
Health Knowledge in Class VII Middle School Students in
Yogyakarta State Middle School 14
Wulan Azva Diana
1
, Sri Winarni
2
, Sriawan
2
1
Master Program in Sport Sciences, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, Jl. Colombo No.1 Yogyakarta, Indonesia
2
Sport Coaching Department, Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta, Jl. Colombo No.1 Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Knowledge, Health, Seventh Grade Students
Abstract: The research intends to determine how high the health knowledge of seventh grade students in SMP Negeri
(State Junior High School) 14 Yogyakarta. This research was descriptive research using survey method. The
research instrument was questionnaires with multiple choice test. The samples of the research were the 34
students of seventh grade at SMP Negeri 14 Yogyakarta. The data analysis technique was using descriptive
quantitative data analysis. Based on the result, the health knowledge of the seventh grade students in SMP
Negeri 14 Yogyakarta is mostly on the medium category. 50% of the students were in medium category,
23.52% of the students were in good category, 14.70% of the students were in less category, 8% of the
students were very less category and 2.94% of the students were in very good category.
1 INTRODUCTION
School is one formal forum that tries to carry out the
process of changing behavior through the education
process. Physical education does not only aim to
make students fit, but also has a role to play in
providing health education. Health education is an
effort to teach students how to maintain and respect
the body as a whole by developing and improving
physical, social, and emotional abilities so that they
have an awareness to achieve a healthy life behavior.
Health education is part of the overall health effort
(promotive, preventive, curative, and rehabilitative)
which focuses on efforts to improve healthy living
behaviors (Kriswanto, 2012).
Physical education (PE) is given in junior high
schools which can cover a variety of cognitive,
affective, and psychomotor aspects. These three
aspects can be achieved by various efforts in the
hope that students can experience the best of
learning. The material taught is about the
development of adolescents, balanced diet of healthy
nutrition, and description of mental health because
health does not only consist of physical health but
also psychological health. The vast majority of
studies show evidence of positive associations of
physical activity and mental health measures.
The researcher conducted a series of observation
regarding the knowledge given during the physical
education learning. However, the time to deliver
health education material was very limited so that
the students could not understand the material
delivered by the teacher. Students could not apply
the health knowledge in everyday life. There are still
many students who have not been able to identify
unhealthy food ingredients in their daily lives, there
are still some students who find it difficult to apply
health knowledge have an issue in controlling
emotions and fighting each other. The hope of
giving good health knowledge physically,
psychologically, and also socially is that students
can apply the knowledge in their daily lives and
become wiser individuals in maintaining health.
Therefore, there is a gap between the health
knowledge that has been given, with what they
practise in everyday life, in terms of balanced
healthy nutrition diet, mental health and sustainable
adolescent development. That healthy lifestyle could
make students a better person. Based on the
description above, the researchers wanted to conduct
a study entitled “Health Knowledge in Seventh
Grade at SMP N 14 Yogyakarta". This study aims to
find out how far health knowledge is delivered for
the students.
Diana, W., Winarni, S. and , S.
Health Knowledge in Class VII Middle School Students in Yogyakarta State Middle School 14.
DOI: 10.5220/0009788204350439
In Proceedings of the 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science in conjunction with the 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports
(YISHPESS and CoIS 2019), pages 435-439
ISBN: 978-989-758-457-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
435

2 RESEARCH METHOD
2.1 Research Type
This research is a descriptive study with a survey
method. The instrument in this study is a
questionnaire in the form of multiple choice
questions. This study describes seventh grade
students’ health knowledge at SMP N 14
Yogyakarta.
2.2 Research Time and Place
This research will be conducted at SMP N 14
Yogyakarta, which is located at Jalan Tentara
Pelajar, Bumijo, Jetis, Yogyakarta City, Yogyakarta
Special Region. The study was conducted on March
2019.
2.3 Research Target/Subject
The population in this study is seventh grade
students, who were in Class VII A, VII B, VII C and
VII D. Each class has 34 students. The researcher
used purposive sampling technique (Suharsimi,
2010) with certain considerations.
2.4 Data, Instrument, Data Collection
Technique
The instrument is a tool that is chosen and used by
researchers in collecting data so that the activity
becomes systematic (Arikunto, 2013). The
instrument in this study was questionnaires. The
questionnaire used in this study is a questionnaire
with close ended questions which answers have been
provided so that the respondent can only choose the
answer that matches his opinion.
Before conducting the trial, the researcher
conducted a validation / expert judgment in this
study with Drs. Sriawan, M.Kes. The trial of the
research instrument was conducted in Yogyakarta
State Middle School 14 with 34 students. Based on
the trial results, it shows that out of 36 questions
there are 4 items that fail, namely numbers 4,9,32
and 35 (r count < r table), the reliability coefficient
is 0,960.
The data needed in this study is in the form of
health knowledge of seventh grade students at SMP
Negeri 14 Yogyakarta. The steps used for data
collection are explained as follows (1) before the
questionnaire was shared, the researcher explained
to the seventh-grade students at SMP N 14
Yogyakarta about the procedure for working on the
question, (2) after all students were clear or
understood about the procedure in working on the
questions, the questions were distributed to all
seventh-grade students who have been agrred to
participate.
2.5 Data Analysis Technique
The data analysis technique used was descriptive
statistical techniques. Descriptive statistics were
used to describe the collected data (Darmadi, 2014).
The analysis used in this study uses quantitative
descriptive techniques with percentages. The
frequency is to find the relative frequency
(percentage) (Sudjiono, 2010) as follows
𝑃 =
𝐹
𝑁
× 100%
(1)
Information:
P = Percentage sought (Relative Frequency)
F = Frequency
N = Number of Respondents
Determination of Score by using Reference Norm
Research (PAN) according to (Syarifudin, 2010) in
Table 1 as follows:
Table 1. Assessment norms
No
Norms
Categories
1
X>M + 1,5 SD upward
Exellent
2
M + 0,5 SD < X ≤ M + 1,5 SD
Good
3
M – 0,5 SD < X ≤ M + 0,5 SD
Sufficient
4
M – 1,5 SD < X ≤ M – 0,5 SD
Less
5
X ≤ M – 1,5 SD
Very Less
(Source: Syarifudin, 2010: 113)
3 RESEARCH RESULTS AND
DISCUSSION
3.1 Research Results
The description of the results on health knowledge
in seventh-grade students at SMP N 14 Yogyakarta
was measured by 32 item questionnaires in the form
of multiple choices, with a score range from 0 to 1.
Based on the results, a minimum value = 15,
maximum value = 30, the mean value is = 24.35,
median = 25, and the standard deviation = 3.52.
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
436

Table 2. Description of health knowledge in seventh-grade
middle school students
Interval
F
%
Categories
> 29,65
1
2,94
Excellent
26,12 - 29,64
8
23,53
Good
22,59 - 26,11
17
50
Sufficient
19,06 - 22,58
5
14,71
Less
≤ 19,05
3
8,82
Very Less
Total
34
100
Table 2 is presented on the following diagram:
Figure 1: Diagram of health knowledge for junior high
school students in class VII in Yogyakarta State Middle
School 14
Based on the table and figure above, it is known
that health knowledge for seventh grade students in
SMP N 14 Yogyakarta were in different category.
2.94% of the student participants were in the
excellent category, 23.52% of the student
participants were in the good category, 50.00% of
the student participants were in the medium
category, 14.70% of the student participants were in
less category and 8.8% of the student participants
were in a very less category. The dominant result in
health knowledge for seventh grade students in
Yogyakarta State Middle School 14 was medium.
3.1.1 Knowledge Factors on Healthy Diet
Knowledge factors on healthy diet in this study were
measured by 10 statements, with a range of scores 0
to 1. The minimum value = 5, maximum value = 10,
mean value = 7.73, median = 8, and standard
deviation = 1.32. It is presented in the following
diagram.
Figure 2: Knowledge factors on healthy diet diagram
Based on the tables and figures above, it can be
seen that the knowledge factor towards healthy diet
which is included in the excellent category is 5.88%,
in the good category is 23.52%, in the sufficient
category is 32.29%, in less category is 26.47 % and
very less categories at 8.82%.
3.1.2 Mental Health Knowledge Factors
The research resulton mental health knowledge
in this study was measured by 12 items, with a range
of scores 0 to 1. It obtained a minimum value = 6,
the maximum value = 12, the mean value = 10.21,
median = 11, and standard deviation = 1.56. It is
presented in the following diagram
Figure 3: Mental health knowledge factors diagram
0,00%
20,00%
40,00%
60,00%
Very
Less,
8.80%
Less,
14.70%
Sufficient
, 50.00%
Good,
23.52%
Exellenct
2.94%
frequencies
Health Knowledge for Seventh
Grade Students
0,00%
5,00%
10,00%
15,00%
20,00%
25,00%
30,00%
35,00%
40,00%
Very
less,
8.82%
Less
26.47%
Sufficie
nt,
35.29%
Good,
23.52%
Excelle
nt,
5.88%
frekuensi
Knowledge Factors on
Healthy Diet
0,00%
10,00%
20,00%
30,00%
40,00%
50,00%
60,00%
Very
…
Less,
11.76%
Sufficie
nt,
23.52%
Good,
52.94%
Exellent,
0.00%
frequencies
Mental Health Knowledge
Factors
Health Knowledge in Class VII Middle School Students in Yogyakarta State Middle School 14
437
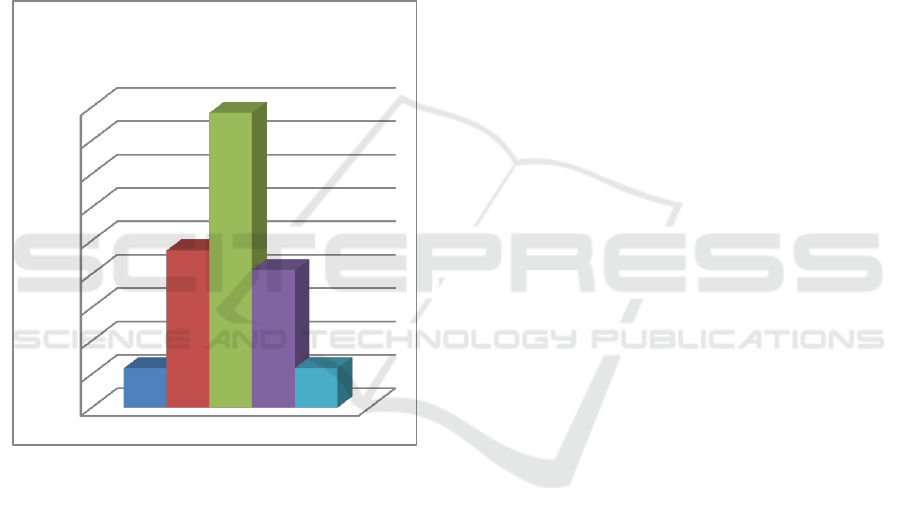
Based on the table and figure above, it is known
that the mental health knowledge factor included in
the excellent category was 0.00%, in the good
category was 52.94%, in the sufficient category was
23.52%, in the less category was 11.76% and the
very less category was very less than 11.76%.
3.1.3 Knowledge on Teenage Development
Factor
The knowledge of adolescent development in this
study was measured by 10 items, with a range of
scores 0 and 1. It obtained a minimum value = 2, a
maximum value = 10, the mean value = 6.41,
median = 6, and standard deviation = 1.94.
Figure 4: Youth development knowledge factors diagram
Based on the tables and figures above, it is
known that the knowledge factors of adolescent
development included in the excellent category was
5.88%, in the good category was 20.58%, in the
sufficient category was 44.11%, in the less category
was 23.52% and in the very less category was less
than 5.88%.
3.2 Discussion
Health knowledge affects health physically,
spiritually and socially, which is known and can
be verified. Health knowledge also includes
healthy lifestyles obtained from observing,
hearing, feeling and can be applied into everyday
life. The results show that the SMP N 14
Yogyakarta students dominnatly have a sufficient
understanding on health knowledge, with a
percentage of 50%. It is found that there are
different characteristics of seventh grade students
in physical education learning process with health
knowledge material. The material which has been
given to seventh grade students affects the
attractiveness of physical education learning.
Some are very interested and vice versa and thus
it might affect the students’ thinking ability. If the
students are interested in health knowledge
material, they will try to listen, seek, and learn so
that they are able to understand the content
material delivered by the teacher. Students lack of
health knowledge, so they have not been able to
apply it in daily life because healthy living will be
applied in daily life if someone has good
knowledge about it. It will further explain how far
is students' knowledge on healthy diet, mental
health knowledge and adolescent development
knowledge. Such good knowledge can support
students' awareness to implement healthy
behaviors.
3.2.1 Healthy Diet Knowledge Factors
Based on the results on healthy diet knowledge,
most of the students were in the sufficient category
(32.29%), which implies that students have
sufficient knowledge about healthy diet. The
students are less interested in knowledge of healthy
diet so that the material explained by the teacher
cannot be accepted by students or students do not
understand what is conveyed by the teacher. The
amount of food information circulating both from
print and social media makes students interested and
will try the food without knowing the ingredients. It
can be seen that the students’ habits of eating
unhealthy foods still exist. There are many students
buying consume junk food (fastfood) or food at
street vendors who usually contain harmful
chemicals and also.
3.2.2 Mental Health Knowledge Factors
The students were mostly in the good category of
mental health knowledge factors with a percentage
of 52.94%. The result implies that most students
have a good understanding of mental health. Mental
health knowledge material provided by the teacher
was largely about behaviors that can be seen by
others and can be felt by oneself in everyday life,
making it easier for students to understand mental
health knowledge. In the learning process, the
teacher provided examples of mental health material
0,00%
5,00%
10,00%
15,00%
20,00%
25,00%
30,00%
35,00%
40,00%
45,00%
Very
Less,
5.88%
Less ,
23.52%
Sufficie
nt,
44.11%
Good,
20.58%
Exellent
, 5.88%
frequencies
Youth Development Knowledge
Factors
YISHPESS and CoIS 2019 - The 3rd Yogyakarta International Seminar on Health, Physical Education, and Sport Science (YISHPESS
2019) in conjunction with The 2nd Conference on Interdisciplinary Approach in Sports (CoIS 2019)
438

as well as students’ empirical experience in school,
family and community so that students can
understand mental health knowledge well. It allows
students’ physical and psychological development to
run side by side which makes a positive impact on
them.
3.2.3 Teenage Development Knowledge
Factors
The students’ knowledge of adolescent development
were mostly included in the sufficient category with
a percentage of 44.11%. It could imply that most
students have understood physical growth because it
can be observed and seen clearly. Students,
therefore, can easily understand the material
presented by the teacher.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS
4.1 Conclusions
The results of the research and discussion above
revealed that mostly the health knowledge of
seventh grade students at SMP N 14 Yogyakarta
were dominnatly in sufficient category. The students
who have sufficient health knowledge were 50.00%,
students with good health knowledge were 23.52 %,
students with less health knowledge were 14.70%,
students with very less helath knowledge were
8.00% and students with excellent health
knowledge were 2.94%.
4.2 Suggestions
Based on the conclusions, there are several
suggestions that need to be conveyed. They are (1)
teachers should give the students more exposure in
health knowledge, (2) schools should always pay
attention to students' health knowledgeas,
knowledge could encourage them to enjoy healthy
living, (3) future researchers in this field should use
a wider sample and population, so that the analysis
of health knowledge for
SMP N 14 Yogyakarta
students
could be identified better.
REFERENCES
Arikunto, S., 2010. Prosedur penelitian suatu pendekatan
praktik. PT Rineka Cipta. Jakarta.
_________., 2013. Prosedur penelitian suatu pendekatan
praktik. PT Rineka Cipta. Jakarta.
Darmadi, H., 2014. Metode penelitian pendidikan dan
sosial. Alfabeta. Bandung.
Kriswanto, E.S., 2012. Konsep, proses, dan aplikasi dalam
pendidikan kesehatan. Fakultas Ilmu Keolahragaan,
Universitas Negeri Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta.
Sudjiono, A., 2010. Pengantar statistik pendidikan. PT
Raja Grafindo Persada. Jakarta.
Syarifudin, B., 2010. Panduan ta keperawatan dan
kebidanan dengan spss. Nuha Medi. Yogyakarta.
Triaca, L. M., Frio, G. S., & Aniceto França, M. T., 2019.
A gender analysis of the impact of physical education
on the mental health of brazilian schoolchildren. SSM
- Population Health, 8, 100419.
doi:10.1016/j.ssmph.2019.10041
Health Knowledge in Class VII Middle School Students in Yogyakarta State Middle School 14
439
