
The Effect of Low-medium Intensity Training on Body Weight, Body
Fat, Visceral, Bmr, Body Age, Whole Subjects, Trunck, Arm, Leg,
Skele Whole Body in Obese Patients
Nawan Primasoni
1
, Danang Wicaksono
1
, Siswantoyo
1
, Okky Indera Pamungkas
1
1
Sport Coaching Department, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, Jl. Colombo No.1 Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Obesity, Exercises, Intensity
Abstract: The study aims to determine the effects of low-medium exercise intensity on body weight, body fat,
visceral, BMR, body age, Whole, cut, arm, leg, skole whole body exercises in obese sufferers. It can be used
to add references to audiences to try a healthy lifestyle by exercising. The study employed an experimental
method using a single group receiving treatment, then administered tests and measurements to determine the
body's response to obesity. The measurements of body composition include weight, body fat, visceral,
BMR, body age, whole subject, cut, arm, legs, skele throughout the body. From the test results, it can be
seen that T calculate from each variable > 0.05 (T-table) and large value significance probability value of
the whole variable > 0.05, then Ha is rejected, meaning that there is no exercise influence low-moderate
varying to the sufferers obesity.
1 INTRODUCTION
Intensity is a measure that indicates the quality of an
excitatory given during the exercise (stimulus in the
form of motion activity). Hidayat (1990) states that
"All explosive movements require great energy."
This means energy expenditure is an indication of
the intensity level of a job. About the intensity of
exercise by Moeloek (1984) explained, "intensity
exercises declare the weight of exercise". Later Chu
(1989:) states "Intensity is effort involved in
performing a given task". So, exercise intensity is
the magnitude of the workout load that must be
completed within a given time. To know an
intensity of exercise or workout is to measure the
heartbeat.
According to Andersen (1999) in general,
exercise intensity starts from 40 to 85% functional
capacity. In people with heart problems, exercise
intensity can be established between 40 and 60%
functional capacity. Duration of exercise can be set
according to one's response to exercise. For
example, a person must have felt recovered within
an hour of exercise. Apart from the intensity-setting
techniques and intensity levels selected, the exercise
intensity is an intensity that can be performed for 15
to 60 minutes. Basically, the final goal of
determining the intensity of the exercise is to give a
clue for someone about the intensity of the exercise
that will be able to provide maximum benefit to him
while minimizing the risk of injury (Slentz, 2004).
According to Suharto (1997:98), the exercise
intensity is a qualitative component that refers to the
amount of work performed in a given time unit. The
intensity of exercise can be highly-rated low based
on several indicators, including: 1) based on the
percentage of speed and strength used in the
exercise, 2) based on the amount of pulse in the
action of the exercise load. Intensity scale to
exercise speed and strength as follows (Suharno,
1993): (1) Super Maximum 101% – upward of the
best achievement, (2) maximum 100% of best
achievement, (3) Maximum sub 80% – 99% of the
best achievement, (4) medium 60% – 70% of Best
Achievement, (5) Low (low) 59% down from best
achievement. Bompa (1983), said that the intensity
level can be measured according to the type or form
of exercise. To exercise speed is measured in
meters/second from the execution of a movement,
while the intensity of the activity overcoming the
load can be measured in kilograms (kg), while for
team sports, it is based on the rhythm or tempo of
the game.
The intensity of exercise is the function of the
nerve stimulation force carried out in the exercise
Primasoni, N., Wicaksono, D., , S. and Pamungkas, O.
The Effect of Low-medium Intensity Training on Body Weight, Body Fat, Visceral, Bmr, Body Age, Whole Subjects, Trunck, Arm, Leg, Skele Whole Body in Obese Patients.
DOI: 10.5220/0009799606150618
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 615-618
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
615

and the strength of stimulation depends on the load
speed of movement, variation of intervals or breaks
between each of them. An element that is not less
important is psychiatric pressure during exercise. So,
the intensity is not merely measured from the effort
done by the muscles only, but also the expenditure
of energy on the nerves during exercise (Bompa,
1994).
The intensity level can be measured according to
the training type. For exercises involving speed, it is
measured in meters per second about the average
movements performed for each minute. The
intensity of the activities used to resist resistance,
can be measured in kg or kg/m (one kg is lifted up as
high as 1 metre against the weight force), while for
team sports, the rhythm of the game can help to
measure its intensity. The intensity of exercise
differs from each other depending on the specificity
of the relevant sports branch (BOMPA, 1994).
The pulse rate is one of the indicators that can be
used to determine the intensity of exercise. The
pulse is a wave that can be felt in the arteries when
the blood is in the pump out of the heart. This pulse
is easily felt in a place where there is an artery
crossing (Sandi, 2016). The blood driven toward the
aortic cystol not only moves forward in the blood
vessels, but also creates a pressurized wave that runs
along the arteries (Kasenda et al,2014). Pulse
frequency can be measured by pressing the
radialistic arteries using the index finger tip and
middle finger until the maximum pulsation can be
detected (Bickley, 2013).
Low-intensity sports have several benefits and
weaknesses, including: 1) Suitable for people who
are just starting to exercise, people who are obese,
and people who are quite advanced, 2) taking long
time so it is suitable for those who Love to enjoy the
sport for a long time, 3) Good for athletes or people
who want to improve endurance skills, such as
marathon, 4) taking long time, so it is not suitable
for those who do not have much exercise time, 5) for
those who want to lose Weight loss, will experience
problems because according to the study of Wilson,
et al., those who perform low intensity only
experience temporary weight loss because the body's
metabolism has been adapted, 6) the risk of
experiencing muscle shrinkage due to lean muscle
many activations.
A number of experts and health institutes suggest
that daily exercise is done with moderate intensity
and adequate duration. It is medium intensity for
150 minutes in a week or high intensity sports for 75
minutes a week. This duration is with a 30-minute
sports pattern in one day for 5 days a week, or with
another division but with the same end result. This
figure applies if you are aiming to maintain health
and weight. However, if you exercise with the aim
of losing weight, it may take a different portion.
That is by increasing the exercise time so that
burning calories occurs even more. Just like the
medicine, weight and age are the determinants of
how much exercise you need.
Sports can be differentiated into three, among
including: light exercise, a person only exercising
during leisure time every week. The approximate
number of calories issued in this type only ranges
from 500 calories per week. In medium or moderate
exercise, exercises are at least over 3 days a week
with an average exercise period of 30 minutes, or
when calculated based on calories ranging from
1000-2000 calories per week. Meanwhile, heavy
exercise is depicted with a longer sport and heavier
than medium sports with energy spent reaching
2000-2500 calories per week.
Researchers from Imperial College London
compared the global Body Mass Index (BMI) of
nearly 20 million adults during the year 1975-2014
with data that the level of global obesity among men
rose tripled, from 3.2 percent to 10.8 press En. For
women, more than doubling, it is up from 6.4
percent to 14.9 percent. That means that there are
266 million men of obesity and 375 million obese
women in the world in the year 2014, with all
mankind increasing heavier 1.5 kilograms every
decade since the year 1975. Researchers found that
2.3 percent of men and 5 percent of women have
become very obese, which means they have a BMI
of more than 35 kilograms per square metre. Every
year the problem of obesity becomes a spotlight that
needs special attention to handle it. The problem of
obesity has become an urgent problem around the
world, especially developed and developing
countries. If the trend of obsity is not immediately
lowered, no death rate will be greater.
Body fat should be done by someone who wants
to lose weight or improve his condition. The body
fat scales provide a clear and accurate picture of
body composition, so that it can lose weight
effectively. Monitoring of body composition should
be done in various stages. Exercise and adjusting the
diet would result in the body fat percentage would
be reduced, however this does not mean it would
lose weight. Exercising the body would produce
more muscle. Muscles are also responsible for
weight loss. With the body fat scales or 14 monitor
body composition, it can track such developments.
Body fat is not the same as body mass. The majority
of our bodies are made up of water, muscles, and fat.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
616
The percentage of body fat is a number that indicates
how much fat you have.
Visceral fat, or abdominal fat, is a type of body
fat that is in the stomach and surrounds the internal
organs. Different types of subcutaneous fats are
piled up under the skin, have less of a negative
impact on health and are easier to lose than visceral
fats. Visceral fat is associated with a number of
negative effects on health, including increased blood
pressure, dementia, heart disease, hormonal
imbalance, and insulin resistance, which can lead to
Diabetes type 2. Fat deposits actually act similarly to
the organ, and secrete substances affecting the
surrounding organs. It is thought that belly fat may
be very risky because it is near the main blood
vessel that carries blood to the liver from the whole
intestine. Some substances are excreted by fat,
especially loose fat cells, can be carried to the liver
and then affect the levels of fat and cholesterol in the
blood. Abdominal fat is also closely related to the
increase in LDL and decreased levels of HDL
cholesterol, as well as breast cancer, endometrial
cancer, and colorectal cancer. Measurements using
regular body scales have not been able to measure
other elements of the body's composition (in this
case, it is related to obesity). This consideration is
used by researchers to use a tool called Body Fat
Monitor.
Obesity is one of the sources/improve some
diseases, including: heart, stroke, high blood
pressure, cancer and many more. Given the danger
from obesity, it is necessary an attempt, a way to
prevent and overcome obesity. The need for a study
that could make the solution of obesity need to
continue to be studied from various angles, not only
from the medical corner, but from the angle of
nutrition, even sports science.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
2.1 Participants
Participants are generalization areas consisting of
objects / subjects that have certain qualities and
characteristics determined by researchers to be
studied and then conclusions are drawn. Population
in this study is Determination of the sample in this
study using purposive sampling techniques, namely
sample techniques with certain considerations
(Notoatmodjo: 2010)
2.2 Study Design
This study is experiment and uses descriptive
quantitative methods.
2.3 Data Collection technique
The data collection technique used test and
measurement. The analysis technique was done
using validity and reliability.
2.4 Statistical Analysis
The data collection technique used test and
measurement. The analysis technique was done
using validity and reliability
3 RESEARCH RESULT AND
DISCUSSION
After obtaining the data, the results were obtained.
Data obtained from these measurements were then
analysed. The data showed that:
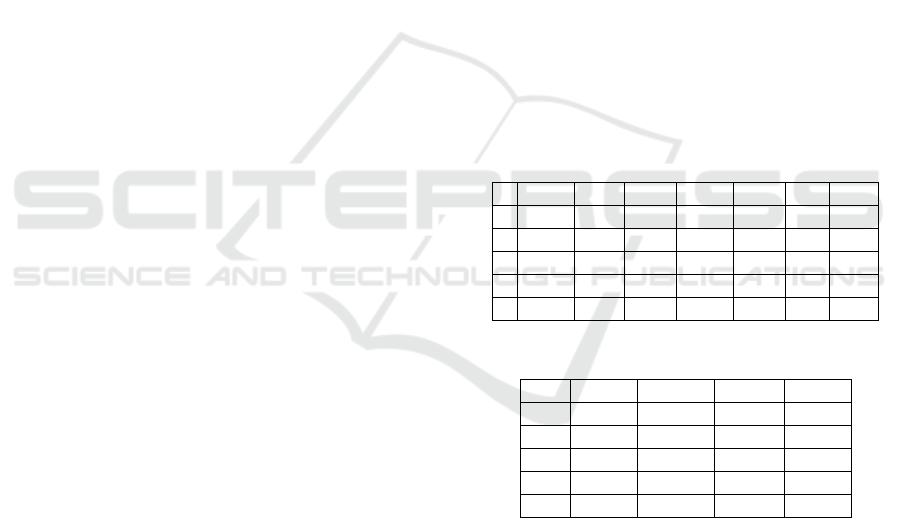
Table 1: Data
Measurement
No BB BF VES BMR BMI BA SW
1 92 41.1 14 1696 33.8 55 39.4
2 93.5 40.9 13.5 1722 33.6 55 39.1
3 84.8 36.5 11.5 1626 31.9 49 35.5
4 69.3 38.9 9 1371 28.8 45 34.7
5 116.8 36 23.5 2258 38.1 61 26.3
Table 2: Data Measurement
NO TR ARM LEG SWB
1 56.9 56.9 56.7 21.9
2 34.6 56.9 56.1 22.1
3 30.8 49 47.5 24.6
4 30.9 54.5 52.1 22.2
5 25 36.5 37.2 27.4
An analysis of the data used to answer the
hypothesis proposed is the presence or absence of
the effect of low-moderate intensity exercise on
body weight, body fat, visceral, BMR, body age,
whole subject, trunck, arm, leg, whole body skele in
obese people. Based on the results of research that
has been obtained with data analysis and hypothesis
testing, it can be concluded that there is no
significant effect of low-moderate intensity exercise
on body weight, body fat, visceral, BMR, body age,
whole subject, trunck, arm, leg whole body skele in
obese people. Exercise that is done is not able to
The Effect of Low-medium Intensity Training on Body Weight, Body Fat, Visceral, Bmr, Body Age, Whole Subjects, Trunck, Arm, Leg,
Skele Whole Body in Obese Patients
617

provide a better change in obese people in weight,
bmr, bmi.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This research aims to determine the influence of
low-moderate intensity exercises on body weight,
body fat, visceral, BMR, body age, whole subject,
Trunck, arm, leg, whole body skele in obese
sufferers from T test results can be seen that T Count
of each variable > 0.05 (T-table) and large value
significance probability value of the whole variable
> 0.05, then Ha is rejected, meaning that there is no
influence of low-moderate intensity exercise against
body weight, body fat, visceral, BMR, body age,
Subject whole, Trunck, arm, leg, skele whole body
in obese sufferers.
Based on the results of the above studies, it
shows that low-moderate intensity exercises are not
able to contribute significantly to obese sufferers.
Low-moderate intensity exercises performed for five
times a week within an hour to a half hour of
training in a month have not shown a change in the
significant of weight of one's body.
The form of the given exercise must be adjusted
to the objectives to be achieved and the
specifications you want to improve. Low-intensity
exercises are aimed at providing treatment in obese
sufferers with a wide range of treatments to improve
overall fitness. The low-medium intensity exercises
in this study consist of several exercises and have
different items each post between: Push up, sit up,
leg curl, leg extension, bench press, Chest press,
squat, and sports-game sports Happy to make
obesity sufferers.
Many factors make a person able to lose weight.
Factors of physical activity and food factors become
the one to be aware of. Both factors go hand-in-hand
to lose weight. In this research, it is not in the
control of food assumptions that are consumption of
obesity. This can also make the factor less
significant in declining weight. In addition, the
psychological guidance factors can also be done in
losing weight. Weight cannot be deducted in an
instant way, but slowly and continue. The correct
exercise and diet program would be very helpful in
weight loss programs. However, it is important to
note that there is an unaltered genetic factor that also
plays a role in obesity.
REFERENCES
Andersen, R. E. 1999. "Exercise, an Active Lifestyle, and
Obesity. Making the Exercise Prescription Work."
Physician and Sportsmedicine.
Dangsina Moeloek dan Arjadino Tjokro, 1984. Kesehatan
dan Olahraga. Jakarta: Fakultas Kedokteran
Universitas Indonesia.
Djoko, Pekik. 2002. Diktat Dasar Kepelatihan.
Yogyakarta. FIK UNY
Bompa T. 1999. Theory and methodology of training.
Human Kinetics, Chicago, IL.
Hartono.2004. Statistik Untuk Penelitian. Pekanbaru:
Pustaka Pelajar Offset
Houmard JA, Tanner CJ, Slentz CA, Duscha BD,
McCartneyJS, Kraus WE.2004. Effect of the volume
and intensity of exercise training on insulin sensitivity.
J Appl Physol. 96(1):101-6.
Hidayat, A. Aziz Alimul, 2008, Pengantar Konsep Dasar
Keperawatan, Jakarta: Salemba Medika.
Kasenda , L., Sentinuwo, S., & Tulenan, V. 2016. Sistem
Monitoring Kognitif,Afektif, dan Psikomotorik Siswa
Berbasis Android. 9(1), E-journal Teknik Informatika,
1-9
Lutan Rusli, dkk. 2000. Dasar-dasar Kepelatihan.
Jakarta: Depdiknas.
Nazir M. 2009. Metode Penelitian. Jakarta. Penerbit:
Ghalia Indonesia
Sandi, N. I. 2016. Pengaruh Latihan Fisik Terhadap
Frekuensi Denyut Nadi. Journal Sport and Fitness. 4
(2).
Sajoto. M 1998. Peningkatan dan Pembinaan
Kekuatan Kondisi Fisik. Semarang: Dahara Prize.
Suharjana. 2013. Kebugaran Jasmani. Jogja Global
Media. Yogyakarta
Sukadiyanto. 2011. Pengantar Teori dan Metodologi
Melatih Fisik, Bandung: CV Lubuk Agung
Sugiyono.2003. Statistik Untuk Penelitian. Bandung:
Alfabeta.
Surya Atmadja Djaja, dkk. 2004. ACSM: Panduan Uji
Latihan Jasmani dan Peresepannya.Penerbit: Buku
Kedokteran IndonesiaEGC
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
618
