
Social Media Features for Improving Organization Business
Performance: A Systematic Literature Review
Karina Nine Amalia
1
and Mahendrawathi
1
1
Information System Department, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords:
Business Performance, Efecttiveness, Feature, Social Media
Abstract:
Social media is a platform to share information that is used by most people today. Business organization must
use social media strategies to gain benefit from it. Knowledge of the features and impact of social media
usage are needed. This systematic literature review aims to identify social media features that affect business
performance. The literature is obtained through searching in two relevant database. The papers are evaluated
by reading in its entirety and evaluating its quality. Features on social media can affect business performance.
The impact of using social media on business organizations includes Word of Mouth, good communication
with customers, consideration and influence on social media. Business organizations must take advantage
of two-way communication to respond and communicate with consumers to find out how certain brands are
perceived in order to obtain full benefits. Social media can also improve business performance by increasing
sales, fostering partnerships
1 INTRODUCTION
Social media is a manifestation of Web 2.0. The
use of web 2.0 provides tools that can facilitate inter-
net users and create social networks using collabora-
tive computer media (Warner-Søderholm et al., 2018).
Social media is a gathering place for consumers.
Therefore, social media is one of the consumer in-
formation warehouses that are used as a means of dis-
seminating information in buying and selling activi-
ties (Shi et al., 2016). The ease of interaction that ex-
ists on social media makes organizations build social
media to improve their social networks. Social media
is used to build relationships with consumers. Social
media developed into a communication tool for orga-
nizations both to communicate with consumers and
with other organizations (He et al., 2015). In recent
years, more than 50% of social media users have be-
come followers of a business organization on social
media (Kim and Chae, 2018), which motivate busi-
ness organizations to increase their investment in so-
cial media. This is shown by international marketing
spending on social media that reach $ 4.3 billion (Ku-
cukaltan et al., 2016).
The ability to interpret the needs and desires of
consumers obtained from data on social media is very
necessary for business organizations. Processing data
obtained to get a decision is a challenge for busi-
ness organizations because until now there are no best
practices to measure the success of the use of social
media with certainty (Suryakumar, 2011).
Business organizations and customers will have
twoway communication during the transaction pro-
cess. In this case social media provides facilities for
business organizations and customers to interact eas-
ily.The use of the latest social media technology in
business organizations makes these business organi-
zations superior to their competitors. The use of so-
cial media for business organizations also has benefits
such as increased efficiency and lower costs (Agwu
and Murray, 2015).
The use of social media has certainly changed the
way business is done. The existence of social me-
dia will open up the possibility of open communica-
tion. This can help business organizations to know
customer needs. Business organizations will certainly
be motivated to actively respond to the needs and even
customer complaints. Social media will also create
many new innovations in business organizations. This
is driven by good communication with customers, in-
put opinions from customers and the presence of feed-
back (Richard et al., 2009). However, business orga-
nizations that use social media must also be willing to
take risks and invest in the latest products and services
to satisfy customers, enhance brand image so they can
have feedback from customers. Therefore, business
Amalia, K. and Mahendrawathi, .
Social Media Features for Improving Organization Business Performance: A Systematic Literature Review.
DOI: 10.5220/0009906501130122
In Proceedings of the International Conferences on Information System and Technology (CONRIST 2019), pages 113-122
ISBN: 978-989-758-453-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
113

organizations need to conduct studies for learning de-
cisions using social media.
Understanding the use of social media and the use
of features that improve business performance is now
considered very important. In order for a business
organization to survive, the organization must imple-
ment more effective measures in the use of social me-
dia in terms of profit, income, and customer feedback
that are used as a reference for success using social
media.
Social media has a big role to play in business
success. One of the other criteria in maximizing the
use of social media features is Customer Relationship
Management (Ali, 2017). This can also identify the
most profitable customers to build better relationships
for the success of business organizations (Matuszak,
2007). Previous research has discussed and studied
the cultural influence or orientation of entrepreneur-
ship from various aspects of technology and stud-
ied organizational performance (Boshoff and Elliot,
2005). However, the effect of social media on im-
proving business organizations, especially those that
discuss specific social media features, is rarely inves-
tigated. Social media features for enhancing the per-
formance of business organizations such as hashtag
features, sharing on various platforms, comments col-
umn etc.
Based on these facts, it is very important to con-
duct a systematic literature review to understand the
features available on social media that can improve
the performance of business organizations. System-
atic literature review is efficient methods to provide
synthesis results in the form of appropriate and up-
to-date information. Systematic literature reviews are
also useful for understand and utilize strategies that
reduce the bias a maximize accuracy (Zaremohzza-
bieh et al., 2014). In the following systematic liter-
ature review, we try to synthesize related features in
social media to improve the performance of business
organizations. The questions examined in this study
are:
RQ1: What are the features that affect business
performance in using social media?
RQ2: What is the impact of the use of social media
in improving the performance of business organiza-
tions?
RQ3: How can social media increase the effective-
ness of business performance?
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Social Media
Social media emerged when Web 2.0 technology
where social media refers to the online platform used
by people to share experiences and opinions includ-
ing their respective perceptions, insights, music, pho-
tos and videos (Lai and Turban, 2008). Whereas Ka-
plan & Haenlin defines that social media is an applica-
tion group based on ideological foundations and web
2.0 technology that enables the creation and exchange
of information by users. Social media is a means or
channel for communicating online in cyberspace. So-
cial media is intended as a site used by individuals to
socialize by meeting old and new friends to be able
to interact with each other. The case with internet so-
cial media certainly has commercial value which is
certainly a concern of business managers. Social me-
dia is also a friend of business organizations with its
presence on the internet (Bacon, 2011).
2.2 Development Feature Social Media
Each social media has different features according to
the purpose of the social media. now in the era of
Web 2.0 is very different from web 1.0 where previ-
ously on web 1.0 only supported the creation of con-
tent to support the products of a business organization.
But in the Web 2.0 era related important elements are
interaction, consumer participation and social skills
(Singh et al., 2008). In all applications the category
Web 2.0 users are the most basic elements, not only
being consumers but users can also contribute with
content. This change also affects the features avail-
able on social media today (Constantinides and Foun-
tain, 2008). The ease of accessing the internet pro-
vides the ease for users to create content. Various
ways that can be done by users through social me-
dia features such as videos, music, photos etc. In web
2.0 this will produce greater energy and can improve
organizational performance. (Elkin-Koren, 2010)
2.3 Organizational Performance
Measurement is very important in special organiza-
tions business organizations. According to Deming
without the presence of measurements improvement
change cannot be measured. Organizational perfor-
mance that draws attention to both organizations that
achieve market-oriented goals and financial goals (Li
et al., 2006). Another thing in multidimensional or-
ganizational performance is different from its defini-
tion. In organizational performance, there are sev-
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
114
eral elements that correlate such as financial results,
customer satisfaction, financial efficiency and ability
to compete. Measurement of organizational perfor-
mance must be expanded into 4 elements (Lee and
Cavusgil, 2006)
3 METHODS
This study uses the Systematic Literature Review
(SLR) method to gain comprehensive insight and find
the trigger factors and inhibitors that have been pro-
duced by previous researchers. A systematic review
was undertaken using six steps guidelines for con-
ducting a systematic literature review in management
(Durach et al., 2017). First, we start by defining the
research question. The required characteristic of the
study is determined based on the research question.
This is followed by retrieving potentially relevant lit-
erature and selecting pertinent literature. Relevant in-
formation from the literature are synthesised and re-
ported.
A literature search is done using two
database sources, namely: 1) Science Direct
(http://www.sciencedirect.com/); 2) Emerald Insight
(http://emeraldinsight.com/). Both databases are used
to search for the same keywords, but extraction is
done differently because each database has a different
search method. In Science direct, it is more flexible
because users can freely type keywords according
to the prescribed coding rules. Science Direct can
also search more than one part simultaneously,
for example, it can combine titles, abstracts, and
keywords. On the other hand, in searching through
the Emerald Insight database, searches can only be
done on one part and cannot be done simultaneously,
such as titles, abstracts, or keywords.
The process of selecting literature is carried out
through the following stages. The first process is
looking for a paper in the relevant database based on
the suitability of the keywords with the title, or ac-
cording to the conditions specified in the plan. Second
step is construction of search keywords using search
terms with Boolean data types AND and OR. Next,
papers that does not meet inclusion criteria and fulfill
exclusion criteria are eliminated. Next step read ab-
stracts from each paper whose title matches and dis-
seminates it based on its abstract relevance. The pa-
pers are evaluated further by reading in its entirety
and evaluating its quality. The last step is choose the
paper that passes the evaluation stage.
The search stage is done by using certain key-
words based on one particular part, such as a title,
abstract, or keyword in the journal. Determination
of keywords must represent the statements contained
in the Research Question. Based on the Research
Question, there are keywords, namely: Social Media,
Feature, Organizational Performance, Business Per-
formance. Searching the literature in the database is
done with the following keywords:
1. In each database, journal searches are carried out
using keywords: (Social Media) AND (Feature)
AND (Organizational Performance) AND (Busi-
ness).
2. Expert search is then used by considering the
keyword contained in the title, abstract and also
keywords: (Social Media) AND (Feature) AND
(Organizational Performance) OR (Social Media)
AND (Feature) AND (Business Performance)
From the selection of literature in accordance
with the inclusion and exclusion criteria above, there
were 183 papers obtained from the Science Direct
database, and after the third step, 40 papers were se-
lected to be studied further. In the Emerald database,
107 papers were obtained, and after the third step, 30
papers were selected to be studied further. 91 papers
were produced from the step relevant to the object of
the study. The next step was to assess each of the liter-
ature. This section is intended to make an election for
a paper that will be reviewed by limiting paper candi-
dates, namely by focusing on journals ranked based
on Q1-Q3 and published from 2015 to the present
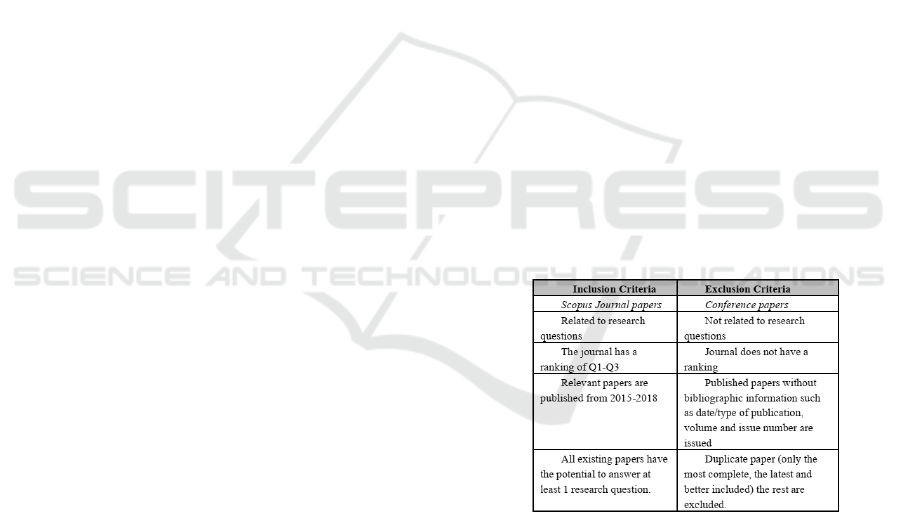
(Figure 1).
Figure 1: INCLUSION AND EXCLUSION CRITERIA.
3.1 Quality Assesment of Selected
Studies
Q uality assessment from selected studies is done by
doing a weighing scale in the selected library using
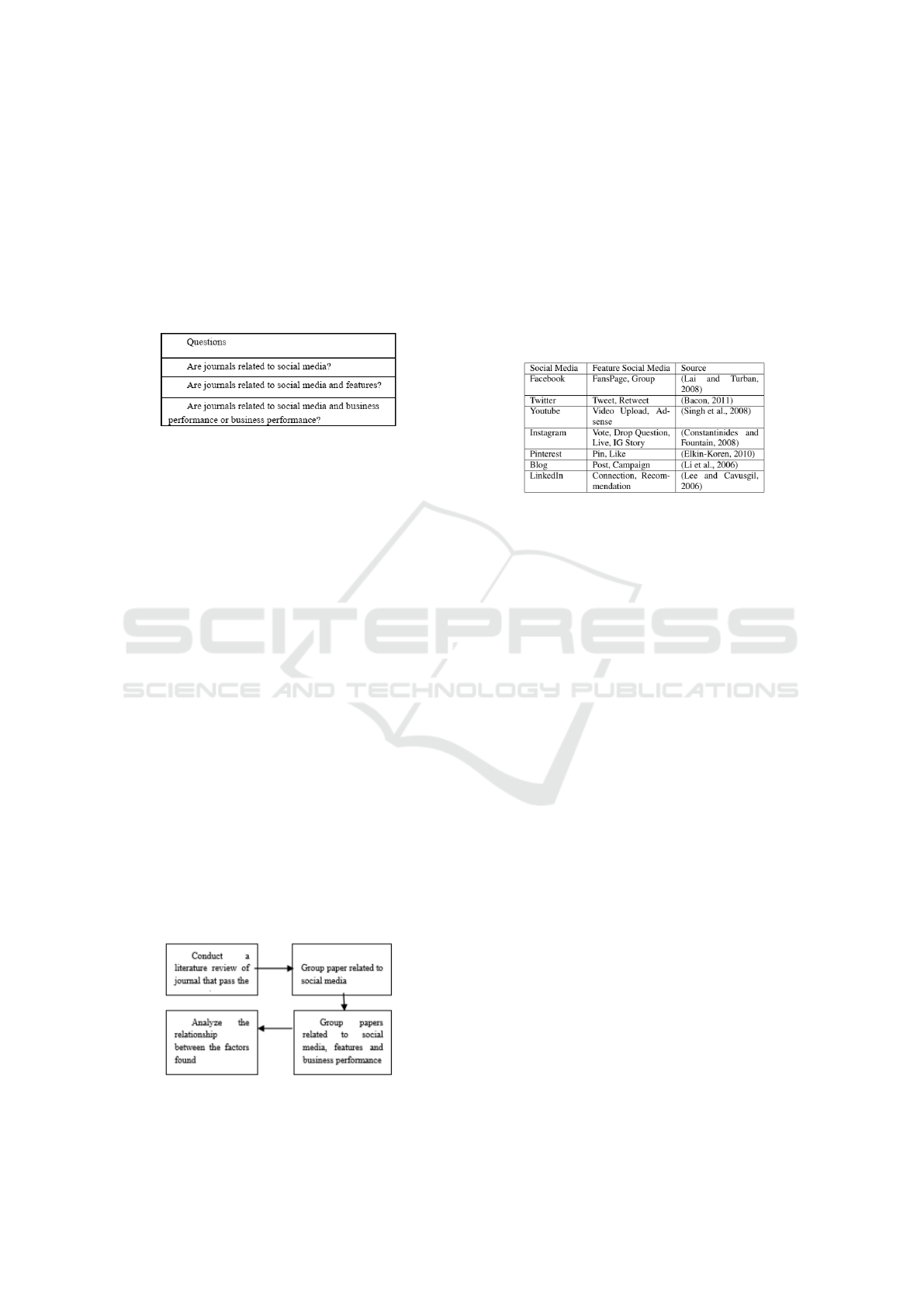
a series of questions. There are three questions as a
reference in determining the quality of the selected
library. Questions are explained in Table 3. The
method of weighting is done by giving a score to each
question, namely ”Yes” = 1 if the answer to the ques-
tion is contained in the selected library, ”Half” = 0.5
Social Media Features for Improving Organization Business Performance: A Systematic Literature Review
115
if the answer to the question is partially or incomplete
in the library selected, or ”No” = 0 ”if the answer to
the question is not contained in the selected library.
Then, the score will be summed, and the final value
in each library will determine the library as a refer-
ence or not on the review that will be carried out. The
list of questions can be seen in table 2 while for the
scores of each question in the libraries tested and se-
lected is described in Figure 2.
Figure 2: The Sample Measurement of Three Tourist Des-
tination.
From a series of analysts conducted, 91 papers
consisting of 66 libraries were not included in the
study and left 25 papers as a reference for review. For
the scores of each question in the libraries tested and
selected are explained in Table 3. Of the 91 papers
analyzed, 25 papers were selected, in this paper the
literature with a test score of at least a score of 2 was
chosen.
3.2 Synthesis
The stages of synthesis are intended to answer the for-
mulation of the problem that has been proposed. The
first step taken at the synthesis stage is to conduct a
review literature on journals that pass the assessment
stage, then make a list of related paper groups regard-
ing social media features that influence business per-
formance. Next, make a list of groups of papers re-
lated to social media and features and make a list of
papers relating to social media and business perfor-
mance or business performance. The stages of syn-
thesis can be seen in Figure 3
Figure 3: Synthesis Steps Flow
4 RESULT
4.1 Social Media Feature Affecting
Business Organization Performance
The first research question is answered by perusing
literature relaed to social media features. Social me-
dia that affect business performance in social media
include Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Instagram, Pin-
terest, Blog, LinkedIn. Features on social media are
presented in Figure 4.
Figure 4: The Sample Measurement of Three Tourist Des-
tination.
In recent years Facebook has begun to associate
itself with a combination of organizational promo-
tions. Due to its popularity, this can be used to in-
fluence consumers. Although the increase in social
media-based Facebook ads on Facebook pages gives
a sign that it will be the primary source of business
marketing on the future of the Internet. According to
(Zaremohzzabieh et al., 2014) ”Facebook is an effec-
tive source for marketing products in a personal way.
According to (Smith et al., 2011) ”Facebook now pro-
vides a variety of ways for online retailers to offer a
more ’social’ buying experience, either by integrating
Facebook features into their own sites or by operat-
ing on Facebook themselves” (Lai and Turban, 2008)
said that ”A Facebook storefront gives marketers ad-
ditional outlets to facilitate promotions and sales op-
portunities and provide synergistic relationships be-
tween consumers and retailers.
Facebook has allowed marketers to customize ad-
vertisements for a particular group of people. Mar-
keters target these individuals on the basis of demo-
graphic information and shared interests. Facebook
has made it possible to reach people who are aimed
at cost-effective and attractive ways than traditional
marketing channels. Today business organizations are
looking for channels, where they can promote their
brands at the lowest and highest possible cost. Face-
book seems to be a partner that fits this need. How-
ever, Facebook doesn’t have a sustainable model for
business because it has a large user base. There are
three different ways of promotion used by brands
through Facebook: i) brand pages, ii) branded appli-
cations, and iii) advertisements.
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
116

In addition, the feature on social media Twitter al-
lows the organization to validate the brands in indi-
vidual level. The utilization of something can be clar-
ified into a short message which may be read by the
readers called tweet. These messages appear on the
time line of the followers. The message can contain
a site link. This site link gives the followers opportu-
nities to spend more time to interact with the online
stuffs. This interaction develops the connection and
loyal communication between the users and the brand
(Triantafillidou and Siomkos, 2018).
Another popular social media is YouTube. In
2005, Jawed Karim introduced YouTube. It has part-
ner features that provide videos of creators which can
be an opportunity to earn money. Small retailers also
have significant opportunities to promote their brands
through a YouTube channel. Various successful small
retailers inserted by YouTube in their main strategy
and introduce their products and services for their au-
diences. There are many ways including webinar,
video and such, to show their products through this
media (Vanessa, 2012).
YouTube is one of the most notable social soft-
ware that is most popular for amateur videos. How-
ever, big corporations also make videos to be pro-
duced commercially covering product review and
commercial. Commercial videos are proliferating to-
day, mainly due to YouTube and this kind of sites.
”Good brands are successfully using YouTube as a
way to gain the customers’ attention and repeat their
brand identities. By thinking out of the box in post-
ing common commercial items and by making pieces
that are established in brand switching, organizations
can influence the substance to assimilate the users that
are more profound and more convincing (Shiau et al.,
2018).
Nowadays, social media that is always visited by
society in the world and has high opportunity to in-
crease the effectivity of business organizations is In-
stagram. One of the features existed is vote feature of
snap-gram on Instagram. It is one of the phase pat-
terns in the model process by adopting social tech-
nology from the main principle that is to build an en-
vironment where the participants can add the values
through interactions (Kucukaltan et al., 2016).
Pinterest is a social media which is also popular
today. Since it was launched, it becomes the third
most popular social media after Facebook and Twitter
(Bata et al., 2018) . Since it was launched in 2009,
Pinterest has become one of the digital platforms that
grew rapidly. The users like its visual layouts that are
curated boards and intuitive mobile applications. The
marketing potential is good, as people commonly use
it to find the new project or product (Mahendrawati,
2018).
Marketing by using a blog is an important tool due
to its specific characteristics. Blog facilitates commu-
nication and plays an active factor which creates and
promotes specific identity to the virtual World Wide
Web directly and has a direct implication for the fi-
nancial economic aspect and social reality (Prodanova
and Van Looy, 2017).
Social media that makes identity as the primary
function is LinkedIn. This social media is claimed
as the tool that is beneficial for the marketer to ”rent
and sell the market.” It facilitate the marketer to reach
the professional group to be a partner, employee or
client in the closing time. This helps the users to
communicate and involve with other people to share
precious information that can produce offline action
in the communication. (Cook, 2008) explains that
specific consumers of LinkedIn group communities
and the users’ login in the LinkedIn group focuses on
the business as well as the common interest. (Kiet-
zmann and Canhoto, 2013) says about LinkedIn and
states that he provides a direct and deep connection
between the owner and Social Media Feature Social
Media Source Facebook FansPage, Group (Lai and
Turban, 2008) Twitter Tweet, Retweet (Bacon, 2011)
Youtube Video Upload, Adsense (Singh et al., 2008)
Instagram Vote, Drop Question, Live, IG Story (Con-
stantinides and Fountain, 2008) Pinterest Pin, Like
(Elkin-Koren, 2010) Blog Post, Campaign (Li et al.,
2006) LinkedIn Connection, Recommendation (Lee
and Cavusgil, 2006) employees that have a potential
and should monopolize this sector for many years in
the future”.
After knowing the features on social media, the
next step was clarifying the social media. (Kang and
Johnson, 2015) and (Bajpai et al., 2012) state that
there are various efforts to explain the structure and
the objectives of the social media. Some description
of social media related to the customers is provided
by (Holsapple et al., 2018). (Bocconcelli et al., 2017)
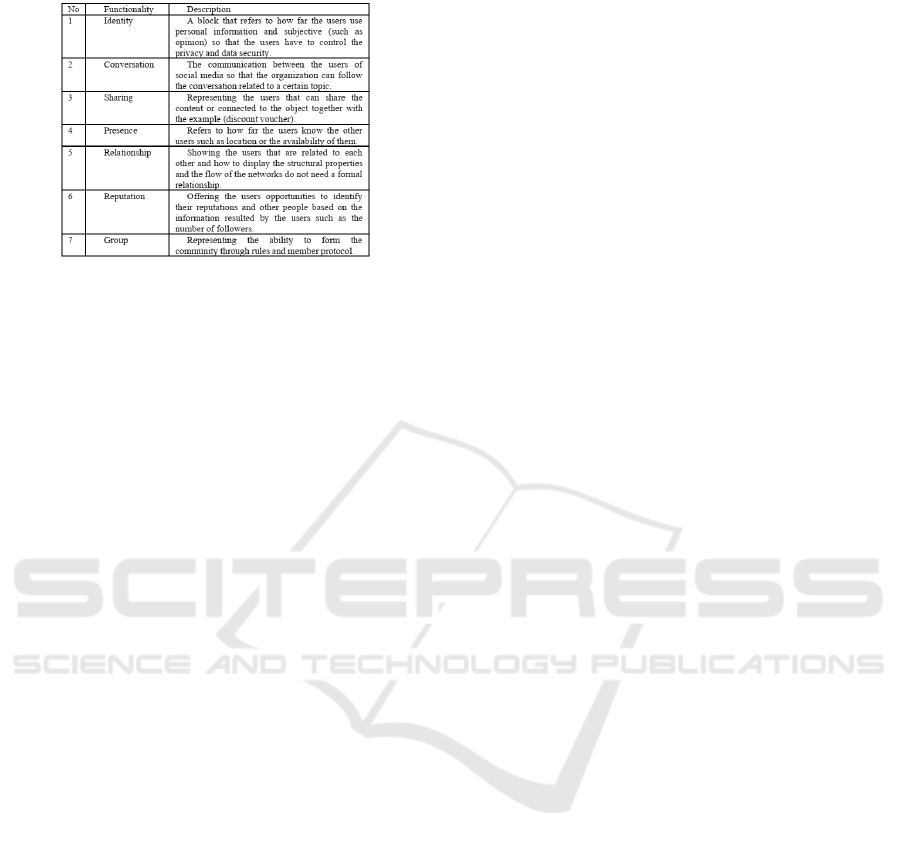
proposed a honeycomb with seven blocks to compare
social media based on the functionalities. The expla-
nation and implication of each functionality are ex-
plained in Figure 5 below.
Social Media Features for Improving Organization Business Performance: A Systematic Literature Review
117
space
Figure 5: SOCIAL MEDIA FUNCTIONALITY.
Social media like facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn ,
where they are included in the main identity function.
For instance, LinkedIn social media, in which each
individual was able to share his education, working
experience show that LinkedIn provided the function-
ality in the form of relationship and reputation as well.
On social media, Facebook’s main functionality
was the relationship in which this social media ”Face-
book” became a place for all individuals around the
world to connect and interact with each other. Face-
book as social media also had the functionalities of
identity, presence, identity, reputation and conversa-
tion functionality. The users were required to fill an
identity to be able to have a conversation, and the
presence of users was always awaited to open Face-
book. YouTube as social media focused on sharing
rather than discussion, group, and reputation. More-
over, Twitter possessed the functionalities of identity,
conversation, presence, sharing, and reputation.
4.2 Impact of Social Media on Business
Organization
The next explanation was about the results and dis-
cussion to answer RQ 2. RQ 2 question the impact
of social media usage on business organization. In
this modern era, the internet becomes the only fastest
way to get consumers’ attention in wide ranges. So-
cial media was one of the ways in which organizations
found it easy to connect with the consumers. Social
media websites such as Facebook, Twitter, Google+
and Pinterest represented great opportunities for busi-
nesses and organizations. Impacts of using social me-
dia on business organizations proposed in the previ-
ous literature will be described in this section.
The first impact was Word of mouth. The social
media platform provided perfect opportunity to take
advantage of word of mouth and spread it more eas-
ily. Social media was growing at the fastest rate in de-
veloping countries. People connected through global
scale and informally participated in each other’s lives
through online observation. ”Liking” a brand on
Facebook could spread quickly to all social media
channels. (Jones and Chin, 2015) points out that con-
sumers feel more comfortable about the opinions of
their peers than the advertisements paid for the busi-
ness. The videos were also able to act as references
to review the products and services through YouTube,
which in many cases were then shared and dissem-
inated through various other social media websites,
this review could play as a basis for consumer pur-
chasing decisions. As a result, companies could pro-
vide products to popular YouTube users for their cus-
tomers to review and create their own brand YouTube
channels with videos about their products (Kietzmann
and Canhoto, 2013).
Also, the impact of using social media on business
organizations was to use social media business orga-
nizations to communicate well with the customers.
Social media is not without its shortcomings. But or-
ganizations can use it as an advantage to interact with
consumers who are not directly satisfied. Consumers
were capable to immediately provide criticism and
suggestions so that in this case business organizations
could take the advantages of social media and promise
to change or improve their products. This service
could be done directly without going through com-
plicated procedures by using only social media. Or-
ganizations could even take this opportunity to ask the
opinion of their consumers about upcoming events or
products about their brands, especially for consumer-
based organizations so that they benefited the organi-
zation to analyze new or upcoming products or ser-
vices.
The next impacts are consideration and influence
on social media. Social media gave a big influence
on business, marketing, and how organizations are
involved with the target market. The use of social
media to share and engage many people continue to
grow for that in terms of business, it can be devel-
oped through the application of a sustainable social
media strategy to successfully exploit situations in a
swift. Another influence of social media was the dis-
covery of ’Trending Topics’, Trends on Twitter refer-
ring to the hashtagdriven topic that was immediately
popular at any given time, Trends were determined by
algorithms which monitored the subjects’ heat based
on whom you follow and where you are (Agwu and
Carter, 2014). This ’trend’ organization helped us find
out what was acceptable and what was not at a partic-
ular time in the market.
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
118
4.3 Social Media for Business
Organization Improvement
In RQ 3, we are going to discuss how social media im-
prove the effectiveness of business performance. Ac-
cording to (Drury, 2008), it takes time to develop a
relationship that leads to sales. However, most busi-
ness organizations that took the time to use social me-
dia find good results in using social media to increase
sales. For example, more than half of marketers who
had used social media for at least three years report
and it helped them to increase sales. More than half
of those who spent 6 hours or more per week found
the same results and 74% of those who spent 40 hours
produced new businesses through their efforts (As-
saad and G
´
omez, 2011).
Social media can increase the effectiveness of
business performance by growing business partner-
ships. The more time marketers invest in social me-
dia networks, the more they get business partnerships.
More than half of marketers who have invested at
least one year in social media marketing claim that
new partnerships have been obtained. More than half
of those who spent only 6 hours per week on so-
cial media are able to build new partnerships (De-
varaj and Kohli, 2003). The use of social media to
improve business partnerships not only get contracts
from other organizations but also can make resellers
to expand the sales network of products or services
that will be marketed. The use of social media in
business organizations can reduce marketing costs so
as to improve business performance by increasing the
existing income. Nearly half of those who spend at
least 6 hours per week on social media efforts see the
benefits of reducing marketing costs. At least 57% of
businesses with 10 or fewer employees agree that so-
cial media reduces marketing costs, while only 40%
of businesses with 1000 or more employees agree (Xu
et al., 2016).
Social media can help improve business improve-
ment by getting loyal customers. Loyal customers in
online marketers are far more likely to develop a loyal
fan base through social media than offline marketers
(Cook, 2008). The use of social media for improving
business organizations, one of which can also provide
market insights. Social media can predict or create the
trend of the latest models among the community so
that knowing market insights can increase the effec-
tiveness of business organizations. The use of social
media in business organizations also provides market
insights. From those who have at least one year of
experience, 69% or more found that social platforms
provide market insights; At least 74% of these ex-
penses at least six hours per week are more likely to
gain market insight.
5 DISCUSSION
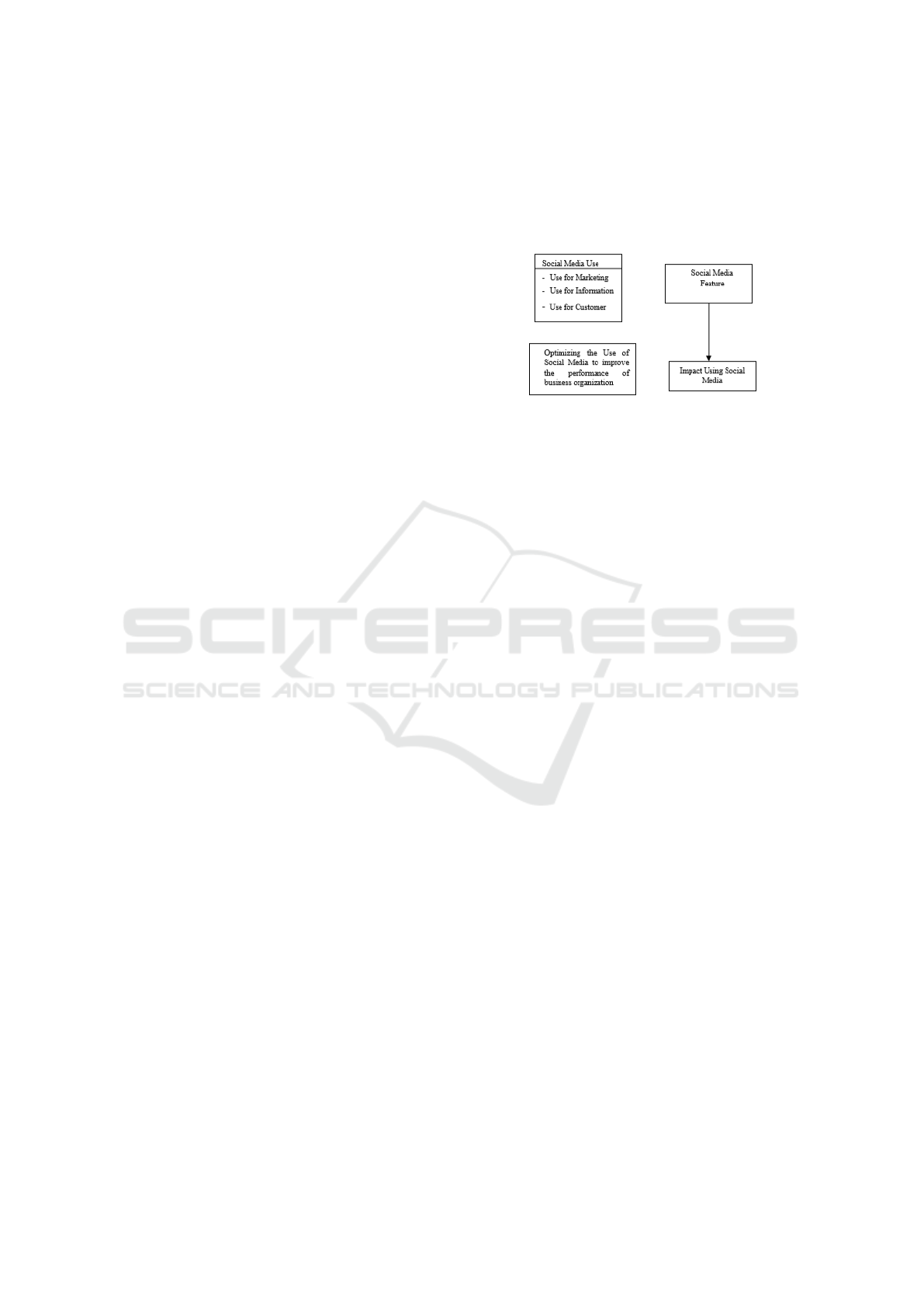
Figure 6: Conceptual Diagram
Based on the previous results, a conceptual model
as shown in Figure 6 is developed. In general, this
conceptual model is based on the literature on infor-
mation technology which provides several case stud-
ies examples to examine the determinants of IT us-
age and the extent of IT usage and business perfor-
mance in an integrative model (Kietzmann and Can-
hoto, 2013). Over the years, research has been car-
ried out to investigate the consequences of various IT
systems. For a technology like social media, which
require open and two-way communication, managers
must act. The entrepreneurship and organizations
must be prepared to face the positive and negative
consequences of using social media. Therefore, the
entrepreneurial orientation of an organization is an
important factor in the use of social media.
This diagram is a description of the SLR objec-
tives that have been carried out. This research dis-
cusses the use of social media from the marketing
sector. Then in the use of social media, a social me-
dia strategy is needed. The social media strategy can
be done by using one of the features available on so-
cial media. After knowing the features, then can be
concluded the impact of using social media so that
business organizations can improve business perfor-
mance.
Organizational orientation is positively related to
the use of social media Innovation, or interactive tech-
nology is more likely and quickly adopted by users.
The important role played by interactivity in the
world of e-commerce and other WWW technologies
have motivated the academics and practitioners to im-
prove their understanding of interactivity concept and
use it effectively (Bata et al., 2018). Social media
is considered as an interactive media. This allows
two-way communication rather than one-way trans-
mission or information distribution for the audience
(Drury, 2008). Social networking platforms, includ-
ing Facebook, YouTube, and Twitter, have spread; e-
Social Media Features for Improving Organization Business Performance: A Systematic Literature Review
119

business sites for marketing that have rushed to in-
tegrate social networking features into websites, en-
able to enhance interactive communication between
consumers, or between consumers and organizations
(Choi and Burnes, 2017).
Next is the use of social media to find informa-
tion. Social media is prevalent in various age groups.
Social networking sites like Facebook, for example,
is a popular social media platform that is most widely
used by students (Agwu and Murray, 2014). Although
the main purpose of using social networking sites is
related to socialization, there is an increase in the
number of individuals who seem to get information
from social networking sites.
Media-sharing site like YouTube is also known as
an important source for news (Singh et al., 2008).
Recently, microblog like Twitter is found to be used
also to get news (Bacon, 2011). Wikipedia has been
known as other popular social media platform which
commonly used as a starting point. The majority
of students would like to start with Wikipedia when
looking for information because it often gives the rep-
resentation about the new concept and also it is a use-
ful source (Larson and Watson, 2011). The use of
social media to find information surely could also im-
prove the effectiveness of a business organization. So-
cial media is expected to give much benefit for the
organization includes information like the easiness in
getting data input from the media user like client and
competitor.
The functionality included features and environ-
ment that facilitated the communication between user
(for example, the ability to of chatting, virtual real-
ity environment in which avatar could interact, screen
sharing), collaboration and cocreation of the con-
tent (for example, in a professional network like
LinkedIn), build reputation, etc. In a different context,
(Smith-Ditizio et al., 2018) It is important to know
the features that could support the improvement of a
business organization’s effectiveness so that it could
optimize the use of social media.
Social media is defined as ”a group of internet-
based application that builds the foundation of ide-
ology and technology of Web 2.0, and it may allow
the creation and exchange of User Generated Con-
tent” (Quaye and Mensah, 2019). Porter defines strat-
egy as ”the creation of a unique and valuable position
which involves a set of different activities”. Mintberg
defines strategy as a plan supported by a decision that
has been made. He illustrates the formulation of strat-
egy as involving interaction between a dynamic en-
vironment and some important processes in an orga-
nization, and it has a different cycle of sustainable-
change. A strategy needs to have a particular ob-
jective, targeted audience and needed sources. The
definition of Information Strategy stated by (DiStaso
and McCorkindale, 2013) and followed by Henfrids-
son and Lind (Miah et al., 2017) is not quite different:
”a process of activity which intended to the aim of
actualizing strategy to use information system in an
organization:”
6 CONCLUSIONS
The aim of this research was to know the features
that could influence the performance of a business
in using social media. The social media were Face-
book, Twitter, YouTube, Instagram, Pinterest, blog,
and LinkedIn. One of the feature examples of social
media in Facebook is a business organization could
integrate Facebook’s features to their own site, so that
eases consumer to get information and widened the
information network shared by the business organi-
zation. The business organization should get profit
from two–ways communication to respond and com-
municate with the consumer in order to find out how
a certain brand is acknowledged, or whether they en-
joy the use of the product. The literature review con-
cluded that social media could have the effect of word
of mouth where social media gave an opportunity to
profit from word of mouth in easier ways. Another
effect of the usage of social media in business orga-
nization was the easiness and quickness of communi-
cation with the client, for instance, complain can be
responded quickly through social media so that the
client is satisfied. The other effect of the social media
utilization was it could be considered and had great
influence in business, marketing, and how organiza-
tion involves with the market target. Furthermore, a
business organization also had an effect in social bak-
ers where the business organization could monitor and
optimize marketing through social media.
Social media could improve business performance
by increasing selling. In addition, social media could
grow business partnership like finding a reseller to ex-
pand the market range of business organization could
get client which resulted in the improvement of the
business organization’s performance. The increase in
the use of social media for business would give insight
about the market for business organization so that they
could get client which resulted in the improvement
of the business organization’s performance. The in-
crease in the use of social media for business would
give insight about the market for business organiza-
tion so that they could improve their organization’s
performance. This research also stated that busi-
ness world develops rapidly through existing constant
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
120

communication in the provided social media. Busi-
ness organization had been given a chance to choose
their potential consumer and at the same time get loy-
alty from their recent consumer. Business organizar-
ion had also been given a chance to be more and di-
rectly understand their consumer
REFERENCES
Agwu, E. and Carter, A.-L. (2014). Mobile phone banking
in nigeria: benefits, problems and prospects. Interna-
tional Journal of Business and Commerce, 3(6):50–
70.
Agwu, E. and Murray, P. J. (2014). Drivers and inhibitors
to e-commerce adoption among smes in nigeria. Jour-
nal of Emerging Trends in Computing and Information
Sciences, 5(3).
Agwu, M. and Murray, J. P. (2015). Empirical study of bar-
riers to electronic commerce adoption by small and
medium scale businesses in nigeria. International
Journal of Innovation in the Digital Economy,, 6(2):1–
19.
Ali, Z. (2017). The effect of social media on the successful
implementation off crm.
Assaad, W. and G
´
omez, J. M. (2011). Social network
in marketing (social media marketing) opportunities
and risks. International Journal of Managing Public
Sector Information and Communication Technologies,
2(1):13.
Bacon, J. (2011). Impact of social media on marketing in-
dustry. Fourth Source.
Bajpai, V., Pandey, S., and Shriwas, S. (2012). Social
media marketing: Strategies & its impact. Interna-
tional Journal of Social Science & Interdisciplinary
Research, 1(7):214–223.
Bata, H., Pentina, I., Tarafdar, M., and Pullins, E. B. (2018).
Mobile social networking and salesperson maladap-
tive dependence behaviors. Computers in Human Be-
havior, 81:235–249.
Bocconcelli, R., Cioppi, M., and Pagano, A. (2017). Social
media as a resource in smes’ sales process. Journal of
Business & Industrial Marketing.
Boshoff, C. and Elliot, R. (2005). The influence of organisa-
tional factors in small tourism businesses on the suc-
cess of internet marketing. Management Dynamics:
Journal of the Southern African Institute for Manage-
ment Scientists, 14(3):44–58.
Choi, H. and Burnes, B. (2017). Bonding and spreading.
Management Decision.
Constantinides, E. and Fountain, S. J. (2008). Web 2.0:
Conceptual foundations and marketing issues. Jour-
nal of direct, data and digital marketing practice,
9(3):231–244.
Cook, N. (2008). Enterprise 2.0: How social software will
change the future of work. Gower Publishing, Ltd.
Devaraj, S. and Kohli, R. (2003). Performance impacts of
information technology: Is actual usage the missing
link? Management science, 49(3):273–289.
DiStaso, M. W. and McCorkindale, T. (2013). A benchmark
analysis of the strategic use of social media for for-
tune’s most admired us companies on facebook, twit-
ter and youtube. Public relations journal, 7(1):1–33.
Drury, G. (2008). Opinion piece: Social media: Should
marketers engage and how can it be done effectively?
Journal of direct, data and digital marketing practice,
9(3):274–277.
Durach, C. F., Kembro, J., and Wieland, A. (2017). A new
paradigm for systematic literature reviews in supply
chain management. Journal of Supply Chain Man-
agement, 53(4):67–85.
Elkin-Koren, N. (2010). User-generated platforms.
He, W., Wu, H., Yan, G., Akula, V., and Shen, J. (2015). A
novel social media competitive analytics framework
with sentiment benchmarks. Information & Manage-
ment, 52(7):801–812.
Holsapple, C. W., Hsiao, S.-H., and Pakath, R. (2018).
Business social media analytics: Characterization and
conceptual framework. Decision Support Systems,
110:32–45.
Jones, B. H. and Chin, A. G. (2015). On the efficacy
of smartphone security: a critical analysis of mod-
ifications in business students’ practices over time.
International Journal of Information Management,
35(5):561–571.
Kang, J.-Y. M. and Johnson, K. K. (2015). F-commerce
platform for apparel online social shopping: Testing
a mowen’s 3m model. International Journal of Infor-
mation Management, 35(6):691–701.
Kietzmann, J. and Canhoto, A. (2013). Bittersweet! un-
derstanding and managing electronic word of mouth.
Journal of Public Affairs, 13(2):146–159.
Kim, W.-H. and Chae, B. K. (2018). Understanding the rela-
tionship among resources, social media use and hotel
performance. International Journal of Contemporary
Hospitality Management.
Kucukaltan, B., Irani, Z., and Aktas, E. (2016). A decision
support model for identification and prioritization of
key performance indicators in the logistics industry.
Computers in Human Behavior, 65:346–358.
Lai, L. S. and Turban, E. (2008). Groups formation and
operations in the web 2.0 environment and social net-
works. Group Decision and negotiation, 17(5):387–
402.
Larson, K. and Watson, R. (2011). The value of social me-
dia: toward measuring social media strategies.
Lee, Y. and Cavusgil, S. T. (2006). Enhancing alliance
performance: The effects of contractual-based versus
relational-based governance. Journal of business re-
search, 59(8):896–905.
Li, S., Ragu-Nathan, B., Ragu-Nathan, T., and Rao, S. S.
(2006). The impact of supply chain management prac-
tices on competitive advantage and organizational per-
formance. Omega, 34(2):107–124.
Mahendrawati, E. (2018). Business process management.
Matuszak, G. (2007). Enterprise 2.0: Fad or future? the
business role for social software platforms. kpmg.
Miah, S. J., Vu, H. Q., Gammack, J., and McGrath, M.
(2017). A big data analytics method for tourist
Social Media Features for Improving Organization Business Performance: A Systematic Literature Review
121

behaviour analysis. Information & Management,
54(6):771–785.
Prodanova, J. and Van Looy, A. (2017). A systematic lit-
erature review of the use of social media for busi-
ness process management. In International Confer-
ence on Business Process Management, pages 403–
414. Springer.
Quaye, D. and Mensah, I. (2019). Marketing innovation
and sustainable competitive advantage of manufactur-
ing smes in ghana. Management Decision.
Richard, P. J., Devinney, T. M., Yip, G. S., and Johnson, G.
(2009). Measuring organizational performance: To-
wards methodological best practice. Journal of man-
agement, 35(3):718–804.
Shi, S., Chen, Y., and Chow, W. S. (2016). Key values driv-
ing continued interaction on brand pages in social me-
dia: An examination across genders. Computers in
Human Behavior, 62:578–589.
Shiau, W.-L., Dwivedi, Y. K., and Lai, H.-H. (2018). Exam-
ining the core knowledge on facebook. International
Journal of Information Management, 43:52–63.
Singh, T., Veron-Jackson, L., and Cullinane, J. (2008).
Blogging: A new play in your marketing game plan.
Business horizons, 51(4):281–292.
Smith, V., Devane, D., Begley, C. M., and Clarke, M.
(2011). Methodology in conducting a systematic re-
view of systematic reviews of healthcare interven-
tions. BMC medical research methodology, 11(1):15.
Smith-Ditizio, A. A., Smith, A. D., and Kendall, W. R.
(2018). Integrating search engine capacity and gen-
der preference within a social media captured author-
ity locus of control. Benchmarking: An International
Journal.
Suryakumar, P. (2011). Making data relevant: The new met-
rics for social marketing. social media news and web
tips mashable the social media guide.
Triantafillidou, A. and Siomkos, G. (2018). The impact of
facebook experience on consumers’ behavioral brand
engagement. Journal of Research in Interactive Mar-
keting.
Vanessa, D. (2012). What do twitter trends mean. Organiz-
ing the world hashtags.
Warner-Søderholm, G., Bertsch, A., Sawe, E., Lee, D.,
Wolfe, T., Meyer, J., Engel, J., and Fatilua, U. N.
(2018). Who trusts social media? Computers in Hu-
man Behavior, 81:303–315.
Xu, J., Wei, J., and Zhao, D. (2016). Influence of social me-
dia on operational efficiency of national scenic spots
in china based on three-stage dea model. International
Journal of Information Management, 36(3):374–388.
Zaremohzzabieh, Z., Samah, B., Omar, S., Bolong, J., and
Shaffril, H. (2014). A systematic review of qualitative
research on the role of icts in sustainable livelihood.
The Social Sciences, 9(6):386–401.
CONRIST 2019 - International Conferences on Information System and Technology
122
