
What Makes Entrepreneur Use Social Media Marketing
Prihatin Lumbanraja, Arlina Nurbaity Lubis
,
and Beby Kendida Hasibuan
Faculty of Economic and Business, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Social Media Marketing, Human Factor, Market Attractiveness, Organic Referral, Entrepreneur
Abstrac: Micro, small and medium enterprises have become the main development wheels of a country. Unfortunately
many of these businesses do not last long with relatively low performance. Low performance makes the
business's attractiveness decrease. The main problems that often occur are problems in the scope of marketing
and financial behavior. This study aims to evaluate the influence of financial and marketing behavior in
driving the performance of MSMEs. A total of 300 SMEs participated in this study. Data were collected using
a research questionnaire. Data were evaluated using multiple linear regression analysis. This research shows
that currently the performance of MSMEs is only influenced by marketing activities. Financial behavior
cannot yet reflect improvements in MSME performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
Higher education has an important role in shaping the
younger generation by providing education to the
younger generation. Higher education is the center of
the young generation for today's adult society (Raval,
2006). Higher education institutions become the right
place in training and creating opportunities for
students to become professionals in the work
environment or encourage them to improve the
entrepreneurial aspect within the scope of objectives
after graduating from higher education. Badal and
Srinivasan (2011) state that people's entrepreneurial
intentions will decrease with age. To support this
statement, Gallup (2013) provides the GALLUP-
HOPE Index which emphasizes that the
entrepreneurial spirit must be nurtured and left early
so that they are ready to start a business or create
things that bring change to the world.
The level of open unemployment at the tertiary
level of graduates in Indonesia has increased from
August 2013 to August 2015 (BPS, 2017). In 2013
the open unemployment rate for university graduates
was 434 thousand and increased to 653 thousand in
2015. This figure indicates a significant increase in
unemployment from university graduates, especially
at the undergraduate level. Lumbanraja et al. (2018)
provides information that although there has been an
increased interest in entrepreneurship from
prospective college graduates, the majority of
prospective graduates still choose to find work rather
than opening their own jobs.
Kuswara represented the Ministry of Research,
Technology and Higher Education (2012)
increasingly aggressively promoting a curriculum
that builds an entrepreneurial spirit and
entrepreneurial skills from various universities. This
mission is related to the plan to create an
entrepreneurial campus. Higher education has an
important role in shaping the younger generation by
providing education to the younger generation.
Higher education institutions become the right place
to train and hone the potential of students either as
professionals or encourage them to build a business
through entrepreneurship as their future career. The
choice of career direction for students who have
completed their studies or graduated is only divided
into two main options, which are job seekers or job
creators. Higher education institutions are a means of
fostering the entrepreneurial abilities of the embryos
of young entrepreneurs so they can compete
competitively in the world of entrepreneurship. The
development of the industrial revolution 4.0 which
makes everything all-round internet (internet of
things) makes entrepreneurs need skills in utilizing
the access of the internet world for the benefit of
entrepreneurship. Duggan and Smith (2013) in their
research showed that two-thirds of cyberspace
communities are active in their social media, such as
YouTube, Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn. Alexa
(2015) shows Facebook's popularity among the world
658
Lumbanraja, P., Lubis, A. and Hasibuan, B.
What Makes Entrepreneur Use Social Media Marketing.
DOI: 10.5220/0009329306580664
In Proceedings of the 2nd Economics and Business International Conference (EBIC 2019) - Economics and Business in Industrial Revolution 4.0, pages 658-664
ISBN: 978-989-758-498-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

is very high, reaching the second position after
Google from the perspective of internet users. Beck
(2015) shows that social media platforms have
become targets of international marketers in
increasing demand for their products.
The use of advertising media through social
media provides many benefits for businesses, for
example increasing the effect of word of mouth from
the comments column and displaying items that will
not fade with time (Chu, 2011). Nair's research (2014)
shows that more than millions of marketers are active
in social media to drive demand for their products and
increase sales. This study seeks to identify factors that
encourage business actors, especially youthpreneur in
higher education to be active in the use of social
media as an advertising platform and evaluate their
impact on business performance.
Many of the business actors refuse to try to market
their products online, especially in paid platforms
because the mindset of young businesses towards
advertising is more directed towards costs than
investment. This study seeks to evaluate the basic
model that can foster the use of industry 4.0 for young
entrepreneurs to expand their markets. Specifically,
this study evaluates factors that influence the use of
advertising platforms on social media.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Entrepreneurship
Understanding entrepreneurship in the study of
literature is very diverse. Hunger and Wheelen (2015)
stated that entrepreneurship is in principle a capacity
for creative thinking and innovative behavior that is
used as a basis, resources, motivators, goals,
strategies / strategies, and tips in facing life's
challenges. Scarborough and Cornwall (2014) argue
that entrepreneurs are people who are able to create
new businesses, and people who are usually directly
confronted with risk are able to identify in achieving
success. Entrepreneur is able to identify various
agreements, and devote all the resources he has to
change the opportunity that is profitable.
Entrepreneurship in this sense is related to the ability
to create new businesses.
Entrepreneurship (entrepreneurship) is also
understood as the soul, spirit, attitude, behavior, and
potential ability of a person in handling businesses
and or activities that lead to efforts to find, create,
implement work methods, technology, and new
products by increasing efficiency in order to provide
services that it's better to get the maximum profit
(2012). Entrepreneurship in this case is a creativity
and innovation that is owned by someone to produce
added value for themselves and benefit others. In
essence, entrepreneurship is the nature,
characteristics, and character of someone who has the
will and ability to realize innovative ideas in the real
world (business) creatively and productively.
Someone who has the potential or entrepreneurial
spirit, he is able to see and assess business
opportunities, gather various resources needed to take
appropriate action and take advantage of business
opportunities.
Research by Lumbanraja et al. (2018) identified
that there is a synergy between the University,
Lecturer Staff, and Students in generating student
career direction in the future. The synergy encourages
students to become job creators or job seekers.
2.2 Social Media Exposure
Social media exposure is related to the intensity of
business actors in the use of social media. Marketers
through social media require active participation in
giving reviews and answering consumer questions
live in order to bind consumers' attention.
2.3 The Human Factor (Capabilities)
Robbins and Judge (2013) define capability as the
capacity of individuals to carry out various tasks in a
job. Every person has strengths and weaknesses in
terms of abilities that make him relatively superior or
inferior to other individuals in carrying out certain
tasks or activities. The capability in this study refers
to the ability of businesses to utilize social media
platforms as a means of advertising for young
entrepreneurs. This capability is evaluated based on
cognitive abilities and actualization abilities.
A person's capabilities play a big role in driving
performance. Krietner also divides that capabilities
are basically divided into two categories, namely
physical capabilities and cognitive capabilities. A
person's capability plays a dominant role in
encouraging individual performance. This shows that
someone who has the capability in acting will
properly carry out the tasks assigned to him. Thus,
young entrepreneurs who have advertising
capabilities will be able to market their products well
through social media platforms.
2.4 Market Aspect (Traffic)
The target of marketing by utilizing social media via
the internet is social media users or the platform, in
What Makes Entrepreneur Use Social Media Marketing
659

other words, traffic. Li and Kannan (2014) show that
there are various buyer characteristics in online store
traffic. Schlosser et al. (2006) states that a prospective
buyer will make security considerations sourced from
the type of ad traffic from the transaction partner.
Pauwels et al., (2016) provide three main categories
in evaluating traffic, namely:
a) Direct Traffic, refers to users who go directly to
social media sites by inputing a website address
or through a bookmark.
b) Referral Traffic, refers to users who go to the
destination of the website, for example through
Facebook ads directed to whatsapp media.
c) Organic traffic, refers to active users
independently searching for product
information through internet media before
consuming it.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Research Time and Characteristics
This research was conducted by conducting a study
of SMEs in the city of Medan. The research location
is focused on several locations in the city of Medan
such as around Universities as most of youthpreneurs
were students, in the business area and other strategic
locations.
3.2 Participant
The unit of analysis in this study is young
entrepreneurs, especially alumni and students from
Higher Education in the City of Medan. The object of
analysis in this study is the perception and actions of
business actors in conducting business management
and the acquisition of the development they
experienced. Because there is no centralized data
from young entrepreneurs in the city of Medan, the
study population is an unidentified population. By
using sample rules on SEM and sample formulations
based on unidentified population, the sample of this
study was stabilized by 200 young entrepreneurs and
taken by non-probability sampling. Their consent
were taken to participate in this study.
3.3 Data Collection Method
Self-administered questionnaires were employed
during our research. The questionnaire in this study
was prepared based on a theoretical study and
adjusted to the MSME's condition that was the object
of research. Therefore, the research questionnaire
requires a validity and reliability test before it is
applied as an instrument for research data collection.
The validity and reliability testing of this instrument
was carried out on 30 MSMEs owners outside the
research sample later. Evaluation of the validity of the
questionnaire is done by face validity by adjusting the
list of questions raised with existing theories, as well
as the Pearson correlation which shows the
correlation value of the total score on each variable.
The instrument reliability test was conducted by
evaluating the Cronbach's alpha value on each
variable proposed in this study
3.4 Data Analysis Method
We employed multiple linear regression to evaluate
the impact of each aspect on its dependent variable,
Social Media Exposure.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Participants’ Characteristics
Characteristics of respondents by sex were carried out
to obtain the distribution of characteristics of business
operators in Medan City based on gender. In general,
Indonesia adheres to segregation where generally
men make a living and women take care of the
household. The results of tabulation of respondents
by sex are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Responden Based on Gender
Gende
r
N
of Sample %
Male 80 40,00
Female 120 60,00
Total 200 100,00
Table 1 provide information that the involvement
of women in the business environment (MSME) is
greater than the involvement of men as entrepreneurs.
This labor force participation indicates that the role of
women in the work environment has increased.
Women prefer entrepreneurship where they can
balance their time between household duties and
duties as an entrepreneur.
The majority of business operators in Medan City
are in the age range of 20 to 29 years (42.5%)
followed by ages 30 to 39 years (36.00%). This
indicates that the spirit of young entrepreneurs in the
city of Medan has begun to grow and increase the
participation of young people in the business
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
660
environment. Some start this business by continuing
the family business, but many also start a business
from scratch.
the majority of business people have the last
education level achieved is high school, followed by
the level of Bachelor education (S1). This shows that
one of the factors that drives business actors is the
problem of education where the last education they
have is generally difficult to find work that can meet
family needs. At present it is very rare for companies
to accept employees with a high school education or
below. Nevertheless, participation of bachelor
graduates (S1) in the business environment itself has
improved.
4.2 Regression Model Evaluation
This research model uses two independent variables
and one dependent variable. The independent
variables used in this study are human aspect and
market aspect of MSMEs Business owner in Medan
City. The dependent variable of this study is the
Social Media Exposure which implemented by the
MSMEs. A total of2300 businesses participated in
this study.
4.2.1 Residual Normality Test
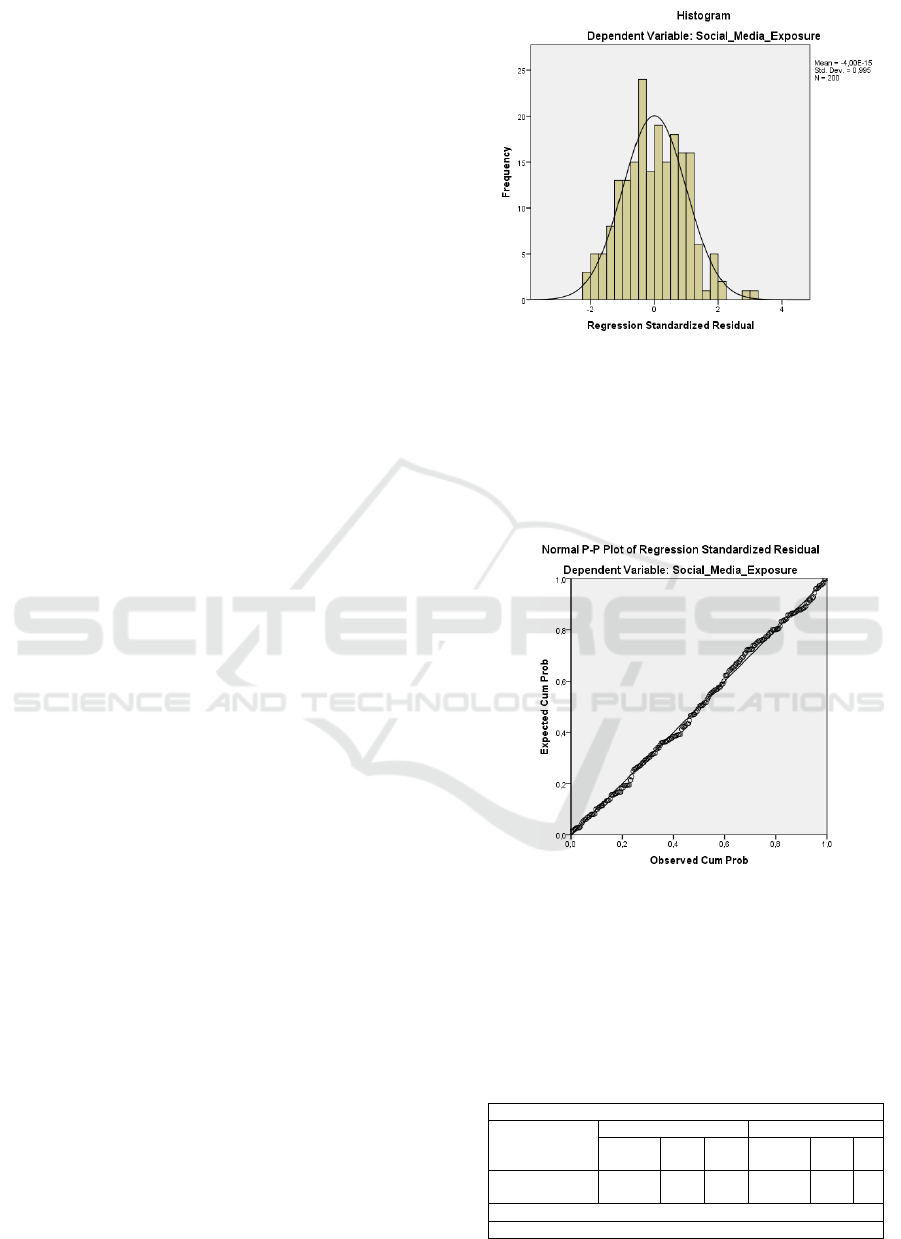
The normality test aims to find out whether the
intruder or residual variable regression model has a
normal distribution. Good data is data that has a
pattern like the shape of a bell on the histogram
diagram. The data normality test used in this study is
the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Criteria for testing one
sample using a one-sided test that is by comparing the
probability with a certain level of significance that is
if a significant value or probability <0.05, then the
distribution of data is not normal and if a significant
value or probability> 0.05, then the data is normally
distributed. Evaluation using graphs is used to
support statistical evaluation results.
Figure 1. Residual Histogram
Figure 1 provides information that in the
histogram graph, the distribution of residual data
leads to bell-shaped; in this case, the residual data can
be categorized as normally distributed. P-P plots are
applied to evaluate this situation more clearly.
Figure 2. Normal P-P Plot
Figure 2 shows that data residuals are spread
evenly along diagonal lines. This condition further
supports that data residuals are normally distributed.
This distribution was evaluated statistically and
summarized in Table 2
Table 2. Normality Test
Tests of Normality
Kolmogorov-Smirnov
a
Shapiro-Wil
k
Statisti
c
df Sig. Statisti
c
df Si
g.
Unstandardize
d Residual
,038 200 ,200
*
,993 200
,4
16
*. This is a lower bound of the true significance.
a. Lilliefors Significance Correction
What Makes Entrepreneur Use Social Media Marketing
661
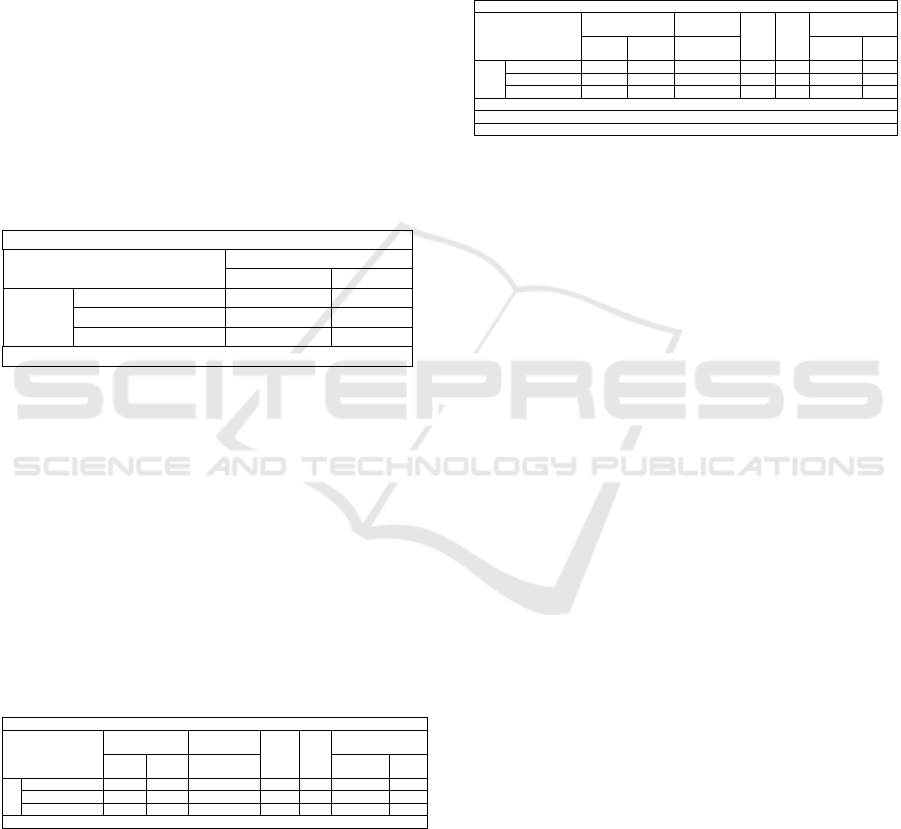
Table 2 provides information that statistically, the
Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Shapiro-Wilk tests, give a
significance value> 0.05 which indicates that the data
residuals are normally distributed. Thus, the
assumption of normality in residual data has been
fulfilled.
4.2.2 Multicollinearity Test
Symptoms of multicollinearity can be seen from the
value of tolerance and VIF (Varⅰance Inflate Factor).
Both measures indicate the variables which are
strongly affecting other dependent variables.
Tolerance is to measure the variable variables of the
dependent variables which are not explained in terms
of the other variables. The value that is used for
Tolerance> 0.1 and VIF <5, then there is no
multicolon.
Table 3. Collinearity Analysis
Coefficients
a
Model Collinearity Statistics
Tolerance VIF
1
(Constant)
Human_Aspect ,991 1,009
Market_Aspect ,991 1,009
a. Dependent Variable: Social_Media_Exposure
Table 3 showed evidence that there is no problem
of multicollinearity of data on the independent
variables of the study. Each element of marketing
communication technology is independent so that the
variables proposed in this model do not affect each
other.
4.2.3 Heterokedasticity Test
Heterokedastity test data in this study were evaluated
using Glesjer-test statistical method. The result is
summarized as follow:
Table 4. Glesjer Test Analysis
Coefficients
a
Model Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t Sig. Collinearity
Statistics
B Std.
Error
Beta Tolerance VIF
1
(Constant) ,317 ,261 1,215 ,226
Human_Aspect ,020 ,055 ,026 ,360 ,720 ,991 1,009
Market_Aspect -,009 ,028 -,022 -,308 ,758 ,991 1,009
a. Dependent Variable: ABSRES
Table 4 indicates that there are no statistically
significant independent variables on the value of
absent data residuals. Thus statistically there are no
data heterocedasticity problems.
The research model has been evaluated qualitatively
based on classical assumptions. The model has
fulfilled the classical assumption criteria so that the
prediction results of this research model are best
linear unbiased estimators and can be used to evaluate
the conditions that occur in the research sample
4.2.4 Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
The results of the regression conducted in this study
are summarized as follows:
Table 5. Regression Result
Coefficients
a
Model Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t Sig. Collinearity
Statistics
B Std.
Erro
r
Beta Tolerance VIF
1
(Constant) ,059 ,450 ,131 ,896
Human_Aspec
t
,668 ,094 ,417 7,089 ,000 ,991 1,009
Market_Aspec
t
,289 ,049 ,349 5,924 ,000 ,991 1,009
a. Dependent Variable: Social_Media_Exposure
F Statistics = 47,126 (Sig <0,05)
Adjusted R Square = 0,317
Table 5 provides information that aspects of
human resources and aspects of market potential are
able to explain 31.7% of the state of social media
exposure from MSMEs. Thus, there are 68.3%
influences from outside the model currently
proposed. The significance level of the F-statistics on
the proposed model <0.05 which indicates that
together, aspects of human resources and market
potential play a role in influencing social media
exposure of MSMEs in Medan City.
Regression models that can be formulated based
on the results of this study are:
Y = 0,059 + 0,668 Human Aspect + 0,289 Market
Aspect + e
The aspect of human resources has a great
influence on social media exposure of entrepreneurs
with a beta value of 0.668 and a significance level
<0.05. Thus, there is sufficient evidence to state that
aspects of human resources have a positive and
significant effect on social media exposure of
business actors. The aspect of human resources is
related to the capabilities of a business actor in
implementing or using social media as marketing
media. This study provides empirical evidence that
the main factor in the use of social media is the ability
of businesses to use existing technology.
Aspects of market potential in this study have a
positive (B = 0.289) and significant (sig <0.05) effect
on social media exposure. In the proposed model this
effect is relatively smaller than the human resource
aspect but still influences the social media exposure.
Thus, there is enough evidence to state that the market
potential of the social media platform has a positive
and significant effect on the social media exposure of
MSMEs in the City of Medan. For every one unit
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
662

increase that occurs from market potential, media
exposure will increase by 0.289 units. This market
potential aspect includes a review of the traffic that
will be obtained from business actors for the social
media marketing activities that it applies. The greater
the market potential that might be obtained, the
greater the level of social media exposure. Thus,
people are getting smarter in choosing social media
marketing platforms in optimizing their market
potential
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
SUGGESTIONS
The era of the industrial revolution makes the role of
e-commerce in the industry increasing. One form of
e-commerce that can be utilized by businesses is
social media marketing. This research indicates that
the intensity of the use of social media from
entrepreneurs depends on their perception of the
market potential of the platform and the ability of
businesses to use social media as marketing media.
The most dominant factor is the self capability to
operate the platform. Nevertheless, business people
are getting smarter in assessing the benefits of social
media marketing and starting to pay attention to the
traffic from the platform that can be obtained to
optimize the demand for their business.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge that the present
research is supported by Universitas Sumatera Utara.
The support is under the research grant TALENTA -
Penelitian Dasar for year 2019
REFERENCES
Alexa. 2015. Top sites: The top 500 sites on the web.
Alfonso, Natalia. 2017. 3 Ways to Enhance Search
Campaigns with Display Advertising, (accessed
February 17, 2019), [available
athttp://advertising.amazon.com/blog/display-
advertising]
Badal, S.B., Srinivasan, R. 2011. Mentor Support Key to
Starting a Business. GALLUP: November 25, 2011
Badan Pusat Statistik. 2017. Pengangguran Berdasarkan
Tingkat Pendidikan, diakses pada 20 Januari 2018
Beck, M. 2015. Facebook accounted for 75% of social ad
spending globally in 2014
Chu, S.-C. 2011. “Viral advertising in social media:
Participation in Facebook groups and responses among
college-aged users,” Journal of Interactive Advertising,
12, 30–43.
Duggan, M., & Smith, A. 2013. Social media update 2013.
Retrieved from
http://www.pewinternet.org/2013/12/30/social-media-
update-2013
GALLUP. (2013). The 2013 GALLUP-HOPE Index. New
York: GALLUP and Operation Hope
Hunger, D.J. dan Wheelen, T.L. 2014. Essential of Strategic
Management, Fifth Edition. USA: Pearson Education
Limited
Kotler, Philip dan Kevin Lane Keller. 2012. Marketing
Management, 14th Edition. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Kumar, Vineet. 2014, “Making ‘Freemium’ Work,”
Harvard Business Review, 92(5), 27–9.
Kuswara, H. 2012. Strategi Perguruan Tinggi Mewujudkan
Entrepreneurial Campus. Jakarta: Kementerian Riset
Teknologi Dan Pendidikan Tinggi Republik Indonesia
Li, Hongshuang and Kannan, P.K. 2014. “Attributing
Conversions in a Multi-channel Online Marketing
Environment: An Empirical Model and a Field
Experiment,” Journal of Marketing Research, 51 (1),
40–56.
Lubis, A.N. 2018. "Evaluating the customer preferences of
online shopping: Demographic factors and online shop
application issue", Academic of Strategic Management
Journal, 17(2)
Lumbanraja, P., Lubis, A.N., and Hasibuan B.K. 2018. The
role of higher education to promote youthpreneur,
paper presented at ICOSTEERR 2018, Universitas
Sumatera Utara.
Munizu, Musran. 2010. Pengaruh Faktor Faktor Internal
dan Eksternal Terhadap Kinerja Usaha Mikro dan Kecil
Di Sulawesi Selatan. Jurnal Manajemen dan
Kewirausahaan, 15, 33-41
Nair, S. 2014. What are Facebook’s revenue sources?,
Retrieved from http://finance.yahoo.com/news/must-
know-assessing-facebook-revenue-170009607.html
Pauwels, Koen, Ceren Demirci, Gokhan Yildirim and
Shuba Srinivasan .2016. “The Impact of Brand
Familiarity on Online and Offline Media Synergy,”
International Journal of Research in Marketing, 33 (4),
739–53.
Raval, D. 2016. What is the role of higher education
institutions in promoting entrepreneurship in India?
Technology Innovation Management Review, 6(5), pp
24-26
Rivai, Vethzal dan Basri. 2005. Performance Appraisal
Sistem yang tepat untuk Minilai Kinerja Karayawan
dan Meningkatkan Daya Saing Perusahaan. Jakarta: PT
Raja Grafindo Persada
Robbins, S.P., dan Coutler, M. 2012. Management, 11th
Edition. New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall
Scarborough, N.M., dan Cornwall, J.R. 2015. Essentials of
Entrepreneurship and Small Business Management, 8th
Edition. New Jersey: Pearson Higher Education
Schlosser, Ann E., Tiffany Barnett White and Susan M.
Lloyd. 2006. “Converting Web Site Visitors into
What Makes Entrepreneur Use Social Media Marketing
663

Buyers: How Web Site Investment Increases Consumer
trusting Beliefs and Online Purchase Intentions,”
Journal of Marketing, 70 (2), 133–48.
Subijanto. 2012. “Analisis Kebijakan Pendidikan
Kewirausahaan di Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan,”
Jurnal Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, Vol 18, No. 2 Edisi
Juni 2012, Balitbang, Kemdikbud
.
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
664
