
Analysis of Financial and Non-financial Performance
Measurement with Traditional and Balanced Scorecard
Approaches: Survey of Local Government Water Utility
in Jambi Province
Salman Jumaili, and Primadi Prasetyo
Faculty of Economics and Business, University of Jambi, Indonesia
Abstract. This study aims to analyze the Measurement of Financial and Non-
Financial Performance using two approaches, the Traditional and the Balanced
Scorecard. The study was conducted at Local Goverment Water Utility (PDAM)
in Jambi Province. The data used is the PDAM Performance Report consisting
of Financial and Non-Financial Reports. The results show the most appropriate
performance measurement is the Balanced Score Card approach in the non-
financial perspective consisting of the Customer perspective, the Internal
Business Perspective, and the Growth and Learning Perspective, rather than the
Traditional Performance Measurement which only focuses on Financial
Performance.
Keywords: Financial performance · Non-financial performance · Traditional
approach · Balanced Scorecard Aproach
1 Introduction
Water is a basic need for living things, including humans. We must manage and manage
water sources and uses so that they can be used efficiently and effectively. Water that
involves the needs of the lives of many people, in its management is monopolized by
the government. This is in accordance with the UUD 1945 Article 33 paragraph (3),
which reads "The earth and water and natural resources contained therein are controlled
by the state and used for the greatest prosperity of the people".
Related to the authority of water management by the region regulated in Article 10
of Law no. 22 of 1999 concerning Regional Government states that "the region has the
authority to manage regional resources available in its territory and is responsible for
preserving the environment in accordance with laws and regulations". From this article
the drinking water service is handed over to the Regional Government and through the
Regional Regulation the implementation is handed over to an agency namely the
Regional Drinking Water Company (PDAM).
Performance appraisal that is commonly done by PDAMs is the measurement of
traditional approaches, namely performance measurements sourced from company
financial information. In Indonesia, the measurement of PDAM performance is also
regulated in the Decree of the Minister of Home Affairs Number 47 of 1999 concerning
Guidelines on Performance Evaluation of Regional Water Supply Companies
234
Jumaili, S. and Prasetyo, P.
Analysis of Financial and Non-financial Performance Measurement with Traditional and Balanced Scorecard Approaches: Survey of Local Government Water Utility in Jambi Province.
DOI: 10.5220/0009854500002900
In Proceedings of the 20th Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics, Management and Accounting (MIICEMA 2019), pages 234-241
ISBN: 978-989-758-582-1; ISSN: 2655-9064
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

(PDAMs). The indicators measured only use three aspects, namely financial aspects,
operational aspects, and administration aspects.
Kaplan and Norton (1996) developed the concept of balanced scorecard (BSC) to
complement financial performance measurements (or known as traditional
measurements) that are important for corporate organizations to reflect new thinking in
an era of organizational competitiveness and effectiveness. This concept measures
company performance by using criteria that describe the company's vision, mission,
and long-term strategy. These criteria are divided into four perspectives: (1) financial
perspective, (2) consumer perspective, (3) internal business process perspective, and
(4) learning and growth perspective.
PDAM is a company engaged in the field of water supply services. One of the
objectives of establishing a PDAM is to meet the needs of the community for clean
water, including the provision, development of facilities and infrastructure services and
distribution of clean water, while the other goal is to participate in developing the
economy to support regional development by expanding employment, and seeking
profit as the main source of financing for the region. PDAM as one of the BUMDs is
expected to be able to provide an adequate contribution.
This study was conducted to determine the differences in financial and non-financial
performance in the PDAM Jambi Province specifically for PDAM Tirta Mayang,
which began implementing the Balanced Scorecard approach in preparing the
Company's Work Budget Work Plan since 2018. The problem raised in this study is
how to measure Financial and Non Performance Finance for PDAMs in Jambi Province
using the traditional approach and by using the Balance Score Card approach, and
which measures are more appropriate for measuring PDAM performance.
2 Literature Review
Performance is a picture of the level of achievement of the implementation of an
activity of an activity / program / policy in realizing the goals, objectives, mission and
vision of the organization as outlined in the formulation of the strategic planning
(strategic planning) of an organization. Performance measurement as a periodic
determinant of the operational effectiveness of an organization, parts of the
organization, and employees based on the targets, standards, and criteria that have been
set previously.
Another understanding of performance measurement is a process of evaluating
work progress against predetermined goals and objectives, including information on
the efficient use of human resources in producing goods and services; quality of goods
and services (how well goods and services are delivered to customers and to what extent
customers are satisfied); the results of the activities are compared with the intended
purpose; and the effectiveness of actions in achieving goals.
2.1 Performance Evaluation with Traditional Systems
In accordance with the Decree of the Minister of Home Affairs of the Republic of
Indonesia Number 47 of 1999 concerning Guidelines for Performance Assessment of
Analysis of Financial and Non-financial Performance Measurement with Traditional and Balanced Scorecard Approaches: Survey of Local
Government Water Utility in Jambi Province
235

PDAMs, several aspects were assessed, including the following; financial aspects,
operational aspects and administrative aspects which are interrelated.
2.2 Measuring PDAM Performance with the Balanced Scorecard
In the Balanced Scorecard concept, not only the financial aspect (Finance) is the
benchmark for company performance, there are three other measurement angles that
are also taken into account, namely Customer, Internal Business Process and Learning
and Growth.
The objectives of the Balanced Scorecard for organizations or companies (Kaplan,
2000) include:
a) Clarify and consume strategies throughout the community.
b) Aligning departmental and individual goals with organizational strategies.
c) Identifying and aligning strategic initiatives.
d) Conduct periodic strategy reviews.
e) Get the feedback needed to improve the strategy.
3 Research Results
3.1 Overview of Financial and Non-financial Performance
Measurement in PDAMS in Jambi Province using the Traditional
Approach
Based on the level of health of the PDAM which is assessed based on BPPSPAM for
2015 to 2017 is considered healthy, although there are still many things that need
attention from management because the achievement of the value of several indicators
that are still below the standards are as follows:
- Financial aspects, Return of Equity (ROE) is still below the minimum standard
that should be 10%. The operating ratio is still above the standard of 0.50 and the
cash ratio is still low when compared to the minimum standard of 100%
- Service Aspect, Customer growth is still below the minimum standard of 10%
Monthly Domestic Water Consumption is still below the standard of 30 M3 per
month
- Operating Aspects, productivity efficiency is still below the standard of 90%, the
level of water loss is still high with a standard of 20%, replacement of water meters
is still low with a standard of 20%
- In the aspect of Human Resources (HR), the employee education and training ratio
is still below the standard of 60% of the total number of employees. The ratio of
training costs is still below the standard of 10% of the total employee costs.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
236
3.2 Measurement of Financial and Non-financial Performance of
Pdams in Jambi Province using the Balance Score Card Approach
3.2.1 Financial Perspective
Performance evaluation of financial aspects in principle is an assessment that includes
the company's ability to create profits and streamline its operational activities.
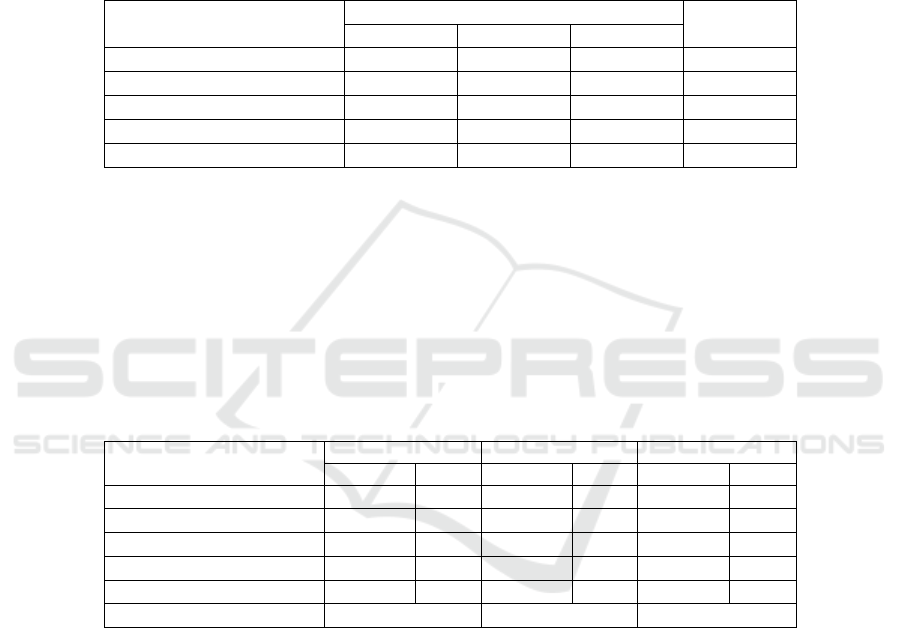
Table 1. Overall Measurement Results of Financial Perspective indicators.
Indicator
yea
r
Good
criteria
2015 2016 2017
Gross Profit Margin 40,06% 42,15% 41,65% >6%
Operating Profit Margin 0,77% −2,49% −0,91% >6%
Return On Asset 0,71%
−1,99% −0,74%
>7%
Current Ratio 63,77% 269,47% 150,06% >200%
Total Asset Turnove
r
92,75% 79,94% 81,17% >100%
From the table above, it can be seen that in the gross profit margin ratio, the
company's financial performance can be assessed as good, then for the current ratio of
companies that need to be active every year, but it must still be done efficiency of assets
owned and properly control current debt. Furthermore, for the operating profit margin
ratio, ROA, and TATO, the company's financial performance is considered bad, the
company must be better able to maximize and manage every resource it has to increase
the company's revenue / profit in order to realize good corporate financial performance.
Furthermore, given the above achievement scores as follows based on guidelines
from BPPSPAM as follows:
Table 2. Results of BPPSPAM Financial Aspects Measurement.
INDICATOR
y
ea
r
2015
y
ea
r
2016
y
ea
r
2017
condition score condition score condition score
Return On E
q
uit
y
2,10% 2 -2,71% 1 -1,03 1
O
p
eratin
g
Ratio
0,99 2 1,02 1 1,01 1
Cash Ratio
14,70% 1 31,26% 1 18,36 1
Billin
g
Effectiveness
93,43% 5 73,21% 1 84,02% 3
Solvenc
y
182,0% 4 375,8% 5 355,7% 5
Value
0,67 0,37 0,48
In line with the results of financial performance measurements conducted by
researchers using several different measurement indicators, the results of BPPSPAM
measurements on the overall financial aspects are considered less healthy.
3.2.2 Customer Perspective
The assessment of customer perspective performance aims to measure several service
indicators that illustrate the level of the company's ability to meet the needs of its
customers.
Analysis of Financial and Non-financial Performance Measurement with Traditional and Balanced Scorecard Approaches: Survey of Local
Government Water Utility in Jambi Province
237
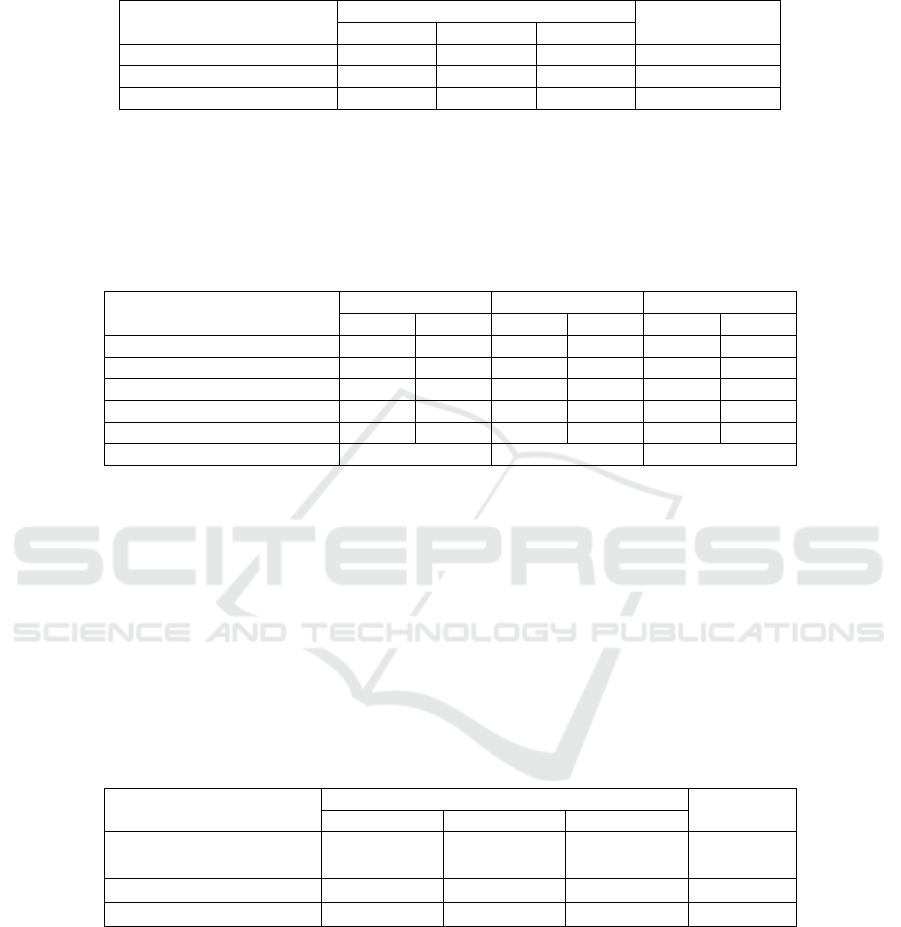
Table 3. Overall Measurement Results of Customer Perspective.
Indicator
yea
r
Good criterion
2015 2016 2017
Customer Retention 96,97% 93,47% 96,09% Increase
Customer Ac
q
uisition 3,03% 6,53% 4,91% Increase
Customer Complaint Level 11,43% 12,57% 6,56% Decrease
Overall customer perspective performance shows that the company's management
is good enough in meeting customer needs and in increasing customer growth for the
company. The company's management must continue to strive to improve performance
in the customer sector because during 2015-2017 there are still several indicators that
experience fluctuations in each year. Next to score the service aspects as follows:
Table 4. BPPSPAM Measurement Results Service Aspects.
INDIKATOR
2015 2016 2017
condition value condition value condition value
Service Coverage 80,35% 5 85,50% 5 87,73% 5
Customer Growth 3,12% 5 6,98% 5 5,17% 5
Com
p
laint Settlement Rate 100,00% 5 98,39% 5 79,88% 5
Pela
gg
an Water Qualit
y
100,00% 5 0,00% 1 80,93% 4
Domestic Water Consum
p
tion 16,35 2 15,77% 2 15,55 2
Weight 1,10 1,03 1,08
BPPSPAM measurement results on the overall service aspects are considered
healthy even though the indicators for customer water quality and domestic water
consumption are still at a low value and must be improved. While in other indicators,
the company's performance is considered good or in the healthy category.
3.2.3 Internal Business Process Perspective
The internal business process perspective in the balanced scorecard highlights various
important processes that support the company's strategy and operational activities.
According to Kaplan and Norton (2001) performance measurement in the perspective
of internal business processes as follows:
Table 5. Measurement Results of Several Internal Business Process Perspective Indicators.
Indicators
yea
r
Good criteria
2015 2016 2017
Water Distribution Time
4 hours to
6 hours
6 hours to
12 hours
12 hours to
24 hours
Increases
N
ew Connection Spee
d
3-6 days 3-6 days 3-6 days decreases
Tera Water Mete
r
0,00% 0,00% 0,00% -
Based on the above table and the results of in-depth interviews with related speakers
as a whole the performance of the perspective of internal business processes shows that
the company's management is quite good in optimizing the company's business
processes and in improving services to consumers. Next to find out the score as
follows:
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
238
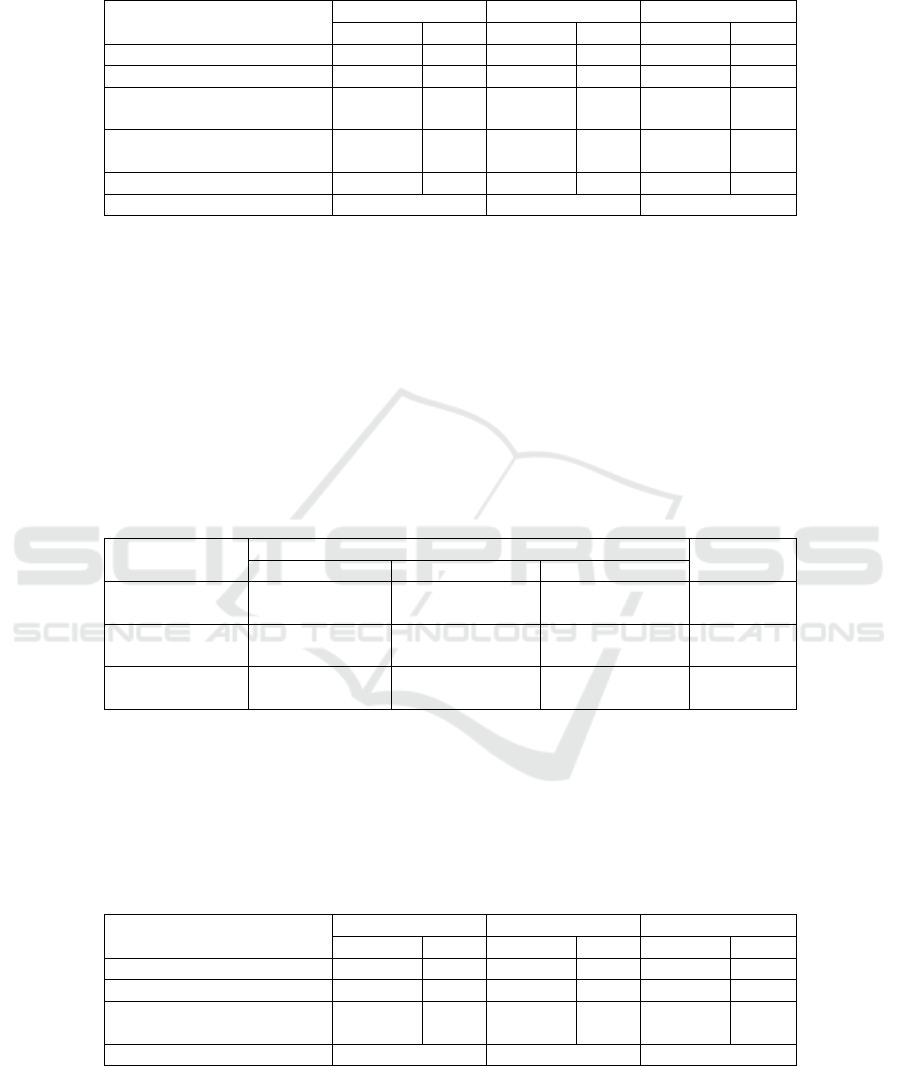
Table 6. BPPSPAM Measurement Results Operational Aspects.
INDICATORS
2015 2016 2017
condition value condition value condition value
Production Efficienc
y
74,45% 3 77,68% 3 68,17% 2
Water Loss Rate 45,86% 1 46,71% 1 44,82% 1
Operating Hours of Service /
Da
y
23 5 24 5 24 5
Operating Hours of Service /
Day
96,53% 5 55,86% 3 28,75% 2
Water Meter Replacement 1,97% 1 3,90% 1 5,24% 2
Wei
g
ht 1,07 0,94 0,87
The results of the measurement of operational aspects by BPPSPAM as a whole are
considered healthy. However, it is necessary to improve performance, especially in the
indicator of the level of water loss, where the existing conditions can be categorized as
unhealthy because they are at a low value. This shows that the company has not been
able to properly overcome the problem of this level of water loss, either caused by a
leaky pipe, broken customer water meter or water theft.
3.2.4 Learning and Growth Perspective
This perspective assessment is whether there is productivity or not to create growth and
improve the performance of human resources owned in the long run.
Table 7. Measurement Results Overall Perspective indicators.
Indicators
y
ea
r
good criteria
2015 2016 2017
Employee
Productivit
y
Rp.235.397920 Rp.244.007.110 Rp.255.307.710 Increasing
Employee
Turnover Rate
0,58% 4,61% 0,57% Decreased
Employee
Absenteeis
m
7,90% 5,50% 3,72% Decreased
Overall the performance of growth and learning perspectives has been good in
improving employee quality, loyalty as well as employee interest and motivation in
work as indicated by the measurement results of the three indicators which are
considered good. Company management must continue to strive for growth and
improvement in the quality of human resources owned by the company in order to
improve overall company performance. Next to find out the score as follows:
Table 8. BPPSPAM Measurement Results Aspects of Human Resources.
INDICATORS
2015 2016 2017
Condition value Condition value Condition value
Number of Em
p
lo
y
ees / 1000 5,29 5 5,00 5 4,78 5
Em
p
lo
y
ee Trainin
g
Ratio 41,40% 3 50,43% 3 27,22% 2
Training Costs Against
Employee Costs
1,16% 1 1,61% 1 0,60% 1
WEIGHT 0,51 0,51 0,47
Analysis of Financial and Non-financial Performance Measurement with Traditional and Balanced Scorecard Approaches: Survey of Local
Government Water Utility in Jambi Province
239

The table above is the result of performance measurement of aspects of PDAM
human resources using different indicators, the results of the measurement of HR
aspects conducted by BPPSPAM as a whole are considered healthy.
4 Conclusion
1 The measurement of the financial and non-financial performance of PDAMs is
measured by the traditional approach showing:
- Financial aspects show Return of Equity (ROE) which is 10% is still below the
minimum standard that should be, operating ratio of 0.50 which is still above the
standard, and Cash ratio of 100% is still low when compared with the minimum
standard.
- Service Aspect of 10% shows that customer growth is still below the minimum
standard and Domestic Water Consumption per month is still below the standard
of 30 M3 per month.
- The Operational Aspect shows that the productivity efficiency is still below the
standard of 90%, the level of water loss is still high with a standard of 20%, and
the water meter replacement is still low with a standard of 20%.
- The aspect of Human Resources (HR) shows that the ratio of employee training is
still below the standard, which is 60% of the total number of employees and the
ratio of training costs is still below the standard of 10% of the total employee cost.
2 Measurement of PDAM's financial and non-financial performance measured by the
Balanced Scorecard approach shows:
a. The results of the measurement of financial perspectives with five indicators
namely the ratio of gross profit, operating profit ratio, return on assets, current
ratio, and total asset turnover can be said to be bad. Whereas on other indicators
the company's financial performance is said to be bad because the measurement
results are far below the good criteria. This shows that the company has not been
able to optimally in the achievement of sound and sustainable financial
management.
b. The results of measuring the customer perspective with three indicators namely
customer retention, customer acquisition, and the level of customer complaints
looks good The company must continue to pay attention to the development of
customer needs and improve service, especially to customer complaints.
c. Measurement of the perspective of internal business processes with indicators
such as time of water distribution, efficiency and effectiveness of production,
speed of new connections, customer service, and lighting of water meters need
to be developed continuously. Then in terms of consumer protection is still bad,
this can be seen from the company has never done customer water meter
illumination in order to maintain honest, fair and transparent orderly measures.
d. The results of measuring growth and learning perspectives show good. Employee
productivity continues to increase every year by motivating and controlling
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
240

work so that employees are increasingly motivated and continue to produce
productivity for the company which will certainly affect other perspectives.
3 The balanced scorecard approach is more appropriate in measuring the financial and
non-financial performance of PDAMs than the traditional approach.
References
Christina, Ni Putu Yessy dan I Putu Sudana, 2013. Penilaian kinerja pada PT. Ardhi Karya
dengan Pendekatan Balanced Scorecard. E-Jurnal Akuntansi. Vol 5, No 3. Universitas
Udayana: Bali.
F., Dewi, W., Tiswiyanti, P., Eko, 2015. Praktik Good Corporate Governance Dan Dampaknya
Terhadap Kinerja Berdasarkan Balanced Scorecard Pada Perusahaan Daerah Air Minum
(PDAM). E-Conference in Business, Accounting, and Management (CBAM) Fakultas
Ekonomi UNISSULA Semarang. Vol 2 No.1 Mai 2015.
F., Ahmad, 2016. Analisis Pengaruh Penerapan Balanced Scorecard Terhadap Peningkatan
Kinerja Perusahaan (Studi Kasus Pada Perusahaan Daerah Air Minum (Pdam) Lamongan).
Jurnal Penelitian Ekonomi dan Akuntansi Volume I No. 1, Februari 2016.
Kaplan, Robert S., dan David P. Norton. 2000. Balanced Scorecard Menerapkan Strategi Menjadi
Aksi. Terjemahan Erlangga: Jakarta.
Mulyadi dan Johny Setyawan, 2001. Sistem Perencanaan Dan Pengendalian Manajemen: Sistem
Pelipat Ganda Kinerja Keuangan Perusahaan. Edisi III. Salemba Empat: Jakarta. Jakarta:
Salemba Empat.
Mulyadi, 2001. Balanced Scorecard: Alat Manajemen Kontemporer Untuk Pelipatganda Kinerja
Keuangan Perusahaan. Edisi II. Salemba Empat: Jakarta. Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Mulyadi. 2005. Sistem Manajemen Strategik Berbasis Balanced Scorecard. Unit Dan Percetakan
Sekolah Tinggi Lmu Manajemen YKPN: Yogyakarta.
Octavyanti, Shelvy, 2014. Analisis Kinerja Melalui Pendekatan Balanced Scorecard
Pada PDAM Surya Sembada Kota Surabaya. Vol. 36 No. 1 Juli 2016
dministrasibisnis.studentjournal.ub.ac.id 203.
Putri, D. Nengah, F., Sudjana, Dwiatmanto, 2016. Analisis Kinerja Perusahaan Dengan
Pendekatan Balanced Scorecard Pada PDAM Kota Malang (Studi Kasus Pada Perusahaan
Daerah Air Minum Kota Malang Periode 2012 -2014). Jurnal Administrasi Bisnis (JAB) Vol.
36 No. 1 Juli 2016 administrasibisnis.studentjournal.ub.ac.id.
Robert, A. N, Vijay Govindarajan, (2003). Management Control System Buku II. Jakarta:
Salemba Empat.
www.pdamjambi.co.id
www.peraturan.go.id
Analysis of Financial and Non-financial Performance Measurement with Traditional and Balanced Scorecard Approaches: Survey of Local
Government Water Utility in Jambi Province
241
