
Yoghurt Quality from Soybean Milk with Carrot Combination (Daucus
Carota L)
Johannes Kurniawan
1
1
Bunda Mulia Tourism Academy, Lodan Raya No.2, Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords:
Soyghurt, Organoleptic Test, Carrot, Vegetable.
Abstract:
Dietary fiber in fruits and vegetables is also beneficial for health which functions to control weight or obesity,
overcome diabetes, prevent digestive disorders, colon cancer, and reduce blood cholesterol and cardiovascular
disease. The method used in this study used the quasi-experimental method. Experimental research is one
type of quantitative research that is very strong for measuring causal relationships. Data collection techniques
in this study were conducted every 8 hours for 3 days. Data collected for the variable physical quality of soy
milk includes 4 parameters, namely color, texture, aroma, and taste. Data collected for each parameter is the
score data obtained from several panelists. The treatment of adding carrot extract by 15% and 30% affects the
quality changes that occur in soy milk-based yogurt. By only distinguishing the addition of 15% and 30%, it
can prove the influence of quality changes on soybean milk yogurt.
1 INTRODUCTION
Vegetables and fruits are a source of dietary fiber that
is easily found in food and is almost always found in
everyday Indonesian dishes, whether raw (fresh veg-
etables) or after being processed into various forms of
cooking. However, lately there has been a change in
food consumption patterns which has caused a decline
in the level of consumption of vegetables and fruits in
almost all provinces in Indonesia. The reduced level
of consumption of vegetables and fruits also causes
changes in patterns of infectious diseases into de-
generative and metabolic diseases. Vegetables are a
source of iron and minerals, and complex B vitamins
are good for the body Food fiber in fruits and veg-
etables is also beneficial for health which functions
to control weight or obesity (obesity), cope with dia-
betes, prevent gastrointestinal disorders, colon cancer,
and reduce blood cholesterol and cardiovascular dis-
ease.
The decline also occurs in urban communities
with high mobility and tend to consume ready-to-eat
foods resulting in a shift in diet from high carbohy-
drate, high fiber, and low fat to low carbohydrate and
fiber, high fat and protein consumption patterns. Car-
rots and tomatoes are some examples of fruits and
vegetables that are rarely consumed directly by the
public even though the nutrition of both is very good
for the body. Carrots are foods that are rich in beta-
carotene and function as body protectors from cell
damage. Vitamin A in carrots can maintain healthy
eyes, skin and hair, and improve the body’s immune
system. Calcium in carrots can maintain healthy
bones and teeth and help work various muscles and
nerves.
One of the things that can be done to increase
the level of consumption of vegetables and fruits is
by modifying the vegetables into foods that are liked
by most people, especially children. Yogurt is a fer-
mented milk product by microbial bacteria. Fermen-
tation of lactose produces lactic acid which works on
milk proteins, making yogurt denser and has a dis-
tinctive texture, flavour, and aroma. Generally yo-
gurt is made using cow’s milk, but with the advance-
ment of biotechnology yogurt can also come from
vegetable milk, for example soyghurt raw material for
milk (soybeans) and cocoghurt (coconut milk). Yo-
gurt has many advantages, one of which can reduce
the symptoms of lactose intolerance. As long as the
fermentation of lactose content in the yogurt drops,
the fermented milk is easier to digest, especially for
lactose sufferers. If milk can on average 90% digested
within 3 hours, then yogurt only takes 1 hour. Living
bacteria in yogurt also produce the lactase enzyme
needed to degrade lactose to glucose and galactose.
Yogurt is more durable than fresh milk (cow’s milk)
which can last up to several days, even up to several
weeks in cold conditions. This is because lactic acid
Kurniawan, J.
Yoghurt Quality from Soybean Milk with Carrot Combination (Daucus Carota L).
DOI: 10.5220/0009858000610066
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Creative Economics, Tourism and Information Management (ICCETIM 2019) - Creativity and Innovation Developments for Global
Competitiveness and Sustainability, pages 61-66
ISBN: 978-989-758-451-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
61

in the yogurt functions like a natural preservative.
Along with the development of food technology,
vegetable milk was introduced as an alternative in-
gredient in making yogurt, whose nutritional value
was not inferior to animal milk yogurt. In order to be
more attractive to increase revenue and add colouring,
with natural dyes namely carrots given there has never
been a research on making yogurt by adding carrots as
colouring and natural flavourings. So that the level of
quality and level of preference is unknown.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Framework
Carrots are seasonal vegetable crops in the form of
shrubs (shrubs) that grow upright with a height be-
tween 30 cm - 100 cm or more, depending on the type
or variety. Carrots are classified as seasonal plants be-
cause they only produce one time and then die. Car-
rot plants have a short life of around 70 - 120 days
depending on the variety. The skin and flesh of car-
rot tubers are yellow or orange. Carrots have short,
almost invisible stems. The yellow color of the carrot
tuber is reddish due to the presence of carotene pig-
ments. The skin is thin and tastes good, crispy, tasty,
and rather sweet. The taxonomic position of carrots is
as follows: Kingdom: Plantae; Race: Umbelliferales;
Division: Spermatophyta; Tribe: Umbelliferae; Sub-
division: Angiosperma; Clan: Daucus; Class: Di-
cotyledonae; Type: Daucus carota L The organs in
carrot plants are(Cahyono, 2013):
1. Leaves
Leaves of carrot plants are compound leaves, dou-
ble or triple double pinnate, and stemmed. Chil-
dren of leaves are lanceolate with leafy edges.
Each plant has 5-7 stems that are rather long, stiff
and thick with a smooth surface, while the leaf
strands are limp and thin. Its function as a place
for photosynthesis to produce substances needed
in the formation of vegetative and generative or-
gans.
2. Stems
The stem of the carrot plant is so short that it is al-
most invisible, round, not woody, rather hard, and
1 - 1.5 cm in diameter. Generally the color is dark
green. The stem is not branched but is overgrown
with long stalks that look like branches. The stem
has a smooth surface and has thickening in the
place where the petiole grows. Its function is as a
way to transport water and food substances from
the ground to leaves and assimilated substances
from leaves to all parts of the plant’s body.
3. Root
The roots of carrot plants include a rooting and
fiber system. Rooting roots will undergo a change
in shape and function to be a storage area for food
reserves, the shape will change to large and round
length to reach a diameter of 6 cm and extend to
30 cm depending on the variety. Rooting roots
that have changed shape and function are known
as ”carrot tubers”. The fiber root attaches to the
enlarged root (tuber), grows sideways and is yel-
lowish (ivory white). Its function is to absorb nu-
trients and water that are needed by plants to carry
out photosynthesis and strengthen the establish-
ment of plants.
4. Interest
Flowers of carrot plants grow on the ends of
plants, in the form of multiple umbrellas, and are
white or pink rather pale. Flowers have short and
thick stems. The florets are located in the same
arch area. Flowers that have undergone pollina-
tion will produce small and hairy fruit and seeds.
The activities carried out in the stages of pro-
cessing soybeans into soy milk consist of several
types, namely: destruction, dilution, boiling I, filter-
ing, mixing of ingredients, boiling II, bottling, and
pasteurization. The sequence of activities in process-
ing soybeans into soy milk can be explained as fol-
lows(Suprapti, 2005):
1. Destruction Destruction activities are carried out
on soybeans that have undergone a softening pro-
cess. Destruction activities use boiling water 10
times the weight of soybeans to be ground. Boil-
ing water is poured little by little during the pro-
cess of destruction or grinding takes place.
2. Dilution Dilution is done to get soy juice with a
protein content of less than 7%. The diluent used
is boiling water from the water used to water soy-
beans in destruction activities
3. Boiling 1 Soybean juice results from dilution are
then boiled but not until boiling (limited to foam
on the surface 2 times).
4. Addition of other ingredients Materials that can be
mixed in the form of sugar, salt, vanilla, sodium
benzoate, pandan leaves, suspension stabilizers
and coloring agents.
5. Boiling II Boiling II is done on soy milk which
has been mixed with other ingredients. Boiling
process is done until boiling for 5 minutes.
6. Bottling Soy milk is packaged using sterile pack-
aging bottles. Filling soy milk is done up to 99%
ICCETIM 2019 - International Conference on Creative Economics, Tourism Information Management
62

of the maximum volume of packaging bottles.
7. Pasteurization Pasteurization is done by steaming
for 5 minutes and soaking with cold water until
the temperature of the bottle and its contents are
the same as the room temperature.
Generally fermented milk products can be divided
into 2 groups, namely fermented milk products and
cheese. Almost all of the initial constituents in fer-
mented milk products still exist, with the exception of
contituents that have been metabolized by microor-
ganisms. In cheese, the portion of most of the initial
contituents of milk is removed in the curd to obtain
the final product. Whereas one of the dairy products
that has been developed is fermented milk, a term for
a dairy product obtained through a fermentation pro-
cess, a process of reforming organic materials carried
out with the help of enzymes produced by microbes.
Yogurt is coagulated milk from lactic acid fermenta-
tion through the activities of Lactobacillus bulgaricus
and Streptococcus thermophilus. Besides being made
from fresh milk, yogurt can also be made from skim
milk (nonfat milk) which is dissolved in water with a
certain ratio depending on the desired thickness of the
product. Apart from animal milk, yogurt can be made
from skim milk mixture with vegetable milk(Afrianti,
2013).
Symbiosis or mutual assistance between microor-
ganisms during growth often occurs in foods contain-
ing 2 or more types of microorganisms. One type
of microbe can produce metabolite products that are
needed for the growth of other microorganisms that
cannot produce them. In contrast, the second mi-
croorganism species produces a nutrient that stimu-
lates the first microorganisms to grow better. Symbio-
sis is found in the production of some fermented foods
such as yogurt. Streptococcus thermophilus initially
hydrolyzed milk protein by extracellular proteinase
enzymes and produced amino acids needed for the
growth of Lactobacillus bulgaricus. Conversely, Lac-
tobacillus produces formic acid which stimulates the
growth of Streptococcus. Both types of bacteria are
needed to produce the desired yogurt product.
Fermentation reactions vary depending on the
type of sugar used in the products and products pro-
duced. Briefly, in milk contains glucose (C6H12O6)
and through fermentation will produce yogurt. This
fermentation reaction is carried out by microorgan-
isms in the form of homofermentative bacteria (Lacto-
bacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus)
and used in food production.
Glucose fermentation is described by considering
several mechanisms used by microorganisms to ob-
tain phosphorylation of substrates using glucose. In
principle, phosphorylation of ADP into ADP can be
paired with both balanced chemical transformations;
Glucose ⇒ 2 Lactic Acid
(C6 H12 O6) (C3 H6 O3)
Or
Glucose ⇒ 2 Ethanol + 2 Carbon dioxide
(C6 H12 O6) (C2 H6 O) (CO2)
In broad outline the factors that influence food
quality are as follows:
a. Color
The color of the ingredients must be combined in
such a way that it does not look pale or the color
is not harmonious. The color combination is very
helpful in consumers’ appetite.
b. Appearance
Expression - looks good enough to eatk is not an
excessive expression. Food must be well seen
while on a plate, where it is an important factor.
Freshness and cleanliness of the food served are
important examples that will affect the appearance
of food either or not to be enjoyed
c. Portion
In each serving of food, a standard portion is
called the standard portion size.
d. Form
The form of food plays an important role in the at-
tractiveness of the eye. Interesting forms of food
can be obtained by cutting various food ingredi-
ents, such as carrots cut in the form of dice or
commonly called dice pieces combined with chif-
fonade cut lettuce which is an irregular cut in veg-
etables.
e. Temperature
Consumers like temperature variations that are
obtained from food from one another. Tempera-
ture can also affect taste, for example the sweet-
ness of a food will be more pronounced when the
food is still warm, while the saltiness of the soup
will be less noticeable when the soup is still hot.
f. Texture
There are many food textures including smooth
or not, liquid or solid, hard or soft, dry or moist.
Thin and smooth levels and forms of food can be
felt through pressure and movement of receptors
in the mouth.
g. Aroma
Aroma is a reaction of food that will affect con-
sumers before consumers enjoy food, consumers
can smell the food.
h. Maturity Level
The level of food maturity will affect the tex-
ture of food. For example, boiled carrots will be
soft enough than boiled carrots faster. For certain
Yoghurt Quality from Soybean Milk with Carrot Combination (Daucus Carota L)
63

foods such as steaks, everyone has their own taste
about the level of maturity of the steak
i. Taste
The taste point of the tongue is the ability to detect
the basis of sweet, sour, salty, bitter. In certain
foods these four flavors are combined to become
a unique and interesting taste to be enjoyed.
3 RESEARCH OBJECTIVES AND
BENEFITS
3.1 Research Purposes
a. To find out the combination of carrots and yogurt
made from soybean milk causes a difference in
quality and level of preference (organoleptic test).
b. To find out the right combination of carrots to
get yogurt made from soybean milk with the best
quality and preferred by panellists.
3.2 Benefits of Research
a. For Researchers
Obtain knowledge or research insights in the field
of food and beverage processing.
b. For Institutions
Enriching the repertoire of knowledge originating
from educational institutions, so as to require in-
stitutions to continue to provide further research
opportunities.
c. For the community
Provide information about the use of soybeans
as an alternative raw material for fermentative
drinks, in the form of yogurt and added with carrot
extract as an increase in the level of preference.
3.3 RESEARCH METHODS
3.3.1 Research Procedure
The method used in this study uses quasi-
experimental methods. Experimental research is
one type of quantitative research that is very strong
for measuring causal relationships. This research was
conducted to find out how much influence the double
entry journal strategy had with the help of wall chart
media on learning to produce short story texts.
Experimental research methods can be interpreted
as research methods used to find the effect of cer-
tain treatments on others under controlled conditions.
Through research on the results of this experimental
trial, the author tried to find quantitative data related
to students’ ability to write short stories. The data
used to analyse the quantitative approach is data in
the form of numbers.
3.3.2 Data Source
The data collection technique in this study is done
once every 8 hours for 3 days. Data collected for
the physical quality variables of soy milk include 4
parameters, namely colour, texture, aroma, and taste.
Data collected for each parameter is the score data ob-
tained from several panellists.
3.3.3 Data Analysis Technique
Data processing obtained in this study was carried out
using Microsoft Excel and SPSS version 25.0. Data
analysis used a one-way ANOVA test based on the
Duncan method at p 5 0.05 and bivariate correlation
test. Data is displayed in the form of graphs and tab-
ulations. The data analysis technique used to test the
hypothesis is the analysis of variance (Anava).
3.3.4 Hypothesis Testing Criteria
The hypothesis carried out in this study is arranged in
the form of statistical hypotheses, namely:
H0 = The addition of carrot extract to soybean milk
yogurt has no effect
H1 = 15% addition of carrot extract to yogurt made
from soybean milk
H2 = 30% addition of carrot extract on yogurt made
from raw soy milk
This statistical hypothesis is tested by comparing the
price of Fcount with Ftable. The hypothesis testing
criteria are as follows;
a. If F count ≤ F table 5% means that H0 is accepted,
H1 is rejected and it is stated that the treatment
given does not significantly affect the length of
time yogurt fermentation is made from raw soy-
bean milk.
b. If the price of F count ≥ F table 5% means that
H0 is rejected, H1 is accepted and it is stated that
the treatment given has a significant effect on the
length of time fermented yogurt made from soy
milk.
4 RESULTS AND OUTREACH
ACHIEVED
Based on the graph data above it can be seen that
the average value of the quality of the yogurt texture
ICCETIM 2019 - International Conference on Creative Economics, Tourism Information Management
64
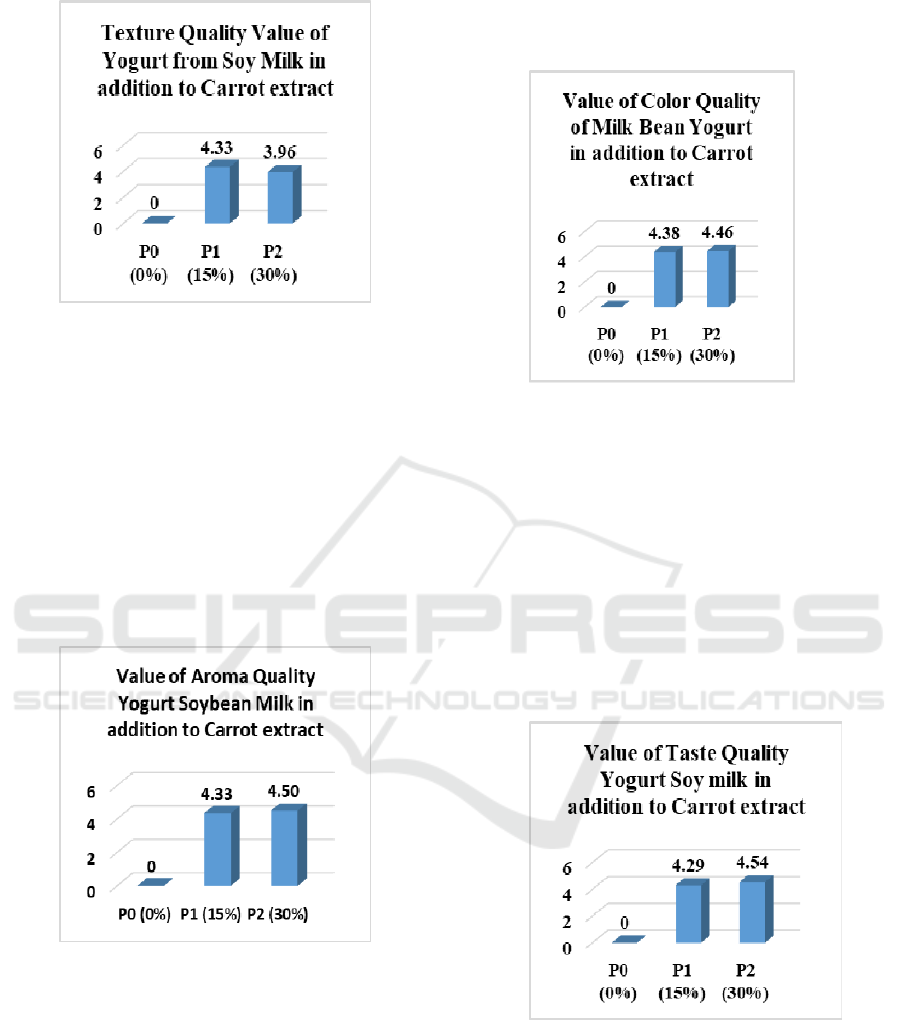
Figure 1: Parameters of Texture Quality of Yogurt Made
from Soybean Milk in addition to Carrot extract
for each treatment level indicates a variation in the
data. This is evident in the average value of the tex-
ture quality of yogurt made from raw milk from soy-
beans added with the highest Carrot extract is in the
treatment of 15% carrot extract which has an average
value of 4.33 with very softer indicators. The aver-
age value of the texture quality of milk yogurt made
from soybeans is added to the lowest Carrot extract
at 30% treatment of carrot extract of 3.96 with a very
soft indicator.
Figure 2: Parameters of Aroma Quality Yogurt Made from
Soybean Milk with additional Carrot extract
Based on the graph data above it can be seen that
the average value of the quality of the yogurt aroma
for each treatment level indicates a variation in the
data. This is evident in the average value of the
aroma quality of yogurt made from raw milk from
soybeans added with the lowest Carrot extract is in the
treatment of 15% carrot extract which has an average
value of 4.33 with indicators very flavourful. The av-
erage value of the aroma quality of milk yogurt made
from soybeans is added to the highest Carrot extract
in the treatment of 30% carrot extract of 4.50 with in-
dicators very flavourful.
Figure 3: Color Quality Parameters of Yogurt Made from
Soybean Milk in addition to Carrot extract
Based on the graph data above, it can be seen
that the average value of the quality of the yoghurt
color for each treatment level indicates a variation in
the data. This is evident in the average value of yo-
gurt color quality from raw milk from soybeans added
with the lowest carrot extract is in the treatment of
15% carrot extract which has an average value of 4.38
with indicators very attractive. The average value of
the color quality of milk yogurt made from soybeans
is added to the highest carrot extract at 30% treatment
of carrot extract at 4.46 with very attractive indicators.
Figure 4: Taste Quality Parameters of Yogurt Made from
Soybean Milk in addition to Carrot extract
Based on the graph data above it can be seen that
the average value of the quality of the yogurt texture
for each treatment level indicates a variation in the
data. This is evident in the average value of yogurt fla-
vor quality from raw milk from soybeans added with
the lowest Carrot extract is in the treatment of 15%
carrot extract which has an average value of 4.29 with
Yoghurt Quality from Soybean Milk with Carrot Combination (Daucus Carota L)
65

very good indicators. The average value of the texture
quality of milk yogurt made from soybeans is added
to the highest Carrot extract in the treatment of 30%
carrot extract of 4.54 with very good indicators.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTION
5.1 Conclusion
Based on the research conducted by the author about
the organoleptic test of yogurt made from soybean
milk based on the addition of carrot extract, it was
concluded that:
a. Treatment of adding carrot extract by 15% and
30% affect the quality changes that occur in soy-
bean milk yogurt. By only distinguishing the ad-
dition of 15% and 30%, it can prove the influence
of quality changes on soybean milk yogurt.
b. By organoleptic tests, respondents were more
likely to say that the texture, aroma, color and
taste of yogurt made from soy milk added with
carrot extract can be accepted and consumed as
yogurt in general.
5.2 Suggestions
Based on research conducted by the author about the
organoleptic test of yogurt made from soybean milk
based on the length of fermentation time, as an input
and consideration material:
a. By being able to add other new variations to be-
come flavorings from other fruit or vegetable ex-
tracts that have never been done to be an attrac-
tion in consuming vegetable yogurt made from
soy milk.
REFERENCES
Afrianti, L. H. (2013). Food preservation technology. Alpa-
beta, Bandung.
Cahyono, B. (2013). Carrots cultivation techniques for
farming analysis. Kanisius, Yogyakarta.
Suprapti, L. (2005). Teknologi pengolahan pangan tepung
tapioka dan pemanfaatannya. PT Gramedia Pustaka:
Jakarta, 80.
ICCETIM 2019 - International Conference on Creative Economics, Tourism Information Management
66
