
Financial Technology Application in Small and Medium Businesses
Christian Herdinata
International business management
Faculty of Management and Business, Ciputra University
Keywords: Financial Technology, Regulation, Financial Literacy, Collaboration
Abstract: Financial Technology (Fintech) has provided access to many parties who do not have a bank account to enter
the formal business sector. The application of Fintech has proven to be able to open greater access to formal
financial services, encourage economic growth, as well as inclusive development and maintenance. To
support the application of Fintech in Indonesia, the purpose of this study is to find agreement, financial
literacy, and collaboration that focuses on the application of Fintech for small and medium businesses in
Indonesia. This research was conducted through quantitative research using multiple regression analysis
techniques. The results of this study are that financial regulation and literacy have no significant effect on the
application of fintech. However, collaboration has a significant effect on the application of fintech. Therefore,
this study provides a complete and comprehensive understanding related to the application of Fintech in small
and medium-sized businesses relating to regulation, financial literacy, and collaboration.
1 INTRODUCTION
Bappenas simulation results, investment financing
needs for infrastructure development in 2018 around
Rp 5,248 trillion. We see Fintech has a great market
capability so that Fintech can improve the welfare of
poor households through business financing, access
to clean water and electricity, and financial
management for education and health. The 2015-
2019 National Medium-Term Development Plan
(RPJMN), inclusive finance, is the government's
effort to realize economic independence by driving
the strategic sector of the domestic economy. The
goal is to increase public access to formal financial
services within the framework of inclusive and
equitable economic development. In line with the
RPJMN objectives, based on the Deloitte Consulting
Survey and the Indonesian Fintech Association in
2016, three things encourage the implementation of
Fintech in Indonesia, namely more explicit
regulation, collaboration, and especially financial
literacy. In response to this, the government will
continue to encourage financial literacy and inclusion
programs so that the target of the Financial Inclusion
Index announced by the government through
Presidential Regulation (Perpres) Number 82 of 2016
concerning the National Strategy for Financial
Inclusion (SNKI) by 75 percent, can be achieved in
2019. However, data OJK shows that only about 67
percent of Indonesian adults in 2016 had access to
formal financial institutions; The World Bank
explained that around 49 million SME units were not
yet bankable. For this reason, adaptive policies on
technology and partnerships with the private sector
and financial services are needed.
In the McKinsey Global Institute report, digital
financial services can provide access to 1.6 billion
people who do not have a bank account to enter the
formal business sector. As many as 95 million new
jobs could be created, and the GDP of developing
countries increased by $ 3.7 trillion. Therefore, the
use of Fintech is proven to be able to open greater
access to formal financial services, encourage
economic growth, and inclusive and sustainable
development. The challenge for Indonesia is to make
the process of development and public service
adaptive to the development of Fintech. Therefore,
the purpose of this study is to find out clear
regulations, collaboration, and financial literacy in
the application of Fintech optimization for MSMEs in
East Java. Therefore, this study wants to find out
whether regulation, financial literacy, and
collaboration have a significant effect on the
application of financial technology?
Herdinata, C.
Financial Technology Application in Small and Medium Businesses.
DOI: 10.5220/0009960801970200
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management (ICBEEM 2019), pages 197-200
ISBN: 978-989-758-471-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
197

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Financial Technology (Fintech)
Creating development for the poor who are
vulnerable and able to access financial services, this
Fintech is one of the strategic solutions to realize
financial inclusion. This solution is dedicated to users
of financial services for payment, trading, capital
market activities, and much more (Ion and Alexandra,
2016). The process of technology substitution in it is
much better for encouraging long-term investment
and capital placement in various productive sectors
(Rong et al., 2013). However, many innovative
products have subsequently failed to reach critical
mass users and even do not exist anymore (Teja,
2017). Hyytinen, Pajarinen, & Rouvinen (2015)
stated that companies that focus their primary
attention on developing superiority products tend to
fail.
Fintech is a new financial technology product that
can facilitate various transactions, both payments,
investments, and insurance (Teja, 2017). Natural
features will produce a high level of comfort so that
the successful application of Fintech can be
optimized. The biggest challenge in developing
financial innovation is a superior product whose
function is accepted in the habit of using the user's
daily payment system without changing user habits
(Teja, 2017). Users do not need to go to banks
anymore and spend their time on credit arrangements,
currency exchange, and many more (Kalmykova and
Tyabova, 2016). These tools make life easier;
however, they pose a serious threat to banks; services
should be created more convenient and useful to
retain clients. Therefore, the bank and credit system
began to change actively (Kalmykova and Tyabova,
2016). This illumination of Fintech will achieve the
goal of user convenience, user comfort, and being
able also to minimize the cost of money creation to
various credit cards that are more familiar among
users (Teja, 2017).
2.2 Regulation
The Fintech market is proliferating, followed by the
emergence of new business start-ups every month,
but on the other hand, there are still no clear legal
regulations from the government related to the
development of this financial technology. Financial
technology is developing so fast that it is challenging
to manage all the innovative features of legal control
(Kalmykova and Tyabova, 2016). Users will
empirically consider the factors that influence the
expectations of both users and organizations in
adopting Fintech, including customer trust, data
security, the added value from fintech itself. Clear
regulations will increase customer confidence, data
security, and user design appearance, which influence
the implementation of FinTech (Stewart and Jurjens,
2018).
2.3 Collaboration
Sterman et al., In Teja (2017), stated that the strategy
of implementing Fintech, whose aim is to achieve
rapid growth, could create the risk of excess industrial
capacity. Thus the company needs to overcome these
problems by becoming a leader in a business
ecosystem through collaboration. By binding a user
network and changing the user's role into a developer,
the assumption is that the company will get more
acceptance (Lu, C., Rong, K., You, J., & Shi, Y.
(2014). Transforming users into developers can open
up new opportunities (Overholm, 2014; McKelvey et
al., 2015). The prospect of its application will grow
faster than competitors when using collaboration
between industry and the business ecosystem.
2.4 Financial Literacy
The Financial Services Authority surveyed in 2013
that the level of financial literacy of the Indonesian
population was divided into four parts, well literate
21.84%, sufficient literate 75.69%, less literate
2.06%, and not literate 0.41%. (www.ojk.go.id,
2017). The survey is based on the knowledge and
beliefs of Indonesians about financial services
institutions, including financial service products,
such as features, benefits and risks, rights, and
obligations related to financial products and services,
to their skills in using them. The potential impact of
Fintech on the financial industry, to create stability
and access to services (Philippon, 2016). Some
financial sectors and startups see Fintech as a gateway
to increase business opportunities. However, on the
other hand, there are also security threats increasing
rapidly and have become a challenge for Fintech
users if users are not equipped with a good
understanding of financial literacy (Stewart and
Jurjens, 2018).
Therefore, in this study, a research hypothesis was
formed relating to regulation, financial literacy, and
collaboration, and the application of financial
technology, as follows:
H1: Regulation has a significant effect on the
application of financial technology
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
198
H2: Financial literacy has a significant effect on
the application of financial technology
H3: Collaboration has a significant effect on the
application of financial technology
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The study was conducted using quantitative. The
research population is MSMEs in East Java. The
sampling technique uses nonprobability sampling,
which is a convenience sampling of 148 MSMEs. The
source of data used in this study came from primary
data through questionnaires and secondary data. The
data measurements were carried out in this study
using a Likert scale. Validity measurement is the
accuracy or accuracy of the test in carrying out its
measurement function Suryabrata (2000) in Rahayuni
(2015). The statement is said to be valid if the
significance value of the correlation is,00.05 or 5%
(Lingga, 2012). Reliability measurements to see the
questionnaire questions can consistently reflect the
construct being measured. A particular item in the
questionnaire must consistently produce things that
are relatively similar to the whole case seen through
measurements with the Cronbach's Alpha technique
with reliability that can be accepted if Cronbach’s
Alpha ≥ 0.6 (Priyatno, 2014: 64). The analysis
technique used in this study is Multiple Linear
Regression.
4 RESEARCH RESULT
The results of this research model show that the F test
is significant so that it meets the goodness of fit of a
model. The research sample consisted of 148 MSME
businesses in the study. The following table is the
results of the F test in Table 1.1
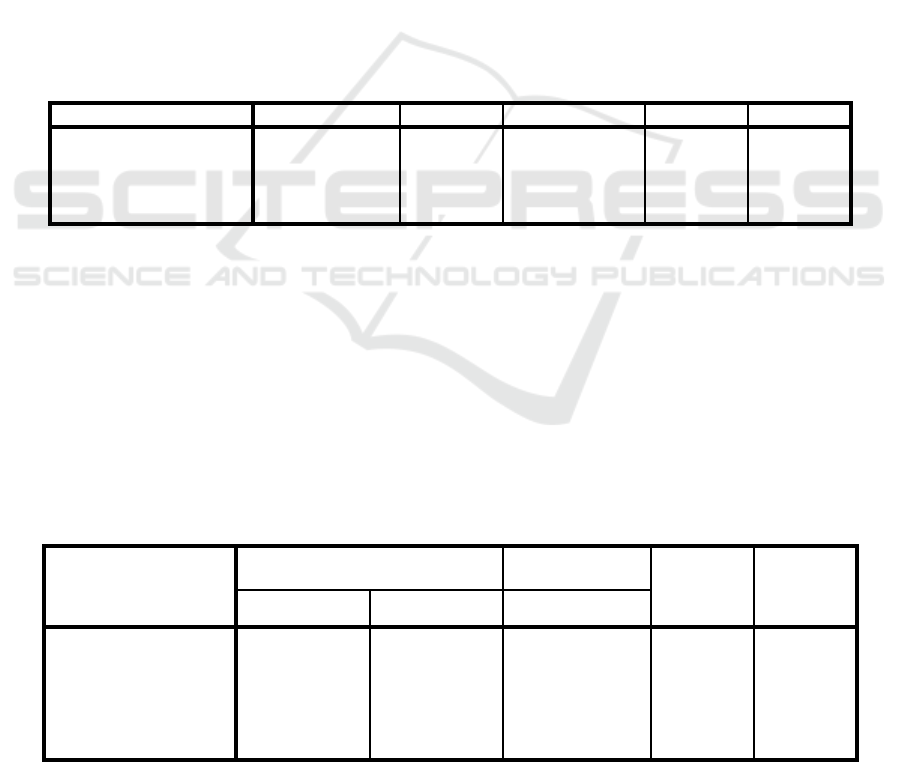
Table 1: Test Results F
Model Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig.
1 Regression 18.470 3 6.157 27.323 .000b
Residual 32.448 144 .225
Total 50.919 147
a. Dependent Variable: Y_PF
b. Predictors: (Constant), X3_Kol, X2_Lit, X1_Reg
The following are the results of the t-test on
testing the effect of regulations on the application of
financial technology found to have no significant
effect with a value of 0.147 greater than 0.05.
Therefore hypothesis (H1) is rejected. Furthermore,
to test the effect of financial literacy on the
application of financial technology, it had no
significant effect with a value of 0.170 greater than
0.05. Therefore, the H2 hypothesis is rejected. On the
other hand, the effect of collaboration on the
application of financial technology found a
significant effect that is equal to 0,000 below 0.05.
Therefore the hypothesis (H3) is accepted. T Test
results can be seen in Table 1.2.
Table 2: Test Results t
Model
Unstandardized Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t Sig. B Std. Error Beta
(Constant) 2.719 .230 11.838 .000
X1_Reg .086 .059 .139 1.457 .147
X2_Lit .106 .077 .116 1.379 .170
X3_Kol .268 .062 .419 4.309 .000 (*)
Information:
Dependent Variable = Y-PF
(*) = Sig. 0.05
Financial Technology Application in Small and Medium Businesses
199

The results showed that the effect of regulations
on the application of financial technology had no
significant effect. This can happen because the
Fintech market is growing so fast, followed by the
emergence of new business start-ups every month.
However, on the other hand, there are still no clear
legal regulations from the government related to the
development of this financial technology. This is in
line with Kalmykova and Tyabova (2016), who
explain that the control of the law is difficult to follow
the development of financial technology that is so
fast.
The effect of financial literacy on the application
of financial technology has no significant effect. This
is in line with the results of the Financial Services
Authority has surveyed in 2013 the level of financial
literacy of the Indonesian population is divided into
four parts well literate 21.84%, sufficient literate
75.69%, less literate 2.06%, and not literate 0.41 %
(www.ojk.go.id, 2017). This shows that the financial
literacy of the Indonesian population is still relatively
low. Therefore, financial literacy is not significant to
the application of financial technology because the
level of financial literacy still needs to be improved.
On the other hand, the effect of collaboration on
financial technology was found to be significant. This
shows that collaboration influences the application of
financial technology to SMEs. This shows MSMEs
must own that collaboration in the application of
financial technology. This is consistent with what
Teja (2017) revealed that collaboration with other
companies in a business ecosystem would produce
competence to achieve a critical mass of minimum
adopters and higher probability so that innovative
financial-related products will be able to be
successfully implemented.
5 CONCLUSION
This study found that financial regulation and literacy
had no significant effect on the application of
financial technology. On the other hand,
collaboration has a significant influence on the
application of financial technology. This shows that
financial regulation and literacy are things that need
to be improved so that the application of financial
technology can be optimized. Collaboration is a thing
that makes a significant contribution to the
application of financial technology. Therefore, the
role of government, the private sector, and society at
large and consumers, in particular, becomes vital in
the success of financial technology.
REFERENCES
Hyytinen, A., Pajarinen, M., & Rouvinen, P. (2015). Does
innovativeness reduce startup survival rates?. Journal of
Business Venturing, 30, 564-581.
Ion, Alexadra. (2016). Financial Technology (Fintech) and
Its Implementation on the Romanian Non-Banking
Capital Market. Practical Application of Science. Vol
IV, Issue 2.
Kalmykova, Ekaterina., Anna Ryabova. (2016). FinTech
Market Development Perspectives. SHS Web of
Conferences. Vol 10.
Lu, C., Rong, K., You, J., & Shi, Y. (2014). Business
ecosystem and stakeholders’ role transformation:
evidence from chinese emerging electric vehicle
industry. Expert Systems with Applications, 41, 4579-
4595.
McKelvey, M., Zaring, O., & Ljungberg, D. (2015).
Creating innovative opportunities through research
collaboration: an evolutionary framework and
empirical illustration in engineering. Technovation, 39-
40, 26-36.
Overholm, H. (2014). Collectively created opportunities in
emerging ecosystems: the case of solar service
ventures. Technovation, 39-40, 14-25.
Rong, Ke., Yongjiang Shi. (2013). Business ecosystem
extension: facilitating the technology substitution.
International Journal of Technology Management. Vol
63 no 3.4.
Stewart, Harrison,. Jan Jurjens. (2018). Data Security and
Consumer trust in Fintech Innovation in Germany.
Teja, Adrian. (2017). Indonesian Fintech Business: New
Innovations or Foster and Collaborate in Business
Ecosystems?. The Asian Journal of Technology
Management. Vol. 10 No. 1 pp 10-18.
Philippon, Thomas. (2016). The Fintech Opportunity.
National Bureu of Economic research.
http://www.nber.org/papers/w22476.
Priyatno, Duwi. (2014). SPSS 22 Pengolah Data Terpraktis.
Andi. Yogyakarta.
www.ojk.go.id, (2017). https: //www.ojk.go.id/id/ data-
dan-statistik/ laporan tahunan/ Pages/ Laporan -
Tahunan - OJK - 2017. aspx 10 september 2019
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
200
