
Marketing Mix Study using Social Media in Hospital
Erlina Puspitaloka Mahadewi
1,3
, Ade Heryana
1
, Herwanto
2
, Rina Astini
3
and Ngadino Surip
3
1
Department of Public Health, Faculty of Health Sciences, Esa Unggul University Jakarta, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Engineering, Krisnadwipayana University Jakarta, Indonesia
3
Doctoral Program, Mercu Buana University, Jakarta, Indonesia
rina_astini@mercubuana.ac.id, dinosurip@gmail.com
Keywords: Behavior, Hospital Brand, Marketing Mix, Marketing Services, Marketing Strategy, Social Media.
Abstract: The hospitals industry with government policy make hospital at the moment has very tight competition, in
private hospitals, need a good marketing strategy to maintain its existence also the new era of Healthcare
National Services (Jaminan Kesehatan Nasional-JKN). The new decade of technology in 5.0. now is frontally
change, disrupt the way people perceive, engage, and consumer branding. Technology in healthcare has also
led to another significant shift in society, the need and or willingness of people to share and behavior respond
to hospital brand. Study to investigate the implication of different social media in areas of gender, economic
profile, ages, education and IT skill of the customers from the hospital. Analysis and result from the data
collection will be based on test of the social media effect in hospital marketing mix services. The study expects
that social media will improve marketing services analysis of the relationship between internet use and
decision to select hospital will be shown that patients who select the hospital. This result analyzes the
relationship between service, price, and decision to select hospital indicating then it can be concluded that
there is a relationship between service price and decision to select a hospital.
1 BACKGROUND
The past 20 years, running hospital business in
Jakarta, Indonesia, now at the moment has very tight
competition, with government policy to allow
international hospitals operating in Indonesia, private
hospitals need a good marketing strategy to maintain
its existence also the new era of Healthcare National
Services (Jaminan Kesehatan Nasional-JKN).
Over the last decade, before 2.0. the social media
technologies using in Indonesia hospitals are
uncommon and very rare in the past, but the decade
4.0. is frontally change, we are now nearly 5.0. after
technology already become lifestyle and habits.
These technologies have also led to another
significant shift in society, the willingness of people
to share information about their personal interests,
relationships, and behavior. They have profoundly
disrupted the way people perceive, engage, and
consumer brands. This new information is leading to
a fundamental change in the way of hospital
management as a company to know the measure,
tracking, and manage the health of their branding
(Reza H. M., 2016). The significant part of how
society has changed information exchange is in the
way consumers think about, comprehend, and discuss
brands. More importantly, customers opinions are
shaped more by social influencers than by the brands
themselves. Consumers now respond to brand
messaging in real-time and voice their ideas about
brands to large peer networks now also faster in the
future.
One of the marketing strategies to be used like
using social media because this is known well with a
low budget. The fact that social media has evolved
not just being a basic tool for collaborative creation
and the sharing of content to becoming an important
part of the present media landscape. Although, some
of the hospital management until today still think that
to determine the effectiveness of the social media
used, for marketing services still can be the important
tools, that's why this research will be choosing the
KPJ Permata Hospital as the first joint cooperation in
the hospital industry in Indonesia, and the result of
this article will be really new highlight point of views
in healthcare especially hospital. This statistical test
will be carried out by the researcher to test the effect
of social media on hospital marketing services.
Katherine Taken Smith, 2017, social media usage
by healthcare organizations has increased
406
Mahadewi, E., Heryana, A., Herwanto, ., Astini, R. and Surip, N.
Marketing Mix Study using Social Media in Hospital.
DOI: 10.5220/0009826004060413
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Health (ICOH 2019), pages 406-413
ISBN: 978-989-758-454-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

dramatically. Since social media platforms appeal to
different groups of people, this prompts the question
of whether certain platforms are more appealing to
people who partake in different health services.
Findings reveal differences in social media usage
depending on the services provided by a hospital.
Findings from this research show that 95% of the top-
ranked hospitals use social media in the world. The
purpose of this study is to examine whether social
media usage varies according to the size of the
hospital and the types of services provided.
Social media depend on mobile and web-based
technologies to create highly interactive platforms via
which individuals and communities share, co-create,
discuss, and modify user-generated content. Social
media refers to the means of interactions among
people in which they create, share, and exchange
information and ideas in virtual communities and
networks. Andreas Kaplan and Michael Haenlein,
2010 define social media as "a group of Internet-
based applications that build on the ideological and
technological foundations of Web 4.0, and that allow
the creation and exchange of user-generated content.
It introduces substantial and pervasive changes to
communication between organizations, communities
and individuals.
Social media differentiates from traditional
industrial media in many aspects such as quality,
reach, frequency, usability, immediacy and
permanence. There are many effects that stem from
internet usage. According to Nielsen, internet users
continue to spend more time with social media sites
than any other type of site.
Modern social media first surfaced in the early
1990s. One of the first social media sites was created
in 1994, and it was called "Geocities." The concept
was for users to create their own websites,
characterized by one of six "cities" that were known
for certain characteristics.
The criticism of social media is about its
exclusiveness as most sites do not allow the transfer
of information from one to another, a disparity of
information available, issues with trustworthiness and
reliability of information presented, concentration,
ownership of media content, and the meaning of
interactions created by social media. There are some
argued that social media has positive effects such as
allowing the democratization of the internet while
also allowing individuals to advertise themselves and
form friendships. But most people associate social
media with positive outcomes, yet this is not always
the case.
Social media marketing refers to the process of
gaining website traffic or attention through social
media sites. Social media marketing programs usually
center on efforts to create content that attracts
attention and encourages readers to share it with their
social networks. A corporate message spreads from
user to user and presumably resonates because it
appears to come from a trusted, third-party source, as
opposed to the brand or company itself. (Moller, K.
2006).
Hence, this form of marketing is driven by word-
of-mouth, meaning it results in earned media rather
than paid media. Social media has become a platform
that is easily accessible to anyone with internet
access. Increased communication for organizations
fosters brand awareness and often, improved
customer service. Additionally, social media serves
as a relatively inexpensive platform for organizations
to implement marketing campaigns.
15% of the tweets in the world, produced by the
people of Indonesia. Ranks are the third after Brazil
and the United States in possession of a twitter
account. There were 4,883,228 Indonesian owned
twitter account and tweet 22,707,725 from Indonesia.
The data is taken until January 2019. Currently,
Indonesia is the second-largest Facebook users, after
the United States. Mid- January to December 2018,
noted the development is fantastic. In the mid-growth
enlarges to 79 million users. Women's figure ranks
first with 59% and the rest is for men.
KPJ Permata Hijau Hospital Jakarta that time not
many hospitals providing services specifically
surgery in Jakarta. The hospital has more than 100
beds.
At this time there are several hospitals that also
provide similar services. Even some of them are
located close to the hospital. Although KPJ Hospital
is well known to the public as specializes in the
general services, the existence of other hospitals
began to be perceived as a threat by the KPJ Permata
Hijau Hospital management. To deal with these
threats, management felt the need for an innovative
marketing strategy. one of the strategies to be used
using social media marketing. This study is to
investigate Marketing Mix Using Social Media For
Hospital (KPJ), Permata Hijau Jakarta, Indonesia.
The objective is to improve marketing services in KPJ
Permata Hijau by using social media, related to two
big issues of the BOD and hospital management
1. KPJ needs to maintain and increase service
concept and service aspects of healthcare?
2. KPJ needs to maintain and increase service quality
by increasing human resources (knowledge,
attitude & skill), upgrade of supportive new
technology, feature, hospital esthetic, instruments
and infrastructures in the digital era?
Marketing Mix Study using Social Media in Hospital
407

2 METHODOLOGY
Much similarity research has been done but there are
none found for Jakarta based joint cooperations
hospital business type. The study will investigate the
effects of different social media in terms of gender,
economic profile, age, education and IT skill of the
customers of the hospital.
A survey questionnaire will be designed and used
as a tool for data collection. The analysis will be done
using the statistical package. The research design will
be using cross-sectional, chi-square tests. The result
from the data collection will be coded and input into
statistical method. Based on the others research this
statistical test will be carried out by the researcher to
test the effect of social media in hospital marketing
services. The study expects that social media will
improve marketing services in KPJ Permata Hijau.
Analysis of the relationship between Internet use and
decision to select hospital will be shown that patients
who decided to select KPJ. The patients will analyze
that they were used and or better to use the internet
(social media) and patients will analyze that they
were poor or not to use social media (Instagram,
Facebook, Twitter, Blog, and Youtube). In the future
KPJ Hospital will need to maintain and increase
service product quality by increasing human
resources (knowledge, attitude & skill), upgrade of
supportive facility technology, feature, hospital
esthetic, instruments and infrastructures as well as all
aspects of service activities existing in the hospital.
The population of this study comprised of the
inpatients and outpatients of KPJ Permata Hijau
Hospital. For measuring customer decision, primary
data was collected from the respondents, were either
the patients themselves or their relatives. Sample
selection, with a random sampling procedure, was
followed. The information was collected through a
pre-designed, structured questionnaire. This design of
the research is a cross-sectional study so that it only
gives a temporary description concerning
independent and dependent variables at the same
time. The relationship between independent and
dependent variables can neither explain causal
correlation but only show possible correlation. Data
were collected by subjective questionnaires so that
the truth of data was dependent on the honesty of
respondents when they answered. Nevertheless, the
researcher had tried to explain the purpose of this
research in order that respondents answered the
questionnaires by a pot luck.
3 THE DECISION TO SELECT
KPJ PERMATA HIJAU
HOSPITAL
According to London and Bitta (2004:2), hospital
consumer behavior is process of decision making
requiring individual activities to evaluate, obtain, use
or regulate goods and services. Cultural factors,
specific culture, social class, social groups and
reference and family groups affect consumer
behavior. In addition, motivation, observation,
learning, personality and self-concept as well as
attitude also affect consumer behavior (Dharmmesta
& Handoko, 1997).
Results of research conducted for patients based
on Decision to Select KPJ will be show that, of total
respondents, the proportion is the same, namely,
those who decided to select “Yes” and or those who
did not decide to select “No” used facilities of KPJ.
Each of the patients has the right to select health
service facilities in marketing (Bagozzi, R.P.
Gopinath, M. & Nyer, P.U. 1999).
Each of the consumers (patients) does various
types of decisions on search, purchase, use of various
products and brands in a certain period. Consumers
make decisions every day or every specific period
without realizing that they make decisions. The
discipline of consumer behavior tries to learn how
consumers made decisions and understand what are
factors affecting and involved in decision making.
In learning consumer behavior, one approach
used is process of decision making. This is can be
meant as a process of evaluation or selection of
various alternatives pursuant to specific interests by
establishing a choice found most profitable. Peter and
Olson (2000: 160) suggested that “decision making of
consumer is a process of integration combining
knowledge to evaluate two or more behavior
alternatives and select one of them”. While Sciffman
and Kanuk (2000: 437) found that “Process of
decision, in principle, is to select one alternative of
various alternatives. In context of consumer behavior,
decision-making can be found as a process where
consumer evaluates various choice alternatives and
select one or more alternatives needed based on
specific considerations. This definition confirms that
a decision does not have to select one of alternatives,
but decision must be based on relevance between
problems and goals.
Consumer behavior will determine process of
decision-making in purchasing health service that
helps KPJ Brands connect with consumers (patient).
The process, according to Basu and Hani (1997: 106),
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
408
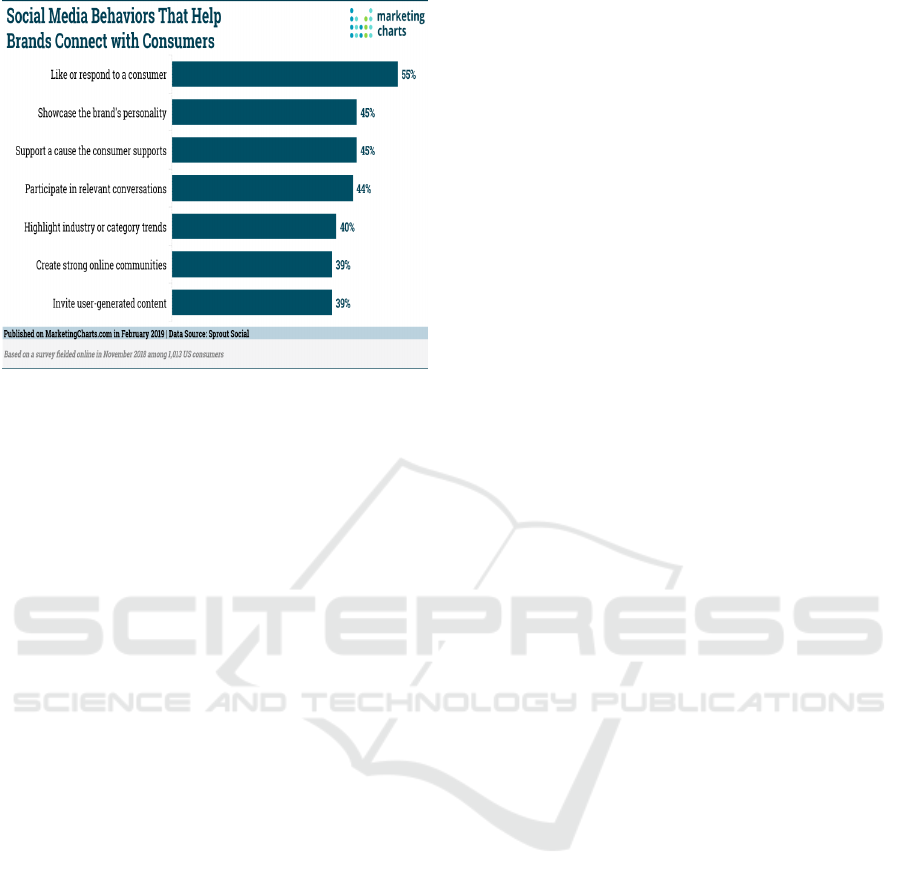
Figure 1: Social Media Behaviors That Help Brands
Connect with Consumers, February 2019.
is approach to solve problems consisting of five
following stages: (1) analyzing or introducing need
and desire; (2) searching information and evaluating
sources; (3) evaluating and selecting purchase
alternatives; (4) deciding to purchase; and (5)
behavior after purchase. All of the processes are not
always conducted by consumers in their purchase.
Some stages of processes which are not implemented
are only possibly found in emotional purchase. Thus,
all of the processes are usually conducted in only
certain situations, such as, in first purchase, or in
purchase of product having high price.
4 INTERNET USE
RELATIONSHIP WITH
DECISION TO SELECT KPJ
HOSPITAL
Analysis of relationship between Internet Use and
decision to select hospital by patients who decided to
select KPJ should be based on the social media.
Social media have vital role in promoting and
socializing KPJ to society, so that people have access
to information on provided service facilities. Before
people use hospital service, they have previously
understood service products provided in hospital.
Therefore, it is important to hospital to increase
marketing activities which so far have been
implemented via social media. The way is easy, cost
is relatively lower, time is not difficult but effect is
high to hospital. Social media are channels or
instruments of social friendship on-line in internet.
Social media users are communicating, interact, send
messages to each other, and mutual sharing and
networking. Andreas Kaplan and Michael Haenlein
(2010), defined that the social media as “A group of
internet-based applications building on basis and
technology bases, and enabling creation and
exchange of user-generated content”.
5 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
PRICE AND DECISION TO
SELECT KPJ HOSPITAL
Studies by Durva Sula, Srinivas, Steve Lysonski and
J. Craigh Andrews (1993) are consistent with studies
by Fan, Jessie X and Jing. J. Xiao (1998) stating that
the style of decision- making is affected by price,
trademark, and promotion.
Price is one of determinant factors in selecting
brands associated with consumer’s decisions to
purchase. When selecting available brands,
consumers would evaluate price not absolutely but
comparing some standard prices as reference to make
purchase transactions. According to Doyle and
Saunders (1985: 56), price determines empirical
evidence stating that a way to reduce price is to
increase threat when price will be raised. Other
factors indicating that consumers also consider past
price and form of expectation of future price which
may not be optimum, if consumers postpone to get the
hospital services in anticipating price of other quality
brands, but price reduction in lower quality brands
will not make consumers move to other similar
quality brands.
This research will be analyzed relationship
between service, price, and decision to select hospital
indicating then it can be concluded that there is
relationship between service price and decision to
select hospital. The analysis means that patients
would be or would not be saying that price was
achievable had chance more times longer to decide to
select KPJ than patients saying that price was
unachievable.
In additions nearly like study by Ribhan (2006)
also examined whether attributes of product, price,
promotion, and distribution of product were factors
affecting brand switching. Results of the research
show that attributes of product did not have real effect
on the brand switching, price, promotion and
distribution of product directly affecting brand
switching. Study by Meyliana (2008) suggested that
factors of availability and service, quality, price,
feature, and advertisement are factors affecting
Marketing Mix Study using Social Media in Hospital
409

consumers in selecting products. This research is
consistent with researches conducted by Durva Sula,
Srinivas, Steve Lysonski and J. Craigh Andrews
(1993), J. Xiao (1993) and Meyliana (2008) stating
that there are relationships between prices and
decision to select hospital service.
6 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
PRODUCT AND DECISION TO
SELECT KPJ HOSPITAL
Product quality is all characteristics and traits of a
product or service affecting ability to meet needs
stated or written (Kotler, 2005). Meaning of
multidimensional quality service is quality pursuant
to health service users and health service provider
(Azwar, 1996).
The results of other research like study by
Meyliana (2008) stating that factor of product quality
affected consumers in selecting products.
Service quality is benchmark to determine
decision to purchase or not of service users, because
service quality would enable to evaluate performance
and feel satisfaction or not of them to service given
by service provider. Zeithaml (1998) suggested that
service quality is result of customer’s assessment for
superiority or specialty of service overall. If produced
values are positive values, this service quality would
affect decision to purchase.
7 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
LOCATION AND DECISION TO
SELECT KPJ HOSPITAL
According to Heizer and Render (2006), goal of
location strategy is to maximize location profit for
company (hospital). Decision of location is frequently
dependent on type of business. An analysis of
location in industrial sector, a made strategy focuses
on maximization of profit. It is caused by
Manufacture Company finding that cost tends to be
different from different locations, while Service
Company finds that location often has impact on
benefit than cost. Therefore, service business with
specific location frequently affect benefit than coast
it means that location for service business should
focus on establishment of business volume and
income.
The analysis of relationship between hospital
location and decision to select KPJ will be show that
there were some patients saying that the location was
difficult or not difficult to access. Results of this can
be concluded that there is relationship or not, between
location and Decision to Select KPJ. This research
can be considering and consistent with research
conducted by Heizer and Render (2006) on
relationship between location and decision to select
hospital. Selection of location for hospital must be
conducted carefully. Although success is not only
dependent on location of hospital, but also factor of
location will affect success of a hospital business.
Customers always consider getting care by seeing
consistent location factor. Therefore, business actors
must consider strategic things in determining
location. Because strategic location is associated with
customers’ decision to purchase or use a product
(Bauer, 1993).
8 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
PROMOTION AND DECISION
TO SELECT KPJ HOSPITAL
Promotion is one vital aspect in marketing
management in marketing services, and it is
frequently said as sustainable process. Promotion
makes individual who is not interested in purchasing
a product previously become individual who is
interested and trying product so that consumer does
purchase. Promotion type or promotional mix,
according to William J. Stanton in Basu Swasta and
Irawan (1990: 349), is combination of best strategy in
variables of advertising, personal selling, and other
promotional media, where all are planned to achieve
goal of sales programs.
Analysis of relationship between activities of
hospital promotion and decision to select KPJ will be
means that patients know or not know that the
promotional activities were good had chance e times
longer to decide to select KPJ than patients will know
that promotional activities were good or poor. The
research is can be conducted by research of Ribhan
(2006) and Meyliana (2008) that finding that
promotion and advertisement have positive effect on
consumers’ decision. Studies by Durva Sula,
Srinivas, Steve Lysonski and J. Craigh Andrews
(1993) are consistent with studies by Fan, Jessie X
and Jing J. Xiao (1998) finding that style of decision-
making is affected by price, brand and promotion. In
addition, study by Ribhan (2006) also examined
whether attributes of product, price, promotion, and
distribution of product are factors affecting brand
switching.
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
410

9 THE MOST DOMINANT
VARIABLE
According to Fandy Tjiptono (2000: 54), product
quality has close relationship with attitude of
consumers’ decision to purchase. Where product
quality gives motivation to consumers make strongly
close relationship with company. In long term, such
relationship enables hospital to understand accurately
expectation of customers and their need for care
service. Results of multivariate analysis using logistic
regression usually indicate that, in fact, variables
significantly associated with decision to select
hospital are use of internet, price, product, location
and promotion. Research in KPJ will be give the new
idea of information about the most factors affecting
patients to decide to select care and treatment in the
hospital was like the factors of product also quality.
Patients that will be motivated them to select
considering that KPJ is one of very specific or
common cases reference well-known in Jakarta, even
in Indonesia, so that each individual experiencing
condition on surgeon or others disease is referred to
the hospital. The research will give KPJ Hospital has
specific service differentiation which is not certainly
owned by other hospitals, so that it always becomes
the hospital management expected as a reference
center hospital in the future.
REFERENCES
Anantha Raj A. A. (2012). The Effect of Marketing Mix
and Customer Perception on Brand Loyalty. IOSR
Journal of Business and Management, 4(2). Retrieved
from: http://iosrjournals.org/iosr-jbm/papers/Vol4-
issue2/A0420111.pdf
Azwar. (1996). Healthcare Quality Services. Jakarta:
Pustaka Sinar Harapan
Bauer (1993). Adverse Exposures and Use of Universal
Precautions Among Perinatal Nurses, Journal of
Obstetric Genycologc & Neonatal, Volume 22, Issue 5,
September 1993, page 429-435.
Bagozzi, R.P. Gopinath, M. & Nyer, P.U. 1999. The role of
emotions in marketing, Journal of the Academy of
Marketing Science, 27(2):184–206.
Bahman Saeidi Pour, Kamran Nazari and Mostafa Emami
(2013). The effect of marketing mix in attracting
customers: Case study of Saderat Bank in Kermanshah
Province. African Journal of Business Management,
7(34), pp 3272-3280. Doi 10.5897/AJBM12.127.
Bannon, D. (2012). State of the media: The social media
report - 2012. New York, NY: Nielsen Holdings N. V.
Barnes, N.G. (n.d). Social media usage now ubiquitious
among US top charities, ahead of all other sectors.
Retrieved from: http://www.umassd.edu/cmr/studies
and research/socialmediatopcharities/
Barnes, N.G. (n.d.). The Fortune 500 and social media: A
longitudinal study of blogging, Twitter and Facebook
usage by America’s largest companies. Retrieved from:
http://www.umassd.edu/cmr/studiesandresearch/bloggi
ngtwitterandfacebookusage/
Bennett, A. R. (1997). The five vs - a buyer’s perspective
of the marketing mix. Marketing Intelligence &
Planning, 15(3), 151-156. Retrieved from:
https://www.deepdyve.com/lp/emerald-publishing/the-
five-vs-a-buyer-s-perspective-of- the-marketing-mix-
S08oars0iY
Borden, N. H. (1965). The concept of the marketing mix. In
Schwartz, G. (Ed), Science in marketing. New York:
John Wiley & Sons, 386-397.
Boyd, D., & Hargittai, E. (2010). Facebook privacy
settings: Who cares? First Monday, 15(8). Brake, D.K.
(2009), The social media bible, tactics, tools &
strategies for businesssuccess. John Wiley & Sons, Inc
Brenner, J. (2013). Pew Internet: Social Networking (Full
Detail). Washington, DC: Pew Internet & American
Life Project: Pew Research Center.
Briones, R.L., Kuch, B., Liu, B.F., & Jin, Y. (2011).
Keeping up with the digital age: how theAmerican red
cross uses social media to build relationships. Public
RelatRev, 37(1):37–43.
Burson-Marsteller. (2009). The Global Social Media
Check-Up Study. Retrieved June 15, 2010, from
www.bursoan-marsteller.com
Burson-Marsteller. (2011). 2011 Fortune Global 100 social
media study. Retrieved June 16, 2011, from
www.burson-marsteller.com
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: CDC eHealth
metricsdashboard. [http://www.cdc.gov/metrics/social
media/index.html].
Chai, L. G. (2009). A Review of Marketing Mix: 4Ps or
More? CCSE International Journal of Marketing
Studies may 2009.
Chew, C., & Eysenbach, G. (2010), Pandemics in the age
of Twitter: content analysisof tweets during the 2009
H1N1 outbreak. PLoS One, 5(11):e14118.
Chong, K. W. (2003). The Role of Pricing in Relationship
Marketing - A Study of the Singapore Heavy
Equipment Spare Parts Industry, PhD Dissertation,
International Graduate School of Management,
University of South Australia.
Culliton, J. W. (1948). The Management of Marketing
Costs. Division of Research, Graduate School of
Business Administration, Boston, MA: Harvard
University.
Curtis, L., Edwards, C., Fraser, K.L., Gudelsky, S.,
Holmquist, J., Thornton, K., Sweetser, K.D. (2010).
Adoption of social media for public relations by non-
profit organizations. Public Relat Rev., 36(1):90–92.
Cutler RP (2000). "Principles of Marketing" translation
Parsayyan A. (1383), published Birthdays.
Dharmmesta, Basu Swastha & Handoko, Hani T. (1997).
Marketing Management Customer Behavior Analysis.
BPFE- Yogyakarta. Indonesia
Marketing Mix Study using Social Media in Hospital
411

Dunay, P. & Krueger, R. (2010), Facebook Marketing for
Dummies. Wiley Publishing,Inc. Ellison, N.B.,
Steinfield, C., & Lampe, C. (2011). Connection
strategies: Social capital implications of Facebook-
enabled communication practices. New Media and
Society, 13(6), 873–892. doi: 10.1177/
1461444810385389
Ellison, N. B., Steinfield, C., & Lampe. C. (2007). The
benefits of Facebook ‘‘friends’’: Social capital and
college students’ use of online social network sites.
Journal of Computer- Mediated Communication, 12(4),
1143–1168.
Ellison, N. B., Steinfield, C., & Lampe. C. (2007). The
benefits of Facebook ‘‘friends’’: Social capital and
college students’ use of online social network sites.
Journal of Computer- Mediated Communication, 12(4),
1143–1168
EMarketer. (2012). Consumers spending more time with
mobile as growth slows fortime online. New York, NY:
eMarketer.
Evans, D., & Bratton, S. (2008). Social Media Marketing:
An Hour A Day. Indianapolis, IN: Wiley.
Farrow, H., & Yuan, Y.C. (2011). Building stronger ties
with alumni through Facebook to increase volunteerism
and charitable giving. Journal of Computer-Mediated
Communication, 16(4), 445–464. doi:10.1111/j.1083-
6101.2011.01550.x
Frey, A. W. (1961). Advertising (3rd ed.). New York: The
Ronald Press.
Frost, J. H., & Massagli, M.P. (2008). Social uses of
personal health information within Patients Like Me, an
online patient community: What can happen when
patients have access to one another’s data. JIMR,
10(3):e15.
Grönroos, C. (1994). From Marketing Mix to Relationship
Marketing: Towards A Paradigm
Shift in Marketing. Management Decision, 32(2), 4-20.
Gupta, A. & Sapienza, H. ‗Determinants of venture capital
firm‘s preference.‘
Hargittai, E. (2007). Whose space? Differences among
users and non-users of social network sites. Journal of
Computer-Mediated Communication, 13(1), 276–297.
doi:10.1111/j.1083-6101. 2007.00396
Hodder Education (n.d). Introduction to the Marketing Mix
- Pricing. [Online] Available: http://www.hodder
samplepages.co.uk/pdfs/cceabus6.pdf.
Holm O (2006). Integerated Marketing Communication:
From Tactics to Strategy Corporate
Communication. An International Journal, 11(1).
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marketing accessed on
04/11/2014
Jernigan, C., & Mistree, B.F.T. (2009). Gaydar: Facebook
friendships expose sexual orientation. First Monday,
14(10).
Junco, R. (2012). The relationship between frequency of
Facebook use, participation in Facebook activities, and
student engagement. Computers & Education, 58(1),
162–171. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.2011.08.004
Kaplan, A. M., & Haenlein, M. (2010). Users of the world,
unite! The challenges and opportunities of social media.
Bus Horiz, 53, 38–59.
Kent, R. A. (1986). Faith in the four Ps: An alternative.
Journal of Marketing Management, 2, 145-154.
Kotler, Philip. 2005. Marketing Management, 1 and 2.
Jakarta: PT. Indeks, Gramedia Group.
Lazer, W. & Kelly, E. K. (1962). Managerial Marketing:
Perspectives and Viewpoints. IL: Richard D. Irwin.
Lazer, W., Culley, J.D. & Staudt, T. (1973). The Concept
of the Marketing Mix, In Britt, S. H. (Ed.), Marketing
Manager’s Handbook. Chicago: The Dartnell
Corporation, 39-43.
Lenhart, A., Purcell, K., Smith, A., & Zickuhr, K. (2010).
Social media & mobile internet use among teens and
young adults. Pew Internet & American Life Project.
Retrieved September 16, 2011 from http://pew
internet.org//media//Files/Reports/2010/PIP_Social_
Media_and_Young_Adults_
Report_Final_with_toplines.pdf
Leonardi, P., Huysman, M., & Steinfield, C. (2013).
Enterprise social media: Definition, history, and
prospects for the study of social technologies in
organizations. Journal of Computer Mediated
Communication, 19(1), October, 1-19.
Levy, J. (2010), Facebook Marketing, Designing Your Next
Marketing Campaign. Indianapolis, Indiana 46240
USA
Lewis, K., Kaufman, J., Gonzalez, M., Wimmer, A., &
Christakis, N. (2008). Tastes, ties, and time: A new
social network dataset using Facebook.com. Social
Networks, 30(4), 330–342. doi:10.1016/j.socnet.
2008.07.002
Low, S. P. & Tan, M. C. S. (1995). A Convergence of
Western Marketing Mix Concepts and
Oriental Strategic Thinking. Marketing Intelligence &
Planning, 13(2), 36-46. Madden, M., & Zickuhr, K.
(2011). 65% of online adults use social networking
sites. Pew
Internet & American Life Project. Retrieved September 16,
2011 from http://www.pewinternet.org/Reports/
2011/Social-Networking-Sites.aspx.
Madden, M., & Zickuhr, K. (n.d.). Social networking
report.http://www.pewinternet.org/Reports/2011/Socia
l-Networking-Sites.aspx].
Mangold, W.G., & Faulds,D.J. (2009). Social media: The
new hybrid element of the promotion mix. Bus Horiz,
52, 357-365.
Mangold, W.G., Faulds, D.J. (2009). Social media: The
new hybrid element of the promotion mix. Bus Horiz,
52, 357–365.
McAfee, A. (2009). Enterprise : New collaborative tools for
your organization’s toughest challenges. Boston, MA:
Harvard Business School Press. McCarthy, E. J. (1964).
Basic Marketing. IL: Richard D. Irwin.
Merchant, R.M., Elmer, S., & Lurie, N. (2011). Integrating
social media into emergency- preparednessefforts. N
Eng J Med, 365(4):289-291.
Mickwitz, G.. (1959). Marketing and Competition. Finland:
Societas Scientarium Fennica, Helsingfors.
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
412

Möller, K. (2006). The Marketing Mix Revisited: Towards
the 21st Century Marketing by E.
Constantinides. Journal of Marketing Management, 22(3),
439-450.
Nguyen, H. (2010), Facebook Marketing in Fashion
Industry, thesis, Arcada University Applied Sciences
International Business.
Nitish,S., Lehnert, K. & Bostick, K. (2012). Global social
media usage: Insights into reaching consumers
worldwide. Thunderbird International Business
Review, 54(5), 683- 700.
Palmer, A. (2004). Introduction to Marketing - Theory and
Practice. UK: Oxford University Press.
Piskorski, M. J. (2011). Social strategies that work. Harvard
Business Review, 89(11), 116–122. Qualman, E.
(2009). Socialnomics, how social media transforms the
way we live and do business. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Radicati, S. (n.d.). Email statistics report, 2011-2015.
[http://www.radicati.com/?p=7261].
Ramesh, S. & Gupta. A. ‗Venture capital and Indian
financial sector.
Rasmussen, A. (1955). Pristeori Eller Parameterteori -
Studier Omkring Virksomhedens Afsaetning (Price
Theory or Parameter Theory - Studies of the Sales of
the Firm. Denmark: Erhvervsokonomisk Forlag.
Reports/2011/Twitter%20Update%202011.pdf].
Reza H. M., A. Halinah, B.A. Asbi, M.S Yajid, J.A Hamid,
Marketing Services Using Social Media in Siaga Raya
Hospital Jakarta Indonesia, Journal of Management and
Science, Vol.14, No 1, June 2016
Ross, C., Orr, E. S., Sisic, M., Arseneault, J. M.,
Simmering, M. G., & Orr, R. R. (2009).
Personality and motivations associated with Facebook use.
Computers in Human Behavior, 25(2), 578–586. doi:
10.1016/j.chb.2008.12.024
Safko, J., & Brake, D.K. (2009).The Social Media Bible.
Hoboken NJ: Wiley.
Schein, R., Wilson. K., & Keelan, J. (2010). Literature
Review On Effectiveness Of The Use Of Social Media.
Brampton, Ontario Canada: Region of Peel, Peel Public
Health.
Shih, C. (2009), The Facebook Era, Tapping Online Social
Networks to Build Better Products, Reach New
Audience, and Sell More Stuff. Prentice Hall.
Smith, A. (n.d.). Twitter update 2011. [http://www.
pewinternet.org/~/media//Files/
Smith, Karen Taken (2017). Hospital Marketing and
Communication Via Social Media, Journal of Service
Marketing Quarterly Volume 38, Issue 3.
Steinfield, C., Ellison, N.B., & Lampe, C. (2008). Social
capital, self-esteem, and use of online social network
sites: A longitudinal analysis. Journal of Applied
Developmental Psychology, 29(6), 434–445.
doi:10.1016/j.appdev.2008.07.002
Stern, J. (2010).Social Media Metrics. Hoboken NJ: Wiley.
Sutton, J. N. (2010). Twittering Tennessee: distributed
networks and collaboration following a technological
disaster. Proceedings of the 7th International ISCRAM
Conference: May 2010; Seattle, WA 2010
[http://www.iscram.org/ISCRAM2010/Papers/113-
Sutton.pdf].
Technorati. [http://technorati.com/blogs/directory/].
Thackeray, R., & Hunter, M. (2010). Use of empowering
youth: Use of technology in advocacy to affect social
change. Journal Comput-Mediat Commun, 15(4):577-
591.
Thackeray, R., Neiger, B. L., Smith, A. L., Sarah B Van
Wagenen. (2012). Adoption and use of social media
among public health departments. Journal BMC Public
Health12:1, 242
Treem, J. W., & Leonardi, P. (2012). Social media use in
organizations: Exploring the affordances of visibility,
editability, persistence, and association.
Communication Yearbook, 36, 143–189.
Turnbull, A.P., Summers, J.A., Gotto, G., Stowe, M.,
Beauchamp, D., Klein, S., Kyzar, K, Turnbull, R., &
Zuna, N. (2009). Fostering wisdom-based action
through Web Communities of practice: An example of
the early childhood family support community of
practice. Infants & Young Children, 22(1):54–62.
Valenzuela, S., Park, N., & Kee, K. F. (2009). Is there social
capital in a social network site?:Facebook use and
college students’ life satisfaction, trust, and
participation. Journal of Computer-Mediated
Communication, 14(4), 875–901. doi: 10.1111/j.1083-
6101.2009.01474.x
Van Waterschoot, W. (n.d). Chapter 9: The Marketing Mix
as a Creator of Differentiation, Blois: The Oxford
Textbook of Marketing, Instructor's Manual, Oxford
University Press. [Online] Available: http://www.
oup.com/uk/orc/bin/9780198775768/freelecturer/manu
al/imchap09.pdf.
VanBoskirk, S. (2009). US interactive marketing forecast,
2009 to 2014. Retrieved November 10, 2010, from
www.forrester.com
Vance, K., & Howe, W. (2009). Dellavale RP: Social
internet sites as a source of public health information.
Dermatol Clin, 27(2):133-136.
Venus referee, the rosta of Ahmad, Abdul Hamid Ebrahimi
(1386). Marketing management of the publisher.
Viswanath, K., Nagler, R. H., Bigman-Galimore, C. A.,
McCauley, M. P., Jung, M., & Ramanadhan, S. (2012).
The communications revolution and health inequalitiesin
the 21st century: implications for cancer control. Cancer
EpidemiolBiomarkers Prev., 21(10):1701–1708.
Vitak, J., Zube, P., Smock, A., Carr, C. T., Ellison, N. B.,
& Lampe, C. (2011). It’s complicated: Facebook users’
political participation in the 2008 election.
Cyberpsychology, Behavior & Social Networking,
14(3), 107–114. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2009.0226
Von Stackelberg, H. (1939). Theorie der vertriebspolitik
und der qualitatsvariation. Smollers Jahrbuch, 63(1).
Weinberg, T. (2009). The New Community Rutes:
Marketing On The Social Web (1st ed.). Sebastopol,
CA: O'Reilly.
Wells, T. & Link, M. (2014). Facebook User Research
Using a Probability-Based Sample and Behavioral
Data. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication,
(January 1
st
, 2014).
Marketing Mix Study using Social Media in Hospital
413
