
The Effect of Financial Literacy on Financial Management Behaviour
with Self-control as Intervening Variable
Shinta Heru Satoto, and Sri Budiwati W. P.
Universitas Pembangunan Nasional Veteran Yogyakarta
Keywords: Financial Literacy, Financial Management Behaviour, Self-Control
Abstract: This research aims to explain the influence of financial literacy on financial management behavior with self-
control as intervening variables. This research was conducted on the management of the Village Owned
Enterprises (BUM Des) in Sleman Regency, with 54 respondents. Used three variables, the data collected
will be tested using the regression and path analysis. This study shows that financial literacy has a positive
effect on financial management behaviour. This study also investigates the indirect effect of financial
literacy on financial management behaviour through self-control. The result shows that the direct effect is
stronger than an indirect effect on the influence of financial literacy on financial management behaviour.
The higher the financial literacy of the BUM Des management, the better the self-control of the
management in spending or consumption based on needs that are planned. So, it can be concluded that the
management's knowledge, skills, and confidence in financial planning and management, combined with
self-control related to financial expenditure, will significantly influence the behaviour of financial
management regarding decision making in the use of village finances.
1 INTRODUCTION
Government efforts to equalize development are
carried out in various ways. One of them is an effort
to equalize welfare in rural areas because the village
is one of the potential places for the country's
economy. The many village potentials that can be
developed and a large number of natural resources
that have not yet been exploited, encourage the
government to issue policies that can support the
development of village potential. The policies made
by the government include those listed in UU No. 6
of 2014 concerning Villages, followed by
Government Regulation No. 60 of 2014 concerning
village funds sourced from the State Budget.
Based on this law, every village has the right to
receive funding from the government sourced from
the state budget. Village funds can be used to
develop village potential, one of which is to
establish village-owned enterprises (BUM Des)
aimed at boosting the economy of village
communities. BUM Des was formed by the village
government to utilize all economic potential, natural
resources, and human resources to improve the
village community. BUM Des is managed by the
village government and also the village community
to strengthen the village economy and is formed
based on the needs and potential that exists in the
village.
The problem that often arises from the existence
of village funds is the ability to manage village
funds. The ability of administrators of village-owned
enterprises to manage village funds is an important
factor in achieving the objectives of the fund. Errors
in management and planning that often occur tend to
be caused by the behaviour of management who do
not have adequate financial knowledge. In general,
two factors influence a person's behaviour, namely,
internal factors and external factors. External factors
include culture, social class, and family. While
internal factors include motivation, the learning
process, and self-concept, in the concept of finance,
the learning process can be interpreted as a person's
knowledge to understand knowledge related to
finance or what is referred to as financial literacy
(Weningsih, 2018). The Organization for Economic
Co-operation and Development / International
Network on Financial Education (OECD / INFE)
(2009) argues that the lack of financial literacy is
recognized as one of the factors that contribute to
financial information decisions that are lacking in
information, thus causing negative impacts. Remund
Satoto, S. and W. P., S.
The Effect of Financial Literacy on Financial Management Behaviour with Self-control as Intervening Variable.
DOI: 10.5220/0009960501790186
In Proceedings of the International Conference of Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management (ICBEEM 2019), pages 179-186
ISBN: 978-989-758-471-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
179

(2010) also states that financial literacy is a
measurement of one's understanding of financial
concepts, and has the ability and confidence to
manage personal finances through appropriate short-
term decision making, long-term financial planning,
and attention to economic events and conditions.
Several studies have shown an influence between
financial literacy and behaviour in financial
management, including research conducted by Robb
& Woodyard (2011), Lusardi & Mitchell (2011), and
Michaud (2017). Robb and Woodyard prove that
functional financial literacy will have a positive
influence on a person's financial behaviour, where
someone will be able to manage or allocate their
finances appropriately. Michaud's research (2017)
found that financial literacy is associated with
increased income and plays an important role in
improving welfare. Michaud stressed that
behavioural interventions also need to be considered
because this will guarantee the achievement of
welfare in the form of increased income when
someone already has an understanding of financial
literacy. Whereas, Lusardi & Mitchell (2011) found
that behavioural factors, such as perceptions about
the importance of financial literacy, satisfaction at a
certain level on understanding financial literacy and
the results obtained, would greatly affect a person's
level of financial management ability. Their research
also found that financial literacy will be very easily
understood through interactions between individuals
in a work environment or a community.
Mistakes that occur in financial management are
also often caused due to a lack of self-control from
someone. Self-control is a person's ability to
maintain behaviour. Someone with good self-control
will have better financial behaviour and will be able
to manage the financial resources they have
(Kiyosaki, 2012). They will not spend on things that
are not needed or for activities that are not useful.
Self-control will lead to wise decision making and
better financial welfare. Besides, self-control will
help someone has a strong self-desire to achieve
success in the future. Lack of self-control will lead
to irrational decision making, low self-confidence,
and destructive behaviour (Younas, et.al; 2019).
Kahneman and Krueger (2010) found the effect of
self-control on financial behaviour. According to
Kahneman, someone with good cognitive abilities
will be able to manage their finances to achieve
goals.
From the results of the pre-survey conducted, it
is known that someone who has sufficient financial
knowledge, will have sufficient self-control in
managing finances. Based on this, this study was
conducted to examine the effect of financial literacy
on financial management behaviour by using self-
control as an intervening variable. The study was
conducted on administrators of village-owned
enterprises (BUM Des) of Sleman regency in
managing village funds obtained from the
government.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW AND
HYPOTHESES
2.1 Financial Management Behavior
Financial management behavior is a determination,
acquisition, allocation and use of financial resources
in accordance with specified objectives (Horne and
Wachowicz (2002). The more active a person's
financial management behavior will be, it can
improve financial welfare, and vice versa, failure in
financial management will lead to negative
consequences in the long run.
Deacon and Firebaugh (1988) define financial
management behavior as a set of behavioral results
in the form of planning, implementation, and
evaluation involving the scope of cash, loan,
investment, insurance, and pension planning. Failure
to manage finances will lead to serious long-term
consequences, not only for someone but also for the
company. Financial behavior as part of financial
management behavior can be measured by looking
at someone's actions, including financial knowledge,
financial attitudes, and locus of control (Dowling, et
al., 2009)
2.2 Financial Literacy and Financial
Management Behaviour
Financial literacy is knowledge and understanding of
financial concepts and risks as well as the skills,
motivation, confidence to apply such knowledge and
understanding to make effective decisions in the
financial context, improving financial well-being,
both individual and community welfare (OECD,
2016: 87). Financial literacy can also be defined as a
combination of awareness, knowledge, skills,
attitudes, and behaviours needed to create financial
awareness and ultimately achieve individual welfare
(OECD, 2011).
Houston (2010: 306-307) explains that financial
literacy shows how well an individual can
understand and use information related to finance.
Financial literacy can also lead to components of
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
180

resources that can be used in financial activities to
improve the quality of life expected from
consumption, such as behaviours that can improve
financial welfare.
According to Braunstein and Welsch (2002: 445-
447), several factors that cause financial literacy
between individuals include 1) technological
changes, 2) increasing debt problems, and 3)
changes in individual finances. According to
Michaud (2017), financial literacy is associated with
better future planning related to the rate of return
from higher deposits, as well as debt with low-
interest rates. For workers, low financial literacy
results in increased financial bankruptcy due to the
high frequency of absences and low productivity.
Also, workers who have financial literacy skills will
better understand the company's financial condition,
especially in times of crisis, which allows workers to
be able to make profitable deals for the parties
involved.
Several studies on the effect of financial literacy
on financial management behaviour, among others,
were conducted by Klapper, Lusardi, and Panos
(2012), Murithi (2012), Stromback, et al. (2017),
and Weningsih (2018). Financial literacy becomes
the main focus of financial education and supports
the creation of awareness about the importance of
welfare in life. Inadequate financial literacy will
affect one's financial decision making. If someone's
financial literacy is high, then someone will have
good behaviour in financial decision making.
Research Murithi (2012) found that understanding
financial literacy has a better effect when something
similar is offered to an individual in a group.
Klapper et al. (2012) proved the influence of
financial literacy on financial behaviour by looking
at the positive influence of financial literacy on the
use of formal services in the financial sector. The
higher the level of financial literacy, the higher the
capacity of deposits, and the lower the amount of
expenditure during a financial crisis. This research
shows that financial literacy can make an individual
face the conditions of economic change through
savings and become a wise person in financial
management.
H1: Financial literacy has a positive effect on
financial management behaviour
2.3 Self-control and Financial
Management Behaviour
Self-control is the ability to control someone to
organize, maintain and direct behaviour that directs
someone to give positive consequences. The ability
to control oneself is related to one's ability to control
emotions and encourage others (Weningsih, 2018).
Self-control is the level at which a person makes
consistent choices (Sutter, et.al, 2013). Self-control
is a non-cognitive skill that is important in
individual decision making, such as consumption
and savings.
According to Schultz and Schultz (2013: 317),
self-control is the ability of a person to exercise
control and manage behaviour with full
consideration before doing something. Self-control
can be influenced by internal factors (such as age,
emotional control, psychological well-being, and
how religious a person is), and external factors (such
as family environment, and peers).
Mischel (2014) states that self-control can be
related to financial literacy, where someone who has
the knowledge and financial literacy abilities will be
able to control themselves in financial management.
Dikria and Mintarti's research (2016) proves that
financial literacy has a positive influence on self-
control. Someone who has the knowledge and skills
about financial literacy combined with self-control
will be more selective in spending. Someone with
high financial literacy will be better able to predict
an event, so they will be more careful in controlling
their finances and making decisions.
H2: Financial literacy has a positive effect on
financial management behaviour with self-control as
an intervening variable.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This study is a quantitative study that aims to
examine the effect of financial literacy on financial
management behaviour with self-control as an
intervening variable. This research was conducted
on the management of the Village Owned
Enterprises (BUM Des) in Sleman Regency, with 54
respondents. Data collection was carried out by
distributing questionnaires consisting of 28 question
items representing 3 variables, consisting of 15
question items for financial literacy variables, 7
question items for self-control variables, and 6
question items for financial management behaviour
variables.
The data used in this study are financial literacy
(independent variable), financial management
behaviour (dependent variable), and self-control
(intervening variable).
The Effect of Financial Literacy on Financial Management Behaviour with Self-control as Intervening Variable
181
3.1 Financial Literacy
Financial literacy is defined as the knowledge, skills,
and attitudes that influence behaviour in improving
the quality of decision making and financial
management to prosper. Financial literacy is
measured using indicators: 1) money management,
2) financial planning, 3) financial well-being, and 4)
financial knowledge (Australian Unity Financial
Wellbeing Questionnaire - design and validation)
3.2 Financial Management Behaviour
Financial behaviour is a study that studies how
psychological phenomena affect financial behaviour.
Financial behaviour measured using indicators: 1)
consumption; 2) debt management; 3) money
management; 4) savings and investment (Strömbäck
et. Al, 2017)
3.3 Self-control
Self-control is related to better financial
management and involves one's ability to resist
desires or impulses to spend excessively. Self-
control is measured using indicators 1) stopping bad
habits; 2) resist temptation; 3) maintain self-
discipline; 4) focus on short-term goals; and 5)
laziness (Strömbäck et. Al, 2017)
The data collected will be tested using the
regression analysis to testing the influence of
financial literacy on financial management
behaviour and from the results obtained later
conclusions will be drawn. To test the direct and
indirect effect of financial literacy toward financial
management behaviour trough self-control, the path
analysis was conducted. Path analysis is the part of
the regression analysis used to analyze the
relationship between dependent variable with
independent variable directly or indirectly through
one or more intermediaries. The path calculation
describes the influence of Financial Literacy (X)
directly and indirectly to Financial Management
Behaviour (Y2) through Self-Control (Y1).
The structural equation used is as follows:
Y1 = β1X+ε1 ………………… sub structural (1)
Y2 = β1X +β2Y1 + ε2 …. …...sub structural (2)
4 RESEARCH RESULTS
4.1 Descriptive Statistics
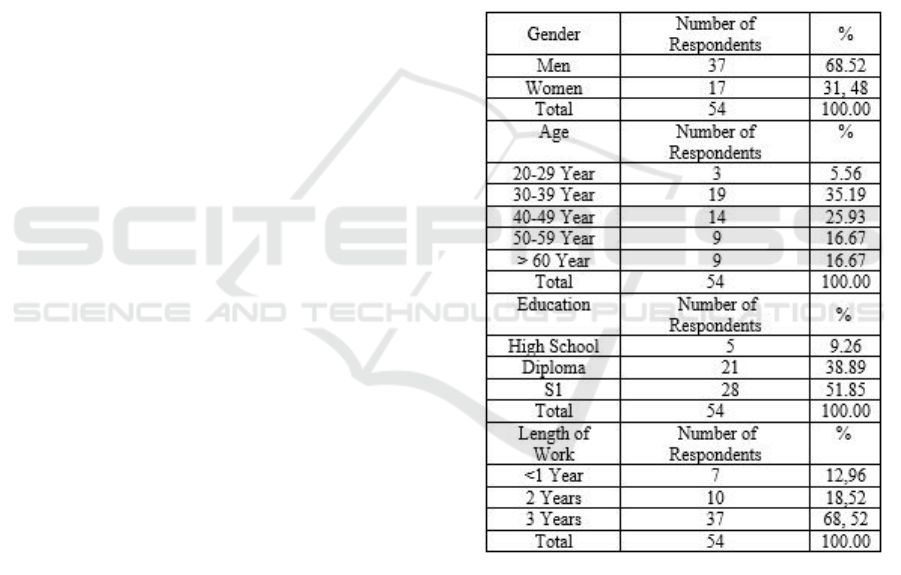
Table 1 below shows descriptive statistics from
research respondents. 68.52% of respondents were
male while the rest were female. The majority of
respondents aged between 30 and 39 years. 9.26% of
respondents had the last high school education,
38.89% had a Diploma education, and the remaining
51.85% had a Bachelor's degree. 68.52% of
respondents have taken care of BUM Des for 3
years, 18.52% have worked for 2 years, and the rest
work for less than 1 year.
Table 1. Characteristics of respondent
4.2 Test Results
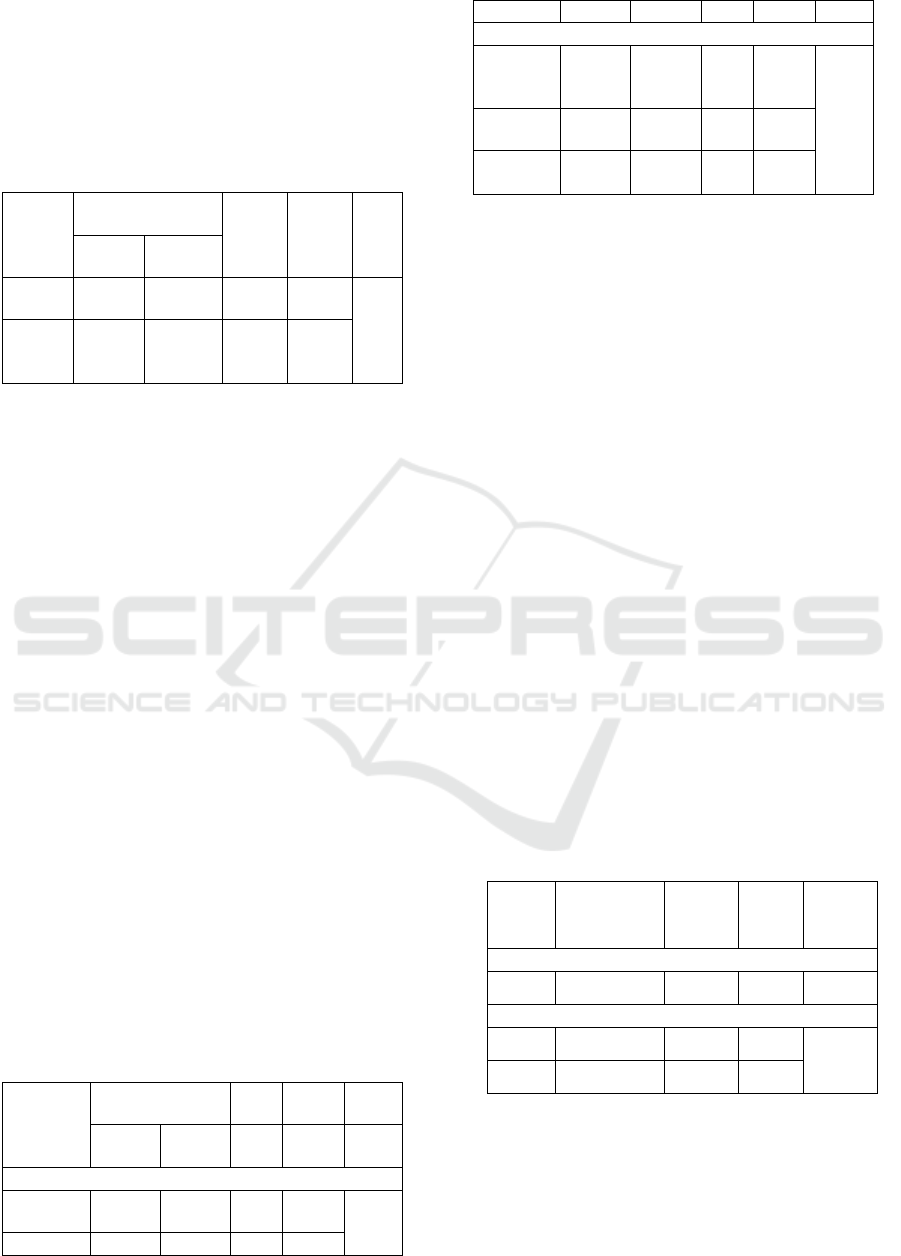
Testing the effect of financial literacy on financial
management behaviour, presented in table 2, shows
that financial literacy has a positive effect on
financial management behaviour as indicated by a
regression coefficient of 0.840 and a significance of
0,000 less than 0.05. These results prove that the
higher the financial literacy of the BUM Des
management, the better their behaviour in managing
village finances.
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
182
Good understanding and sufficient knowledge
along with the expertise possessed in terms of
savings, loans, and investments will make an
individual wiser in making financial decisions to
achieve goals in the future.
Table 2. Testing the influence of financial literacy on
financial management behaviour
Model Unstandardized
Coefficient
t. Sig
R
2
B Std
Error
Const
ant
0,59
5
7,771
1,70
7
,000
0,73
9
X
0,84
0
4,374
9,63
5
,000
Financial problems often occur because of errors
in financial management such as making wrong
decisions in spending that tends to cause someone to
be more consumptive. Lusardi and Mitchell (2017)
state that the lack of understanding of products and
mechanisms in the financial markets, as part of
financial literacy, results in suboptimal decision
making related to investment. In this case, financial
literacy is associated with an inability to make
decisions regarding managing deposits (savings),
low participation in financial markets (van Rooj,
Lusardi, and Alessie, 2011) and low ability to
diversify in portfolios (Guiso and Jappelli, 2009).
Regarding loans (credit), someone with a low
level of financial literacy tends to decide to take
loans at a higher cost. A person who uses credit to
finance expenses often experiences excess loans
because of excessive spending activities, such as
spending on clothing purchases, electronic
equipment, vehicles, and recreational activities
funded by loans (Lucks, K., 2016). Therefore,
someone with the right level of financial literacy
tends to be more rational in spending and will be
better at managing their finances. Based on the
results, the first hypothesis (H1) is acceptable, that
financial literacy has a positive effect on financial
management behaviour.
Table 3. Summary of the Regression Analysis
Model Unstandardize
d Coefficient
t. Sig R2
B Std
Error
Sub structural X Y1
Constant 1,265 ,338
3,7
49
,000
0,537
XY1
,657 ,085 7,7
,000
71
Sub structural X Y1 Y2
Constant
-,087 ,338
-
,25
8
,79
7
0,72
9
XY2
,486 ,110
4,4
05
,00
0
Y1
Y2
,539 ,123
4,3
74
,00
0
Table 3 shows the result of regression analysis
on the effect of financial literacy on financial
management behavior with self-control as an
intervening variable. On the influence of financial
literacy on self-control, the result shows that the
regression coefficient of financial literacy variables
of 0.657, significant at 0,000. It shows that there is a
positive influence on financial literacy on self-
control. The higher a person's financial literacy, the
better someone will be in self-control related to
financial activities carried out. Self-control is the
ability of a person to exercise control and manage
his behavior before deciding to do something.
Someone with good financial literacy will be able to
control himself and will be more careful in using his
money and have various considerations before
taking an action
The results of testing the effect of financial
literacy on financial management behavior with self-
control variables as intervening variables in table 3
show the regression coefficient of financial literacy
variables of 0.486 and self-control regression
coefficient of 0.539, both significant at 0,000. This
shows that financial literacy has a positive effect on
financial management behavior with self-control as
an intervening variable.
Table 4. Summary of the Path Analysis
Model
Path
Coefficie
nt
T Sig.
R2
Sub structural 1 (X Y2 )
X
0,463 4,405 ,000
0,537
Sub structural2 (X Y1 Y2 )
X
0,733 7,771 ,000
0,739
Y1
0,460 4,374 ,000
The result of path analysis in Table 4 shows that
the path coefficients of variables financial literacy is
0.733, and the path coefficient for self-control is
0.460, and significant at 0.000. This shows that there
is an indirect effect of financial literacy on financial
management behaviour through self-control. The
indirect effect of financial literacy on financial
The Effect of Financial Literacy on Financial Management Behaviour with Self-control as Intervening Variable
183
management behaviour is (0.733) x (0.460) =
0.33719. While the direct effect of financial literacy
on financial management behaviour is 0.463,
significant at 0.000. Thus, it can be concluded that
the direct effect of financial literacy on financial
management behaviour is greater than the effect of
financial literacy on financial management
behaviour through self-control variables. The effect
between variables is presented in the following
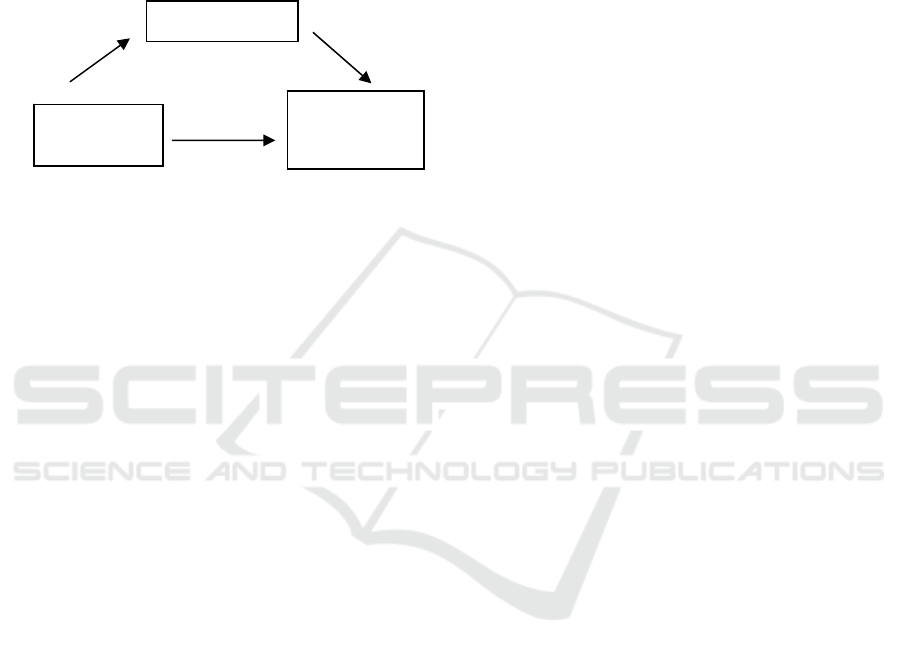
figure 1
0,733 0,460
0,463
Figure 1. Effect of Financial Literacy on Financial
Management Behaviour with Self-Control as an
intervening variable
The result of this study is consistent with the
study of Weningsih (2018) and Ramalho and Forte
(2018). Ramalho and Forte (2018) show the positive
influence of financial knowledge as part of financial
literacy on self-control, and the positive influence of
financial knowledge on the behavior of financial
management, both directly and through self-control.
Weningsih (2018) shows that financial literacy hurts
consumptive behaviour with self-control as
intervening variable. Financial literacy combined
with self-control will make more selective
consumption pattern. Financial literacy,
accompanied by good self-control will lead to good
financial management behaviour. Some person who
has good self-control will be more careful in
managing his finance and will try to be an intelligent
person in carrying out various financial activities.
Based on the results, the second hypothesis (H2)
is acceptable, that financial literacy has a positive
effect on financial management behaviour through
self-control as intervening variables.
5 DISCUSSION
The results indicate a positive influence of financial
literacy on the financial management behaviour of
the village caretaker-owned business (BUM Des)
entities village in Sleman district. This shows that
financial literacy in the management of the BUM
Des in Sleman Regency in terms of village financial
management shows good results. Administrators can
plan and manage village finances well, such as
managing funds to pay debts, have financial
planning for things in the future, and unforeseen
needs, and have sufficient basic financial
knowledge. So it can be concluded that the
management of the BUM Des in Sleman Regency
has good financial literacy and the financial
behaviour of the management in financial planning
and managing the business unit's finances has been
done appropriately and adequately.
Indirectly, self-control as an intervening variable
influences the relationship of financial literacy to
financial management behaviour. This indirect effect
shows that the higher the financial literacy of the
BUM Des management, the better the self-control of
the management in spending or consumption based
on needs that are planned, and not based on
conditions for a moment, as well as the ability of the
board to think for goals long-term. This will
significantly affect the management in making
financial decisions in achieving public welfare. The
management's knowledge, skills, and confidence in
financial planning and management, combined with
self-control related to financial expenditure, will
greatly influence the behavior of financial
management regarding decision making in the use of
village finances. This will significantly support the
achievement of the objectives of village fund
granting, namely improving the village economy and
achieving the welfare of the village community.
6 CONCLUSION
Financial literacy can be defined as a person's
ability, understanding, and skills to manage their
finances to reduce management errors in making
financial decisions for welfare purposes. This
financial literacy is related to general financial
knowledge about deposits and loans, investment,
and security guarantees. Good financial literacy will
greatly affect the behaviour of financial
management, both in terms of planning, controlling,
and making financial decisions. The high financial
literacy will affect self-control. The higher the
financial literation, the better one's self-control will
be in carrying out financial management. Self-
control is often associated with one's ability to
control and manage behaviour before making a
decision. In terms of financial management, self-
control is an activity that drives a person to make
savings by reducing impulsive purchases (Otto,
Davies &Charter, 2004). Someone with good
Self-Control
Financial
Literacy
Financial
Management
Behaviou
r
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
184

financial literacy, combined with self-control ability,
will produce good management behavior. Good
financial management will be crucial for the
achievement of the long-term goals of the formation
of a Village-Owned Enterprise that is improving the
village economy and achieving the welfare of the
community.
REFERENCES
Braunstein, S., Welsch, C., 2002, Financial Literacy: An
Overview of Practice, Research, and Policy, Federal
Reserve Bulletin, pp 445-447
Brown, M., Henchoz, C., Spycher, T., 2016, Culture,
Financial Literacy, and Self Control
Christian, RP, Komalasari, F., Hadiansah, I., 2016, The
Effect of Financial Literacy and Attitude on Financial
Management Behavior and Satisfaction, International
Journal of Administrative Science & Organization,
September 2016, Volume 23, Number 3
Deacon, R.E., Firebaugh, F.M., 1988 Family Resources
Management; Principles and Applications, Toronto:
Allyn & Bacon
Dowling, N.A., Corney, T., Hoiles, L., 2009, Financial
Management Practices and Money Attitudes as
Determinants of Financial Problems and
Dissatisfaction in Young Male Australian Workers,
Journal of Financial Conceling and Planning, 20(2): 5-
13
Dikria, Okky , and Mintarti, 2016, Pengaruh Literasi
Keuangan dan Pengendalian Diri terhadap Perilaku
Konsumtif Mahasiswa Jurusan Ekonomi
Pembangunan Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Negeri
Malang angkatan 2013, Jurnal Pendidikan Ekonomi,
9(2), pp 143-155
Guiso,L., A.T., Jappelli., 2009, Financial Literacy and
Portofolio Diversification, Working Paper
Houston, S.,J., 2010, Measuring Financial Literacy, The
Journal of Consumer Affairs, 44(2),pp 296-316
Kahneman, D., and Krueger, AB, 2010, Of subjective
well-being, 20 (1): 3-24
Kebede, M., Klauer, N., and Kumar, J., 2015, Financial
Literacy and Management of Personal Finance: A
Review of Recent Literature, Journal of Finance and
Accounting www.iiste.org, Vol.6, No.13, 2015
Klapper, LF, Lusardi, A. &Panos, GA (2012): "Financial
Literacy and The Financial Crisis," National Bureau of
Economic Research (NBER) WORKING PAPER
SERIES, Working Paper 17930, [online], at
www.nber.org/papers/w17930 [accessed on February
5, 2015
Letkiewitz, J., C., 2012, Self Control, Fiancial Literacy
and Financial Behavior of Young Adults, Disertation,
Graduation Program on Human Ecology, The Ohio
StateUniversity
Lucks, K.E., 2016, The Impact of Self Control on
Investment Decisions, MPRA Papers, No. 73099
online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/73099
Lusardi, A. and Mitchell, O., 2011," Financial Literacy
Around the World: An Overview ", Discussion Paper
02 / 2011-023, Netspar Discussion Papers
Mischel,W., 2014, The Marsmallow Test: Mastering Self-
Control(4ed), New York:Little Brown and Company
Morgan, P.J., and Trinh,L.Q., 2019, Determinants and
Impacts of Financial Literacy in The Lao PDR, Asian
Development Bank Institute, ADBI Working Paper
928
M. Rizky, D.,P., Nadia, A., 2018, Analysis Factorss
Influencing Financial Management Behavior,
International Journal of Academic Research in
Busines and Social Sciences, Vol 8, No.8, August
2018, pp 308-326
Nguyen, M.,T., Thao, P.,T., 2015, Factor Affecting
Personal Financial Management Behaviors: Evidence
fro Vietnam, Proceedings of the Second Asia-Pacific
Conference on Global Business, Economics, Finance,
and Social Sciences (API5Vietnam Conference,
Danang-Vietnam, 10-12 July
OECD. (2013) "OECD / INFE Toolkit for Measuring
Financial Literacy and Financial Inclusion: Guidance,
Core Questionnaire, and Supplementary Questions
Organization for Economic Co-operative and
Development (OECD), 2016, International Network
on Financial Education (INFE), International Survey
of Adult Financial Literacy Competencies, Paris,
available at: www.oecd-International-Survey-of-
Adult-Financial-Literacy-Competencies.pdf (accessed
18 March 2017)
Parrotta, JL, & Johnson, PJ, 1998, The Impact of Financial
Attitudes and Knowledge on Financial Management
and Satisfaction of Recently Married Individuals.
Financial Counseling and Planning, Vol. 9, No. 2. PP.
59-75.
Ramalho, T.B., and Forte, D., 2019, Financial Literacy in
Brazil-Do Knowledge and Se;f-Confidence Relate
With Behavior?, RAUSP Management Journal,
Vol.54, No.1, pp 77-95
Remund, D.I., 2010, Financial Literacy Explicated: The
Case for a Clearer Definition in an Increasingly
Complex Economy, Journal of Consumer Affairs,
Vol.44, No.2, pp 276-296
Robb, CA, & Woodyard, USA, 2011, Financial
Knowledge and Best Practice Behavior. Journal of
Financial Counseling and Planning, Volume22 Issue 1
of the
Stromback, C., Lind, T., Skageruld, K., Västjäll, Tinghog,
G., 2017, Does Self-Confidence Predict Financial
Behavior and Financial Well-Being? Jounal of
Behavioral and Experimental Finance, 14,pp 30-38
Sutter, M., ngerer,S., Glaetzee-Ruetzler, D.R., Trautmant,
S.T., 2013, Impatience and Uncertainty: Experimental
Decisions Predict Adolescents’Field Behaviour, The
American Economic Review, 103(1), pp.510-531
Weningsih, R.T., 2018, The Effect of Financial Literacy
on Consumptive Behavior with Self-Controls as
Intervening Variables, Undergraduate Thesis,
University Yogyakarta State
The Effect of Financial Literacy on Financial Management Behaviour with Self-control as Intervening Variable
185

Younas, W., et.al, 2019, Impact of Self Control, Financial
Literacy and Financial Behavior on Kiyosaki, RT,
2012, Financial Well-Being, The Journal of Social
Sciences Research, Vol. 5, Issue 1, pp: 221-218,
RichDad Poor Dad.
Available:http://www.csce001.com/edit_zoop/uploadfi
le/system/20150408/20150408135909188.pdf
Van Rooij,M., Lusardi., A., and K. Alessie, 2011,
Financial Literacy, Retirement Planning, and
Household Wealth, Economic journal, 122, pp 449-
478
ICBEEM 2019 - International Conference on Business, Economy, Entrepreneurship and Management
186
