
The Evaluation of Yogyakarta Tennis Achievement Development
System
Abdul Alim
1
, Risti Nurfadhila
1
1
Sport Coaching Department, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, Colombo Street, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Evaluation, Tennis achievement development
Abstract: Sport Achievement is associated with the reputation of a country. Almost all countries make various efforts
to improve their sports achievements, because in fact they realize that with sports the name of the country
can be lifted up to the highest class. Sports achievements development system is one of the pillars that
greatly supports the achievement of sports achievements, the highest sport achievement can only be made
through a systematic, planned, regular and continuous development program. This study aims to evaluate
tennis achievement development system in Yogyakarta. This study is an evaluation research. The subjects in
this study consist of 19 tennis athletes, 12 tennis coaches, and 14 supporting staff. This study used a CIPP
model from Daniel Stufflebeam to measure tennis achievement development system condition. A CIPP
model consists of stages on context, input, process, and product. The data were collected using
questionnaires and analysed using a descriptive analysis. The results showed that tennis achievement
development system in Yogyakarta is at poor level. Research results from athletes, coaches and supporting
staff indicate tennis achievement development system in Yogyakarta is still in the poor category.
1 INTRODUCTION
Facts show that general tennis performance in
Indonesia has decreased. Various efforts in
improving sports achievements have been carried
out by the government. One of the efforts made is to
increase the quantity and quality of sports coaching.
Sports coaching is a very important factor in
advancing and improving sports achievements,
because the level of development depends on sports
coaching. The role of achievement coaching must be
programmed optimally, to organize the coaching
nets in accordance with the programs that have been
arranged in the athlete's coaching system. Special
guidance is needed in finding new seeds and in
improving performance. Optimal performance is
obtained from the efforts of high athletes as well as
good coaching in stages and continuously. Gradually
fostering achievement has implications for the
importance of evaluations that must be carried out
periodically from the athlete's selection stage to the
final stages of the implementation of the training
program and achievements.
The concept of coaching athletes to be able to
achieve optimal performance must be done in stages
and continuously until the peak performance.
Achieving the ultimate achievement of student
coaching cannot be done individually, but must be
systemic. The starting point of the coaching stage is
sports promotion. Sports promotion is the stage that
forms the basis for achieving targets or goals from
fostering a sport. A good speaker will be able to
maximize input to be fostered into athletes who
excel, on the contrary the stage of improper
installation can make the input of prospective
athletes or talents can not be netted maximally, so
the results of the sports coaching process cannot be
achieved optimally.
In fostering the achievements of tennis, the
scouting of talented athletes is absolutely held as
early as possible. This scouting aims to get the seeds
of talented athletes as successors to high-achieving
athletes. Talented players are likened to quality raw
materials for processing into high-quality goods. To
achieve the goal of being an athlete or tennis player
who excels is not easy, because it takes awareness,
discipline, patience, and perseverance. Achievement
cannot be achieved in a matter of weeks or months,
but annually through gradual improvement in the
results of regular practice.
572
Alim, A. and Nurfadhila, R.
The Evaluation of Yogyakarta Tennis Achievement Development System.
DOI: 10.5220/0009797805720575
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 572-575
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

The discussion suggests that sports achievement
development system is a very important part of highl
level achievement, but the tennis achievement
development system in Yogyakarta has not been
studied.
Based on the explanation above, a study
regarding the evaluation of tennis achievement
development system in Yogyakarta is required. This
issue becomes the basis of the research to conduct a
research entitled as “The Evaluation of Yogyakarta
Tennis Achievement System”.
2 THEORETICAL REVIEW
2.1 Evaluation Program
Evaluation is a tool or procedure used to find out
and measure something in an atmosphere with
predetermined ways and rules. In addition to using
tests, data can also be collected using questionnaires,
observations, and interviews or other forms of
appropriate instruments (Nurhasan, 2001: 3).
Program evaluation is a systematic investigative
activity about something valuable from an object.
Another opinion (Denzin and Lincoln, 2000: 83)
says that program evaluation is oriented around the
attention of the policy maker of the funder
characteristically including the cause question about
the degree to which the program has achieved the
desired goal. Decisions made are made as indicators
of performance appraisal at each evaluation stage in
three categories: low, moderate and high.
There are many program evaluation models
developed by experts that can be used to evaluate
programs. Evaluation of the CIPP model is a concept
offered by Stufflebeam with the view that the
important purpose of evaluation is not to prove but
to improve (Stufflebeam, H McKee and B McKee,
2003: 118).
Evaluation of the CIPP model can be applied in
various fields. Nana Sudjana and Ibrahim (2004:
246) translate each of these dimensions with the
following meanings: 1) Context: the situation or
background that influences the planning of the
development program; 2) Input: the quality of inputs
that can support the achievement of the development
program; 3) Process: implementation of the program
and use of facilities in accordance with what has
been planned; 4) Product: results achieved in the
administration of the program.
2.2 Sport Achievement Development
System
Sport achievment development sytsem is an effort
made consciously, planned, organized, and directed
to achieve a predetermined goal, while according to
several experts and sources about coaching,
including, the implementation of a sports coaching
includes several components namely organization,
training programs, trainers, athletes , facilities and
infrastructure, funding, support and environment
(Sajoto, 1995: 2-5).
To foster sporting achievements in educational
institutions, in each education channel sports activity
units, sports classes, training and training centers,
sports schools, and staged and sustainable sports
competitions will be held (Undang-Undang Sistem
Keolahragaan Nasional, 2005: article 25 paragraph
6). Guidance and development of educational sports
is carried out with due regard to the potential,
abilities, interests, and talents of students as a whole,
both through intracuricular and extracurricular
activities (National Sports System Act Number 3,
2005: article 25 paragraph 4). According to
Wahjoedi, et al. (2009: 12-14) fostering superior
sports is carried out using the approach of science
and technology (Science and Technology) in
accordance with the coaching cycle from beginning
to end. Sports experts from all over the world agree
on the need for coaching stages to produce high
sports achievements, namely through the stages of
massaging, breeding and achievement.
According to Junaidi (2003: 49), it is mentioned
that the promotion of early age sports is an effort to
move early childhood to do sports activities as a
whole. With the aim of involving as many athletes in
sports as achievement, awareness arises of the
importance of sports achievement as part of efforts
to improve sports nationally. In this case, it is
required to have a good strategy, namely: (1)
providing adequate sports facilities and
infrastructure in elementary schools, (2) preparing
for the provision of sports instructors who are able to
move sports in schools, (3) holding inter-class
competitions, (4) motivating, both from within and
from outside, (5) holding demonstrations against
athletes who excel, (6) stimulating children's interest
through mass media, television, video, etc. (7)
collaborating between schools and the community
especially parents.
Nurseries are a pattern that is applied in an effort
to attract talented scientists who are researched
scientifically. What is meant scientifically is to nett
athletes with scientific application (Science and
The Evaluation of Yogyakarta Tennis Achievement Development System
573

Technology), to choose early childhood children
who are happy and love to exercise then are
identified to be athletes. In this way the development
of early childhood to become an athlete and to
achieve achievement will be higher faster (Said
Junaidi, 2003: 50). Some important considerations
for obtaining superior athlete seeds are presented as
follows: 1) Talent and high potential brought from
birth have a more dominant contribution compared
to the coaching and other supporting processes, so
finding potential athlete seeds is very important, 2)
Avoiding waste in the coaching process if the athlete
being coached has high potential brought from birth,
3) The need for Indonesia is encouraged by the
search for superior athlete seeds at an early age.
According to Bompa (1990) in (KONI, 2000: 7)
talent identification can be done by natural methods
and scientific selection methods; 1) Natural selection
is a selection with a natural approach to develop
children, then grow into athletes. 2) Scientific
selection is a selection that applies scientific
(IPTEK). Choosing young children who like to
exercise can be identified as athletes.
3 METHOD
3.1 Research Design
This research employed evaluation model.
3.2 Research Subjects
This study is an evaluation research. The subjects in
this study were 19 tennis athletes, 12 tennis coaches,
and 14 supporting staff.
3.3 Instrument and Data Collecting
Technique
The data collecting technique was using
questionnaire (CIPP Model). This CIPP model was
chosen because it is a program evaluation model that
covers all components of the management system,
so that the results of the evaluation can present
information about the weaknesses and strengths of
each system component.
In the implementation of the tennis training
program, the context component is very helpful in
determining the quality of training, while the quality
of training is the only step that must be taken to
reach the peak of performance (achievement).
Therefore the support of the government by
providing the necessary facilities such as standard
facilities and infrastructure is crucial. The human
resource input component is absolutely essential for
the initial requirements for fostering achievement so
that it is very necessary to input that meets the
criteria for quality human resources, which will
determine the Yogyakarta tennis coaching program.
Process component in this case is the process of
implementing athlete selection, preparation and
implementation of training programs to find out how
far the trainer is in preparing athletes. After that, the
evaluation will be predictable. Product component is
an embodiment of the effectiveness of the
processing of context, input and process
components. The product is also an illustration of
the quality of tennis coaching that has been carried
out
3.4 Data Analysis Technique
The data analysis technique was done using
percentage.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Result Descriptive Analysis
The data analysis results are presented as follows:
4.1.1 Perception of the Tennis Achievement
Development System by Athletes
The data Perception of The Tennis Achievement
Development System by Athletes is described as
follows:
Table 1: Perception of the Tennis Achievement
Development System from Athletes
No Cate
g
or
y
Percenta
g
e
1Poo
r
60,0
2Goo
d
40,0
Total 100,0
According to the table above, it has been known
that the category of Perception of The Tennis
Achievement Development System by Athletes is on
poor category (60.0%).
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
574
4.1.2 Perception of the Tennis Achievement
Development System by Coaches
The data Perception of The Tennis Achievement
Development System by coaches described as
follows:
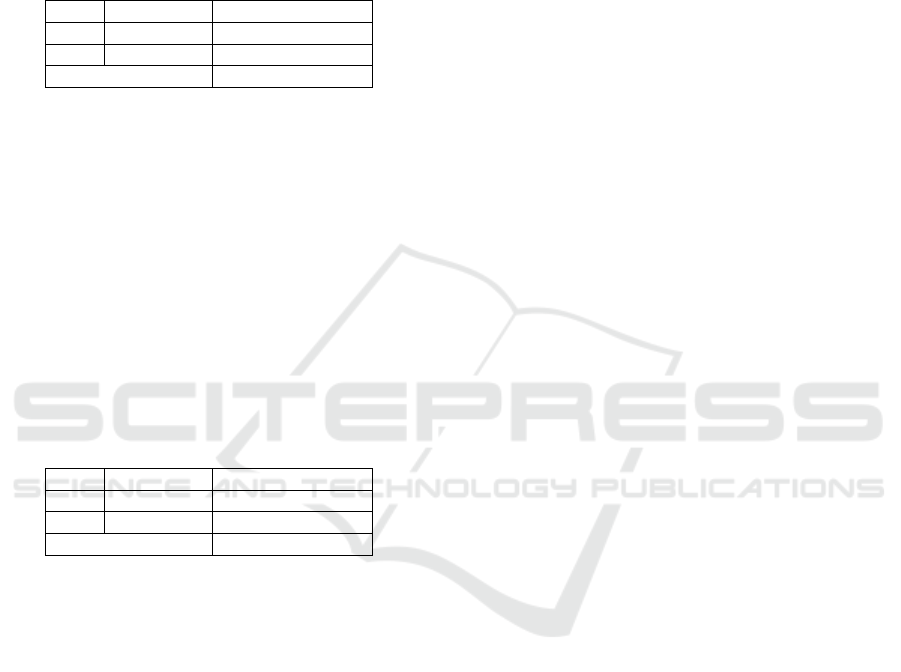
Table 2: Perception of the Tennis Achievement
Development System by Coaches
No Category Percentage
1 Poo
r
65,0
2 Goo
d
35,0
Total 100,0
According to the table above, it has been known
that the category of Perception of The Tennis
Achievement Development System by coaches is on
poor category (65.0%).
4.1.3 Perception of the Tennis Achievement
Development System by Supporting
Staff
The data Perception of the Tennis Achievement
Development System by supporting Staff is
described as follows:
Table 3: Perception of the Tennis Achievement
Development System by Supporting Staff
No Category Percentage
1 Poo
r
55,0
2 Goo
d
45,0
Total 100,0
According to the table above, it has been known
that the category of Perception of The Tennis
Achievement Development System by supporting
staff is on poor category (55.0%).
5 DISCUSSION
The research result has indicated that tennis
achievement development system in Yogyakarta is
at poor level. Research results from athletes, coaches
and supporting staff indicate that tennis achievement
development system in Yogyakarta is still in the
poor category.
When viewed in more detail, the factors which
are still obstacles in tennis achievement
development system in Yogyakarta are the problems
of budget and the welfare of athletes, coaches and
supporting staff; as well as the implementation
process of tennis achievement development process
that is less than good from the selection of trainers,
selection of athletes and the process of implementing
training.
6 CONCLUSION
The research result has indicated that tennis
achievement development system in Yogyakarta was
at poor level. Research results from athletes, coaches
and supporting staff indicate that tennis achievement
development system in Yogyakarta was still in the
poor category.
REFERENCES
Bompa Tudor O. (1990). Theory and Methodology of
Training. Debuque, Iowa: Kendall/Hunt Publishin
Djoko Pekik Irianto. (2002). Dasar Kepelatihan.
Yogyakarta: FIK UNY
Junaidi, S. (2003). Pembinaan olahraga usia dini.
Semarang: Universitas Negeri Semarang
M. Fransazeli Makorohim. 2015. Evaluasi program
pembinaan tim bola voli puteri Sumatera Selatan.
Journal Sport Area.
Nurhasan. 2001. Tes dan Pengukuran dalam Pendidikan
Jasmani. Jakarta: Direktorat Jenderal Olahraga.
Stufflebeam, D.L. H McKee and B McKee. 2003. The
CIPP Model for Evaluation. Paper presented at the
2003 Annual Conference of the Oregon Program
Evaluation Network (OPEN). Portland, Oregon.
Wahjoedi.2001. Evaluasi Pendidikan Jasmani. Rineka
Cipta. Jakarta
Undang-Undang Keolahragaan Nasional 2005 pasal 25
Undang-Undang Sistem Keolahragaan Nasional pasal 25
ayat 4
The Evaluation of Yogyakarta Tennis Achievement Development System
575
