018. Analisis Hambatan
Belajar Pada Materi Trigonometri Dalam Kemampuan
Pemahaman Matematis Siswa. IndoMath: Indonesia
Mathematics Education, 1(2), 109.
A. Turnip, M. A. Suhendra and Mada Sanjaya W. S.,
2015. Brain-controlled wheelchair based EEG-SSVEP
signals classified by nonlinear adaptive filter. IEEE
International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics
(ICORR), Singapore, 2015, pp. 905-908, doi:
10.1109/ICORR.2015.7281318.
M. Turnip et al., "An application of online ANFIS
classifier for wheelchair based brain computer
interface," 2015 International Conference on
Automation, Cognitive Science, Optics, Micro
Electro-Mechanical System, and Information
Technology (ICACOMIT), Bandung, 2015, pp. 134-
137, doi: 10.1109/ICACOMIT.2015.7440192.
A. Turnip, A. I. Simbolon, M. F. Amri and M. A.
Suhendra, "Utilization of EEG-SSVEP method and
ANFIS classifier for controlling electronic
wheelchair," 2015 International Conference on
Technology, Informatics, Management, Engineering &
Environment (TIME-E), Samosir, 2015, pp. 143-146,
doi: 10.1109/TIME-E.2015.7389763.
A. Turnip, T. Hidayat and D. E. Kusumandari,
"Development of brain-controlled wheelchair
supported by raspicam image processing based
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
636

Raspberry pi," 2017 2nd International Conference on
Automation, Cognitive Science, Optics, Micro
Electro--Mechanical System, and Information
Technology (ICACOMIT), Jakarta, 2017, pp. 7-11,
doi: 10.1109/ICACOMIT.2017.8253377.
A. Turnip, D. Soetraprawata and T. A. Tamba, "EEG-
SSVEP signals extraction with nonlinear adaptive
filter for brain-controlled wheelchair," 2015 15th
International Conference on Control, Automation and
Systems (ICCAS), Busan, 2015, pp. 1870-1873, doi:
10.1109/ICCAS.2015.7364667.
Motor Speed Control toward Wall Surface Angle based on HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
637
