
Variation of Soaking Time on Asphalt Concrete Properties using
Anti Stripping Materials
Anni Susilowati
1
, Eko Wiyono
1
, Pratikto
1
, Roihans M. I.
1
1
Department of Civil Engineering, State Polytechnic of Jakarta, Jln. Prof. Dr. G. A. Siwabessy, Depok , Indonesia
Keywords: Wetfixbe, Soaking time, Marshall property
Abstract: The purposes of this study were to obtain Marshall property values and determine the optimum submersion
time in AC-WC asphalt concrete mixture using anti-stripping added ingredients. Marshall specimens were
made with an optimum asphalt content of 6%, wetfixbe content of 0.3% to asphalt and each was made with
a variation of submersion time 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 36 and 48 hours. The method of implementation is
by mixing the wetfixBe first with asphalt, then aggregate according to the proportion of the ideal gradation
of the mixture. Marshall testing method based on SNI 06-2489-1991. The results of the study found that the
addition of submersion time can increase the percent value of Void Filled with Bitumen (VFB) and flow and
reduce the percent of Void in Mix (VIM), percent of Void in the Mineral Aggregate (VMA), Stability, and
Marshall Quotient. The submersion period that still meets Marshall property is at the soaking time of 3 to 45
hours. The Optimum Soaking Time for asphalt concrete mix is 24 hours, with VMA value 17,80%, VFB
74,04%, VIM 4,63%, Stability 1071.76 kg, flow 3.25 mm and MQ 360 kg / mm, asphalt concrete mixture
meets Bina Marga 2018 specifications.
1 INTRODUCTION
Water is one of the factors causing road damage,
both from rainwater and water from the road
drainage system. Submerging asphalt concrete mix
can cause the release of aggregate granules from
asphalt and peeling off asphalt from road pavement,
according to (Djalante, 2011) that one of the most
important aspects in highway planning is the effort
to protect roads from water. According to
(Nurhuduyah, 2009) that the effects of continuous
immersion damage are faster than ordinary
immersion. Soak the asphalt mixture Hot Rolled
Sheet-Wearing Course (HRS-WC) either
continuously or periodically in high tide has a
greater effect than the use of laboratory water. To
increase the bond between the aggregate and asphalt
by adding anti-peeling additives or more commonly
known as the anti-stripping agent.
Moisture susceptibility is the tendency towards
the peeling of asphalt mixtures. Exfoliation usually
starts at the bottom of the asphalt mixture layer and
usually moves upward. That situation is a gradual
loss of power over the years, which causes many to
arise on the surface such as grooves, folds, waves,
raveling, cracking, etc. (Krebs and Walker,1971). In
specification ( Bina Marga, 2018), stickiness and
anti-stripping agent must be added in liquid form to
the mixture.
Werfix BE is an anti-chemical stripping that
useful for improving bonding and stabilizing the
mixture between aggregate and asphalt, especially in
the rainy season as a result of research (Susilowati
and Wiyono, 2015).
The quality of asphalt concrete mixes in the field
is influenced by the process of making mixtures in
the laboratory or Asphalt Mixing Plant (AMP),
laying and compaction in the field. To get the
characteristics of asphalt concrete mixture and its
effect on water immersion, testing is done using a
device Marshall, by settling the specimen first
before removing it from the mold and then settling it
for approximately 24 hours at room temperature.
Then measure thickness, weight, and immerse
the test specimen in the water at room temperature
for 24 hours. According to (Amal, 2009) that
immersion variation of 2 to 72 hours is very
influential on the nature of the mixture Marshall and
the plastic melt value, it is necessary to add
materials that can be used as an asphalt concrete
mixture, so that the asphalt concrete mixture is
resistant or waterproof.
132
Susilowati, A., Wiyono, E., Pratikto, . and M. I., R.
Variation of Soaking Time on Asphalt Concrete Properties using Anti Stripping Materials.
DOI: 10.5220/0009967900002905
In Proceedings of the 8th Annual Southeast Asian International Seminar (ASAIS 2019), pages 132-137
ISBN: 978-989-758-468-8
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Some previous studies that support this research
include research by (Nurhuduyah, 2009) This is
indicated by the durability value of the asphalt
mixture in the immersion with low tide compared to
the asphalt mixture immersed in laboratory standard
water. According to (Arifin et all, 2008), Decreased
mixed performance due to the influence of rainwater
content on the characteristics of the Marshall Laston
mixture. From the results of these experimental
studies, it has been concluded that in general the
characteristics of the Marshall Laston mix have
decreased with increasing rainwater content. This
research (Sanusi, 2012) used an experimental
method on a mixture of laston with optimum asphalt
content of 6% of the total weight of the aggregate
levels filler Replacement used vary from 4%, 5%,
6%, 7%, 7.91% to the total weight of aggregates
with immersion for durability testing: 30 minutes (0
days), 1 day, 7 days and 14 days. The results showed
the greatest stability was a mixture with a filler
cement then carbide waste with an immersion of 14
days. According to (Kosim, 2013), The results of all
the LASTON mixtures obtained showed that the use
of the addition of a proportion additive filler cement
of 4% to the concrete asphalt mixture would
increase the stability of the mixture, with long
immersion in water for 3 days. By using the
proportion of adding an additive filler cement of 4%
to the asphalt concrete mixture, a pavement material
will be obtained which can withstand heavy traffic
loads, during the service life of the road. (Fauziah
and Handaka, 2017), that the effect of rainwater on
characteristics Marshall and the durability of the
mixture Split Mastic Asphalt, using two types of
asphalt as binding material, namely Starbit E-55
asphalt, and AC 60/70 asphalt is that the longer the
rainwater immersion time the mixed stability value,
Marshall Quotient and the value of the index of
retained strength decreases and the value of melt
increases. SMA mixes that use Starbit E-55 asphalt
bonding materials can maintain performance
Marshall and durability due to better rainwater
compared to SMA mixes with AC 60/70 asphalt
binding materials. The stability of fly ash and stone
dust tends to decrease after 72 hours of soaking,
with an even more drastic decrease in fly ash.
Whereas Portland Cement shows the inverse.
Portland cement as aggregate filler showed
improvement along with the increase in immersion
time (Latifah, et all, 2012). According to (Pratama
and Fauziah, 2017) The Longer immersion in
Aspalht Porous Based Buton Granular Asphalt
(BGA) can increase the value of VIM, VFB, Flow
and reduce VMA, stability and Marshall Quetient.
The longer time immersion of seawater can decrease
the durability index values of asphalt concrete with
and without substitution EVA waste (Rahmi, et all,
2017). According to (Angga, 2016), That the
retained strength as well as tensile strength of
mixtures with Retona were obtained better in each
duration of seawater immersion than those with
asphalt pen 60/70. According to (Rizal, et all, 2017),
the influence of the LTOA process on the porous
asphalt with BGA and without BGA showed that the
performance of porous asphalt with 2.5% BGA
super passed the mixture without BGA.
This study aims to obtain the property values
Marshall of AC-WC asphalt concrete mixtures in
the variation of immersion time and determine the
optimum immersion time by using anti-added
ingredients stripping that meet the specifications
(Bina Marga, 2018).
2 RESEARCH METHOD
The research method is an experimental method by
making hot mix asphalt concrete specimens, with
0.6% asphalt content, Wetfixbe content 0.3% of the
weight of asphalt.
This research was conducted at the Civil
Engineering Test Material Laboratory, State
Polytechnic of Jakarta.
The materials used in this study are Esso asphalt,
the coarse aggregate of crushed stone, stone ash and
filler of portland cement and anti-Stripping Wetfix
Be. Hot asphalt concrete mixed specimens with
immersion time variation of 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21,
24, 36 and 48 hours. Each variation was tested 3
(three) times. Then the test is performed Marshall to
get the VMA, VFB, VIM, Stability, Meltability, and
Marshall Quotient (MQ) values. The stages in this
study can be illustrated with the flow chart as
follows
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The Results of Aggregate and Asphalt Tests of
physical aggregate, both for fine aggregates and
coarse aggregates all meet the Specifications [4].
Test results with a density greater than 2.5
indicate that aggregates can be used for roads with
high traffic volume. The results of the physical
properties of aggregate are presented in Table 1.
Variation of Soaking Time on Asphalt Concrete Properties using Anti Stripping Materials
133

Table 1. Fine and Coarse Aggregate Test Result
Tests Results ofTesting
Requirement
Bina Marga
2018
Fine Aggr
Coarse
Aggr
Min Max
-Bulk Specific Gravity 2.57 2.56 2.5 -
-SSD Specific Gravity 2.61 2.61 2.5 -
-Apparent Specific
Gravity
2.68 2.70 2.5
-Water Absorption(%) 1.59 2.15 - 3
As for the Physical Examination Results, of
Asphalt with WetfixBe all of them meet
Specifications [4]. According to the test results, that
asphalt is included in the group with Penetration of
60/70 and a minimum of 48
0
C softening points;
suitable for roads with high traffic volume. The
results of physical asphalt examinations in Table 2.
Table 2. Hard Asphalt Test Results
Testing
Results
of
Testing
Requirement
Bina Marga 2018
Min Max
Penetration(mm) 65 60 70
Specific Gravity 1.02 0.92 1.06
Softening Point
O
C
48.5 45 -
Ductility(mm) 101 100 -
3.1 Planning Mixed Marshall Test
Object
Calculation of proportion of mixture using rough
aggregate passes 19 mm size filter and retained on
the 4.75 mm filter and used as fine aggregate is
stone ash which passes the 4.75 mm filter size and
retained on the 0.075 mm filter size. The filler used
by cement passes 0.075 mm sieve more than 75%.
Figure 1. Combined Aggregate Gradation Graph
Determination of Asphalt Level Variation is
done by calculating the initial estimate of the asphalt
level of the plan (Pb). Estimated asphalt content is
obtained from the following result.
Pb=[0.035 (% CA) + 0.045 (% FA) + 0.18 (% F)] +k
= [0.035 (40.7%) + 0.045 (52.6%) + 0.18 (6.7%)] x
0.75 = 5.99% ≈ 6%
Estimated ideal asphalt levels obtained from
calculation 5, 99%, used for making test specimens
with added wetfixbe 0.3%.
3.2 Marshall Test Results
Marshall test results for the variation of immersion
time at KAO 6.0%, and Wetfix Be 0.3%,
recapitulation is presented in Figure 3a to 3f.
a. Percentage of Voids in Mineral
Aggregate (VMA)
Based on the results of statistical tests it was found
that the immersion time had less effect on VMA.
This is indicated by the F value and the significant
value> 0.05 and the R-square value of 0.164, which
means that the variation of immersion time has an
effect of 16.4% on VMA. The result of the test also
shows that VMA value tends to decrease with
increasing immersion time, although the decrease is
small. The average VMA values obtained from the
test results are: 17.99%, 18.02%, 18.23%, 17.58%,
18.12%, 18.12%, 18.08%, 18.03%, 17.80%, 17.77%
and 17.90%. The specification of the VMA value
required by Bina Marga 2018 is at least 15% so that
the results of the overall VMA value test meet the
required specifications. (As in Figure 2a)
b. Percentage of Voids Filled with Bitumen
(VFB)
Based on the results of statistical tests it was found
that the immersion time did not affect VFB. This can
be seen from the R square value of 0.409 which
means that the variation of immersion time has an
effect of 40.9% on VFB. The test results also
showed that the VFB value increased according to
the addition of variations in the immersion time. all
results obtained from testing meet the 2018 Bina
Marga specifications of at least 65%. (As in Figure
2b).
c. Percentage of Voids in Mix (VIM)
Based on the results of statistical tests it was found
that immersion time affects VIM. This can be seen
from the R square value of 0.422 which means that
the variation of immersion time has an effect of
42.2% on VIM. The smaller the pore is left the more
water-resistant and the less air in the asphalt
concrete which results in a stronger asphalt film
oxidizes with air and becomes brittle. VIM value
still meets the requirements according to 2018 Bina
ASAIS 2019 - Annual Southeast Asian International Seminar
134
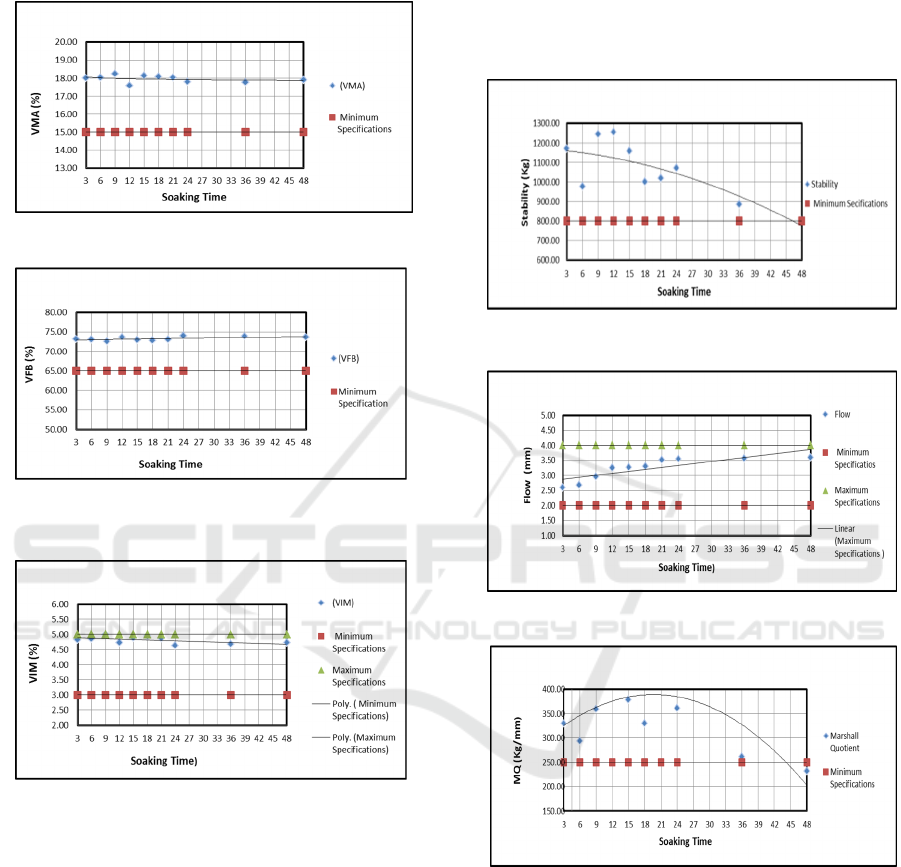
Marga specifications, namely 3.0 - 5.0% (As in
Figure 2c).
Figure 2a. VMA Graph
Figure 2b. VFB Graph
Figure 2c. VIM Graph
d. Stability
Based on the results of statistical tests indicate that
immersion time has a significant effect on stability.
This can be seen from the R-square value of 0.606
which means that the variation of immersion time
has an effect of 60.6% on stability. The test results
show that the value of stability obtained tends to
decrease. The average stability values obtained from
the test results on the variation of each immersion
time are: 1170.77; 975.23; 1245.03; 1254.93;
1158.39; 998.74; 1017,31; 1071.76; 884.88; 800.73
kg. The test results on the variation of immersion
time of 3 hours to 45 hours still meet specifications
(Bina Marga, 2018). The decrease in the value of
stability indicates a decrease in the ability of the
pavement layer (AC-WC) in receiving traffic loads.
The longer the layer of pavement (AC-WC) is
submerged in water, the less durable it is. (As in
Figure 2d)
Figure 2d. Stability Graph
Figure 2e. Flow Graph
Figure 2f. MQ Graph
e. Flow
Based on the results of statistical tests indicate that
the immersion time affects the melt. This can be
seen from the R square value of 0.523 which means
that the variation of the immersion time of 3 to 48
hours has an effect of 52.3% on the melt. the test
results show that the value flows with the addition of
soaking time up and down. The value flow still
meets the requirements according to the 2018 Bina
Marga specifications, namely 2-4 mm is at the time
Variation of Soaking Time on Asphalt Concrete Properties using Anti Stripping Materials
135
of immersion of 3 hours to 48 hours. (As in Figure
2e).
f. Marshall Quotient
Based on the results of statistical analysis showed
that the soaking time affects the Marshall Quotient.
This can be seen from the R square value of 0.586,
which means that the variation of immersion time
has an effect of 58.6% on Marshall Quotient. The
Marshall Quotient (MQ) value rises to a certain
extent then decreases with increasing immersion
time starting from 3 Hours to 48 Hours. The MQ
value that meets the requirements according to the
2018 Bina Marga specifications, namely a minimum
of 250 kg / mm, is at the time of immersion of 3 to
45 hours. (As in Figure 2f).
Determination of the Optimum Immersion Time,
after all Asphalt concrete properties have been
known, then the Optimum Immersion Time can be
determined from this Marshall test. To obtain the
Optimum Immersion Time a marshall chart is made
in Figure 3.
Mixed characteristic values generated in the test
Marshall in Figure 4. All parameters Marshall that
meet the requirements are in the Immersion Time
range 3 to 45 hours. From these results, it can be
concluded that:
Optimum Soaking Time = {(3 + 45}: 2 = 24;
Then Optimum Soaking Time is 24 Hours.
Table 3. Results of Mechanical Properties by Using
Optimum Soaking Time
Figure 3. Determining the Optimum Soaking
From the results of the Time Chart
4 CONCLUSION
Statistical test results show that:
Based on the research by making hot mix asphaltic
concrete specimens, with 0.6% asphalt content,
Wetfixbe content 0.3% of the weight of asphalt, with
the various of immersion time, it can be concluded.
Variation of immersion time from 3 hours to 48
hours affects significant to VFB, VIM, Stability,
Flow, and Marshall Quotient values but has less
effect on the VMA value because of the significant
value >0.05.
The addition of immersion time can increase the
% of Voids Filled with Bitumen (VFB) and Flow
and reduce the % of Voids in Mix (VIM), Voids in
Mineral Aggregate (VMA), Stability, and Marshall
Quotient.
The immersion time that still meets Marshall
property is the time of soaking 3 to 45 hours. The
Optimum Soaking Time for asphalt concrete mix is
24 hours, with VMA value 18.06%, VFB 72.29%,
VIM 5.03%, Stability 1071.76 kg, flow 3.25 mm and
MQ 360 kg / mm.
The variation of soaking time on Asphalt
concrete with 24 hours meets the specifications of
Bina Marga 2018.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
On this occasion the authors would like to express
their deepest gratitude to all those who have helped
this research, especially to the Head of PPPM State
Polytechnic of Jakarta, who has distributed funds
from the State Polytechnic of Jakarta DIPA.
REFERENCES
Amal, Andi S. 2009. Variations of Soaking in Asphalt
Concrete Mixes on Marshall Stability Values,
GAMMA, Volume IV, Number 2, March 2009: 81-85.
[Internet]. Available at: ejournal.umm.ac.id
Angga, Baskara K. M. at all.2016. Analysis Retained
Stablitty Index of Asphalt Porous Based Buton
Granular Asphalt (BGA). 2016.
http://repository.unhas.ac.id/bitstream/handle/1234567
89/21508/jurnal.docx?sequence=1
Arifin, Z., Jakfar, L., and Martina, G. 2008. Effect of
Rainwater Content on Marshall Characteristic Values
and Residual Strength Index (IKS) of Concrete
Asphalt Layers ( Laston). Journal of Civil
Engineering, 2 (1): 39-45. [Internet]. Available at:
http: //www.academia.edu/…Disses.
Djalante, S. 2011. Effect of Asphalt Concrete Resilience
(AC-BC) Using Asbuton Grain Type 5/20 on Sea
Water Judging from Mechanical Characteristics and
Durability. Journal of Transportation Engineering and
Management, I: (1): 57-68. [Internet]. Available at
http://jurnal.untad.ac.id/jurnal/index.php/JRMT/article
/view/713 Accessed March 29, 2018.
ASAIS 2019 - Annual Southeast Asian International Seminar
136

Fauziah M., Handaka A. 2017. of Starbit E-55 Asphalt to
Withstand Declining in Split Mastic Asphalt
Utilization Performance Due to Rainwater Immersion
Mixture of Transportation Journal Vol. 17 No. April 1,
2017: 11-20. [Internet]. Available at e-journal.
unpar.ac.id/index.php/journaltransportasi/article/
Accessed March 29, 2018.
General Specifications of Bina Marga Division 6, 2018,
Asphalt Pavement, Directorate General of Highways.
Kosim, Zainuddin. 2013. The Effect of Addition of
Cement Filler and Water Immersion Time on the
Durability of Concrete Asphalt Layer (Laston)
http://download.portalgaruda.org/article.php?article=1
55293&val=4006&title=PARUH%20PAMAMASI%2
0FILL. Accessed 2 April 2018.
Latifa, E.A. et all 2012. Performance of Hotmix Asphaltic
Concre with Various Filler Affected by Flood.
Proceeding of Annual SOUTH East Asian
International Seminar (ASAIS) 2012. I: (l): 51-57.
Nurhuduyah, N., Dato, AK, and Parung, H. 2009. Study of
Water Puddles on Road Damage in Gorontalo City.
Symposium XII FSTPT. Petra Christian University
Surabaya, 14 November 2009.
Pratama, B.A., Fauziah. 2017. Comparison of the
performance of a hot rolled asphalt (HRA) mixture
with 60/70 pen asphalt and retona blend 55 asphalt
with varying duration of sea water immersion.
Teknisia Journal.Vol XXII, No. Mei 1, 2017:324-333.
Rahmi Rizal, et all. 2017. Pengaruh Lama Rendaman AIR
Laut terhadap Durabilitas Campuran Aspal Beton
menggunakan Aspal Pen 50/70 yang disubstitusi
Limbah Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA). Teknik Sipil
Journal University Syiah Kuala. Vol. 6. No. Mei 3,
2017: 271-282. http://journal.
Unsyah.ac.id/JTS/article/download/9843/7803.
Rizal, M. et all (2017). Performance Of Porous Asphalt
Affected By Aging Process. International Journal of
Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET) . Vol. 8.
Issue 6.June 2017,pp.1023-
1033.www.iaeme.com>IJCIET_08_06_111>
Robert D. Krebs and Richard D Walker. 1971. Highway
Materials. McGraw Hill Inc.
Sanusi, 2012. Durability of Concrete Asphalt Mixtures
using Portland Cement Filler, Carbide Waste and Coal
Waste, https://digilib.uns.ac.id/. .. = / Durability-mix-
asphalt-concrete-using-filler-se; Accessed March 29,
2018.http://journal.uii.teknisia/article/download/8290/
7971.
Susilowati, Anni and Wiyono, Eko (2015), Use of Anti-
Stripping Materials for Asphalt Concrete Mixtures,
Poly-Technology Journal, Vol 16, No 1 (2017).
[Internet]; Available at journal.
pnj.ac.id/index.php/politeknologi/article/viewFile/871/
562 Journal. Accessed 2 April 2018.
Variation of Soaking Time on Asphalt Concrete Properties using Anti Stripping Materials
137
