
Clinical Psychology Problems of Maturity Period to Adulthood for
Male Students of IAIN Langsa
Iqbal, Mauloeddin Afna
IAIN Langsa
Keywords: Clinical Psychology, Maturity, Rahmatan lill ‘Alamin, Adulthood.
Abstract: This article projected about the clinical psychology problems for male-students of IAIN Langsa about how
they face flourishing into manhood. Their overwhelming testosterone emergences male inclination to be a
male for dominant, egoistic, and flamboyant were examined through questioner from the first year class of
IAIN Psychology team. This article also projected about the abstained of fatherhood roles, the single-mother
to raise their son, and how the institute commitment to rejuvenate the abstained father role and help the
single mother or father to enroll their children. The institute projected the regulation of the Islamic
rejuvenation of cultural identity in teaching man as the concept of humanity caliphates in world, rahmatan
lill ‘alamin. The Islamic vary concepts of education identity about either fostering the people when father or
mother, or both are no longer existences. The article also proposed about the role of an Institution, IAIN
Langsa, accommodates the cultural fostering with Islamic tradition, to help student when they facing the
abstained of parent role models. The Article addressed field research triangulation for connecting directly
with the students with heterogeneous backgrounds. In conclusion, the article propelled about solution for
intangible governments consular institution for university-institute level by inquiring the male students’
clinical psychology problem when they are about starting higher educational institution period.
1 INTRODUCTION
The male students is often in crisis of flourishing
into manhood. With the exposed of traumatic events,
local conflicts, broken-home and involved juvenile
delinquency criminal cases, the crisis post a threats
for life-experiences. The students with clinical
psychology problems emergences mental disorders
for fostering in selection of role model as life-path.
Yet, this lead to the stability of mental and
motivation influenced for broaden field, i.e.
educational, socials, and even personal. Moreover,
the crisis also possess pressures for the students who
miss the role model of parents, the abstained of the
fatherhood. Actually, the students who face this
crisis should be taken on attention to clinical
psychology and education. The attention to resolve
male-students in crisis marks as the socials
responsibility of settling role model for life-skill as
male whom born as leaders.
The Students aged 10 to 19 who belong to teen
groups (Papalia, Olds & Feldman, 2001) and
UNICEF studies found that there were 1.2 billion
adolescents at that time. The UNICEF study also
found that 80% of these teenagers are in developing
and inhabiting suburbs such as squatters and in areas
of armed conflict and post disaster, (UNICEF,
2002). The adolescents who grown up in high-risk
environment are vulnerable exposed to a variety of
traumatic and violence experiences. Therefore, they
have a high probability of experiencing emotional,
mental health and social disorder (Paglicci, Roberts
et al, 2002). The exposes of traumatic and violence
lead into unresolved crisis and entrapped the
students in unbroken chains link. Mathews (2009) et.
all also highlighted out about the impact of crisis
also involved both personal and social. Indeed, the
crisis also affect to their academic achievements,
lecturer-students relationship, and so on. The
students with clinical psychology problems tend to
destroy themselves. Thus, the tendentious are the
objectives of protections to stay intact
communication as social-relationship goals.
The prime goals of education is to preserve the
human growing up process. This articles projects
about the Islamic education in preserving the male-
students to fulfill their life cycles of adolescent
period. The rejuvenation is a form of conservation,
Iqbal, . and Afna, M.
Clinical Psychology Problems of Maturity Period to Adulthood for Male Students of IAIN Langsa.
DOI: 10.5220/0009440701810188
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Psychology (ICPsy 2019), pages 181-188
ISBN: 978-989-758-448-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
181

which expects changes and restored in behavior,
attitudes and ways of thinking, especially those
related to managing natural resources and
ecosystems (Setiono, 2011. 2). The process for a
male to be an alpha, the decision taker, leader, and
so on. In Islam, the nature of human, called as fitrah.
The concept of education is generated on the role
models of being Male. Moreover, the concepts also
marks as the former prominent systems for fulfilling
the abstained of parents. The article also projected
about the institution milestone as social recognition
for preserving and protecting young generation,
then, support their role as Rahmatan lill ‘Alamin
concepts.
The concepts of Rahmatan lill ‘Alamin in Islamic
tradition is the filtration and catalyst in parallel of
moral standing. The humanity filtration of fitrah to
being aware of external environments with respects.
It develop human fitrah as human catalyst by certain
moral roles, being aware and respect to the values of
humanity norms with universal diversity (Shihab,
519: 2017). These parallel standing shall draw clear
direction to keep the psychological aspects
intangible strong to face frictions and fulfilling
humanity right to life as a male, alpha-male, pack
leader in Islam, also called as -caliphate. The
parallel concepts of Rahmatan lill ‘Alamin will act
as fostering to those whose is orphans.
The article projected about the educational
concepts of Rahmatan lill ‘Alamin in Islamic
tradition became the fostering standard for healing
treatment of the clinical psychology problems for
male-students about how do flourishing into
manhood. Its fitrah specific features about following
the glorious prophets, Muhammad Saw, as Islamic
tradition role model in teaching a manner that make
a man to a man.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 The Fostering Milestones of Fitrah
in Rahmatan Lill ‘Alamin Concepts
Islamic educational tradition projects the fostering
milestone of young generation with the guidance of
glorious Al Qur’an:
Translation “and we have not sent you, (O,
Muhammad), except as a mercy to the worlds” (QS.
Al-Ambiya. 21:107). This milestone of the glorious
prophet teaching is universally objective. The
teaching is about humanity and harmony. In
addition, the glorious supports mentioned in al-
Ahzab.
Translation “There has certainly been for you, (O,
Muhammad), in the Messenger of Allah an excellent
pattern for anyone whose hope is in Allah and the
Last Day and (who) remembers Allah often” (Al-
Ahzab. 33:21).
The scriptures clearly pointed out about the
Islamic correspondence example in fostering young
generation that based on the glorious prophets’
traits, i.e. Sidiq (Honesty), Fathanah (Wise),
Amanah (Trustworthy), and Tabliqh (Deliver). The
honesty and trustworthy are resemble to emotionally
intelligences (EQ), and developed for social
interactions. Then, the wise and deliver are resemble
to intelligence quotient (IQ). These are the proper
role model for fostering process of young
generation.
The four glorious prophets’ traits are the
milestone to develop educational system that enable
to propose resolution clinical psychology in social
community. Moreover, the article propose these
traits as the exemplification of role model in
supporting growing male-students. Nata (2017)
believed that the fitrah of male students are
awareness sympathy attitude for personality and
environment. The moral values standing on
righteous for mutual relationship, man to man, man
to animal, and so on base on the intervention of self-
gratitude life-human-environments. The concepts of
Rahmatan lill ‘Alamin enable the students to act as
human that aware to the diverse environments,
acknowledge to follow role model, and self-
actualization with tolerances and harmony life.
These concepts enable the students to execute and
take decision with responsibility for male standing.
In addition, Nata (2017) and (Shihab, 519: 2017)
confirms about the very concept of teaching is the
fitrah of being man in contemporary eras. On the
other words, The Handbook of PPI (2014) called the
interventions of adults consistently generate positive
advantages, huge numbers of which seem to suffer
over sensibly extensive periods. Life-appreciation
instructs to more prominent gratitude, life
fulfillment, good faith, pro-social conduct (Emmons
& McCullough, 2003), positive affect (PA)
(Emmons & McCullough, 2003). The concepts of
Rahmatan lill ‘Alamin emergences the intervention
to consolidate human and their surroundings.
ICPsy 2019 - International Conference on Psychology
182
3 RESEARCH METHOD
The article applied field study to investigate the
relationships or interactions between sociological,
psychological and educational variables for research
in social community. Kerlinger (2000: 585) believed
that clinical psychology disorders attempting to test
the variables of students’ personal life interaction
and environments. According to Babbie (2001),
survey methodology is the best method for
collecting data from a large population through
sampling techniques. This study also attempted to
see the main variables of the research, namely
mental health, learning motivation, and the
relationships that exist amongst students in Aceh.
There are two specific extern factors of Aceh
condition with affected disasters and years of arms
conflicts. The samples were selected through
Korchin and Cowan approaches (1982); the
selection of informed consensus; minimization of
potential maltreatment, and confidentiality. To
collect required data, the researcher adapted Self-
Report Questionnaires (SRQs), the learning
motivation scale and the student interview protocol.
For interview protocol instruments, researchers are
guided by protocols as suggested by Glesne and
Pushkin (1992) and Creswell (1994).
Table 1: Instruments, Objectives, and Targeted Samples.
Instruments Samples Contents
Self-Report
Questionaire
(SRQ)
Students (Dep. Kes RI, 2008;
(Riskesdas), 2007;
(WHO), 1994).
Intrinstic
Motivation
Inventory
(IMI)
Students Translated by Herlyna
(2004) dan Ryan (2004)
Student
Interview
Protocols
Students The applied format of
Glesne dan Peshkin
(1992), Creswell (1994).
Measuring mental health is by using Self Report
Questionnaire (SRQ), (MOH RI, 2008; Rikesdas,
2007; WHO, 1994). WHO have developed this
instrument to screen for psychiatric disorders
especially in various developing countries. There are
a total of 20 item items, which must be answered in
form or with yes or no. SRQ has been widely used in
various countries and is translated in various
languages such as Arabic, Afrika, Amhari, Bengali,
Malaysia, Spain, and others including Indonesia.
SRQ designed as a scale to be filled by the subject
itself but can also be given through interviews to
illiterate subjects. The selection validity measured
multiple validity variables; face, content, criterion,
and construct; which is aligned with WHO standard
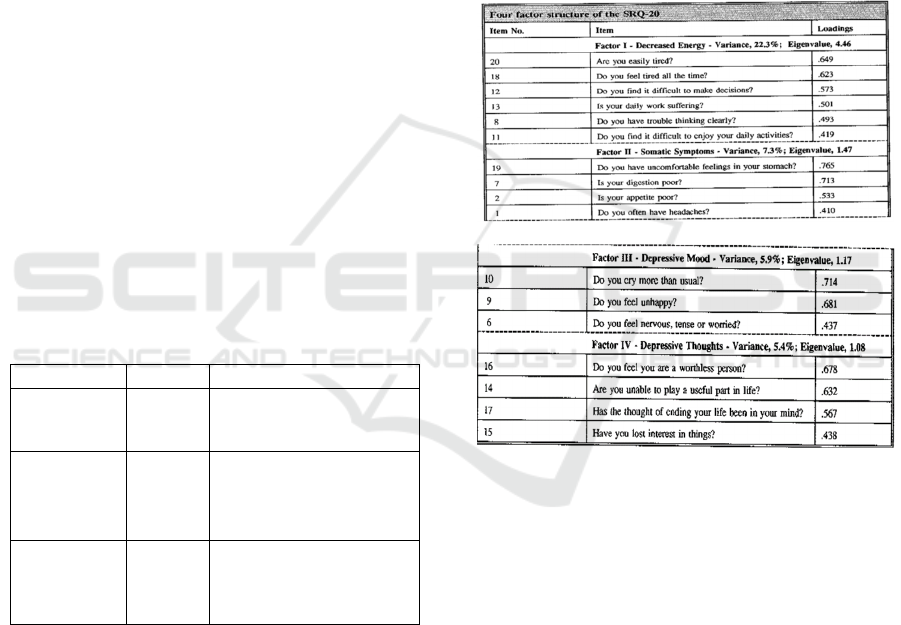
indexes (WHO, 1994). Based on the factor analysis
conducted on SRQ scale given to 1182 samples in
Brazil, Lacoponi and Mari in WHO (1994) have
identified four factors consisting of items that have a
value of 40 samples or more. The decreased energy
factor I, consisting of depression and anxiety items,
while somatic items have a large value or scaling
factor II. Factor III is labeled depressive mood and
factor IV is labeled depressive thought. See Figure
1.1
Figure 1: The Results of the SRQ Factor Analysis by
Lacoponi and Mari (in WHO, 1994: 26-27).
In the answer form given score 1 for the marked
answer (yes) and 0 for the answer (no). The cut off
value that separates those who have mental illness is
14, while those with a score of over 14 show that
they are free from mental health problems. Thus, the
maximum score for the measuring instrument in this
study is 20. It is important to note that SRQ is only a
preliminary screening tool to see indications of
mental health problems. To determine an analysis of
mental health problems it is still necessary that an
expert who has the authority to provide a diagnostic
clinical psychologist or psychiatrist. SRQ has been
officially used in a variety of basic mental health
issues in Aceh (Ministry of Health, 2008; Riskesdas,
2007).
Clinical Psychology Problems of Maturity Period to Adulthood for Male Students of IAIN Langsa
183
To address Gender stereotypes, Muris (2007)
introduced about the common opinions about the
proper characteristics to address boys as males-
being. However, it is generally assumed to
biological basis (MacCoby, 200b), taken into
environmental development of influenced role in
society. Form early age on, community address boys
and girls differently for their flowering stages. For
their own life, a severe reality introduced
The children about how to behave and act in
natural-way, yet nurture also generated the flowering
stages. Moreover, when the children turn to mature
being, their behaviors promote the gendered basic
characteristics. In nature and nurture, the children
develop reflection of personality, activity, and
performance (Berk, 2006). Then, the boys tend to
masculinity, as girls go femininity; however, there
are chances for reverse cross-characters. Ollendick,
Yang, Dong, Xia, and Lin (1995) proposed about the
reverse cross-characters is about the variations to
traumatically nurture exposure for children when
there are developing. These are critical for managing
felling fearfully and anxious. The expression of
concern and anxiety is in agreement with the female
role, that is usually no inheritable by ladies and
which tolerates the expression of negative emotions
and connected behaviors. Actually, dreadfulness and
uneasiness are conflicting with the manly sexual
orientation part. Such feelings are less
acknowledged in boys who are anticipated to act
bravely and to show dynamic and deliberate
adapting behavior. The study of the reverse cross-
characters, conducted by Brody, Hay, and
Vandewater (1990), discovered about relationship
between role and orientation with indexed
Emotional Story Task in 120 non-clinical referred
aged 6 – 12 years. The results indicated that female
rumored who has higher levels of concern toward
peers than boys did. Significantly, role orientation
accounted for a lot of the variance in predicting
concern than did the child’s sex. Generally, boys and
girls who have higher to peer communication about
how became the real environment. In addition,
Ginsburg and Silverman (2000) referred gendered
role influence with anxiety disorders raging for 6
and 11 years. Thus, the children who complete a
questionnaire about measuring masculinity and
femininity.
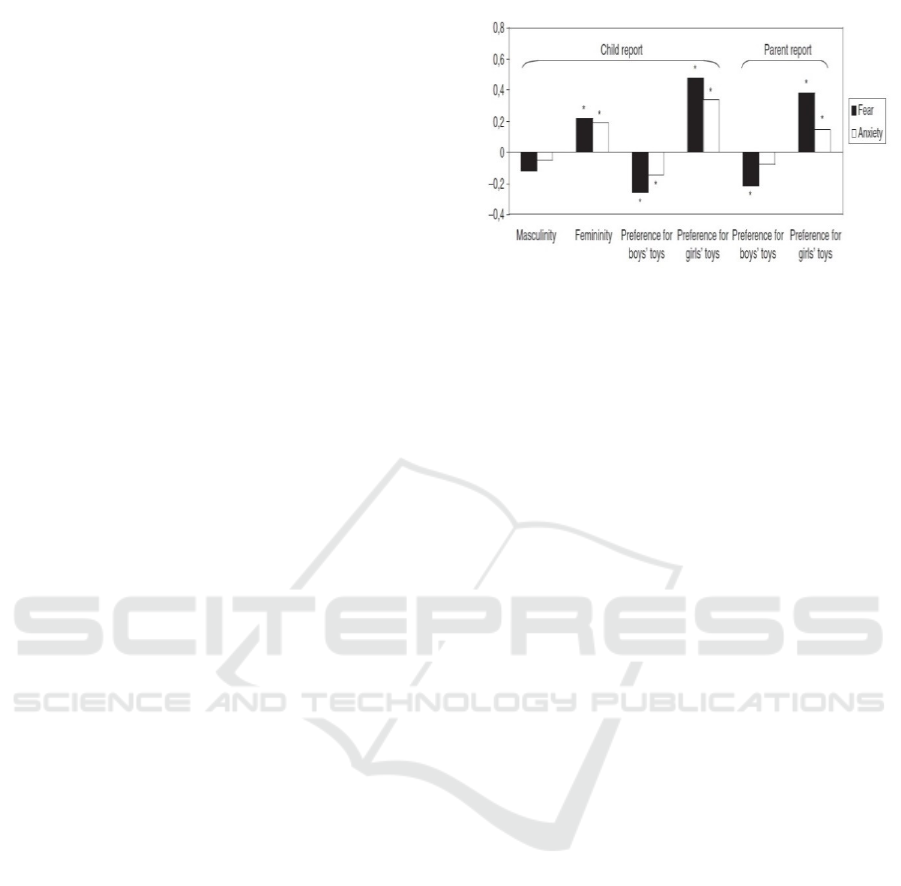
Children who are completed theses cross-
traumatically nurture assesses children preferences,
fear, and anxiety. Then, the result generated the
indexed the selection preference. (See Figure 2).
Figure 2: Correlations between gender and toy and activity
preferences, fear and anxiety scores, on the other hand, in
a sample of nonclinical children aged 10 to 13 years. *
Significant correlation at p < .05. Based on: Muris et al
(2005).
Altogether, the supporting parent and institution
put gender role orientation in theoretical develop the
proper nature and nurture by designed as it growing
phases.
4 RESULT
4.1 Clinical Psychology of
Male-students’ Disorders
This article focused about the clinical psychology of
male-students’ disorder for intellectual, emotional,
psychological, social and behavioral maladjustment.
It engaged to the particular students’ flourishing
periods. The objective of preserving the students’
attitude and their achievements, for those who were
facing crisis, and orphaned. The article also founded
that the abstained of father role would be solved
when the proper role models are exist among the
students, there are possibility of single parent
advisory to the students. The result projected several
clinical psychology of male students in IAIN
Langsa:
1. Psychiatric disorders that are related to social
anxiety, paranoia and believe in something that
does not make sense. The students with this
disorder will avoid a close relationship because
of their personal adverse effects. In addition, he
also believed in something related to paranormal
and superstition. However, not all superstitious
people include personality disorders. This
disorder usually only occurs 3% of the
population and is more likely to attack male
students. The cause of this disorder is uncertain,
ICPsy 2019 - International Conference on Psychology
184

but the possibility arises because of errors in
brain function and genetic factors. Characteristics
of schizotypal disorders with difficult to get close
to other people, thinking, expressing yourself and
using strange and unnatural words, behave
strangely, feel able to read people's thoughts, feel
nervous or tense with people who don't agree
with him, nervous and paranoid social situations
with other people. The way to treat this disorder
is with various types of therapy in psychology
psychotherapy or it can be combined with a
psychologist with a psychiatrist.
2. Paranoid Personality Disorder is a psychiatric
disorder that tends to be paranoid, suspicious and
does not trust people. He is usually more
sensitive, irritable and connects everything with
scary things. Another person is an adverse
aggressor who wants to hurt, and harm him so he
rebels in order to maintain his pride. He often
threatened, rebelled, refused about his mistakes.
He often acts a priori and convicts something
without investigating first. The cause of this
disorder is also certain, but tends to be possible
due to artificial or reality environment. Occurs in
men or women at the beginning of the 18-20
yearly phase. The types of paranoid personality
disorders are: easy personality is swayed, reacts
to everyday experiences with a sense of surrender
and inferiority and blames others, a more
aggressive personality. It is rude very sensitive to
something that is his right, the characteristics of a
paranoid personality disorder are, excessive
sensitivity to rejection and failure, tends to hold
grudges, refuse to forgive hurts or minor
problems, forcing personal rights by
misinterpreting the attitudes of others, repeated
suspicion of partner loyalty, and feeling himself
most important. Usually, indeed someone with
this disorder does not want to be treated because
he will tend to feel suspicious, but if he is willing
to be treated, then counseling and psychotherapy
is the solution. Because the combination of the
two will make the handling process faster.
3. Schizoid Personality Disorder is a psychiatric
disorder that does not want to connect with other
people, full of secrets, being cold and apathetic
towards others. To create a desire to socialize,
people with schizoid disorder will create their
imagination in complete and exclusive detail.
Schizoid itself still has something to do with
schizophagia and schizophrenia. Someone with
this personality disorder will have a negative
impact on himself because he does not have good
social status. Researchers believe that the causes
of dual-personality disorders are genetic factors
and parenting. Characteristics of personality
disorders; do not want to get along with other
people, prefer delusion, choose to live without
other people's interference, difficult to be happy,
not interested in intimate relationships, be cool,
lack of humor, difficulty expressing, not
motivated, and do not react when praised or
criticized. It take handling this personality
disorder is rarely faced with the clinical world, so
effective treatment is still unknown.
4. Antisocial Personality Disorders is a personality
disorder that tends to fight the rights of others.
Someone with this disorder has a moral who is
not seen, has committed a crime or violated the
law and behaves aggressively. The cause of
antisocial disorders is not yet known, but
scientists believe that there are disorders of brain
structure and aggressive behavior of parents. The
characteristics of antisocial personality disorders
are make yourself happy, take actions that are
unpleasant to others, easily bored and acts
without thinking, do everything you can to get
what you want, aggressive and often fighting,
have a criminal trial, and have no guilt. The
treatments of this disorder is very difficult,
because those who feel the impact of this
disorder are the community itself is not the
culprit. If you want to do a handler, then
psychotherapy with speech therapy is very
possible.
5. Borderline Personality Disorders is a psychiatric
disorder that has unstable emotions with
abnormal behavior and lack of self-control. The
main characteristic of this personality disorder is
his rapidly changing emotions. At first, he was
happy and laughed, he would then cry. He also
tends to do something that threatens life, feels
empty and endangers others. In addition, he is
also at risk of consuming alcohol, drugs and
depression. This disorder often appears around
early adulthood or after the end of adolescence.
Scientists say that the causes of this personality
disorder are usually genetic factors, brain
disorders, the environment, wrong relationships
or because of a pile of traumatic events. The
characteristics of borderline personality disorder
are Fear of being left or ignored, emotions that
go up and down due to trivial events, hard builds
and maintains relationships, act without thinking,
Clinical Psychology Problems of Maturity Period to Adulthood for Male Students of IAIN Langsa
185

there is a desire to commit suicide, feel alone and
empty, it is easy to get angry, when stressed, he
will feel paranoid, hallucinations, numbness,
daydreaming and often forget. The treatment this
disorder is with psychotherapy or with a
combination of drugs. Even though there is no
specific medication, there are drugs that can
reduce symptoms such as depression,
impulsivity, aggression or anxiety. The drugs
given can be antidepressants, antipsychotics or
mood stabilizers by prescription. Alternatively, it
could be inpatient care in a hospital to protect
patients from committing suicide or hurting
others.
6. Histrionic Personality Disorders is a distraction
to look for more attention with seductive or
inappropriate behavior to be accepted by others.
It appears in the adult phase, someone with this
disorder has a cheerful, broad, enthusiastic and
flirtatious character. The percentage of this
disorder is 2-3% of the population and 4 times
often experienced by women. People with this
disorder will be more provocative in sexual,
striking, and selfish, always want to be praised
and easily influenced by others. Scientists due to
the formation of the environment and genetic
factors believe the cause of this personality
disorder. On the other hand, there is another
guess, which this disorder appears because of
discipline formed and imitates the behavior of
people around them. The characteristics of
histrionic personality disorder are feel
uncomfortable if not looked at, being flirtatious,
provocative and ensure that he is the center of
attention, always worry about the opinions of
others, easily influenced, drama and overacting,
being intimate, imitate the speech style of a real
character or film, and use the physical to pay
attention. Someone who has this disorder often
thinks that this is not a type of personality
disorder. However, if someone wants to be dealt
with, then psychotherapy is an effective handler.
7. Narcissistic Personality Disorders is a psychiatric
disorder that considers itself important, happy to
be overly praised and unable to understand the
feelings of others. Someone with this disorder
often thinks of ways to succeed and get success
or busy thinking about his appearance.
Narcissism itself is taken from Greek mythology
about someone named Narcissus who is looking
for true love. Although many women came, he
refused. Until one day, he saw a beautiful figure
in the reflection of water. He fell in love with the
reflection, then plunged himself into the pool,
until he died in the pond. The figure in the
reflection of water is actually himself. With a
story like this, one can find that narcissistic
characteristics themselves are loving themselves.
The causes of this personality disorder are
genetic and environmental factors. It could also
be due to preferential treatment since childhood.
However, to get valid results, there needs to be a
diagnosis of a psychologist or psychiatrist. The
characteristics of personality disorders are
believe that he is unique, have fragile self-
esteem, angry if other people are ignorant, envy
the success of others, their needs must be above
others, selfish, like to use other people. The
Treatment is with psychoanalysis and CBT
therapy. There are no specific drugs, but
psychiatrists can prescribe depressants, anxiety
or other drugs.
Based on the seven fact above, the clear
explanation shared about clinical psychology of
male-students’ disorder. These seven disorders are
occurred to male-students and trigger stimuli
references level of fear and anxiety level that lead to
malfunction disorder.
5 DISCUSSION
The vulnerabilities and risk factors like negative
learning experiences, disagreeable life events, and
adverse family factors can create kids additional
probably to develop anxiety disorders. Fortuitously,
there are protecting effects, which may serve to
safeguard kids and adolescents against the event of
insecurity that tally a male adolescent psychological
issues (as conducted by Cicchetti & Cohen, 1995).
Then, Masten (2011) proposed about protection of
relation to the development of anxiety problems in
youths. It should be noted that the article devotes
attention to factors and processes that have already
been discussed in the context of the male-students’
fitrah as the part of Rahmatan lill ‘Alamin concepts.
The develop fitrah ideas of Rahmatan lill ‘Alamin
promoted the adaptation outside circumstance. In
conclusion, the article employed a person-based
approach, the male-students’ fitrah as the part of
Rahmatan lill ‘Alamin concepts, as milestone of
Islamic tradition teaching. The fact that resilience is
an inferential construct that's supported the
judgments of threat and adaptation has caused issues
within the assessment and study of this idea (Luthar,
ICPsy 2019 - International Conference on Psychology
186

1999). The approaches silent that known resilient
adolescents who adapt well in spite of risk and
adversity and so compared them to dysfunctional
adolescents who fail to adapt below adverse
circumstances with relevancy variety of protecting
childhood variables. By definition, resilient
adolescents displayed higher levels of worldwide
self-worth and psychological well-being than their
dysfunctional counterparts. Social society support
are previewed this notion fits nicely with theories
that judge importance to social relationships in
children’s development toward adulthood once the
abstained of parent role happens. Children perceived
their family as less ancillary displayed higher levels
of teacher-reported internalizing symptoms. Most
significantly, proof was conjointly found for the
hypothesized analgesic impact of family support:
that's, the negative impact of disagreeable life events
on children’s internalizing symptoms was
considerably reduced by high levels of perceived
family support. The disorders proof on top of was
summarized indicating that negative life events seem
to extend the danger for issues. The samples
projected that positive life events, and specifically
positive social events, e.g., participating in enjoyable
social activities, and organized by the institution,
IAIN Langsa. These findings suggest that socially
supportive experiences may protect youths against
the emergence clinical disorders for male students.
6 CONCLUSION
This article summarized a variety of the male-
students’ fitrah as the part of Rahmatan lill ‘Alamin
concepts, as milestone of Islamic tradition teaching,
in terms for clinical psychology disorders solutions.
These protecting variables are definitely concerned.
Yet, it ought to even be mentioned that they are
doing not appear to be terribly specific to childhood
anxiety, however rather play a job during a broad
vary of psychological disorders in youths. This may
counsel that the majority of those factors shouldn't
be considered key constructs within the pathological
process of hysteria disorders in kids and adolescents,
notably male-students. However, it ought to be
unbroken in mind that such protecting factors
typically play a mediating or alleviative role within
the method between threat and stress. On the one
hand, and also the emergence of high concern and
anxiety, on the opposite hand, which suggests that
these variables might eventually build the distinction
between traditional and abnormal concern and
anxiety reactions in youths.
REFERENCES
(QS. Al-Ahzab. 33:21). Lihat Ahmad Mushthafa al-
Maraghy, Tafsir al-Maraghy, Juz XVII, (Beirut: Dar
al-Fikr, tp. th).
(QS. Al-Ambiya. 21:107). Lihat Ahmad Mushthafa al-
Maraghy, Tafsir al-Maraghy, Juz XVII, (Beirut: Dar
al-Fikr, tp. th).
Archer, J., 2006. Testosterone and human aggression: an
evaluation of the challenge hypothesis. Neurosci.
Biobehav. Rev. 30, 319–345.
Babbie, Earl. 2010. The Practice of Social Research (12th
ed.). Wadsworth: Cengange Learning
Berk, L. E. (2006). Child Development. Boston: Pearson
Education. Eighth Edition. Illinois State University.
Creswell, J. W. (1998). Qualitative inquiry and research
design: Choosing among five traditions. Thousand
Oaks, CA: Sage.
Ginsburg and Silverman (2000) Gender role orientation
and fearfulness in children with anxiety disorders. J
Anxiety Disord. 2000 Jan-Feb;14(1):57-67. PMID:
10770236.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10770236
Glesne, C., & Peshkin, A. (1992). Becoming qualitative
researchers: An introduction. White Plains, NY:
Longman.
Kerlinger, Fred N., & Lee, Howard B. (2000) Foundations
of Behavioral Research (4
th
ed), Orlando: Harcourt
College Publisher
Korchin, Sheldon J. Cowan, Philip A. (1982). Ethical
Perspectives in Clinical Research. Handbook of
Research Methods in Clinical Psychology. New York:
John Wiley, 1982: 59-94.
Leslie R. Brody, et all (1990). Gender, gender role
identity, and children's reported feelings toward the
same and opposite sex. The Journal of Social Sciences
Research. Volume 23, Issue 7–8, pp 363–387. Kluwer
Academic Publishers-Plenum Publishers,
https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00289226.
Lisa Rapp-Paglicci, Chris Stewart, William Rowe, J.
Mitchell Mille, (2002) Addressing the Hispanic
Delinquency and Mental Health Relationship through
Cultural Arts Programming A Research Note from the
Prodigy Evaluation, SAGE Journal: Journal of
Contemporary Criminal Justice, Volume: 27 issue: 1,
page(s): 110-121, published online: April 17,
2011; Issue published: February 1, 2011
Maccoby, Eleanor E. (2000). Perspectives on gender
development. SAGE Journal International Journal of
Behavioral Development. Published December 1,
2000 Research Article. Stanford University, California,
USA. https://doi.org/10.1080/016502500750037946
Mathews, Tara., Dempsey, Margaret.,& Overstreet, Stacy.,
(2009) Effects Of Exposure To Community Violence
On School Functioning:The Mediating Role Of
Clinical Psychology Problems of Maturity Period to Adulthood for Male Students of IAIN Langsa
187

Posttraumatic Stress Symptoms Behaviour Research
And Therapy 47, 586–591 Doi:10.1
Muris, Peter (2007). Normal and Abnormal Fear and
Anxiety in Children and Adolescents. Elsevier 30
Corporate Drive, Suite 400, Burlington, MA 01803,
USA
Nata, Abuddin (2018). Islam Rahmatan Lil Alamin
Sebagai Model Pendidikan Islam Memasuki Asean
Community. Online Article,
http://abuddin.lec.uinjkt.ac.id/articles/islam-rahmatan-
lil-alamin-sebagai-model-pendidikan-islam-memasuki-
asean-community retrived on 10 June 2018.
Ollendick, et all (1995) Perceptions of fear in other
Children and adolescents: The role of gender and
friendship status. The Journal of Abnormal Child
Psychology 23(4):439-52. DOI: 10.1007/BF01447207
Palapattu, Newman Kingery, and Ginsburg, (2006)
Gender Role Orientation and Anxiety Symptoms
among African American Adolescents. In Journal of
Abnormal Child Psychology 34(3):441-9 ꞏ July 2006
Papalia, Diane E., Olds, Sally Wendkos., Feldman, Ruth
Duskin., (2001) Human Development (8
th
Ed), New
York: Mc Graw Hill
Setiono, Djoko (2011) Pendidikan konservasi. Dalam
pelatihan pendidikan konservasi alam angkatan 26.
Makalah disajikan dalam the Indonesian wildlife
conservation foundation (IWF) dan Balai Taman
Nasional Alas Purwo Banyuwangi, 18-19 Juli 2011
Shihab, H.M. Quraish (2009). Tafsir al-Mishbah, Pesan,
Kesan dan Keserasian al-Qur’an, Jilid 8, Ciputat:
Lentera Hati.
The Ministry of Health (2008). Riset Kesehatan Dasar
(RISKESDAS) Laporan Nasional 2007 Badan
Penelitian dan Pengembangan Kesehatan Departemen
Kesehatan,
The study of Young in Conflicts, The State of the World’s
Children (2002). The United Nations Children’s Fund
(UNICEF) Publication report, UNICEF, UNICEF
House, 3
rd
UN Plaza, New York, NY 10017, USA.
https://www.unicef.org/sowc02/pdf/sowc2002-eng-
full.pdf
Wiley, John. (2014). The Wiley-Blackwell Handbook of
Positive Psychological Interventions, edited by Acacia
C. Parks, Stephen M. Schueller. John Wiley & Sons
Ltd, the Atrium, Southern Gate, Chichester, West
Sussex.
World Health Organization (1994). Programme on Mental
Health.WHO/MSA/MNH/PSF/97.4 about measuring
quality of Life. The World Health Organization Quality
Of Life Instruments (The Whoqol-100 and the
Whoqol-Bref).
ICPsy 2019 - International Conference on Psychology
188
