
The Effect of Leadership Style and Work Environment on Work
Stress and Employee Performance
Alvin Arifin
Universitas Bahaudin Mudhary Madura, Jl. Raya Lenteng No. 10, Sumenep, Indonesia
Keywords: Leadership style, work environment, work stress, employee performance.
Abstract: This research examines the effect of leadership style and work environment on work stress and employee
performance. This research was conducted at the batik convection center in Sumenep Regency, which is one
of the largest batik convection centers on the island of Madura. The data used are primary data through
distributing questionnaires to employees. The sample used is the entire population totaling 72 employees or
the so-called saturated sample. This study uses a partial least square model using an analysis tool in the form
of smartPLS software. Partial least square analysis analyzes both the direct effect of the variable and the
indirect effect. In previous research, leadership and environment directly influence performance significantly.
The results in this study indicate that leadership style has no significant effect on employee performance,
work environment has a positive and significant effect on employee performance, leadership style has a
positive and significant effect on work stress, work environment has a positive and significant effect on work
stress, work stress has a positive and significant effect on work stress. Leadership style has a positive and
significant effect on employee performance through work stress with p-value 0.028 < 0.05 indicates a
significant indirect effect. The work environment has a positive and significant effect on employee
performance through work stress with p-value 0.012 < 0.05 indicates a significant indirect effect.
1 INTRODUCTION
Employee performance is the result of all the work
that the employee has completed. Performance
criteria can be either good or bad results for each job.
It is necessary to classify a job as good or bad. Good
performance is usually based on the results of the job
whether it matches the job description or not.
Employee performance is closely related to
leadership style. Complete work following the
instructions from the leader using a leadership style
strategy. A leader needs to choose a leadership style
that suits the characteristics of his employees. This
technique of influencing employees is called
leadership style.
Employee performance is the most important goal
in a company or organization. Several methods and
strategies need to be implemented to improve
employee performance (Mathews & Khann, 2016).
Performance is a description of the achievement of an
application of activities or policies in realizing the
goals, objectives, vision, and mission of an
organization which are formulated based on the
strategic planning of an organization (Putri, Ekowati,
Supriyanto, & Mukaffi, 2019). Employee
performance has an important role in the organization
so that high-performing employees are considered a
valuable asset of the organization (Rorong, 2016),
(Samson, Waiganjo, & Koima, 2015).
Employee performance in an organization is an
important aspect of maintaining the productivity
generated by the company (Saidi et al., 2019). The
quality of employee performance can be influenced
and depends on the safety and comfort of working
conditions and the workload of employees (Malik,
Ahmad, Gomez, & Ali, 2011).
Performance indicators are (Samson et al., 2015):
Error rate;
Work results.
Leadership style is a way for leaders to influence
their subordinates. A leader is someone who can
influence group activities in an organization to
achieve organizational and individual goals
(Dhamodharan & Arumugasamy, 2011). The
leadership style has a very important relationship for
employees as an additional encouragement to
improve their performance results (Hussain, Akhtar,
Inayatullah, Afzal, & Gillani, 2017).
236
Arifin, A.
The Effect of Leadership Style and Work Environment on Work Stress and Employee Performance.
DOI: 10.5220/0010306700003051
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies (CESIT 2020), pages 236-242
ISBN: 978-989-758-501-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Leadership style is used by a leader as a liaison
between leaders and employees and motivates
employees to stay involved in their duties (Kelly &
Hearld, 2020). The relationship between leadership
style and work stress, namely the application of an
effective leadership style promoting good
communication and interaction, is important for
employees to reduce work-related stress levels
(Kakada & Deshpande, 2018).
Leadership style indicators are (Dhamodharan &
Arumugasamy, 2011):
Coercion;
Authority;
Affiliation;
Democratic;
Setting steps or actions;
Coaching.
The work environment is an environment where
employees work. A good environment accompanied
by good infrastructure can make employees perform
well too. It can be seen in developed countries how
infrastructure plays an important role in the ease with
which employees work. Therefore management
support in creating a good workplace environment is
very important.
The work environment is a place for various
activities that can be characterized by the number of
interactions among employees at work (Soriano,
Kozusznik, & Peiró, 2018). A fundamental aspect of
the workplace environment that contributes to
employee behavior is the layout of the office space
(Kamarulzaman, Saleh, Hashim, Hashim, & Abdul-
Ghani, 2011). Work environment is a view or
physical work environment where a group of people
work together to achieve certain goals. This can cover
many aspects, for example: lighting, work area
design, temperature, etc (Desa, Khoon, & Asaari,
2018).
An attractive working atmosphere and a
supportive environment have increasingly escalated
to the point where employees accumulate the superior
use of their skills, competencies, and knowledge to
perform efficiently (Hafeez, Yingjun, Hafeez,
Mansoor, & Rehman, 2019). Company support for
employees in the workplace can have a positive
impact on employee performance (Nadia &
Fathurahman, 2018).
Work environment indicators, namely (Suifan,
2019):
Ensuring employee safety;
Motivating;
Reciprocating performance;
Providing a sense of security;
Relationships between colleagues;
Increasing employee participation.
Work stress is an employee's emotional state at
work. Work stress can be caused by pressure at work.
Not only the pressure at work but also the result of an
unfavorable environment that results in discomfort at
work. Maintaining the emotional state of employees
is very important because it has an impact on
employee performance.
Work stress and performance have always been an
important issue for managers. Various studies have
tried to answer the question of what determines the
decline in employee performance. It was identified
that work experience related to stress causes
employees to underperform. Inadequate information
about how to do the job properly, excessive
expectations, relationships with coworkers and
superiors, extensive work pressure, and a lack of
understanding of job descriptions can cause
employees to feel dissatisfied with their work and
performance, lack of commitment to the company,
experiencing stress so that it has an impact on their
performance (Ahmad, Salleh, Bakar, & Sha’arani,
2018).
Work stress is defined as a dangerous physical and
emotional response that occurs when workloads do
not match the abilities, resources, or needs of
workers. Stress has a major impact on business and
the economy whether it is experienced at work or
home and affects a growing number of workers
around the world (Baysak & Yener, 2015). Stress is
usually caused by the disruption of employees at
work (Tambalean, 2014).
Indicators of job stress are (Abbasi, 2018):
Guilt;
Anger;
Depression.
Companies engaged in batik convection where
there are sales targets that must be achieved make this
research important as a description of the condition of
the employees. This research was conducted at a batik
convection factory in Sumenep, which is one of the
largest on the island of Madura.
The formulation of the research problems are: (1)
is there a direct effect of leadership style on employee
performance? (2) is there a direct effect of the work
environment on employee performance? (3) is there a
direct effect of leadership style on work stress? (4) is
there a direct effect of the work environment on work
stress? (5) is there a direct effect of work stress on
employee performance? (6) is there an indirect effect
of leadership style on employee performance through
work stress? (7) is there an indirect effect of the work
The Effect of Leadership Style and Work Environment on Work Stress and Employee Performance
237
environment on employee performance through work
stress?.
The objectives of this study are: (1) to analyze the
direct influence of leadership style on employee
performance, (2) to analyze the direct effect of the
work environment on employee performance, (3) to
analyze the direct effect of leadership style on work
stress, (4) to analyze the direct effect of the work
environment. on work stress, (5) analyzing the direct
effect of work stress on employee performance, (6)
analyzing the indirect effect of leadership style on
employee performance through work stress, (7)
analyzing the indirect effect of work environment on
employee performance through work stress.
2 METHOD
This research is quantitative. The data collection
technique uses a questionnaire that is distributed to
respondents. This research was conducted at the
Sumenep regency convection factory.
The population of this study were 72 employees
of the batik convection factory in Sumenep district.
The sample in this study is to use the entire population
as a saturated sample. This research data analysis
using smartPLS software.
The conceptual model in this study can be
described as follows:
.
Figure 1: Conceptual framework of the research.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Data analysis using SmartPLS software with the
following output models:
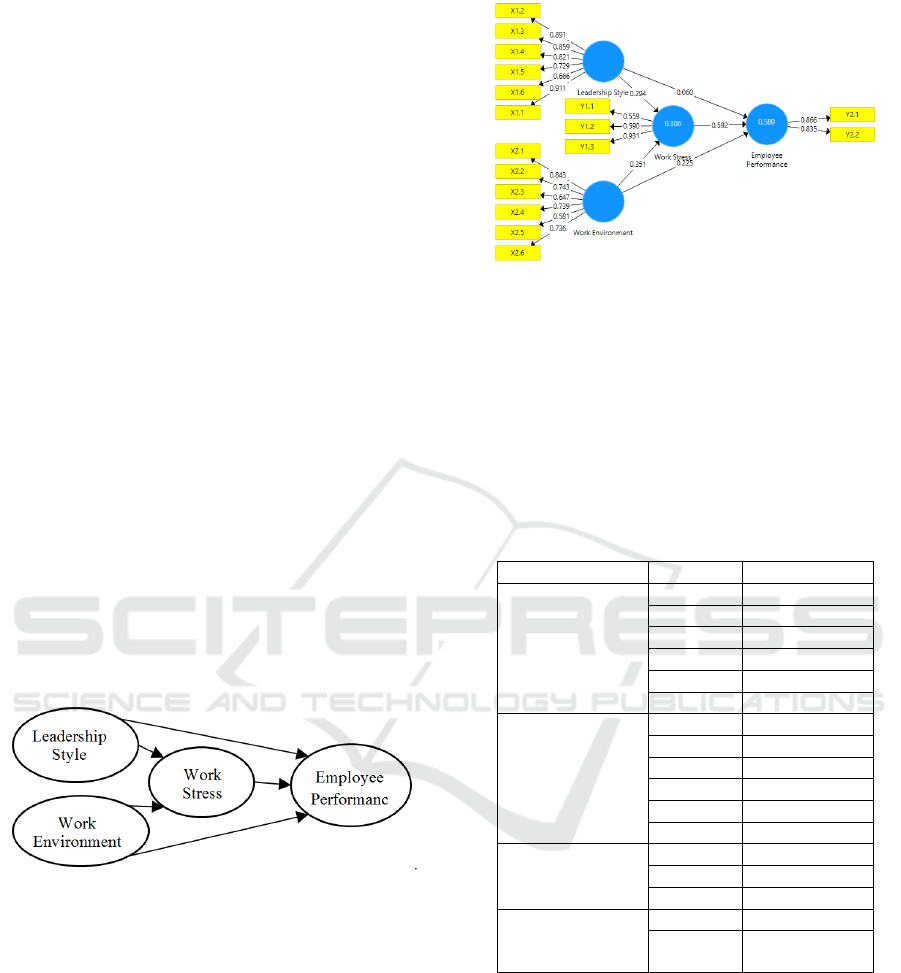
Figure 2: Output data.
The SmartPLS output results in outer loading
which is then used for validity testing. The validity
test is used to test the validity of the research
instrument. The validity test criteria for the outer
loading value of 0.5 to 0.6 are considered sufficient,
for the number of indicators of latent variables
ranging from 3 to 7.
The results of the validity test are as follows:
Table 1: Validity test result.
Variables Indicators Outer Loadin
g
Leadership
X1
X1.1 0.911
X1.2 0.891
X1.3 0.859
X1.4 0.821
X1.5 0.729
X1.6 0.666
Work
Environment
X2
X2.1 0.843
X2.2 0.743
X2.3 0.647
X2.4 0.739
X2.5 0.581
X2.6 0.736
Work Stress
Y1
Y1.1 0.559
Y1.2 0.590
Y1.3 0.931
Employee
Performance
Y2
Y2.1 0.866
Y2.2 0.835
Source: SmartPLS 3.0 Output, 2020
From the outer loading, it shows that all indicators
have a value above 0.5 so that all indicators are valid.
After the validity test, then move on to the
reliability test. The reliability test tests the reliability
of the variables of a study. Reliability test criteria if
the Composite Reliability value is above 0.70; AVE
(Average Variance Extracted) is above 0.50 and
Cronbach's Alpha is greater than 0.60.
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
238
The results of the reliability test in this study are
as follows:
Table 2: Reliability test result.
Variables
Composite
Reliabilit
y
Cronbach’s
Alpha
AVE
Leadership
St
y
le
0,923 0,900 0,669
Work
Environment
0,864 0,819 0,518
Work Stress 0,746 0,608 0,509
Employee
Performance
0.840 0.620 0.724
Source: SmartPLS 3.0 Output, 2020
From the results of the reliability test, it shows that
the output is following the criteria so that these
variables are reliable.
The results of the validity and reliability tests
show that the variables are valid and reliable so that
the causality test or influence test can be done.
Testing criteria is if the direct effect shows the t-
statistic result is greater than the t-table value (t-table
= 1.96) then the variable relationship is significant.
The results of the direct effect test between
variables are as follows:
Table 3: Direct effect result.
Variables
Origina
l
Sam
p
le
T-
Statistic
s
P-
Value
s
Leadership Style ->
Employee
Performance
0.060 0.579 0.563
Leadership Style ->
Work Stress
0.294 2.356 0,019
Work Environment -
> Employee
Performance
0.225 2.220 0.027
Work Environment -
> Work Stress
0.351 2.713 0.007
Work Stress ->
Employee
Performance
0.592 7.863 0.000
Source: SmartPLS 3.0 Output, 2020
The direct effect results, firstly shows that
leadership style does not affect employee
performance. The second result shows that the
leadership style has a positive and significant effect
on work stress. The third result shows that the work
environment has a positive and significant effect on
employee performance. The fourth result shows that
the work environment has a positive and significant
effect on work stress. The final result shows that work
stress has a positive and significant effect on
employee performance.
After conducting the direct effect test, then the
indirect effect test is carried out. The results of the
indirect effect test are as follows:
Table 3: Indirect effect result.
Variables
Origina
l
Sam
p
le
T-
Statistic
s
P-
Value
s
Leadership Style ->
Employee
Performance
0,174 2,202 0,028
Work Environment -
> Employee
Performance
0,208 2,515 0,012
Source: SmartPLS 3.0 Output, 2020
The results of the indirect effect test show that
leadership style has an indirect effect on employee
performance through work stress positively and
significantly. The results of the indirect test further
show that the work environment also has an indirect
effect on employee performance through work stress
positively and significantly.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the data analysis, it can be
concluded that the leadership style does not have a
significant influence on employee performance with
a p-value 0.563 > 0.05 indicates a not significant
direct effect. Whatever leadership style does not
affect their performance. The results of this study
strengthen the research from Prabowo, Noermijati, &
Irawanto (2018); Madanchian, Hussein, Noordin, &
Taherdoost (2016). The results of this study weaken
the research from McAlearney, Hefner, Robbins, &
Garman (2013); Orabi (2016).
The work environment has a positive and
significant effect on employee performance with p-
value 0.019 < 0.05 indicates a significant direct effect.
The better the work environment, the better the
employee's performance. The results of this study
strengthen the research from Palese et al., (2019);
Loidl et al., (2016). The results of this study weaken
the research from Samson, Waiganjo, & Koima
(2015); Jayaweera (2015).
Leadership style has a positive and significant
influence on work stress with p-value 0.027 < 0.05
indicates a significant direct effect. It is necessary to
be careful in determining the leadership style used so
The Effect of Leadership Style and Work Environment on Work Stress and Employee Performance
239

as not to stress employees. The results of this study
strengthen the research from Ahmad, Salleh, Bakar,
& Sha’arani (2018); Laschinger, Wong, & Grau
(2013). The results of this study weaken the research
from Abbasi, (2018); (George, Chiba, & Scheepers,
2017)
The work environment has a positive and
significant effect on work stress with p-value 0.007 <
0.05 indicates a significant direct effect Companies
need to prepare a good work environment so as not to
cause stress to employees. The results of this study
strengthen the research from Bhat (2017); Schulte
(2014). The results of this study weaken the research
from Stults-Kolehmainen & Sinha (2014); Yikealo,
Yemane, & Karvinen (2018).
Work stress has a positive and significant effect
on employee performance with p-value 0.00 < 0.05
indicates a significant direct effect. More companies
need to pay attention to employee stress levels so as
not to affect performance. The results of this study
strengthen the research from Akter & Rahman
(2012); Pandey (2020). The results of this study
weaken the research from Hussein, Abu-Salih, &
Saket (2016); Murali, Basit, & Hassan (2017).
Leadership style has an indirect effect on
employee performance through work stress with p-
value 0.028 < 0.05 indicates a significant indirect
effect. If the choice of leadership style and stress
control on employees will improve employee
performance significantly. The results of this study
strengthen the research from Mohammed, Saleh,
Nusari, & Isaac, (2018); Jung, Chow, & Wu (2008);
Bernanthos (2018); Wang & Liang (2020); Kristanto
& Edward (2020).
The work environment has an indirect effect on
employee performance through work stress with p-
value 0.028 < 0.05 indicates a significant indirect
effect. If the work environment is accompanied by
minimizing the influence of stress on employees, it
will significantly improve employee performance.
The results of this study strengthen the research from
Yaacob (2014); Junquera & Barba-Sánchez (2018);
Bae (2017); Li et al., (2020); Schaaijk et al., (2020);
Pindek, Howard, Krajcevska, & Spector (2019);
Koźluk & Zipperer (2014).
REFERENCES
Abbasi, S. G. (2018). Leadership Styles: Moderating
Impact on Job Stress and Health. Journal of Human
Resources Management Research, 2018, 1–12.
Ahmad, A., Salleh, A. M. M., Bakar, K. A., & Sha’arani,
K. A. W. (2018). The impact of leadership styles and
stress on employee turnover intention in Terengganu
hotel community. International Journal of Engineering
and Technology(UAE), 7(3), 38–42.
Akter, N., & Rahman, M. S. (2012). Impact of Stress on
Task Performance : An Empirical Study. Journal of
Business Administration, 27(October), 57–76.
Bae, H. S. (2017). Empirical Relationships of Perceived
Environmental Uncertainty, Supply Chain
Collaboration, and Operational Performance: Analyses
of Direct, Indirect and Total Effects. Asian Journal of
Shipping and Logistics, 33(4), 263–272.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajsl.2017.12.010
Baysak, B., & Yener, M. İ. (2015). The Relationship
Between Perceived Leadership Style and Perceived
Stress on Hospital Employees. Procedia - Social and
Behavioral Sciences, 207, 79–89.
Bernanthos, B. (2018). The Direct and Indirect Influence of
Leadership, Motivation and Job Satisfaction Against
Employees’ Performance. European Research Studies
Journal, 21(2), 236–243.
https://doi.org/10.35808/ersj/998
Bhat, R. H. (2017). Environmental Stressors and Its Impact
on Human Being. International Journal of Humanities
and Social Sciences., 5(1), 37–40.
Desa, N. M., Khoon, T. L., & Asaari, M. H. A. H. (2018).
Work Stress Toward Work Environment, Management
Support, and Employee Satisfaction among Employees
of Public Organizations. International Journal of Asian
Social Science, 8(1), 1–11.
Dhamodharan, K., & Arumugasamy, G. (2011). Effect of
Occupational Stress on Executives’ Leadership Styles.
Public Policy and Administration Research, 1(4), 1–8.
George, R., Chiba, M., & Scheepers, C. B. (2017). An
investigation into the effect of leadership style on
stress-related presenteeism in South African knowledge
workers. SA Journal of Human Resource Management,
15(0), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.4102/sajhrm.v15i0.754
Hafeez, I., Yingjun, Z., Hafeez, S., Mansoor, R., &
Rehman, K. U. (2019). Impact of Workplace
Environment on Employee Performance: Mediating
Role of Employee Health. Business, Management and
Education, 17(2), 173–193.
Hussain, M., Akhtar, S., Inayatullah, Afzal, M., & Gillani,
S. A. (2017). Effects of hospital service quality on
patients satisfaction and behavioural intention of
doctors and nurses.
Saudi Journal of Medical and
Pharmaceutical Sciences, 3(8), 907–916.
Hussein, A. M. A., Abu-Salih, M. S., & Saket, L. Z. Al.
(2016). Impact of Job Stress on Job Performance among
the Employees of Jordan Research Journal of Social
Sciences Impact of Job Stress on Job Performance
among the Employees of Jordan. Research Journal of
Social Sciences, 9(2), 1–9.
Jayaweera, T. (2015). Impact of Work Environmental
Factors on Job Performance, Mediating Role of Work
Motivation: A Study of Hotel Sector in England.
International Journal of Business and Management,
10(3), 271–278.
https://doi.org/10.5539/ijbm.v10n3p271
Jung, D. D., Chow, C. W., & Wu, A. (2008). Towards
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
240

understanding the direct and indirect effects of CEOs’
transformational leadership on firm innovation.
Leadership Quarterly, 19(5), 582–594.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leaqua.2008.07.007
Junquera, B., & Barba-Sánchez, V. (2018). Environmental
proactivity and firms’ performance: Mediation effect of
competitive advantages in Spanish wineries.
Sustainability (Switzerland), 10(7).
https://doi.org/10.3390/su10072155
Kakada, P., & Deshpande, Y. M. (2018). The Empirical
Study of Work Environment and Job Stress among
Technical Faculty, 20(1), 29–33.
Kamarulzaman, N., Saleh, A. A., Hashim, S. Z., Hashim,
H., & Abdul-Ghani, A. A. (2011). An overview of the
influence of physical office environments towards
employees. In Procedia Engineering (Vol. 20, pp. 262–
268).
Kelly, R. J., & Hearld, L. R. (2020). Burnout and
Leadership Style in Behavioral Health Care: a
Literature Review. Journal of Behavioral Health
Services and Research.
Koźluk, T., & Zipperer, V. (2014). Environmental policies
and productivity growth – a critical review of empirical
findings. OECD Journal: Economic Studies, 155–185.
Kristanto, H., & Edward, Y. R. (2020). The Effect of
Leadership Style and Communication on Employee
Performance through Job Satisfaction as a Mediation
Variable at PT. Trans Sumatra Agung in Medan.
International Journal of Research and Review, 7(9),
171–181.
Laschinger, H. K. S., Wong, C. A., & Grau, A. L. (2013).
Authentic leadership, empowerment and burnout: A
comparison in new graduates and experienced nurses.
Journal of Nursing Management, 21(3), 541–552.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2834.2012.01375.x
Li, T., Xiong, Q., Luo, P., Zhang, Y., Gu, X., & Lin, B.
(2020). Direct and indirect effects of environmental
factors, spatial constraints, and functional traits on
shaping the plant diversity of montane forests. Ecology
and Evolution, 10(1), 557–568.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.5931
Loidl, V., Oberhauser, C., Ballert, C., Coenen, M., Ciez, A.,
& Sabariego, C. (2016). Which environmental factors
have the highest impact on the performance of people
experiencing difficulties in capacity? International
Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,
13(4), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13040416
Madanchian, M., Hussein, N., Noordin, F., & Taherdoost,
H. (2016). Effects of Leadership on Organizational
Performance. Economics and Education Effects, 115–
119.
Malik, M. I., Ahmad, A., Gomez, S. F., & Ali, M. (2011).
A study of work environment and employees’
performance in Pakistan. African Journal of Business
Management, 5(34), 13227–13232.
Mathews, C., & Khann, I. K. (2016). Impact of Work
Environment on Performance of Employees in
Manufacturing Sector in India: Literature Review.
International Journal of Science and Research (IJSR)
,
5(4), 852–855.
McAlearney, A. S., Hefner, J., Robbins, J., & Garman, A.
N. (2013). The role of leadership in eliminating health
careassociated infections: A qualitative study of eight
hospitals. (S. T., L. H., & S. G.T., Eds.), Advances in
Health Care Management. College of Medicine, Ohio
State University, Columbus, OH, United States.
https://doi.org/10.1108/S1474-8231(2013)0000014009
Mohammed, R., Saleh, M., Nusari, M., & Isaac, O. (2018).
The Effect of Leadership Style on Organizational
Performance: Organizational Commitment as a
Mediator Variable in the Manufacturing Sector of
Yemen. International Journal of Management and
Human Science (IJMHS), 2(4), 2590–3748.
Murali, S. B., Basit, A., & Hassan, Z. (2017). Impact of Job
Stress on Employee Performance. International
Journal of Accounting, Business & Management, 5(2),
13–33.
Nadia, & Fathurahman, H. (2018). Relationships between
Physical Working Environment Employee Well-being,
and Employee Commitment in Hospital Management.
Bisnis & Birokrasi Journal, 24(3).
Orabi, T. G. A. (2016). The Impact of Transformational
Leadership Style on Organizational Performance:
Evidence from Jordan. International Journal of Human
Resource Studies, 6(2), 89.
Palese, A., Grassetti, L., Bressan, V., Decaro, A., Kasa, T.,
Longobardi, M., … Watson, R. (2019). A path analysis
on the direct and indirect effects of the unit environment
on eating dependence among cognitively impaired
nursing home residents. BMC Health Services
Research, 19(775). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-
019-4667-z
Pandey, D. L. (2020). Work Stress and Employee
Performance: an Assessment of Impact of Work Stress.
International Research Journal of Human Resource
and Social Sciences, 7(05), 124–135.
Pindek, S., Howard, D. J., Krajcevska, A., & Spector, P. E.
(2019). Organizational constraints and performance: an
indirect effects model. Journal of Managerial
Psychology, 34(2), 79–95.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JMP-03-2018-0122
Prabowo, T. S., Noermijati, & Irawanto, D. W. (2018).
Leadership and Work Motivation on Employee
Performance Mediated by Job Satisfaction. Journal of
Applied Management (JAM), 16(36), 171–178.
Putri, E. M., Ekowati, V. M., Supriyanto, A. S., & Mukaffi,
Z. (2019). The Effect of Work Environment on
Employees’ Productivity. International Journal of
Science and Research (IJSR) ISSN (Online Index
Copernicus Value Impact Factor, 14(5), 2319–7064.
Rorong, S. V. (2016). The Impact of Physical Work
Environment Toward Employee Performance at PT.
Bank Negara Indonesia Manado Regional Office.
Emba, 4(1), 441–450.
Saidi, N. S. A., Michael, F. L., Sumilan, H., Lim, S. L. O.,
Jonathan, V., Hamidi, H., & Abg Ahmad, A. I. (2019).
The Relationship Between Working Environment and
Employee Performance. Journal of Cognitive Sciences
and Human Development, 5(2), 14–22.
Samson, G. N., Waiganjo, M., & Koima, J. (2015). Effect
The Effect of Leadership Style and Work Environment on Work Stress and Employee Performance
241

of Workplace Environment on the Performance of
Commercial Banks Employees in Nakuru Town.
International Journal of Managerial Studies and
Research (IJMSR), 3(12), 76–89.
Schaaijk, A. Van, Baloch, A. N., Thomée, S., Frings-
Dresen, M., Hagberg, M., & Nieuwenhuijsen, K.
(2020). Mediating factors for the relationship between
stress and work ability over time in young adults.
International Journal of Environmental Research and
Public Health, 17(7).
https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072530
Schulte, P. M. (2014). What is environmental stress?
Insights from fish living in a variable environment.
Journal of Experimental Biology, 217(1), 23–34.
https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.089722
Soriano, A., Kozusznik, M. W., & Peiró, J. M. (2018). From
office environmental stressors to work performance:
the role of work patterns. International Journal of
Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(8).
Stults-Kolehmainen, M. A., & Sinha, R. (2014). The effects
of stress on physical activity and exercise. Sports
Medicine (Vol. 44).
Suifan, T. S. (2019). the Effects of Work Environmental
Factors on Job Satisfaction: the Mediating Role of
Work Motivation. Business: Theory and Practice,
20(0), 456–466.
Tambalean, F. P. (2014). the Effect of Work Stress and
Leadership Styles on Employee Performance Pt. Bni
(Persero) Tbk. Manado Branch. Jurnal Riset Ekonomi,
Manajemen, Bisnis Dan Akuntansi, 2(4), 301–308.
Wang, L., & Liang, X. (2020). The influence of leaders’
positive and implicit followership theory of university
scientific research teams on individual Creativity: The
mediating effect of individual self-cognition and the
moderating effect of proactive personality.
Sustainability (Switzerland), 12(6).
https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062507
Yaacob, Z. (2014). The direct and indirect effects of
customer focus on performance in public firms.
International Journal for Quality Research, 8(2), 265–
276.
Yikealo, D., Yemane, B., & Karvinen, I. (2018). The Level
of Academic and Environmental Stress among College
Students: A Case in the College of Education. Open
Journal of Social Sciences, 06(11), 40–57.
https://doi.org/10.4236/jss.2018.611004
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
242
