
Internal and External Factors That Influence Behaviour of
Physicians in Charge of Service (DPJP) within Completeness of JKN
Inpatient Discharge Summary in St. Carolus Hospital
Demi Sahhan
1
, Syefira Salsabila
1
and Witri Zuama Qomarania
2
1
Study Program Master of Public Health, Department of Health Information Management,
Esa Unggul University, Indonesia
2
Study Program Master of Epidemiology, Department of Health Information Management, Esa Unggul University,
North Arjuna Street 9, Duri Kepa, Kebon Jeruk District, East Jakarta, 11510, Indonesia
Keywords: DPJP’s Behavior, Discharge Summary, JKN, Internal, External, Personality.
Abstract: The incomplete discharge summary can allow inaccuracies in the diagnosis code and affect the INA-CBGs
payment rates, thereby impacting the JKN patient claim process. Completeness of filling discharge summaries
is the responsibility of Physicians in Charge of Services (DPJP) as a direct implementer of services in
hospitals. This study aims to analyze the influence of internal and external factors on DPJP’s behavior within
completeness JKN inpatient discharge summaries. This research is a quantitative study with a cross-sectional
research design. The population in this study is DPJP as many as 46. The sample used a saturated sample.
Based on the results of multiple linear regression analysis, internal factors (gender, personality) and external
factors (education, work environment) simultaneously have no significant effect on DPJP’s behavior in
completeness JKN inpatient discharge summaries (p-value 0.070). While partially internal factors
(personality) significantly influence DPJP’s behavior in filling JKN discharge summaries (p.value 0.033) and
other variables do not. In conclusion, there is no influence between internal and external factors
simultaneously on DPJP's behavior in filling out discharge summaries. While partially internal factors
(personality) significantly influence the behavior of DPJP in filling JKN discharge summaries at Carolus
Hospital.
1 INTRODUCTION
In early 2014, government had implemented health
insurance for the public called JKN. The National
Health Insurance (JKN) is carried out using a
mandatory social health insurance mechanism based
on Law Number 40 of 2004 concerning the National
Social Security System with the aim of fulfilling the
basic needs of adequate public health provided to
everyone who has paid their contributions or
contributions paid by the Government. The National
Health Insurance (JKN) is organized by the Health
Insurance Administering Agency or called BPJS
(SJSN Advocacy, 2011).
The problems that occur at this time in the JKN
claim process are inseparable from the
incompleteness of discharge summaries. The
incompleteness of this discharge summary can allow
inaccuracies in the diagnosis code and affect the INA-
CBGs payment rates, thereby impacting the
obstruction of the JKN patient claim process. In the
implementation, the completeness of discharge
summaries is the responsibility of the Physicians in
Charge of Services (DPJP) as the direct executor of
services in hospitals, the compliance behavior in
filling out discharge summaries in full is the
responsibility of physicians and other health
professionals (Menkes, 2014).
Based on previous research related to the
completeness of inpatient discharge summary carried
out by Ardhika at Mulia Hati Wonogiri Hospital in
2014, it showed that the complete review of reporting
information filled in the incoming diagnosis items as
many as 58 (70%) resumes filled in, final diagnostic
items were 58 (70%), surgery items 53 (64%),
historical summary items 35 (42%), examination
results and supporting items 28 (34%), development
items during treatment 23 (28%), and patient
condition items by 50 (60%). The completeness of the
authentication review filled in the items date was 32
152
Sahhan, D., Salsabila, S. and Qomarania, W.
Internal and External Factors That Influence Behaviour of Physicians in Charge of Service (DPJP) within Completeness of JKN Inpatient Discharge Summary in St. Carolus Hospital.
DOI: 10.5220/0009570201520158
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Health (ICOH 2019), pages 152-158
ISBN: 978-989-758-454-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

(38%), the physicians signature item was 33 (40%),
and the physicians' name item was 47 (57%)
(Ardhika, 2014)
This was also at Fatmawati General Hospital in
2015 by Apriyantini, obtained from 100 documents,
98% were obtained for complete primary diagnosis,
39% for incomplete secondary diagnosis, 95% for the
complete primary procedure (Apriyantini, 2016).
Problems related to completing discharge
summary form filling also still occur in 2017,
conducted by Elvisa at Prof. Orthopedic Hospital Dr.
Soeharso Surakarta, showed the completeness of
important reports on JKN patient discharge summary
forms on the final diagnosis items by 77% and on the
history items of disease by 76%, completeness of
authentication on JKN patient discharge summary
forms on physician's name items by 77%, physicians's
signature 71% and date items 75% (Elvisa, 2017).
Some of the previous studies above prove that the
problem of incomplete inpatient discharge summary
still occurs in several hospitals every year. In
implementing this discharge summary form must be
filled out by physicians/ dentists who carry out
medical practice in accordance with Permenkes No.
269 / MENKES / PER / III / 2008. Thus, problems
related to the incompleteness of this discharge
summary can be directly influenced by the behavior
of the Physicians in Charge of Services (DPJP) in
terms of filling out (Permenkes, 2008).
The behavior of physicians in filling out inpatient
discharge summaries is influenced by various factors.
Internal and external factors become one of the most
fundamental factors in influencing behavior that
explains the development of behavior from inside and
outside the individual. One of internal factor that
influences behavior is gender, this is reinforced in
research conducted by Puspito at Hermina Hospital
Depok in 2011, the results of the analysis showed that
physicians with female gender tended to complete
higher discharge summary completion with an
average completeness by 84.4% compared to men
with an average of 74.4%
(Puspitosari, 2011).
This is supported by research conducted by Rina
in 2016 at Queen Latifa General Hospital. The results
show that there is a significant correlation between
gender variables and physician behavior in filling out
discharge summaries (p.value = 0.02), alpha 5%
(Rina, 2016).
Internal factors that can also influence behavior
are personality. Based on research conducted by
Nasyroh in 2017, the Pearson correlation between
personality (Big Five Personality) and employee
performance behavior is 0.362 with a significance
score (p.value = 0.049), alpha 5%. It states that there
is a correlation between personality (big five
personalities) with employee performance behavior
(Nasyroh,2017).
In addition, external factors can also influence the
behavior of physicians in filling out discharge
summaries, in this case, explained by variables of
education and work environment. Based on the
results of previous studies conducted by Warsi in
RSUD dr. Soeratno Gemolong Sragen in 2012
obtained the results of a statistical test of the
correlation between the type of education with the
behavior of filling out the discharge summary,
showing a significance value (p.value = 0.047), alpha
5%. Therefore, there is a correlation between the type
of education with the behavior of filling out discharge
summaries (Warsi, 2012).
Then, work environment factors/ work conditions
on physicians' behavior, it was proven in previous
research conducted by Nelfiyanti at Haji Hospital
Medan in 2009 with the results of statistical tests
showing significance values (p.value = 0.01), alpha
5%. This shows that there is a correlation between the
work environment/ working conditions and
physicians' behavior within the completeness JKN
discharge summary (Nelfiyanti, 2009).
Based on observations related to completing JKN
inpatient discharge summaries in Sint Carolus
Hospital in the 2018 period, with an average of 424
JKN inpatient visits each month, in fact, there are still
incomplete discharge summaries with an average
monthly 31.8% or 135 files for the DPJP category
(Specialist), while around 3.3% or as many as 14 files
for General Physicians (Carolus, 2018).
Based on the description above, the researcher
interested in conducting research with the title
"Internal and External Factors That Influence the
Behavior of Physicians in Charge of Services (DPJP)
in Completeness JKN Inpatient Discharge Summary
in St. Carolus Hospital".
2 RESEARCH METHOD
This research is a quantitative study with a
crosssectional research design. The population in this
study is DPJP as many as 46. The sample used a
saturated sample. The research hypothesis was tested
using multiple regression analysis.
The approach taken in this study is a quantitative
approach to the research design using observational
descriptive-analytic studies. Describing the internal
factors (gender, personality) and external factors
(education, work environment), from other aspects,
Internal and External Factors That Influence Behaviour of Physicians in Charge of Service (DPJP) within Completeness of JKN Inpatient
Discharge Summary in St. Carolus Hospital
153
are analytic because researchers want to know the
effect of internal and external factors on DPJP’s
behavior within completeness JKN inpatient
discharge summary in St. Carolus Hospital
(Notoatmodjo, 2017).
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Univariate Analysis of Internal
Factors (Gender, Personality) and
External (Education, Work
Environment)
3.1.1 Internal Factors (Gender and
Personality)
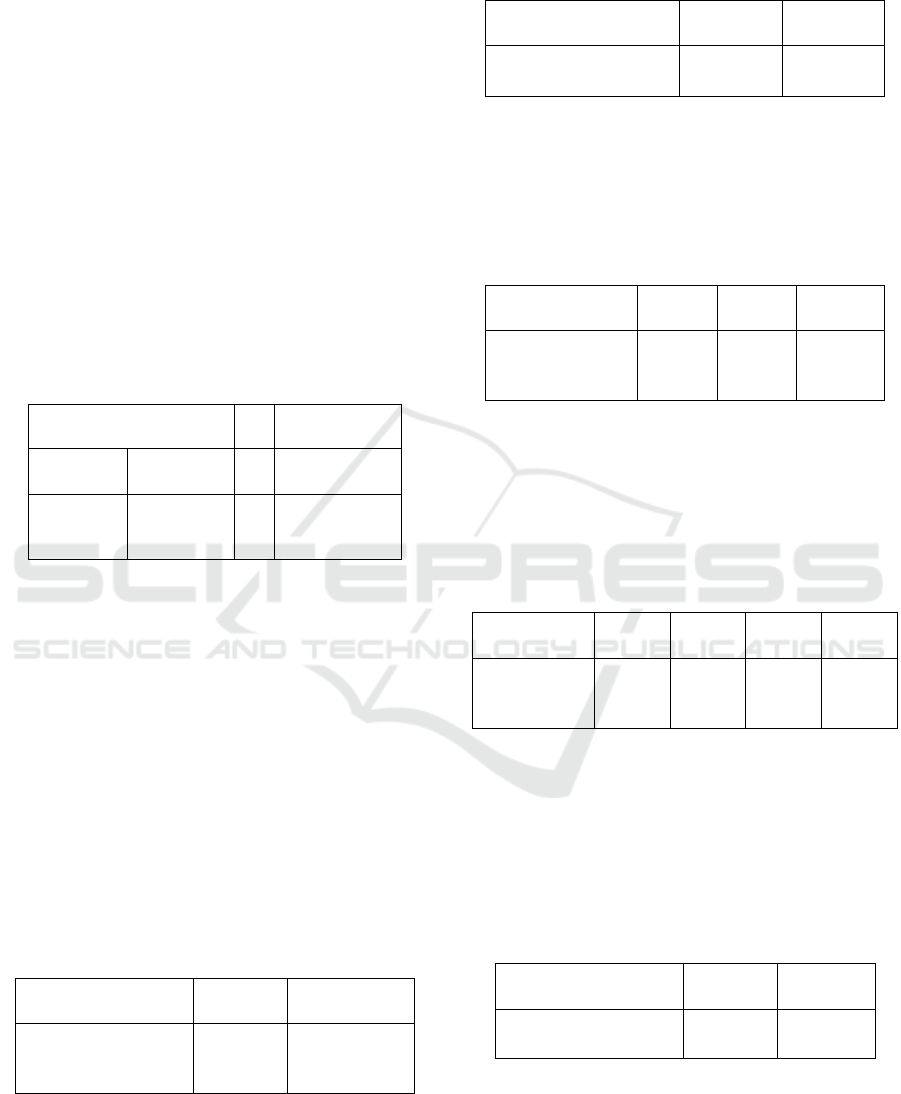
Table 1: Gender and Age.
Characteristic N Percentage
(%)
Gender Male
Female
29
17
63,0
37,0
Age 28-49 years
50-60 years
61-71 years
35
7
4
76,1
15,2
8,7
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on table 1, a total of 29 (63.0%) respondents
were male and 17 (37.0%) female. The majority of
respondents have an age range of 28-49 years by
76.1% (35 respondents), 15.2% (7 respondents) aged
50-60 years and 8.7% (4 respondents) aged 61-71
years.
It can be concluded that 46 respondents in St.
Carolus are mostly 29 (63%) men and most have an
age range of 28-49 years with a total of 35
respondents (76.1%).
The distribution of respondents' answers based on
statement items related to Personality variables is
described in the following table:
Table 2: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Personality (item 1).
Statement item 1 Highly
Agree
Agree
I like to be in groups
when I have free time
at work
13
(28,3%)
33 (71,7%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 1, out of 46 respondents
there were 33 (71.7%) respondents answered Agree
and 13 (28.3%) answered Highly Agree.
Table 3: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Personality (item 2).
Statement item 2 Highly
Agree
Agree
I can quickly make a
decision if needed
8
(17,4%)
38
(82,6%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 2, out of 46 respondents
there were 38 (82.6%) respondents answered Agree
and 8 (17.4%) answered Highly Agree.
Table 4: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Personality (item 3).
Statement item 3 Highly
Agree
Agree Less
Agree
I enjoy working
with friends to do
work
12
(26,1%)
33
(71,7%)
1 (2,2%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 3, out of 46 respondents
there were 33 (71.7%) respondents answered Agree,
12 (26.1%) answered Highly Agree and 1 (2.2%)
answered Less Agree.
Table 5: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Personality (item 4).
Statement item 4 Highly
Agree
Agree Less
Agree
Disagree
I always
friendly to my
co-workers
11
(23,9%)
25
(54,3%)
9
(19,6%)
1 (2,2%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 4, out of 46 respondents,
there were 25 (54.3%) respondents answered Agree,
11 (23.9%) answered Highly Agree, 9 (19.6%)
answered Less Agree and 1 (2.2%) answered
Disagree.
Table 6: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Personality (item 5).
Statement item 5 Highly
Agree
Agree
I am responsible for
what I do
27
(58,7%)
19
(41,3%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 5 out of 46 respondents
there were 19 (41.3%) respondents answered Agree
and 27 (58.7%) answered Highly Agree.
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
154
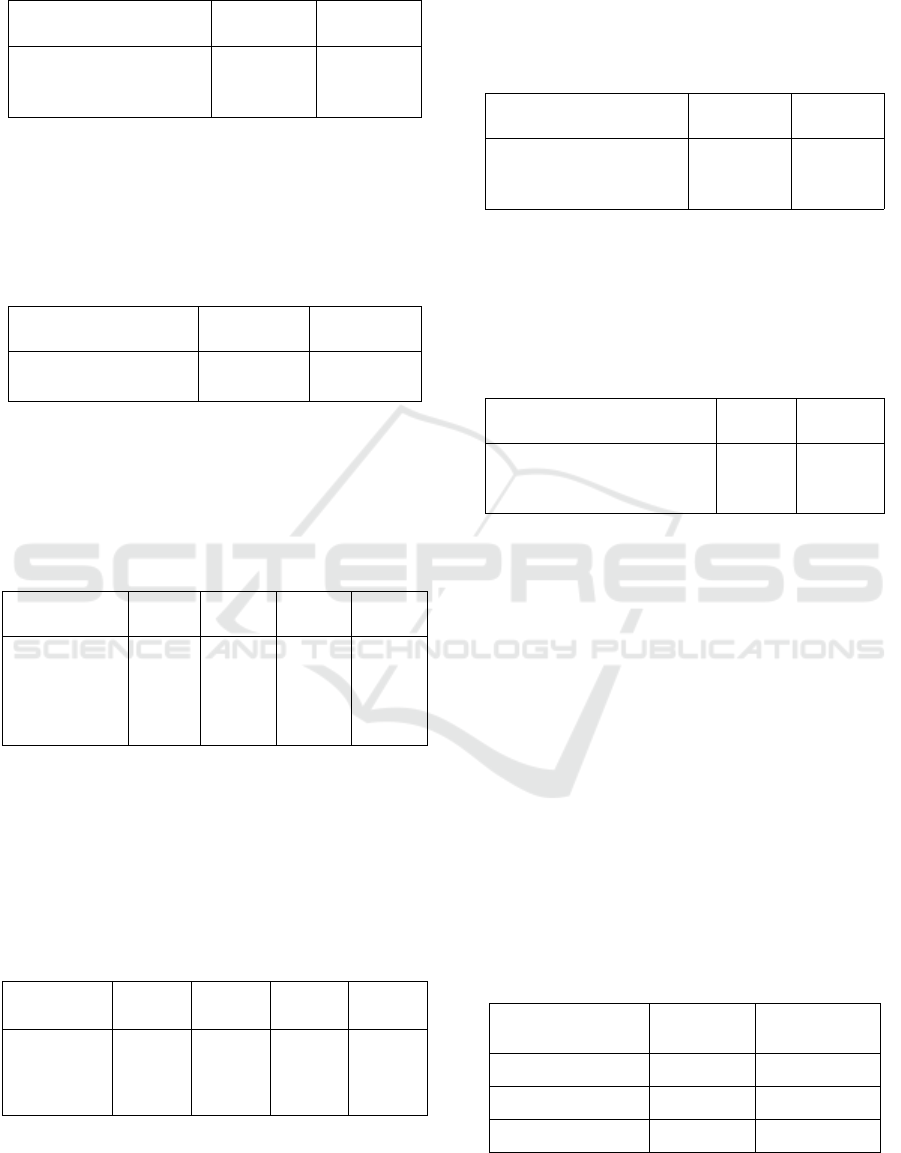
Table 7: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Personality (item 6).
Statement item 6 Highly
Agree
Agree
I do every job well as
expected by the
organization
19
(41,3%)
27
(58,7%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 6, out of 46 respondents,
there were 27 (58.7%) respondents answered Agree,
19 (41.3%) answered Highly Agree.
Table 8: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Personality (item 7).
Statement item 7 Highly
Agree
Agree
I always careful in
completing every job
11
(23,9%)
35
(76,1%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 7, out of 46 respondents,
there were 35 (76.1%) answered Agree and 11
(23.9%) answered Highly Agree.
Table 9: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Personality (item 8).
Statement
item 8
Highly
Agree
Agree Less
Agree
Disagree
I am calm in
dealing with
everything that
happens at
work
9
(19,6%)
27
(58,7%)
7
(15,2%)
3 (6,5%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 8, of the 46 respondents
there were 27 (58.7%) respondents answered Agree,
9 (19.6%) answered Highly Agree, 7 (15.2%)
answered Less Agree and 3 (6.5%) answered
Disagree.
Table 10: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Personality (item 9).
Statement
item 9
Highly
Agree
Agree Less
Agree
Disagree
I able to
control
emotions
well
17
(37,0%)
21
(45,7%)
5
(10,9%)
3
(6,5%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 9, out of 46 respondents,
there were 21 (45.7%) respondents answered Agree,
17 (37.0%) answered Highly Agree, 5 (10.9%)
answered Less Agree and 3 (6.5%) answered
Disagree.
Table 11: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Personality (item 10).
Statement item 10 Highly
Agree
Agree
I easily accepted the new
rules set by the
organization
7 (15,2%) 39
(84,8%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 10, out of 46 respondents
there were 39 (84.8%) respondents answered Agree
and 7 (15.2%) answered Highly Agree.
Table 12: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Personality (item 11).
Statement item 11 Highly
Agree
Agree
I am actively looking for
information that fits with my
work
20
(43,5%)
26
(56,5%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 11 (I am actively looking
for information that fits with my work), of the 46
respondents there were 26 (56.5%) respondents
answered Agree and 20 (43.5%) answered Highly
Agree.
Conclusions can be drawn from all items related
to personality statement, showing that the highest
percentage of answers is in item 10 (I easily accepted
the new rules set by the organization) with alternative
answers Agree of 84.8%. This shows that respondents
tend to more easily accept new rules set by the
organization, and can be categorized into personality
types Openness to a new experience.
3.1.2 External Factors (Education and
Work Environment)
Table 13: Distribution of Physician Education in St.
Carolus Hospital.
Type of education Total Percent %
Spesialist 41 89,1
Subspesialist 5 10,9
Total 46 100
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Internal and External Factors That Influence Behaviour of Physicians in Charge of Service (DPJP) within Completeness of JKN Inpatient
Discharge Summary in St. Carolus Hospital
155
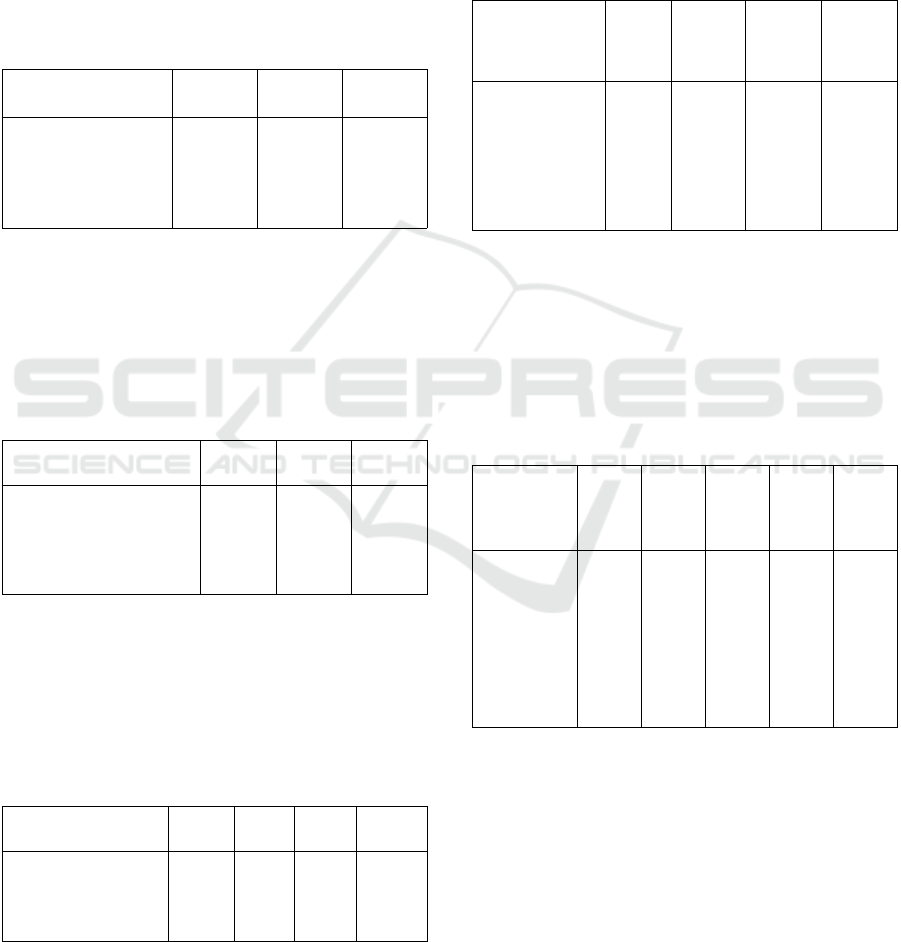
Table 13 shows that of the 46 DPJP respondents in St.
Carolus, the number of respondents in the type of
specialist education had 41 (89.1%), while the
number of respondents in the type of subspecialty
education was 5 (10.9%). So, it can be concluded that
respondents with the type of specialist education in
St. Carolus is more than subspecialist respondents.
The distribution of respondents' answers based on
statement items related to work environment
variables is described in the following table:
Table 14: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Work Environment (item 1).
Statement item 1 Highly
Agree
Agree Less
Agree
The hospital
environment
supports the carrying
out of discharge
summary filling work
14
(30,4%)
31
(67,4%)
1
(2,2%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 1, out of 46 respondents
there were 31 (67.4%) respondents answered Agree,
14 (30.4%) answered Highly Agree and 1 (2.2%)
answered Less Agree.
Table 15: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Work Environment (item 2).
Statement item 2 Highly
Agree
Agree Less
Agree
Facilities which available
at the hospital supporting
the implementation of
completeness discharge
summary
15
(32,6%)
30
(65,2%)
1
(2,2%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 2, out of 46 respondents
there were 30 (65.2%) respondents answered Agree,
15 (32.6%) answered Highly Agree and 1 (2.2%)
respondent answered Less Agree.
Table 16: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Work Environment (item 3).
Statement item 3 Highly
Agree
Agree Less
Agree
Disagree
Physicians office is
uncomfortable in
carrying out discharge
summary filling
10
(21,7%)
27
(58,7%)
8
(17,4%)
1
(2,2%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 3 (Physicians' workspace
settings are less comfortable in carrying out medical
resume filling), from 46 respondents there are 27
(58.7%) respondents answered Agree, 10 (21.7%)
answered Highly Agree and 8 (17.4%) answered Less
Agree and 1 (2.2%) answered
Disagree.
Table 17: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Work Environment (item 4).
Statement item 4 Agree Less
Agree
Disagree Strongly
Disagree
Workflow in the
hospital causes the
implementation of
completeness
discharge
summary not
optimal yet
4
(8,7%)
5
(10,9%)
31
(67,4%)
6
(13,0%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 4, of the 46 respondents
there were 4 (8.7%) respondents answered Agree, 5
(10.9%) answered Less Agree, 31 (67.4%) answered
Disagree and 6 (13.0%) answered Strongly
Disagree.
Table 18: Distribution of Respondents' answers related to
Work Environment (item 5).
Statement
item 2
Highly
Agree
Agree Less
Agree
Disagree Strongly
Disagree
Hospital
Management
had been
monitoring the
completeness
of filling out
discharge
summary
documentation
1
(2,2%)
9
(19,6%)
5
(10,9%)
25
(54,3%)
6
(13,0%)
Source: Primary Data Analysis, 2019
Based on item statement 5, from 46 respondents
there were 9 (19.6%) respondents answered Agree
and 1 (2.2%) answered Highly Agree, 5 (10.9%)
answered Less Agree, 25 (54.3%) answered Disagree
and 6 (13.0%) answered Strongly
Disagree.
The respondents' distribution above shows the
highest percentage is in item 1 (The hospital
environment supports in carrying out of discharge
summary filling work) with alternative answers
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
156

Agree of 67.4%. It can be concluded that 46
respondents tended to agree that the hospital
environment was supportive in carrying out of
discharge summary filling work.
The highest percentage for alternative answers
Disagree is in item 4 (Workflow in the hospital causes
the implementation of completeness discharge
summary not optimal yet) of 67.4%. It can be
concluded that about 31 (67.4%) of respondents
disagreed that the workflow in the hospital causes the
implementation of completeness discharge summary
not optimal yet.
The statement of Disagreement is also found in
item 5 (Hospital Management had been monitoring
the completeness of filling out discharge summary
documentation) by 25 (54.3%). It can be concluded
that 46 respondents tended to disagree that hospital
management monitored the completeness of filling
out discharge summary documentation.
3.2 Regression Model of Internal
Factors and External on DPJP’s
Behavior within Completeness JKN
Discharge Summary
Regression analysis was performed using multiple
linear regression analysis. This analysis was
conducted to see the predictions and effects of each
independent variable on DPJP’s behavior within the
completeness JKN discharge summary
simultaneously. The best model selection is chosen by
the backward method.
Based on the selection for multivariate modeling,
there are several variables that enter the regression
model as follows:
Table 19: Multiple Regression Linear Model.
Variable B Sig
Constant 38,571 0,000
Gender 1,559 0,204
Personality 0,400 0,033
Source: SPSS Output, 2019
Interpretation on Table 19. above, the value (a) =
38,571 and regression coefficient value (b1) = 1,559,
regression coefficient (b2) = 0,400.
Y = a + b
1
.X
1
+ b
2
.X
2
Based on the results above, the equation can
predict DPJP’s behavior within the completeness
discharge summary by using gender and personality
variables. The meaning of the coefficient, as follows:
1. Gender does not significantly influence
DPJP’s behavior within the completeness JKN
discharge summary, with a significance of
0.204. So, there is no contribution of the
influence given by gender to DPJP's behavior.
2. Personality has a significant effect on DPJP’s
behavior within the completeness JKN
discharge summary, with a significance of
0.033. Each personality value increases by 1
point and other variables are considered fixed,
then the DPJP’s behavior within the
completeness discharge summary will increase
by 0,400.
It can be concluded that personality variables have
the biggest influence on DPJP’s behavior within the
completeness JKN discharge summary with a value
of B = 0,400.
Table 20: Anova.
Model F Sig.
2,832 0,070
Based on Table 20. F test results (simultaneously)
it can be seen that the significance value (P-value) is
equal to = 0.070. P-value is 0.070 > 0.05, it can be
concluded that there is no significant effect between
internal and external factors simultaneously on
DPJP’s behavior within completeness JKN inpatient
discharge summary.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Characteristics of respondents with male gender in
St.Carolus Hospital were more in number with 29
(63.0%) compared to 17 (37.0%) women. The
majority of respondents work in St. Hospital. Carolus
in the age range of 28-49 years, amounting to 35
(76.1%).
Based on the distribution of respondents' answers
related to Personality. This shows that most of DPJP
in St. Carolus Hospital has the personality type of
Openness to new experience as many as 39 (84,8%).
The type of education at St Carolus Hospital tends
to be dominated by a specialist with a total of 41
(89.1%) compared to subspecialists who only amount
to 5 (10.9%).
Based on the distribution of respondents' answers
related to the Work Environment, most respondents
at St. Carolus Hospital agreed that the work
Internal and External Factors That Influence Behaviour of Physicians in Charge of Service (DPJP) within Completeness of JKN Inpatient
Discharge Summary in St. Carolus Hospital
157

environment of the hospital was supportive in
carrying out discharge summary filling work with a
percentage of 67.4%.
However, this has not been supported by the
hospital management in monitoring the completeness
of filling out discharge summary documentation, as
many as 25 (54.3%) of 46 respondents answered
Disagree.
The conclusion from the results of multiple linear
regression test shows that there is no simultaneous
influence of internal factors (gender, personality) and
external factors (education, work environment) on
DPJP’s behavior within completeness JKN discharge
summary in St. Carolus Hospital with a significance
value of 0.070. While partially Personality variables
have a significant effect on DPJP’s behavior within
completeness JKN inpatient discharge summary with
a significance value of 0.033.
5 SUGGESTION
In improving the performance of health practitioners,
especially the Physicians in Charge of Services
(DPJP) related to the completeness of clinical
documentation, especially discharge summary, it
needs a process of monitoring and evaluation as well
as improving workflow so that it can launch a clinical
documentation implementation system at St. Carolus
Hospital.
A strict policy is given regarding discipline and
physicians' compliance in filling out discharge
summary, both in the form of reward/punishment.
This will be easy because it is supported by the
personality type of DPJP’s behavior in St. Carolus
Hospital who tends to easily accept the new rules set
by the organization.
It was expected that further research development,
should be focusing more on the influence of behavior
which affects the performance.
REFERENCES
Advocacy, SJSN, 2011. Handbook of JKN Socialization
within SJSN. Jakarta
Menkes, 2014., INA-CBG System Technical Instruction. J
Craniofac Surg. 2014;19(4):1089–91.
Ardhika, 2014, Analysis of Discharge Summary
Completion for Patient of Hyperplasia of Prostate.
Middle Java: Mulia Hati Wonogiri Hospital.
Apriyantini, D., 2016. Correlation Analysis of Discharge
Summary Completion toward INA-CBG’s Bills
Standard in Teratai Inpatient Installation. Jakarta:
Fatmawati Hospital. 2016; 2:194–203.
Elvisa, 2016. Analysis of Completeness of JKN Inpatient
Discharge Summary in Orthopaedic Hospital Prof. Dr.
Soeharso. Surakarta
Permenkes, 2008. 269 Menkes/Per/III/2008. About
Medical Record. Jakarta
Puspitosari, D., 2011. Analysis of Individual
Characteristics and Extrinsic Motivation on Physicians
Performance in Completion Discharge Summary.
Jakarta: Hermina Hospital Depok
Yulida, Rina, 2016. Correlation of Physicians
Characteristics with Completeness of Operation
Report. Yogyakarta: Queen Latifa Hospital.
Nasyroh, Muslim, 2017. Correlation between Personality
(Big Five Personality Model) with Employee
Performance. Jakarta: Polytechnic APP.
Maryati, Warsi, 2014. Correlation between Physicians
Characteristics with Completeness of Discharge
Summary. Surakarta: APIKES Citra Medika.
Nelfiyanti., 2009. The Effect of Nurse Knowledge and
Motivation on Completeness of Nursing Care Form.
North Sumatera: Haji Medan Hospital
Carolus S., 2018. Recapitulation of Incompleteness of JKN
Inpatient Discharge Summary in Period of 2018.
Central Jakarta.
Notoatmodjo, 2017. Research Design. Jakarta: PT Rineka
Cipta.
ICOH 2019 - 1st International Conference on Health
158
