
The Competence of the Intership 2 Student-teachers of Physical
Education Program of FKIP Bengkulu University
Dian Pujianto
1
1
Physical Education, FKIP Bengkulu University, Bengkulu
Keywords: Competence, Student-Teachers, Internship 2
Abstract: This study aims to reveal the satisfaction level of users towards graduates of physical education study
program of FKIP Bengkulu University. This research was conducted since the data gained from tracer
studies are not enough to assess the level of satisfaction of users of physical education program graduates in
the city of Bengkulu. This study uses a descriptive survey approach. The subjects of this study were
physical education teachers in Bengkulu city. A questionnaire was used as a research instrument to measure
the level of satisfaction of physical education teachers by looking at 4 competencies of the student-teachers
who joined Internship 2 program. The results show that physical education teachers have a good level of
satisfaction in general. The student-teachers’ pedagogical competence falls into the category of good; their
professional competence falls into the category of good; their social competence falls into the category of
very good, and; their personal competence falls into the category of good. Based on the results of the study,
it can be concluded that the users can receive physical education program graduates of the physical
education study program of Faculty of Teacher Training and Education Science (FKIP) Bengkulu
University with a good satisfaction level.
1 INTRODUCTION
The teacher competence as an indicator of
professional teachers is a necessity at this time.
Professional teachers are teachers who have
pedagogical, professional, personal, and social
competencies (Undang-Undang No. 14, 2005). The
Physical Education Study Program of FKIP
University of Bengkulu as one of the providers of
physical education teacher candidates in Bengkulu
province has the task of forming physical education
teacher candidates who have the 4 competence
characteristics mandated by law.
The physical education study program of FKIP
University of Bengkulu already has a lecture
program that is in line with KKNI. Unfortunately,
the level of satisfaction from the users is still
unknown. Based on this reason, it is necessary to
conduct empirical studies. Teacher competencies are
needed in improving the learning process so that the
learning outcomes can be optimal. Teacher’s
competence can be known through empirical studies.
The following is the result of research about
competencies of elementary school physical teachers
done by Pujianto et al., (2014).
Table 1: Competencies of elementary school physical
teachers in Bengkulu.
Categor
y
Percentage (%)
Ver
y
Goo
d
27,27
Goo
d
31,83
Mediu
m
31.81
Less 6,82
Very Little 2,27
Total 100
Based on Table 1, it can be concluded that there
are teachers who still have very low competence,
which is 2.27% of the population. This is a serious
challenge for the physical education study program
of FKIP Bengkulu University. The low competency
of elementary school physical teachers is no surprise
since they have no linear educational background in
physical education.
Competence of good teachers will bring a
positive influence on the teaching and learning
process in the classroom (Werdayanti and Rear,
2008). The results of this study imply that a
professional teacher who has a good category in the
4 teacher’s competencies can provide a good
influence in increasing student learning motivation,
460
Pujianto, D.
The Competence of the Intership 2 Student-teachers of Physical Education Program of FKIP Bengkulu University.
DOI: 10.5220/0009788704600464
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 460-464
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
so that the learning process becomes conducive thus
producing satisfying learning outcomes.
Professional teachers have the ability to implement
those 4 competencies in the learning process.
Professional teachers are not necessarily able to
master those 4 competencies instantly. Starting from
being a student, a teacher has been educated to
master these 4 competencies, both in the classroom
and when they carry out teaching practices in
schools which is called as ‘internship’.
Internships are mandatory courses for student-
teachers. This course provides experience on how to
teach in real situations and how to socialize in a
school education institution. Empirically,
assessments that measure the level of satisfaction of
prospective users of graduates of physical education
program in Bengkulu have not been conducted
before. Assessment of the competence of student-
teachers is based on the point of view of physical
education teachers in state schools in Bengkulu.
An assessment of a physical education teacher
would be more appropriate, because a physical
education teacher has the characteristics and
understanding of the concept of teacher competence
on physical education. Therefore, based on this
reason, an empirical study is needed to measure the
level of satisfaction of physical education teachers
who hold a teacher certificate in Bengkulu towards
the graduates of the physical education study
program at FKIP Bengkulu University.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
This type of research is qualitative descriptive
research. Qualitative descriptive research actually
describes a phenomenon that exists in nature
(Maksum, 2012). The subjects in this study were 35
physical education teachers teaching at the state
secondary schools who hold teacher certificates. The
object of the research is the competence of the
student-teachers who joined internship 2.
The data obtained in this study are from the
questionnaire. The questionnaire contained questions
relating to 4 components of competence, namely
pedagogical, professional, personal, and social.
Assessment of items uses the Likert scale (Kathleen,
2012). The data analysis technique used is the
analysis of the frequency of answers from
respondents. There are 40 question items with each
competency covered in 10 questions. The
distribution of the questions are as follows:
Table 2: Questionnaire item distribution.
Competence Question Item
Pedagogical 1,5, 9,13,17,21, 25,29,33,37
Professional 2,6, 10, 14,18,22,26,30,34,38
Personal 3,7, 11,15,19,23,27,31,35,39
Social 4,8, 12,16,20,24,28,32,36,40
Based on Table 2, there are 40 questions used to
obtain the data about the competence of the
internship student-teachers. After the data were
obtained the total score was then categorized as
follows:
Table 3: The categories of competence of internship 2
student-teachers.
Interval Class Cate
g
or
y
1,5SDI> X Ver
y
Goo
d
Mi+0,5SDI < X ≤ Mi+1,5SDI Goo
d
Mi-0,5SDI < X ≤ Mi+0,5DI Mediu
m
Mi-1,5SDI < X ≤ Mi-0,5SDI Less
X ≤ Mi-1,5SDI Ver
y
Little
(Sudjana, 2001)
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Results
The data were obtained after the questionnaire was
analyzed by looking at the frequency of the answers
from the questionnaire distributed. The following is
an overview of the data obtained:
Table 4: The description of the pedagogical competence
data of the student-teachers
Description Pedagogical Competence
Total 1412
Max 46
Min 30
Mean 40,34
Table 4 illustrates that pedagogical competence
has the highest score of 46 and the lowest score of
30 with an average score of 40.34. Next, the
following is the description of the professional
competence data:
The Competence of the Intership 2 Student-teachers of Physical Education Program of FKIP Bengkulu University
461
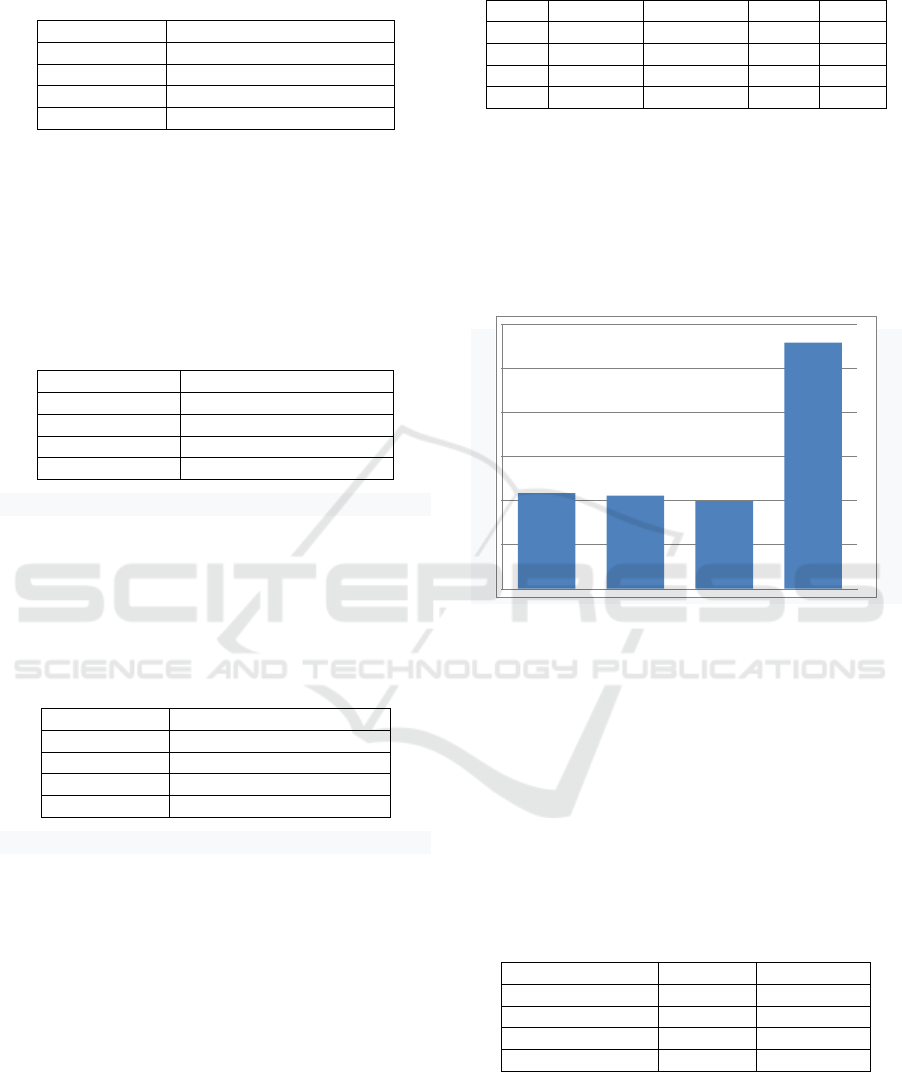
Table 5: The description of the professional competence
data of the student-teachers.
Description Professional Competence
Total 1408
Max 45
Min 33
Mean 40,22
Table 5 illustrates the professional competence
of internship 2 student-teachers with the highest
score of 45, the lowest score of 33, and the average
score of 40.22. Next, the following is an illustration
of the personal competence of the internship 2
student-teachers:
Table 6: The description of the personal competence data
of the student-teachers.
Descri
p
tion Personal Com
p
etence
Total 1399
Max 44
Min 33
Mean 39,97
Table 6 explains the personal competence of the
internship 2 student-teachers with the highest score
of 44 and the lowest score of 33 and the average
score of 39.97. Finally, the following is the social
competence of the internship 2 student-teachers:
Table 7: The description of the social competence of the
student-teachers.
Description Social Competence
Total 1651
Max 49
Min 39
Mean 47,17
Table 7 explains the condition of the social
competence of the internship 2 student-teachers with
the highest score of 49 and the lowest score of 39
with an average score of 47.17. Based on the results
of the research, it can be concluded that the social
competence of the internship 2 student-teachers has
the highest average score, that is 47.17. The personal
competence, on the other hand, has the lowest
average score, that is 39.97. The following is the
description of the overall research data:
Table 8: Description of the research results data.
Desc. Peda
g
o
g
ical Professional Personal Social
Total 1412 1408 1399 1651
Max 46 45 44 49
Min 30 33 33 39
Mean 40,34 40,22 39,97 47,17
Based on Table 8, it can be seen that the
pedagogical competence has the average score of
40.34, the professional competence has the average
score of 40.22, the personal competence has the
average score of 39.97, and the social competence
has the average score of 47.17. This information can
be illustrated in the following bar chart:
Figure 1: The competence of the student-teachers.
Figure 1 explains the level of the competence of
the student-teachers of physical education study
program of FKIP Bengkulu University who joined
Internship 2. The student-teachers’ social
competence has the highest average score and their
pedagogical competence is ranked second, whereas
their professional competence is ranked third and
their personal competence is ranked fourth. The
categorization of their competence is presented
below.
Table 9: The competence categories of the Internship 2
student-teachers
Competencies Mean Categor
y
Pedagogical 40,34 Good
Professional 40,22 Goo
d
Personal 39,97 Goo
d
Social 47,17 Ver
y
Goo
d
Based on Table 8, there are 3 competencies
which fall into the good category, namely
pedagogical, professional and personal competence.
Student-teachers’ social competence, on the other
hand, falls into the very good category
.
36
38
40
42
44
46
48
Pe
d
a
g
o
gi
c
a
l
P
r
o
f
e
s
s
i
on
a
l
P
e
r
s
o
n
al
So
c
ia
l
Competencies
Competencies
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
462

3.2 Discussion
Teacher competence is a requirement that must be
owned by a teacher or an educator. Teacher
competence education must be started to be taught to
the prospective teacher in the college and in the
teacher training programs so that they will have an
adequate capability to carry out the teaching and
learning process effectively and efficiently. This
study reveals the level of satisfaction of high school
physical education teachers who already held
teacher certificate towards the internship teaching
programs done by the student-teachers. The
competencies examined in this study were
pedagogical competence, professional competence,
personal competence, and social competence.
Based on the results of research, it turns out that
the social competence of the student-teachers has the
highest average score, which falls into the excellent
category. The high social competence of the
Internship 2 student-teachers seems to be influenced
by their good abilities in socializing with the school
environment. Moreover, in the lecture process, the
student-teachers are required to be able to interact
with the surrounding community, both through
sports tournament activities and social service
activities. The effect of community activities to
strengthen social competence is supported by the
results of research done by Ashsiddiqi which states
that social competence can be improved through
community activities (Ashsiddiqi, 2012).
Student-teachers’ pedagogical competence in
this study falls into the category of good. Generally
speaking, pedagogical competence is the ability to
educate students or manage the learning process. In
the lecture process, the student-teachers are given
the task to lead the class as a basis of managing
learning activities. From this learning experience,
they have experience in classroom management, and
to improve pedagogical competence, an internship or
a professional training program (PLP) is needed
(Suherman, 2014).
Student-teachers’ professional competence falls
into the good category. In general, to improve his or
her professional competence, a teacher must have a
linear educational basis which is included in the
graduate program (Teachers, Competence, Within,
and Program, 2014). The results of this previous
study are in accordance with the results of this
research, that the Internship 2 student-teachers have
joined teacher training program for 6 semesters so
that they already have good professional
competence.
Good personal competence means that a teacher
must become a role model for his or her students
(Ma'arif, 2017). In line with the results of previous
studies, this study finds that the personal
competence of the Internship 2 student-teachers are
in the good category, regardless the fact that in
general, they have the lowest average scores. their
personalities are generally good, but in some cases,
there were several things which could not be set as
examples for the students in the schools.
Based on the results of this study, in general, the
competence of the Internship 2 student-teachers at
the physical education program falls into the good
category. Good teacher competence can help
students develop their potential. Good teacher
competence is also able to solve all the problems
that are owned by students (Polat and Arif, 2012).
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the results of the research, it can be
concluded that: (1) the social competence of
Internship 2 student-teachers of physical education
program falls into the category of good, (2) their
pedagogical competence falls into the good
category, (3) their professional competence falls into
the category of good, and (4) their personal
competence falls into the good category. In general,
the lecture process in the physical education study
program of FKIP Bengkulu University has provided
a good level of satisfaction for users of graduates.
REFERENCES
Ashsiddiqi, M. H., 2012. Kompetensi sosial guru dalam
pembelajaran dan pengembangannya, XVII (14), 61–
67.
Kathleen, M., 2012. Research Methods in Physical
Education and Youth Sport.
Maksum, A., 2012. Metodologi Penelitian dalam
Olahraga. Unesa University Press. Surabaya.
Ma’arif, M. A., 2017. Analisis Konsep Kompetensi
Kepribadian Guru PAI menurut Az-Zarnuji. Istawa, 2,
35–60.
Polat, S., & Arif, M., 2012. The Relationship Between the
Teachersâ€TM Intercultural Competence Levels and
the Strategy of Solving Conflicts, 46(1996), 1961–
1968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.05.411
Pujianto, D., Insanistyo, B., 2014. Pemetaan profil dan
kompetensi guru pendidikan di kota bengkulu,
10(April), 30–34.
Sudjana, 2001. Metoda Statistika. Tarsito. Bandung
The Competence of the Intership 2 Student-teachers of Physical Education Program of FKIP Bengkulu University
463

Suherman, A., 2014. Pengembangan model program
pelatihan profesi untuk meningkatkan kompetensi
pedagogis mahasiswa pgsd penjas. Cakrawala
Pendidikan, 33(1), 138–146.
Teachers, F., Competence, P., Within, D., & Program, B.,
2014. World Conference on Educational Sciences -
wces 2013 future teachers professional competence
development within bachelor program –, 116, 4829–
4833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.01.1033
Undang-Undang No 14. 2005. Undang-Undang No 14
Guru dan Dosen.
Werdayanti, A., & Rear, 2008. Fakultas Ekonomi
UNNES, 3 (1), 79-92.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
464
