
Foreign Tourist Satisfaction at Museum
Yansahrita
1
, I Made Bayu Yustika Putra
2
, and Dyah Sugandini
2
, Tri Wahyuningsih
2
1
STIE Trisna Negara
2
Universitas Pembangunan Nasional Veteran Yogyakarta
Keywords: Tourist Satisfaction, Tourist Attraction, Quality of Travel Destinations
Abstract: Tourism is an industrial opportunity that has a very wide network and can even develop other business
fields and is a very profitable opportunity for a particular country. Tourist satisfaction can be influenced by
Travel Attractions and Service Facilities, and according to the Quality of Travel Destinations can also
influence consumer behavior. This research is a survey research using a questionnaire. The population in
this study were all foreign tourists visiting the Yogyakarta and South Sumatera museum and with sampling
techniques convenience sampling. Multiple linear regression analysis was used to examine the relationship
between variables in this study.
1
INTRODUCTION
The Tourism Industry is one of the most important
sectors in several local economies, mainly because
of the ever-increasing contribution to regional
income, but also because of the opportunities offered
for further growth (Karakitsiou et al., 2007).
Tourism is an industrial opportunity that has a very
wide network and can even develop other business
fields and is a very profitable opportunity for a
particular country. Tourist satisfaction can be
influenced by Travel Attractions and Service
Facilities, and according to the Quality of Travel
Destinations can also influence consumer behavior
in determining destination destinations (Rajaratnam
et al., 2011). This study aims:
a.
To find out and analyze the influence of
Attraction on the satisfaction of Foreign
Tourists in the Yogyakarta and South
Sumatera Museum.
b.
To find out and analyze the effect of the
Facility on the satisfaction of Foreign Tourists
in the Yogyakarta and South Sumatera
Museum.
c.
To find out and analyze the effect of
Accessibility on the satisfaction of Foreign
Tourists in the and South Sumatera Museum.
d.
To find out and analyze the effect of
Destination Quality on the satisfaction of
Foreign Tourists in the Yogyakarta Museum.
2
LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Tourist Satisfaction
2.1.1 Understanding Satisfaction
Zeithaml and Bitner (2003) suggest that satisfaction
is a much broader concept than merely an
assessment of service quality, but is also influenced
by other factors, such as situation factors, individual
background, and product quality.
The perception of the quality of tourist
destinations felt by tourists during and after visiting
tourist destinations is the quality of tourism and
affects tourist satisfaction. Satisfaction is a measure
that shows how well expectations are met regarding
satisfaction from customer needs. Tourist
satisfaction research has often been applied because
it has an important role in the survival of each
tourism product, service, and tourist destination
(Gustroy et al. 2003, 2007).
The disconfirmation model is the one most often
used in previous satisfaction studies (Erevelles and
206
Yansahrita, ., Putra, I., Sugandini, D. and Wahyuningsih, T.
Foreign Tourist Satisfaction at Museum.
DOI: 10.5220/0009961202060210
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management (ICBEEM 2019), pages 206-210
ISBN: 978-989-758-471-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Leavitt, 1992). Based on this approach, satisfaction
is seen as evaluating individual responses.
Between what is received and what is expected
(Liljander and Strandvik, 1997). Therefore, the
quality of service performance evaluated by
consumers in terms of reference or comparison basis
is generally referred to as the standard of expectation
or comparison. The individual decisions resulting
from this comparison are referred to as
disconfirmation of expectations, which reflects if the
service is better or worse than expected.
Based on this, expectations, performance, and
disconfirmation are the most important variables that
contribute to customer satisfaction (Oliver, 1997).
To complete, loyalty to service providers is
considered as the main consequence of satisfaction
(Yu and Dean, 2001).
2.2 Destination Attractiveness
2.2.1 DefnTravel Attractions
Gunn (1972, 1998) suggested that without tourist
attraction, there would be no tourism. Lew (1987)
adds that without tourism, there will be no tourist
attraction. The importance of tourist attraction is a
condition for developing tourism in certain areas.
Lew (1987) defines a tourist attraction as all
elements of a tourist destination that draw tourists
from their permanent residence and refers to the
geographical and climate characteristics of a
particular location, activities in which tourists can
participate according to the experience they
remember.
Mayo and Jarvis (1981) define attractiveness as
the perceived ability of a goal to provide individual
benefits. Gartner (1996) defines tourist destinations
as the center of the tourist experience, and he also
stresses the importance of management by saying
that almost all features can be a tourist attraction if
marketed properly and adequately presented.
Hu and Ritchie (1993) define tourist attraction as
a reflection of the feelings, beliefs, and opinions one
has about the desired perceptions of destinations to
meet special needs and satisfaction for certain
individuals. "
2.2.2 Classification of Tourist Attractions
Tourism
Objects are heterogeneous and the essence of each
Different tourist attraction. For example, natural
attractions, night tours, historical tourism, and
spiritual tourism are examples of tourist destinations.
The essence of each of these tourist attractions is
different, but if all tourist destinations are properly
presented and marketed then it can become an
attraction perfect tourism McIntyre, Hetherington
and Inskeep (1993) classify factors of tourist
attraction into the following categories:
1)
natural tourism resources,
2)
cultural and historical heritage,
3)
climate conditions,
4)
infrastructure,
5)
services and tourist facilities
In addition to the above tourist attraction factors,
the tourist attraction is influenced by several main
factors of tourism component ta include Attractions,
Amenity, and Accessibility.
1)
Attraction
Cooper (2000) mentions that Attraction is a form
of cultural activity, natural beauty, and events that
motivate tourists to come to visit. Attraction
(Attraction) is all about nature, culture, events,
recreation, and entertainment, which is an attraction
so that people want to come to visit a tourist
destination and can be entertaining when people
watch the attraction.
2)
Facilities (Amenity)
Cooper (2000) states that Amenity includes
facilities and services provided for tourists in tourist
destinations. Amenity is all facilities contained in a
tourist destination that supports tourist activities to
enjoy the tourist destination area.
3)
Accessibility
Includes distance from the highway, road
conditions, and vehicles to tourist attractions.
According to cooper (2000), Accessibility is the
provision of transportation facilities to reach
destinations easily. Accessibility can also be said as
facilities for tourists to reach tourist destinations in
the form of vehicles, transportation systems,
terminals, and pre-highway facilities.
2.3 Quality Travel Destinations
(Destination Quality)
The Quality tourist destination is defined as a
location group of attractions, facilities, and tourist
services (Kim and Brown, 2012), and the
combination of these features is a tourism product at
the destination (Zabkar et al.,2010). Zakbar
highlighted the existence of two frameworks for
classifying the attributes of tourist destinations,
namely Attractions, access, additional facilities, and
services) and (tourist attractions, access, facilities,
packages available, activities and additional
services).
Foreign Tourist Satisfaction at Museum
207

Previous studies conducted by Lopez-Toro et al.,
(2010); Eusebio and Vieira, (2013); Chen et al.,
(2011); Moutinho et al., (2012) using different
important attributes aimed at assessing the quality of
tourist destinations. This study does not focus on
rural tourism destinations. Apart from the growth of
rural tourism in many developed and developing
countries. The study states that the quality of rural
accommodation (Lourerio and Gonzalez, 2008) or
Farm tourism (Rozman et al., 2009). Because of the
scope of this study, relevant attributes for measuring
the quality of rural tourism destinations have been
identified and used.
The perception of the quality of tourist
destinations felt by tourists during and after visiting
tourist destinations is the quality of tourism and
affects tourist satisfaction. Rajaratnam et al., (2011)
in his research stated that there were 8 (eight)
attributes of the quality of tourist destinations
namely Amenities which include facilities and
services provided for tourists in tourist destinations
(Cooper, 2000), Accessibility, namely the provision
of transportation facilities to reach destinations
(Cooper, 2000) and Logistics, Core Tourism
Experience (experience in tourist attractions),
Hygiene or cleanliness, Information, Security or
security, Value for Money and Hospitality.
2.4 Effects of Tourist Attractions on
Tourist Satisfaction Tourist
Attractions namely, as all elements of tourist
destinations that attract tourists from their permanent
residence and refer to the geographical and climate
characteristics of a particular location, activities
where tourists can participate according to the
experience they remember. Satisfaction is a feeling
happy or disappointed someone who arises because
of comparing the perceived performance of products
or results against their expectations (Kotler, 2009).
As explained in the definition above, satisfaction is a
function of perception or impression of one's
performance or service and expectations. Renewal
and making purchases. Travel Attractions are
influenced by several main factors, including
Attractions, Amenity, and Accessibility.
According to Basiya and Rozak (2012), the
attractiveness of tourist destinations is the main
motivation for visitors to travel. Basiya and Hasan
(2012) in his research concluded that the quality of
natural attractions(natural attraction), the quality of
tourist attraction in the form of the architecture of
the building(building attraction), cultural attractions
(cultural attraction), and attraction of social (social
attraction) have a direct and positive relationship to
tourist satisfaction.
H1: Attraction positively influences Tourist
Satisfaction of Yogyakarta Vredeburg Museum
H2: Facilities (Amenity) has a positive effect on
Yogyakarta Vredeburg Museum
H3: Accessibility (Accessibility) tourist
satisfaction has a positive influence on Tourist
Satisfaction of Yogyakarta Vredeburg Museum.
2.5 Effect of Quality of Tourist
Destinations on Tourist Satisfaction
The Quality of tourist destinations is defined as the
location of a group of attractions, facilities, and
tourist services (Kim and Brown, 2012), and the
combination of these features is a tourism product at
the destination level (Zabkar et al., 2010). Zakbar
highlighted the existence of two frameworks for
classifying the attributes of tourist destinations,
namely Attractions, Access, Facilities, and
Additional Services).
Rajaratnam et al. (2011) state that the perception
of the quality of tourist destinations has a significant
effect on satisfaction, which subsequently has a
significant effect on consumer behavior. From the
above explanation, it can be drawn the following
research hypothesis:
H4: There is a positive influence on the quality
of tourist destinations on tourist satisfaction of the
Yogyakarta and South Sumatera museum.
3 RESEARCH METHODS
This research is a survey research using a
questionnaire. The population in this study were all
foreign tourists visiting the Yogyakarta Vredeburg
Fort Museum and with sampling techniques
convenience sampling. Multiple linear regression
analysis was used to examine the relationship
between variables in this study.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Characteristics of Respondents
Based on the demographic characteristics of the
respondents can be seen in table 1.
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
208
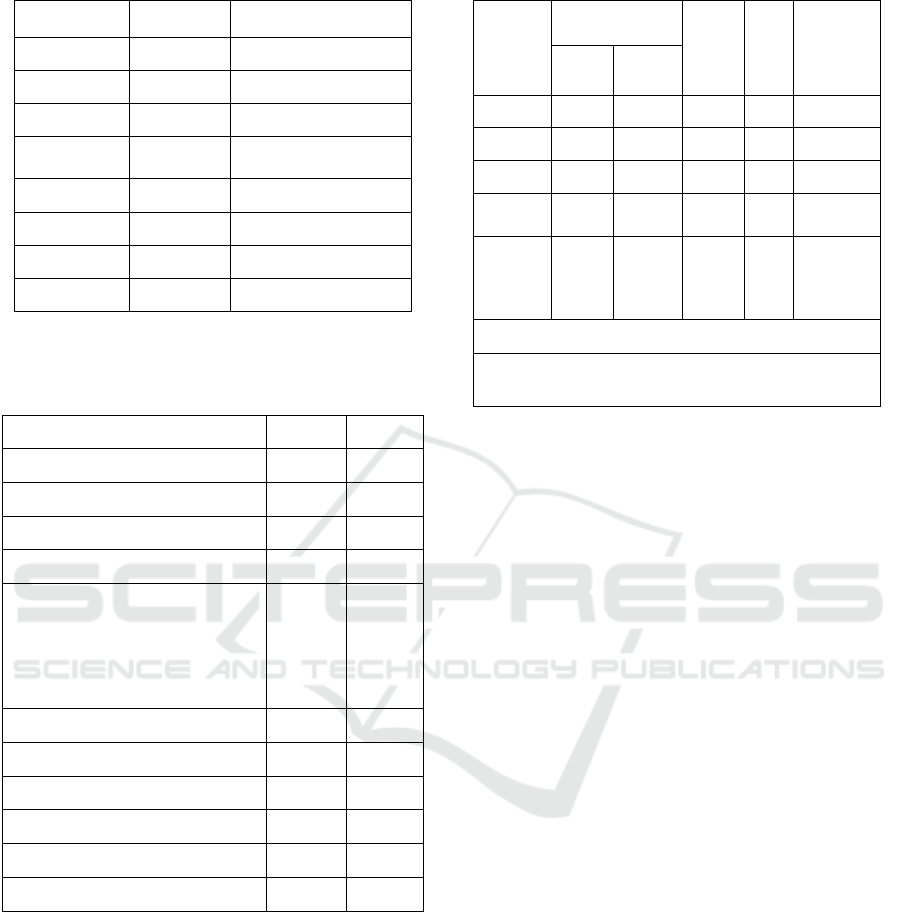
Table 1. Demographics of respondents
Gender Number Percentage (%)
Female 36 36%
Male 64 64%
Public
Private
Employees
28 28%
Student 35 35%
Entrepreneur 10 10%
Civil Servants 4 4%
Other 23 23%
Characteristics of respondents based on tourist
origins can be seen in table 2.
Table 2. Origin data of tourists
countries
Dutch 21 21%
Australia 15 15%
Belgium 8 8%
Canadian 5 5%
Prassian, Spanish, Norway ,
Thailand, Hungary, Uzbek,
Bangladesh, Ghanaian, Bosnia,
Jamaica, Myanmar, Jordan,
Kiribati, Bulgaria, Ireland,
Singapore,
13
13%
Netherlands 4 3%
British 12 12%
Polish 2 2%
Malaysia 2 2%
American 12 12%
German 6 6%
4.2 Results of Multiple Regression
Analysis
Results of multiple regression analysis regarding the
influence of Travel Attractions, namely Attraction,
Facilities ()Accessibility, Accessibility, and Quality
of Tourist Destinations (Destination Quality) on
Satisfaction of Wisatawan as follows:
Table 3.
Model
Unstandardized
Coefficients
t
Sig
.
Remarks
B
Std.
Error
(Constant) 35 439 10 149 3,492 .001
Things 147 .052 2,854 .005 Significant
Facility 121 .057 2128 .036 Significant
Accessibil
ity
140 .058 2401 .018 Significant
Quality
Travel
Destinati
ons
534
.055
9742
.000
Significant
dependent variable (Y): Satisfaction rating
F count: 587 759
Sig. F: 0.000 Adj R2 : 0.960
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the above research, it can be
concluded as follows:
a.
Tourist Attraction ie, Attraction has a positive
effect on Tourist Satisfaction Museum.
b.
Travel Attractions, namely Facilities
(Amenities), have a positive effect on the
Tourist Satisfaction of the Museum.
c.
Travel Attractions, namely Accessibility has a
positive effect on the Tourist Satisfaction of
the Museum.
d.
The Quality of a Tourist Destination has a
positive effect on the Tourist Satisfaction of
the Museum.
REFERENCES
Basiya R and Hasan Abdul Rozak. 2012, Journal of
Quality of Tourist Attraction, Satisfaction and
Intention of Foreign Tourist Return Visit in Central
Java: The Dynamics of Tourism Vol. XI No. 2.
Chen, CM, Lee, HT, Chen, SH and Huang, TH (2011),
"Tourist behavioral intentions in relation to service
quality and customer satisfaction in Kinmen National
Park, Taiwan", International Journal of Tourism
Research, Vol. 13 No. 5, pp. 416-432.
Cooper (2000) "Tourism Principles and Practice Second
edition." United States of America: Longman, 2000
Damir KRESIC, MA 2011, International Journal: Index of
Destination Attractiveness (IDA): A Tool for
Measuring Attractiveness of Tourism Destinations,
Institute for Tourism, Zagreb, Croatia
Foreign Tourist Satisfaction at Museum
209

De Ruyter, JC, JMA Bloemer, and P. Peters (1997).
Merging service quality and service satisfaction: An
empirical test of an integrative framework, Journal of
Economic Psychology, 18 (4), 387-406.
Erevelles, S., and Leavitt, C. (1992). A Comparison of
Current Models of Consumer Satisfaction /
Dissatisfaction. Journal of Consumer Satisfaction,
Dissatisfaction and Complaining Behavior, 5: 104-
114.
Eusebio, C. and Vieira, AL (2013), "Destination attributes'
evaluation, satisfaction and behavioral intentions:
structural modeling approach", International Journal of
Tourism Research, Vol.15No.1, pp.66-80.
Gartner, WC (1996). Tourism Development - Principles,
Processes, and Policies. New York: Van Nostrand
Reinhold.
Ghozali, Imam. 2011, Multivariate Analysis Application
with the IBM SPSS Program, Fifth Matter,
Dipenogoro University Publisher Agency, Semarang.
Grigoroudis, E. and Y. Siskos (2010). Customer
satisfaction evaluation: Methods for measuring and
implementing service quality, Springer, New York.
Gunn, CA (1979, 1988). Vacationscape: Designing
Tourist Regions. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Hu, Y., & Ritchie, BJ (1993). MEASURING
Destination Attractiveness: A Contextual Approach.
Journal of Travel Research, 32 (2), 25-34.
Karakitsiou, A., A. Mavrommati, A. Migdalas, and K.
Tsiakali, (2007). Customer satisfaction evaluation in
the tourism industry: The case of Chania, Foundations
of Computing and Decision Sciences, 32 (2), 111-124.
Kim, AK and Brown, G. (2012), "Understanding the
relationships between perceived travel experiences,
overall satisfaction, and destination loyalty", Anatolia:
An International Journal of Tourism and Hospitality
Research, Vol. 23 No. 3, pp. 328-
347.
Kotler, Philip and Kevin L. Keller. 2009. Marketing
Management Edition 13, Vol. 1 & 2.
Prenhalindo : Erlangga: Jakarta.
Lew, AA (1987). A Framework of tourist attraction
research. Annals of Tourism Research, 14 (4), 553-
575.
Liljander, V., and Strandvik, T. (1997). Emotions in
Service Satisfaction. International. Journal of Service
Industry Management, 8 (2): 148-169.
Lopez-Toro, AA, Diaz-Munoz, R. and Perez Moreno,
S. (2010), "An assessment of the quality of a tourist
destination: the case of Nerja, Spain", Total Quality
Management, Vol. 21 No. 3, pp.269-289.
Loureiro, SMC and González, FJM (2008), "The
importance of quality, satisfaction, trust, and image in
relation to rural tourist loyalty", Journal of Travel and
Tourism Marketing, Vol. 25 No.2, pp.117-136.
Mariana Tsitsiloni, Evangelos Grigoroudis and Constantin
Zopounidis. 2012, Service Quality Evaluation in The
Tourism Industry: A SWOT Analysis Approach,
International journal of Financial Engineering
Laboratory
Mayo, EJ, & Jarvis, LP (1981). Psychology of Leisure
Travel. Boston: CBI Publishing Co.
McIntyre, G., Hetherington, A., & Inskeep, E. (1993).
Sustainable tourism development: guide for local
planners. Madrid: UNWTO.
Moutinho, L., Albayrak, T. and Caber, M. (2012), "How
far does overall service quality affect destination
customers' post-purchase
behavior?", International Journal of Tourism Research,
Vol.14 No.4 , pp.307-322.
Naisbitt, J. (1995). Global paradox, Nicholas Brealey
Publishing, London.
Oliver, RL (1997). Satisfaction: A Behavioral Perspective
on the Consumer. New York: McGraw – Hill.
Payangan, Otto R. 2014. Marketing of Tourism Services.
Bandung: IPB Press.
Rozman, C
ˇ., Potocˇnik, M., Pažek, K., Borec, A.,
Majkovicˇ, D. and Bohanec, M. (2009), "A multi-
criteria assessment of tourist farm service quality",
Tourism Management, Vol. 30 No.5, pp.629-637.
Spreng, RA and RD McKoy (1996). An empirical
examination of a model of perceived service quality
and satisfaction, Journal of Retailing, 72 (2), 201-214.
Suryadana, M. Liga and Vanny Octavia. 2015.
Introduction to Tourism Marketing. Bandung:
Alfabeta
Rajaratnam, Sushila Devi and Nair, Vikneswaran., Sharif,
Saeed Pahlevan., And Munikrishnan, Uma Thevi.
(2011), Destination Quality and Tourists' Behavioral
Intentions: Rural Tourist Destinations in Malaysia.
Emerarld International Journal.
Yu, YT., And Dean, A. (2001). The Contribution of
Emotional Satisfaction to Consumer Loyalty.
International Journal of Service Industry Management,
12 (3).
Zabkar, V., Brencic, MM and Dmitrovic, T. (2010),
"Modeling perceived quality, visitor satisfaction and
behavioral intentions at the destination level", Tourism
Management, Vol.31No.4, pp.537-546.
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
210
