
The Effect of Roll Slide Mobilization and Traction Manual on Knee
Pain Scale Intensity Patients with Osteoarthritis
Tati Murni Karokaro, Isidorus Jehaman, Rahmad Gurusinga, Kardina Hayati, Siti Sarah Bintang, Sari
Desi Esta Ulina Sitepu, and Abdi Lestari Sitepu
Faculty of Nursing and Physiotherapy, Institut Kesehatan Medistra Lubuk Pakam, Indonesia
Keywords: Roll Slide Mobilization, Traction Manual, Knee pain Scale Intensity, Osteoarthritis patients.
Abstract: Osteoarthritis was a chronic joint disease that is characterized by abnormalities in the cartilage of the joints
and nearby bones. Cartilage (cartilage) is the part of the joint that lines the end of the bone, to facilitate the
movement of the joint. The occurrence of osteoarthritis is influenced by various risk factors such as age (aging
process), genetic, obesity, joint injury, anatomical anomaly, metabolic disease and inflammatory joint disease.
The objectives of this research is to determine the effect of roll slide and manual traction mobilization on the
intensity of the knee pain scale in patients with osteoarthritis. The method used a quasi-experimental one
group pre and post test, with a sample of 22 respondents. Pain scale measurement using VAS, using paired t-
test analysis. The results of the test showed that there was an influence of the provision of Slide Slide and
Manual Traction Mobilization to decrease the intensity of the knee pain scale with the results of paired sample
t-test results obtained p-value <a (0,000 <0.05). The Conclusion there was the effect of providing roll slide
mobilization and manual traction on the intensity of the knee pain scale patients with osteoarthritis. The
researcher suggests to the next researcher add the number of samples and longer time so that the results
obtained are more optimal.
1. INTRODUCTION
Humans are living things, the characteristic of living
things is moving. Humans move to needs of life in
daily activities. The one that often experience
disturbances are the joints, especially the knee joints,
which have quite heavy movements and are mostly
used by humans in carrying out activities and meeting
their daily needs. Impaired motion and function in
humans will result in pain or decreased functional
ability, so that it can limited physical activity and
sufferers depending on the help of others. Many
factors or caused that can cause these disorders, one
of which is Osteoarthritis where degenerative joint
disease occurs in the knee joints caused by various
factors (Triyono, 2018).
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint
disorder and the leading cause of disability in elders.
In 2015, the World Health Organization estimated
that 18.0% of women and 9.6% of men 60 years of
age or over suffer from symptomatic OA. Among
people with symptomatic OA, 80% have some
limitation in mobility and 25% are unable to perform
their major daily activities (Zhang and Niu, 2016).
Indonesia is sufferers of osteoarthritis are 5% at the
age of <40 years, at the age of 40-60 years reaching
30%, and 65% at the age of> 61 years. For knee
osteoarthritis the prevalence in Indonesia is also quite
high, reaching 15.5% men and 12.7% women of all
osteoarthritis sufferers (Adhiputra, Putra 2017).
Based on data from RISKESDAS 2018, the
prevalence of joint disease in Indonesia is around
7.3% and osteoarthritis (OA) or arthritis is a common
joint disease. Although it often occurs with age, or
known as degenerative disease, joint disease has
occurred in people in the age range of 15-24 years
(prevalence rate around 1.3%), the prevalence rate
continues to increase in the age range of 24-35 years
(3, 1%) and the age range is 35-44 years (6.3%).
Osteoarthritis is a non-inflammatory joint
disorder that affects old, chronic, and slow
progressive joints that eventually causes joint and
disability failure. These degenerative and progressive
joint diseases occur in about 250 million people
worldwide, 27 million people in the United States 3,
4 Elderly (around 35% of patients over 65 years old)
are women, while African-American populations are
at the highest risk of developing OA.5,6, and in India
there are more than 10 million cases annually and 60
Karokaro, T., Jehaman, I., Gurusinga, R., Hayati, K., Bintang, S., Sitepu, S. and Sitepu, A.
The Effect of Roll Slide Mobilization and Traction Manual on Knee Pain Scale Intensity Patients with Osteoarthritis.
DOI: 10.5220/0009467801490156
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology (ICHIMAT 2019), pages 149-156
ISBN: 978-989-758-460-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
149
million cases and will be at ranked 3rd in the world in
2025. Pain also originates from bone due to
stimulation of the periosteum because osteophytes are
recipients of nociceptive pain. There are 3 places that
distinguish pain, namely: 1. Sinovum, occurs due to
inflammatory reactions that arise due to the crest in
joint fluid, 2 Damage to the soft tissue can be
ligament tears, joint capsules and meniscus damage.
The process of Osteoarthritis is different for each
person that we can see like in Figure 1 (Kumar, &
Gupta 2017, Khon 2016).
Figure 1: The Process of Osteoarthritis
The cause of osteoarthritis in every daily activity
can be an emphasis on the joint area, especially the
joints that become the weight of the body such as
ankles, knees, and pelvis, degenerative changes that
initiate primary osteoarthritis, while age, obesity,
trauma, and other causes are factors that cause
secondary osteoarthritis (Ganu, Merchant, 2018).
The results of research conducted by Pandya,
Sheth, 2017 found that manual traction is effective for
reducing pain and can increase functional activity and
a decrease in pain in osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint
That the roll-slide is used to mobilize the joints if
there is limited space for joint motion due to the
shortening of capsuleligamentair and can reduce Pain
and can maintain joint ROM, (Pandya, Sheth, 2017).
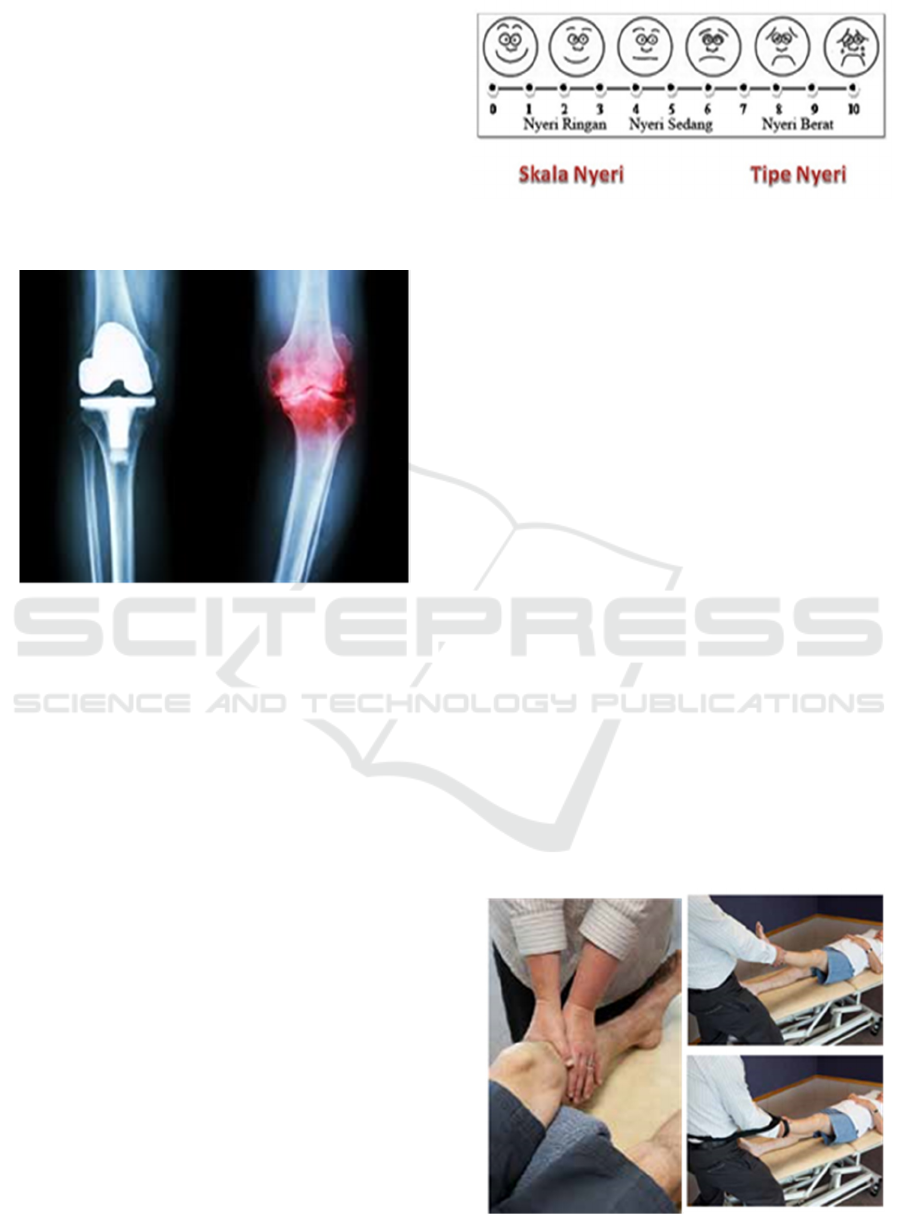
Measurement of pain response felt by patients can
be measured using the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) is
a measure of pain intensity that is considered the most
efficient that has been used in research and clinical
settings. VAS is generally presented in the form of
horizontal lines. In its development, the VAS method
of presentation is given the numbers 0-10, "0" is no
pain and "10" shows very severe pain, that we can see
like in Figure 2 (Klimek, Bergmann, Biedermann, et
all, 2017).
Figure 2: Visual Analog Scale (VAS)
Manual Traction is a technique used to treat joint
dysfunction such as pain, stiffness, reversible joint
hypomobility. Traction is a passive motion that can
be done at a slow speed. This traction can stimulate
biological activity by flowing synovial fluid that can
carry nutrients in the avascular portion of the joint
cartilage on the joint surface and fibro cartilage in the
joints (Pandya, Sheth, 2017).
Roll slide mobilization in the knee joint is one
form of mobilization in the form of passive motion in
the knee joint that is adapted from physiological
movements that occur when flexion and extension are
in accordance with osteokinematics of the knee joint
and intra articular elements have rotational,
translational and spin motion. Roll slide mobilization
is used to mobilize the joints if there are mechanical
limitations or shortening of the capsuloligament and
can maintain joint ROM while minimizing pain.
Dosage and use: a) Degree I: Roll slides with small
amplitudes are applied parallel to the surface of the
joint and carried out at the beginning of the degree of
movement. Used to reduce pain b) Degree II: Bone
moves parallel to the surface of the joint until slack
and tissue around the joint tighten. Used to reduce
pain c) Degree III: Bone moves parallel to the joint
surface with a large enough amplitude that we can see
like in Figure 3 (K. Hanoch & P. Elavaration in 2016).
Figure 3: Roll Slide Mobilization and Manual Traction.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
150
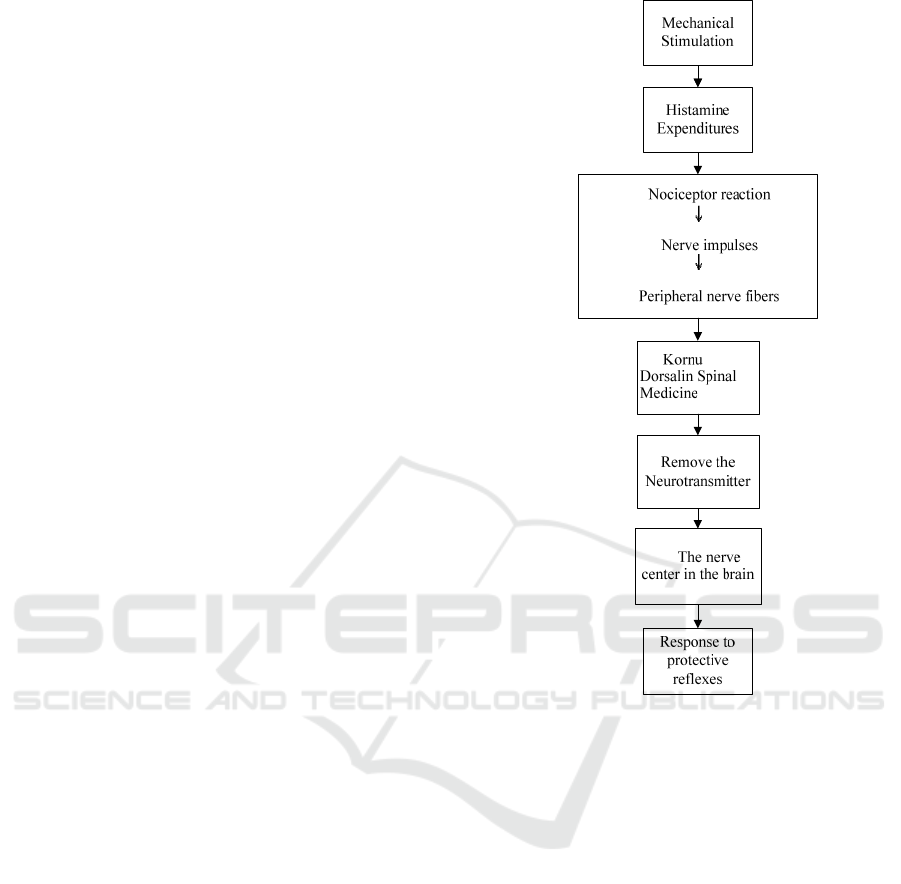
Pain is an unpleasant subjective and emotional
sensory obtained related to actual or potential tissue
damage or describes the condition of the damage.
Pain stimulation received by nociceptors on the skin
can be high or low intensity such as stretching and
temperature as well as by tissue lesions. Necrotic cells
release K + and intracellular proteins. Increased
extracellular K + levels will cause depolarization of
nociceptors, whereas proteins in some circumstances
will infiltrate microorganisms, causing
inflammation/inflammation. As a result, pain
mediators are released such as leukotrienes,
prostaglandin E2, and histamine which will stimulate
nociceptors so that dangerous and harmless stimuli
can cause pain (hyperalgesia or allodynia).
In
addition, the lesion also activates blood clotting
factors so bradykinin and serotonin will be stimulated
and stimulate nociceptors. If there is occlusion of
blood vessels there will be ischemia which will cause
accumulation of extracellular K + and H + which then
activates nociceptors. Histamine, bradykinin, and
prostaglandin E2 have a vasodilator effect and
increase vascular permeability. This causes local
edema, increased tissue pressure and also occurs
nosisepto stimulation. When nociceptors are
stimulated, they release the peptide substance P (SP)
and the peptide-related calcitonin gene (CGRP),
which will stimulate the inflammatory process and
also produce vasodilation and increase vascular
permeability. Vasoconstriction (by serotonin),
followed by vasodilation, may also be responsible for
migraine attacks. This nociceptive impulse causes
pain that we can see like in Figure 4 (Ardinata, D,
2017, and Zhang and Niu, 2016).
Figure 4: Physiology of Pain
Based on preliminary surveys at Grandmed Lubuk
Pakam Hospital, the number of physiotherapy
patients in 2018 was 7857 patients in poly
physiotherapy at grandmed hospitals, whereas
specifically in osteoarthritis sufferers in January to
December 2018 there were 960 people. The average
number of patients per month is 80 patients per
month.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
The location of this research was carried out at the
Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital, this research was
conducted with a Quasi-experimental with one group
pretest-posttest design model (Sugiyono, 2017). The
purpose of this study was to determine the effect of
roll slide mobilization and manual traction on the
intensity of the knee pain scale in osteoarthritis
sufferers. The samples in this study was taken 22
The Effect of Roll Slide Mobilization and Traction Manual on Knee Pain Scale Intensity Patients with Osteoarthritis
151
people with inclusion criteria: patients who
experience knee osteoarthritis pain who visited poly
physiotherapy at Grandmed Lubuk Pakam Hospital,
Age 40 to 65 years, male and female sex, and
exclusion criteria were: Patients with
osteoarthritisknee due to other causes or not due to
nerve disorders such as bone TB pain or malignancy
in other cases of knee osteoarthritis, knee
osteoarthritis patients who get other treatments and
patients who receive pharmacological therapy in pain
management. The data collection techniques were
carried out using purposive sampling technique
which was done by entering every patient who met
the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The instrument
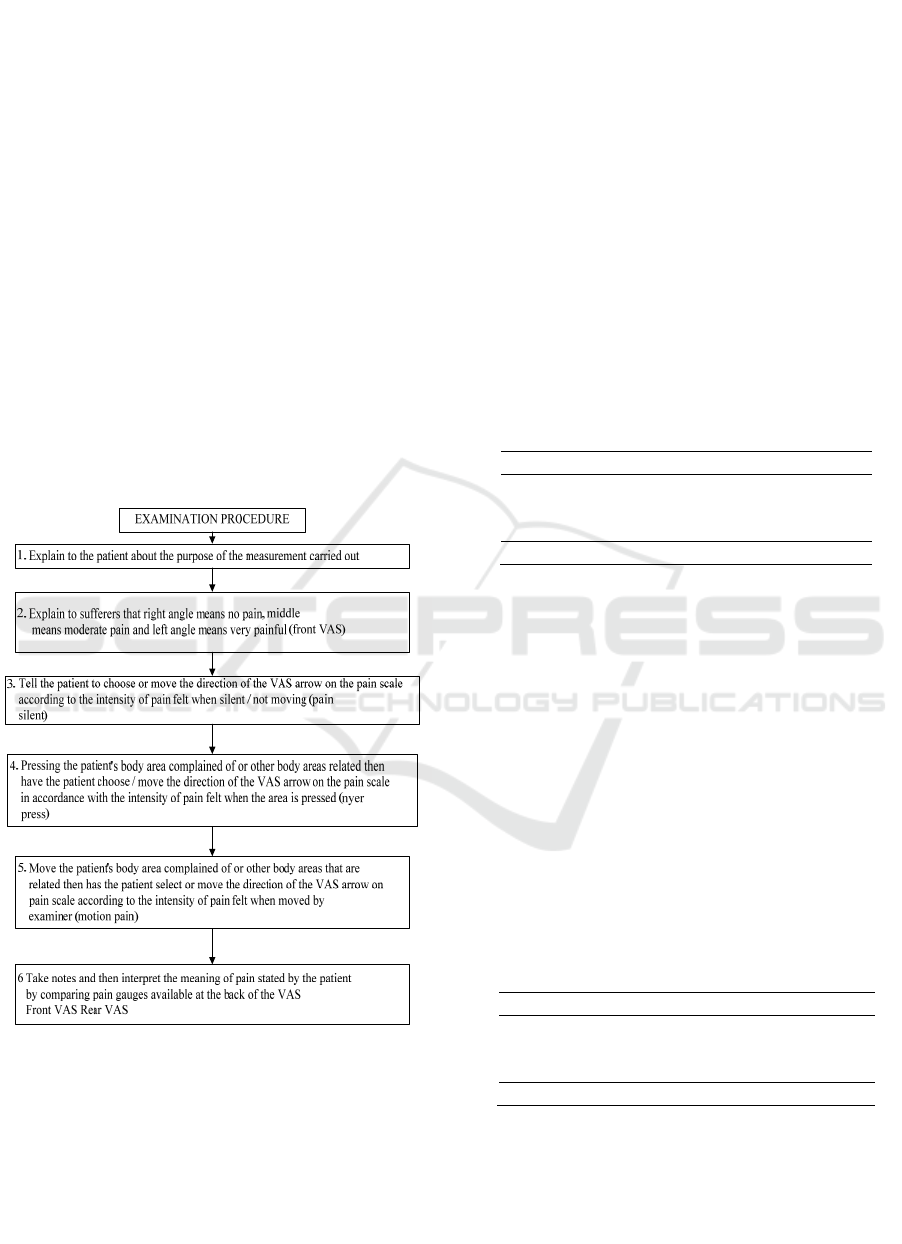
used was an observation sheet. Measurement of pain
scale is done by VAS which is divided into 3
assessments given numbers 0-10, "0" category of no
pain, 1-3 categories of mild pain, 4-6 categories of
moderate pain, 7-9 categories of aches and "10
"Shows extreme pain. The implementation procedure
can be seen in the figure 5 below:
Figure 5: Examine Procedure
Before the intervention is carried out, the pain
scale is measured first to ensure the pain value felt by
the sample, after the pain scale is obtained from the
sample, then it is continued with 3 times a week of
roll slide and manual traction interventions.
Measurements were taken again after the intervention
was given whether there was a decrease in pain scale
or not, then data were analyzed using paired sample
t-test.
3 THE RESULTS AND
DISCUSSION
Based on Table 1, the scale of knee pain scale before
Roll Slide and Manual Traction Mobilization
intervention in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis
found that the dominant knee pain scale is moderate
pain by 16 respondents (72.7%), mild pain by 5
respondents (22.7%), while severe pain 1 respondent
(4.5%).
Table 1: Distribution of Knee Pain Scale values
before Roll Slide Mobilization and Manual Traction
interventions on Osteoarthritis Sufferers.
Pain Scale n %
Mild Pain 5 22,7%
Middle Pain 16 72,7%
Heav
y
Pain 1 4,5%
Total 22 100%
Based on Table 2, the Knee Pain Scale value after
Roll Slide Mobilization and Manual Traction
intervention in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients shows
that the dominant pain scale is mild pain as much as
9 respondents (40.9%), moderate pain is 8
respondents (36.4%), whereas pain slightly 5
respondents (22.7%).
The Average of Knee Pain Scale before giving
intervention in patients with Osteoarthritis, it is mean
value of the knee pain scale prior to the intervention
of Roll Slide Mobilization and Manual Traction in
Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis found the average
pain value is 2.82 with a standard deviation of 0.501
Table 2: The Distribution of Knee Pain Scale values
after Roll Slide Mobilization and Manual Traction
interventions on Osteoarthritis Sufferers.
Pain Scale n %
Little Pain
5 22,7%
Mild Pain
9 40,9%
Middle Pain
8 36,4%
Total 22 100%
The average Knee Pain Scale before giving
intervention in patients with Osteoarthritis, it is mean
value of the knee pain scale after Roll Slide and
Manual Traction Mobilization intervention in Knee
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
152

Osteoarthritis Patients showed an average value of
2.14 with a standard deviation of 0.774.
The average Knee Pain Scale after Roll Slide
Mobilization and Manual Traction Intervention in
Patients with Osteoarthritis, the value of difference
intensity of the knee pain scale before and after the
intervention of Roll Slide Mobilization and Manual
Traction in Patients with Osteoarthritis Knee obtained
is 0.682 with a standard deviation of 0.568 and p-
Value 0,000 which means that there is an effect of
giving Roll Slide Mobilization and Manual Traction
in Patients with Osteoarthritis.
Difference in Pain Scale Intensity Before and
After the Intervention of Roll Slide Mobilization and
Manual Traction in People with Osteoarthritis, the
value of the difference in the intensity of the pain
scale before and after the administration of Roll Slide
Mobilization and Manual Traction in Patients with
Osteoarthritis in the Knee obtained a Mean value of
0.682 with a standard deviation of 0.568 and 0,000,
which means there is an effect of giving Roll Slide
Mobilization and Manual Traction in Osteoarthritis
Sufferers.
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Average Pain Scale before
Administration of Roll Slide
Mobilization and Manual Traction
in Osteoarthritis Sufferer
The results of research conducted on 22 people on the
measurement of the VAS value before the
administration of Roll Slide Mobilization and Manual
Traction techniques that have mild pain values of 5
people (22.7%), moderate pain of 16 people (72.7%),
and annoying pain 1 people (4.5%). Osteoarthritis is
a chronic joint disease that is characterized by
abnormalities in the cartilage of the joints and nearby
bones. Cartilage will result in bones rubbing against
each other, resulting in symptoms of stiffness, pain
and restriction on the endi movement means that
osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease
associated with joint cartilage damage. Osteoarthritis
is chronic, slow progressive and is characterized by
changes in susceptible joints and the formation of
new bone on the joint surface. Osteoarthritis often
affects joints that support weight such as vertebre,
pelvis, knees, and ankles. The occurrence of
osteoarthritis is influenced by various risk factors
such as age (aging process), genetic, obesity, joint
injury, anatomical anomaly, metabolic disease and
joint inflammation, osteoarthritis is influenced by
various risk factors such as age (aging process),
genetic, obesity, injury joints, anatomical anomalies,
metabolic diseases and diseases of joint inflammation
(Endang, 2016, Ismaningsih, 2018 & Bove, Smith,
Bise, 2018).
Other studies that are in line with this research
were conducted in India in 2016 where the p value
was less than 0.01 which showed that the average
pain score at the level before and after the treatment
was not the same, this can occur because of manual
cervical traction techniques with heating pads
superficial TENS was found to be the best and
effective way to relieve pain and restore the active
function of patients in daily life with a significant
increase in symptoms that bring good patient results.
(Khan, Yasmeen, Ishaque, 2016 and Pandya, Sheth,
2017, Anwer, Alghadir, Zafar, 2018).
4.2 Average Pain Scale after
Administration of Roll Slide
Mobilization and Manual Traction
in Osteoarthritis Sufferers
The results of research conducted was 22 peoople on
the measurement of VAS values after the
administration of Roll Slide Mobilization and Manual
Traction techniques that have a slight pain value of 5
people (22.7%), mild pain 9 people (40.9%) and
moderate pain 8 people (36.4%). Roll Slide
Mobilization Technique is one form of mobilization
exercise in the form of passive motion in the knee
joint that is adapted from physiological motion that
occurs arthrokinematic motion where in the tibia
there is a roll toward the dorsal and the slide towards
the dorsal as well so as to obtain stretching of the
ligamenter capsule ligamenter which does not occur
excessive stretching on one part given the exercise.
This exercise is expected to stimulate biological
activity by flowing synovial fluid that carries
nutrients to the avascular part of the joint cartilage on
the joint surface and fibrocertilago joints. Repeated
movements in the slide roll mobilization will increase
microcirculation and more liquid will come out so
that the water content and matrix in the tissue
increases and the tissue is more elastic. manual
traction techniques that are carried out repeatedly in
the movement of traction will improve the micro-
circulation and fluid that is released a lot so that the
water and matrix content in the tissue can increase
and the tissue becomes more elastic. In addition, the
traction motion elements are almost the same as the
physiological movements of the knee joint in flexion
movements so as to increase and maintain the
The Effect of Roll Slide Mobilization and Traction Manual on Knee Pain Scale Intensity Patients with Osteoarthritis
153

elasticity of the capsules, ligaments, and muscles, any
mechanical dysfunction needs to be corrected through
mechanical means. Therefore manual therapy in the
form of traction tends to shift the joints at the level of
the articular surface. The combination of mechanical
and sports traction for patients with cervical
radiculopathy improves function and reduces pain
(Bukhari, Rehamn, Ahmad, Naeem 2016).
The results of the research related to the above
study were conducted at the Meerut LLRM campus
in 2018 where the assessment was conducted on day
-1 of the intervention and was reassessed after 15 days
of intervention. Group A VAS scores showed an
overall percentage of 18%, group B experienced an
overall percentage decrease of 32%. ROM scores of
group A decreased by an overall percentage of 30%
group B decreased by 34% overall, where the results
showed that mechanical cervical traction and manual
traction with nerve mobilization
techniques were
almost equally efficient in reducing pain and
increasing range of motion, this can be occur due to
neck span movements and decreased level of
neck
disability in two therapeutic interventions namely
intermittent
cervical traction combined with neck
strengthening exercises in nerve mobilization
combined with neck strengthening exercises that we
can see like in Figure 6 (Xu, Chen, Wang, 2017 and
Sarfaraj & Deepali, 2018).
Figure 6: Manual Therapy Technique for the Slide Slide
Method on the Knee Joint
4.3 The Effect of Difference in Pain
Scale before and after
Administration of Roll Slide
Mobilization and Manual Traction
in Osteoarthritis Sufferers
The results of the study prior to the administration of
Roll Slide Mobilization and Traction Manual
revealed the average value of the pain scale before
2.82 with SD = 0.501 while after the administration
of Roll Slide Mobilization and Traction Manual it
was known the average value of the pain scale was
2.14 with SD = .774 while the results of the study of
the difference in pain scale before and after the
administration of Roll Slide Mobilization and
Traction Manual amounted to 0.682 with SD = 0.568.
The statistical test results obtained p-value <α (0,000
<0.05), it can be concluded there is an influence
before and after the administration of roll slide and
manual traction mobilization in knee osteoarthritis
sufferers. The results of this study are in accordance
with research conducted by Pandya, Sheth (2017) on
the "Effect of Mechanical Traction on Pain And
FunctionIn Subjects With Osteoarthritis Knee" given
to osteoarathrits patients with a frequency of twice a
week in osteoarthritis patients the healing phase can
reduce pain in knee.
In line with research conducted in India in 2015
that there was a significant increase in the range of
motion of subjects treated with manual therapy (P
value for all cervical spine movements <0.005). This
can occur because intermittent traction increases
circulation to tissues and reduces swelling thereby
helping to reduce inflammatory reactions from nerve
roots. Therapy is performed with the first 2 stages,
namely to form stretches that extend all vertically
oriented neck soft tissue, and the second to reduce the
strength of heavy bearing compression on the surface
of the joints, intervertebral discs and intervertebral
foramina of the cervical spine. In manual therapy,
direct tensile force is applied at the level of the
affected spine. When traction separates the spinous
processes, the size of the intervertebral foramina
increases thereby reducing compressed nerve roots to
provide faster assistance in radiation and also increase
intervertebral motion at these levels. Thus manual
mulligan traction can be considered the treatment of
choice for cervical spondylosis with or without
radiculopathy. Roll Slide and Manual Traction
Mobilization Measures with the determined intensity,
frequency and time are very effective for
osteoarthritis sufferers who experience knee pain,
because this intervention can stimulate biological
activity by flowing synovial fluid that carries
nutrients to the avascular part of the joint cartilage on
the joint surface and joint fibrocystilage so that pain
is reduced (Bosmia & Kotwal, 2015, Xu, Chen,
Wang, 2017).
Research conducted in Australia in 2016 showed that
toe distance significantly increased with one nerve
mobilization session (p <0.01) or static stretching (p
<0.01). The effects of static stretching interventions
on toe touch are consistent, which report similar
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
154

changes in the sit and range test, an alternative that is
highly correlated with the finger touch test. The
results of this study indicate that mobilization of the
nerves is also an effective method for increasing toe
touch distance. (Curtis, Retchford, Khalaf & Jeline
2016
5 CONCLUSIONS
Knee pain scale prior to intervention Slide Slide
and Manual Traction Mobilization on Patients
with Knee Osteoarthritis found the average pain
value is 2.82 with a standard deviation of 0.501
The scale of knee pain after the intervention of
Roll Slide Mobilization and Manual Traction on
Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis found an
average
value of 2.14 with a standard deviation
of 0.774.
Difference intensity of the knee pain scale
before and after the intervention of
Roll Slide
Mobilization and Manual Traction in Patients
with Osteoarthritis Knee obtained is 0.682 with
a standard deviation of 0.568 and p-Value 0,000
which means there is an influence on the
provision of Roll Slide Mobilization and
Manual Traction in Osteoarthritis Sufferers
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thank you for the:
To all patients who were willing to be
respondents in this research
The Managing Director of the GRANDMED
Lubuk Pakam Hospital who has given
permission for the researcher to be completed
properly
The Rector of Health Institute MEDISTRA
Lubuk who has given permission and support
conducting this research.
REFERENCES
Ardinata, D. (2017). Multidimensional nyeri. Jurnal
Keperawatan Rufaidah Sumatera Utara.
Curtis, Retchford, Khalaf & Jeline. 2016. Acute effects of
neural mobilization and static hamstring stretching on
multi-joint flexibility in a group of young adults.
Journal of Novel Physiother.
Chen, Zhan, Marszalek, 2018. Manual therapy for knee
osteoarthritis pain: a systematic review and meta-
analysis. Elsevier Inc. Volume 26
French, Brennan, White, et all, 2017. Manual therapy for
osteoarthritis of the hip or knee – A systematic review.
Journals & Books. Volume 16, Issue 2
Hameed, Waqas, Akhtar at al., 2017. Effect of Manual
Therapy on Knee Osteoarthritis (OA) Pain, A
Randomized Control Trial. International Journal of
Research Studies in Medical and Health Sciences
Ismaningsih, Selviani, I. (2018). Muskuler taping dan
strengthening exercise untuk meningkatkan kapasitas
fungsional. Pekan Baru: Jurnal Ilmiah Fisioterapi
(JIF).
Klimek, Bergmann, Biedermann, et all, 2017. Visual
analogue scales (VAS): Measuring instruments for the
documentation of symptoms and therapy monitoring in
cases of allergi crhinitis in every day health care
Kisner, C and Colby, LA, 2017. Therapeutic exercise
foundations and techniques (therapeudic exercise:
foundations and techniques). 7th Edition, Kindle
Edition. F.A. Davis Company, Philadelphia.
K. Hanoch & P. Elavarasi, 2016. Department of oral
medicine and radiology, SD Dental College & Hospital,
Parbhani, Maharashtra, India, Department of Oral
Medicine and Radiology, Dayananda Sagar Dental
College and Hospital, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Journal of Advanced Clinical & Research Insights
(2016)
Khan, Yasmeen, Ishaque, et all, 2016. Effectiveness of
manual traction and other physiotherapy treatment in
the management of painful cervical radiculopathy.
International Journal of Physiotherapy. Vol 3(3), 286-
290, June (2016). ISSN: 2348 – 8336
Kohn BA, Sassoon MD, Fernando MD, (2016). Kellgren-
lawrence classification of osteoarthritis. Clinical
Orthopaedics and Related Research. journal Volume
474, No 8.
Kumar, A., Goel, S., Gupta, R. & Gupta, B.M. (2017).
Osteoarthritis research in India: Ascientometric
assessment of publications output during 2007-16.
International Journal of Information Dissemination and
Technology, 7(3), 157-161.
RISKESDAS. (2018). Laporan Hasil Riset Kesehatan
Dasar (Rikesdas) Nasional. Jakarta.
Sarfaraj MD & Deepali. (2018). Effectiveness of manual
cervical traction and mechanical cervical traction with
neural mobilization in cervical radiculopathy.
International Journal of Advance Research and
Development. Volume 3, Issue 5.
Sugiyono. (2017). Metode penelitian kuantitatif, kualitatif,
dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta, CV.
World Health Organization (2016). Action plan for the
prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases in
the WHO European Region.
Abdel-aziem, Soliman, Mosaad, et all. 2018. Effect of a
physiotherapy rehabilitation program on knee
osteoarthritis in patients with different pain intensities.
The Journal of Physical Therapy Science. Vol. 30, No.
2.
The Effect of Roll Slide Mobilization and Traction Manual on Knee Pain Scale Intensity Patients with Osteoarthritis
155

Ganu, Merchant, 2018. Effect of retrowalking on pain,
functional disability and functional mobility in patients
with chronic knee osteoarthritis. International Journal
of Health Sciences & Research. Vol.8; Issue: 11.
Anwer, Alghadir, Zafar, 2018. Effects of orthopaedic
manual therapy in knee osteoarthritis: a systematic
review and meta-analysis. Volume 104, Issue 3,
Pages 264–276.
Xu, Chen, Wang, 2017. The effectiveness of manual
therapy for relieving pain, stiffness, and dysfunction in
knee osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-
Analysis.
Bove, Smith, Bise, 2018. Exercise, manual therapy, and
booster sessions in knee osteoarthritis: cost-
effectiveness analysis from a multicenter randomized
controlled trial. Vol. 98 Number 1.
Pandya, Sheth, 2017. Effect of mechanical traction on pain
and functionin subjects with osteoarthritis knee.
International Journal of Physiotherapy and Research,
Int J Physiother. Vol 5 (4): 2198-02.
Zhang and Niu, 2016. Shifting gears in osteoarthritis
research towards symptomatic osteoarthritis. Arthritis
Rheumato. HHS Public Access. Boston.
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
156
