
The Effect of Implementing Internal Control System, Accounting
Standards Implementation, Management Commitment to Quality
Financial Report
Nurlinda, Erlina, Azhar Maksum, and Rina Bukit
Department of Accounting, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Prof. T.M Hanafiah, SH, Kampus USU, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords SPI, Accounting Standards, Management Commitments, QFR
Abstract: Government good quality financial report becomes an important indicator in assessing the financial
performance of the entity. This research was quantitative-qualitative study used primary data sourced from
the questionnaire. Data was processed using multiple linear regression. The results showed that there was a
positive and significant influence on the implementation of internal control systems, the implementation of
accounting standards and management commitments to the quality of financial statements. The quality of
financial statements showed quite good quality. The quality of finance was not maximally caused by human
resource factors, change-changing rules, intimely budgets, lack of coordination between parts and leadership
commitments that are not very good.
1 INTRODUCTION
Financial management in Indonesia, especially within
the scope of the public sector, has undergone a lot of
changes or improvements along with the spirit of
government's financial management reform. Thus,
financial statements must be prepared in accordance
with the provisions applicable in order to produce
quality financial statements, because bad financial
statements can pose negative implications such as
community confidence to fund managers public
(government) decreases, financial reporting is
unpredictable which results in increasing investment
risk so that investors will be afraid to invest, donors
will reduce or discontinue their assistance, the quality
of the decision becomes bad, financial statements
may not reflect the actual performance (Mardiasmo,
2009).
One of the indicators that can show quality
financial statements is shown in the opinion of the
auditor acquired by the entity (Mahmudi, 2016). The
less material findings of inspection results then the
entity will get a good opinion, because the quality
financial report should be free of material, accurate
and accountable (Mutiana, Diantimala, & Zuraida,
2017). A good opinion suggests that compiled
financial statements have fulfilled qualitative
characteristics consisting of relevant, reliable,
comparable and understandable. These charisma
qualities can be achieved if the financial statements
are structured according to applicable standards and
the entity implements adequate internal control. A
quality financial statement will be one of the
successful performance indicators of the financial
management of the Grant Fund. Thus, the top
management commitment is needed to encourage,
direct, influence its staff toward the achievement of
various objectives of the entity including the control
program (Pasaribu, 2009).
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The explanation of the agency theory is related to a
contractual relationship between the principal and the
contracting agent to perform services for principal
interests including the delegation of power in decision
making (Jensen & Meckling, 1976). If it is associated
with a theory of agency in which entity management
acts as an agent having a contract on the principal to
conduct activities or represent the interests of the
principal for their benefit through the delegation of
some authorizing decisions to agents, of course
reporting is an important information for the principal
to protect the authority that has been given, and for
Nurlinda, ., Erlina, ., Maksum, A. and Bukit, R.
The Effect of Implementing Internal Control System, Accounting Standards Implementation, Management Commitment to Quality Financial Report.
DOI: 10.5220/0009215704270434
In Proceedings of the 2nd Economics and Business International Conference (EBIC 2019) - Economics and Business in Industrial Revolution 4.0, pages 427-434
ISBN: 978-989-758-498-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
427
the entity is a tool to account for the authority
received.
The agency's problems are due to the contractual
relationship between the principla and agent. The
problem in the relationship between the principla and
agent occurs because there is an information
asymmetry where the principal will trust the
information presented in the financial statements of
the agent after being examined independently. The
management's commitment to follow up on the audit
results will result in improvements in the preparation
of good financial statements. Management's
commitment based on the thought of financial
performance in the form of quality financial
statements rests on this theory, the management of the
company is done by adherence to the prevailing rules
and regulations (Rachmad, 2011). Financial
statements are information that is a form of an agent's
responsibility for the trust given principla. Benardi,
Sutrisno, & Assih (2009) mentioned that in agency
relations, the agent is obliged to provide periodic
reports on its performance to the principal, and
further the principal will assess the performance of
the agent based on the financial statements delivered.
The three pillars supporting the theory of new
institutions consist of regulative, normative and
cultural-cognitive (Scoot, 2008). This theory
describes three important mechanisms related to the
existence of institutions that are incorporated into the
environment, which compel (coersive), the process to
mimic the actions (mimetic), and the existing norms
(normative) of the environment to provide space for
In determining the policies and supporting ways to
achieve the quality of institutional performance. The
implementation of accounting standards and
implementation of internal control is a regulative
pillar aspect in the form of mandatory rules and the
terms of the coercion that must be implemented by
the entity. While the management commitment in the
effort to repair and evaluate is carried out as a follow-
up of the test results conducted by independent parties
is an aspect of the normative pillar. Management
compliance, hopes on improving the quality of
financial statements, compliance and moral burden
resulting from the audit findings are a normative
pillar aspect. Pillar cultural-cognitif is interpreted
how the action performed by the top management will
be imitated (mimetic) by the staff. The actions taken
by the top management became an example of the
persistence of its ranks. An example of the
submistibility of the staff, cultural-cognitif is
ultimately a management action that supports and
gives space to the implementation of accounting
standards and implementation of internal control
systems. It should be recognized that as good as any
standard or system in the end will not go well if there
is no support from the top management, because the
managerial factor is one of the determinants of the
quality of financial statements (Purwati, 2016). The
implementation of integrity, conducive and
disciplined leadership by the top management being
role model and exemptured by staff will be a working
culture in the entity. This culture will certainly
support the effectiveness of the implementation of
accounting standards and the implementation of
internal control systems to produce quality financial
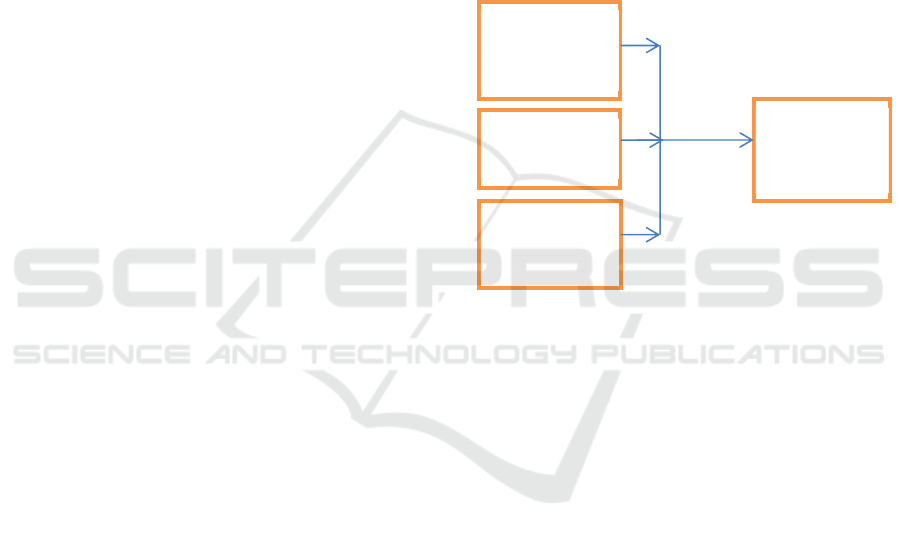
reports. Thus the framework of the research concept
can be described as follows:
Figure 1: Conceptual framework
2.1 The Effect of Implementing
Internal Control System on the
Quality of Financial Statements
Referring to the results of the examination found
several causes that are the reason the Government's
financial statements are not yet reliable and qualified
one of them is due to weak internal control, whereas
the results acknowledge that the implementation of
Internal controls play an important role in preventing
and detecting cheating on the entities (Young et al.,
2018). Some research results related to the
implementation of Internal control system (SPIP) and
quality of financial report are still found differences
in results, where there is no influence of internal
control system to the quality of financial report
(Muda et al., 2018). The results showed that the
implementation of the influential SPIP was
discovered by Julita & Susilatri (2018); Mutiana,
Diantimala, & Zuraida (2017); Yunita, Tanjung, &
Anggraini (2015); & Rahmatika, (2014); Upabayu, &
Putra (2014); Syarifudin, Surasni, & Inapty (2016);
(S, Taufik, & Hariyani, 2015). The findings show that
Financial
Reporting
Quality (KLK)
Comitment Top
Management
(KTM)
Impelementatio
n of Internal
Control System
(SPI)
Implementatio
n of Accounting
Standard (SA)
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
428

the better the implementation of internal controls will
be the better quality of the resulting financial
statements. Significant pegaruh from the application
of SPIP to the quality of financial statements found
by Onyulo (2017); Erviana (2017); Kesuma, Anwar,
& Darmansyah (2017); Mailoor, Sondakh, &
Gamaliel (2017); Purwati (2016); Susilawati & Riana
(2014). Thus the hypothesis of this research is:
H1: Implementation of internal control system
affects positively and significantly to the quality of
financial statements
2.2 The Influence of Implementation
Accounting Standards on the
Quality of Financial Statements
The implementation of accounting standards is a
standard that binds entities to implement them in the
process of drafting financial statements. The
implementation of accounting standards is binding
and mandatory. Referring to the findings of the
auditor which causes the quality of financial
statements not yet adequate is the occurrence of
inconsistency in the implementation of accounting
standards (SA). The results of previous research
found differences in results explaining the effect of
implementing accounting standards on the quality of
financial statements. Julita & Susilatri (2018) found
that the implementation of accounting standards has
no effect on the quality of financial statements.
Wisdom, Damilola, Inemesit, & Opeyemi (2017),
Sako & Lantowa (2018) found a positive relationship
between the implementation of IPSAs-based
standards with the quality of financial statements.
Abang'a (2017); Onyulo (2017); Ijeoma &
Oghoghomeh (2014); Yusniar et al. (2016); Rahman,
Hardi, & Diyanto (2015); Nelia K (2015); Upabayu
et al. (2014); Suwanda (2015); Abdullah, (2010)
found a positive and significant influence of SAP's
application to the quality of financial statements.
Thus it can be concluded that the preparation of
financial statements in accordance with accounting
standards will improve the quality of financial
statements. Based on the conclusion, the research
hypothesis is:
H2: The implementation of Government
accounting standards has a positive and significant
effect on the quality of financial statements.
2.3 The Effect of Management
Commitment to Quality of
Financial Statements
As soon as any standard or system will eventually not
go well if there is no commitment to support from top
management, because the managerial factor is one of
the determinants of the quality of financial statements
[(Purwati, 2016); (Usman, 2010)]. According to BPK
RI, one of the factors that affects the quality of
financial statements is the commitment of leadership,
especially the commitment to present reliable
information in the financial statements of the entity
that is realized with the commitment to follow up
recommendations Inspectors and follow-up results of
the test of BKP [(Silviana, 2012). Rachmawati
(2018)]. Sutaryo & Sinaga (2018) suspect in addition
to factors such as the characteristics of internal
auditors, local external factors such as regional head
commitment as local executives are also suspected to
have influence on the maturity of implementation of
internal control system .
Management commitments in the public sector
are the commitment of regional head/head of office,
which is one of the commitments on the follow up of
examination recommendation results. (Silviana,
2012). Silviana (2012); Tambingon, Yadiati, & Kewo
(2018); Kibet (2016) found that regional head
commitments have a positive effect on the quality of
financial statements. The higher the commitment of
the management will further improve the quality of
financial statements [(Fitriani, 2017); (Tambingon et
al., 2018); Mahlil & Yahya (2017)]. Research
conducted by Rahmatika (2016) found different
results, where top management support has negative
and significant influence on fraud level, as well as
fraud level has negative and significant influence to
the quality of financial statements. The principal
element in implementing the internal control system
is one of the umbrella elements that shade the other
elements. Commitment to the leadership to be the
determinant of other internal control system elements
(Sudarno, 2018). Sudarno (2018) found that effective
internal control systems improve the quality of
financial statements if the operator has high
competence and has a strong leadership commitment.
Based on explanation above, hypotheses can be
compiled as follows:
H3: Management commitments affect the quality
of financial statements
The Effect of Implementing Internal Control System, Accounting Standards Implementation, Management Commitment to Quality
Financial Report
429
3 METHOD
This research was quantitative-qualitative study used
primary data sourced from the questionnaire using a
Likert scale of 1-5. The respondent of this research
was one of the ministries. Data was processed using
multiple linear regression. Classification criteria for
X and Y variables. The highest score (the number of
respondents in the highest score) = 47 x 5 = 235, and
the score was lower (the number of respondents were
the lowest score) = 47 X 1 = 47. Thus the score range
is as follows: Score range = (235-47) = 38
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Descriptive Analysis
Table.1 showed that the application of SPI was at a
fairly effective range for SPI Indicators 1 (130), SPI
4 (140) and SPI 5 (150). The SPI 2 (176) and SPI 3
(172) indicators demonstrate effective SPI
implementation. In total, the variable SPI shows a
percentage of 65.36%, meaning that SPI is quite
effective to improve the quality of financial
statements.
Table. 1 Review of indicators of implementation Internal
control System (SPI)
Indicators Score
Total
Score
Standart
%
SP1 1
SPI 2
SPI 3
SPI 4
SPI 5
130
176
172
140
150
235
235
235
235
235
55,32
74,89
73,19
59,57
63,83
Total 768 1175 65,36
Table 2. indicated that the implementation of
accounting standards was at the very ineffective range
for the SA indicator 8 (37.02%). Indicator SA 1
(42.55%), SA 2 (49.79%), SPA 3 (44.68%) Indicates
a less effective range. Indicator SA 4 (75.74%), SA 5
(71.06%), SA 6 (72.77%), SA 7 (78.72%) and SA 9
(71.06%) Effectively demonstrates the
implementation of SA. In total, the SA variable
showed a percentage of 60.38%. This value was good
practice that implementing SA was quite effective to
improve the quality of financial statements.
Table 2. Review of indicators of Implementation
Accounting standard Implementation (SA)
Indicators Score
Total
Score
Standart
%
SA 1
SA 2
SA 3
SA 4
SA 5
SA 6
SA 7
SA 8
SA 9
100
117
105
178
167
171
185
87
167
235
235
235
235
235
235
235
235
235
42,55
49,79
44,68
75,74
71,06
72,77
78,72
37,02
71,06
Total 1.277 2.115 60,38
Table 3. showed that the management's
commitment was at a less committed range for a KM
1 indicator (55.74%), KM 2 (47.23%), KM 3
(53.19%) and KM 5 (52.77%). Indicator only KM 4
(78.72%) Show a committed range. A total variable
management commitment showed a percentage of
57.53%. This value indicates that management was
less committed in the process of improving the
quality of financial statements.
Table 3. Review of Indicators Commitment Top
Management (KTM)
Indicators Score
Total
Score
Standart
%
KM 1
KM 2
KM 3
KM 4
KM 5
131
111
125
185
124
235
235
235
235
235
55,74
47,23
53,19
78,72
52,77
Total 676 1175 57,53
The calculated result in table 4 showed the
indicator KLK 1 (63.83%) and KLK 4 (62.98%) was
at a fairly good range, while the KLK indicator 2
(58.30) and KLK 3 (48.98%) were in less good range.
In total the KLK variable is worth 58.51%. The result
of the calculation indicates that the Y variable means
the quality of financial statements entered in the "less
good" criteria.
Table 4. Review of indicators the Financial Reporting
Quality (KLK)
Indicators Score
Total
Score
Standart
%
KLK 1
KLK 2
KLK 3
KLK 4
150
137
115
148
235
235
235
235
63,83
58,30
48,94
62,98
Total 550 940 58,51
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
430

The results of the validity and reusability test
showed all variables and instruments of valid and
realistic statements. The quality variables of financial
statements (0.9036), internal control systems
(0.7273), accounting Standards (0.7815),
Management commitments (0.7784) have a value
greater than 0.70 (Nunnalli, 1994)., thereby inferred
variables are declared Realible. The validity test was
conducted to measure the legitimate or valid absence
of a questionnaire (Ghozali, 2016). The questionnaire
is declared valid by comparing the R count value by
R table. If the sample count (n) = 47 and the
magnitude of DF can be calculated by the formula DF
= N-2 Then, for sample 47 is diped DF = 45. By using
the Auxiliary table R count for a significant rate of
5% obtained value 0.2876. All indicators are declared
valid.
The data processing results showed the R Square
value for each variable. The internal control system
implementation (X1) variable has a value of R2 of
0.283. This result means that the internal control
system implementation variables are able to explain
the variation in the quality of the financial statements
by 28.3%, while the implementation of accounting
standards has an R2 organization of 0.283 which
means that this variable Able to explain the variation
in the quality of financial statements of 28.3% and the
management commitment variables are able to
explain the variation in the quality of financial reports
of 0268 which means that the variable management
commitments are able to explain the variation in As
much as 26.8%. Complete data processing results can
be seen in table 6.
In unison R2 indicates a figure of 0374 or 37.4%,
this figure represents three independent variables
consisting of implementing an internal control
system, the implementation of accounting standards
and management commitments is able to explain the
variation The quality of the financial report is 37.4%,
while 62.6% is described by other variables outside
of this study. After obtaining the next R2 value step
is to test the data to answer the research hypothesis.
By using table 8 above, this study obtained the
following results:
From Test Anova or F test by looking at a
significant rate the value F count is 0.000 then
compared to the α value if the value of the default is
< α then the regression model can be used to predict
the dependent variable or can be said unison
dependent variables affect the dependent variable
(Ghozali, 2016). The Value F-table at significance
level 5% is calculated using the formula of degree of
freedom (df 1) = k-1 and DF 2 = n-K. With the
formula obtained the results of DF 1 = 3-1 = 2, and df
2 = 47-2 = 45, thus the value of Ftabel is 2.81. Test
result using α = 5% where F count > F table is 8,549
> 2.81 then it can be stated that the application of
accounting standards, internal control, management
commitments influence simultaneously on the quality
of financial statements.
Partial influence between dependent variables
and independent variables can use Thitung and
significance levels are smaller than α (5%). To know
the results of the hypothesis is influenced by
comparing the value of Thitung with this. The value
is obtained by using formula DF: N-k = 47-2 = 45.
Thus the test results for the one hypothesis are
"there is a positive and significant influence of
internal control system on the quality of financial
statements". The value of Thitung at a significant rate
of α 5% obtained a value of 2,014, thus if comparing
the value of Thitung with this 4,119 > 2,014 can be
interpreted that there is a positive influence
implementation of internal control system to quality
of financial statements (receive H1). Further testing
the significance value for the internal control system
implementation variables indicates the number 0.000,
hence by comparing the result to α 5% then 0.000 >
0.05 can be concluded that the implementation of
internal control system Significant impact on the
quality of financial statements.
The test result for the two hypotheses is "a
significant influence on the implementation of
accounting standards for the quality of financial
statements". Based on testing found a value of
Thitung for variables independent of the
implementation of Accounting standard 4,349 Thus if
comparing the value of Thitung with this then 4,216
> 2.014 can be interpreted that there is a positive
influence the standard implementation accounting for
the quality of financial statements (receive H2).
Further tests of significance rate with α 5%, hence the
level result of the significance of the accounting
Standards implementation variable indicate a number
0.00 < 0.05. These results indicate that the accounting
standard applicability variable significantly affects
the quality of financial statements.
The next test result for the three hypothesis is
"there is a significant influence on management
commitments to the quality of financial statements".
The result of T test obtained Thitung value for the
independent variable implementation of accounting
standard 4,060 > 2.014 can be interpreted that there is
a positive influence of management commitment to
the quality of financial report (Received H3). The test
result level significance finds the value 0.000 < 0.05.
These results indicate that a variable management
The Effect of Implementing Internal Control System, Accounting Standards Implementation, Management Commitment to Quality
Financial Report
431

commitment significantly affects the quality of
financial statements.
5 DISCUSSION
The Effect of implementing internal control
systems on the quality of financial statements
The result of the calculation showed that the internal
control system has positive and significant effect on
the quality of financial statements. Calculation results
per indicator showed at quite effective range. The
results of our interviews show data that human
resources are still an obstacle in the implementation
of effective SPI. A short time of implementation of
activities caused by long budget approved is also an
obstacle in implementing SPI. Besides, there are 2
similar activities in the budget in the end causing
confusion that impacts on the application of SPI, plus
less coordination between parts and commitment of
low leadership to the cause of the lack of
effectiveness Application of SPI.
The effect of implementing accounting standards
for quality financial statements
The calculation results showed that the
implementation of accounting standards was positive
and significant against the quality of financial
statements. Calculation results per indicator showed
at quite effective range. Our interviews showed an
understanding of the accrual base was good, and
understood the accrual-based concept. These results
indicate that the management staff is educated in
accounting so that it ultimately strengthens the
implementation of government accounting standards
on the entities. Although the results of the test showed
quite effective results, but the results of our
interviews also found that there was still confusion in
the interachievement if there are new rules that arise
given the lack of socialization of regulatory changes
the new one. This confusion eventually led to the
respondent being confused and hesitant in carrying
out the transaction, the use of standards, the rules and
format of frequently changing reports which
eventually became an obstacle in implementing a
good accounting standard.
The Influence of implementation management
commitment to the quality of financial report
The calculation results showed that the
implementation of management commitments was
positive and significant against the quality of
financial statements. Calculation results per indicator
showed at quite effective range. The results of our
interviews show that management's commitment was
not too high in the follow up on inspection results.
Constraints on human resources (human resources)
who have no understanding of how to follow up on
the inspection results become the main constraint of
the entity in the follow up of the test results plus the
more often scheduled employees. Besides, the test
result that was not coordinated with the entity was the
cause on the quality of repairs made by the entity.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The research results showed a positive and significant
influence on the implementation of internal control
systems, the implementation of accounting standards
and management commitments to the quality of
financial statements. The quality of financial
statements showed a fairly good range, caused by
human resource factors, change-changing rules,
intimely budgets, lack of coordination between parts
and not good leadership commitment.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge that the present
research is supported by Ministry of Research and
Technology and Higher Education Republic of
Indonesia. The support is under the research grant
Disertation of Year 2019.
REFERENCES
Abang’a, A. O. (2017). Determinants of quality of financial
reporting among semi -autonomous government
agencies in Kenya. Strathmore University. Retrieved
from http://su-plus.strathmore.edu/handle/11071/5581
Abdullah, M. W. (2010). Pemoderasi Kompetensi Sumber
Daya Manusia Terhadap Peningkatan Kualitas Laporan
Keuangan Daerah Kabupaten Bone. Jurnal Ilmiah
Akuntansi Peradaban, Vol. III(No. 2), 45–65.
Afiah, N. N., & Rahmatika, D. N. (2014). Factors
Influencing The Quality Of Financial Reporting And Its
Implications On Good Government Governance
(Research on Local Government Indonesia).
International Journal of Business, Economics and Law,
5(1), 111–121.
Benardi, M., Sutrisno, & Assih, P. (2009). Faktor-faktor
Yang Memengaruhi Luas Pengungkapan Dan
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
432

Implikasinya Terhadap Asimetri Informasi (Studi Pada
Perusahaan-Perusahaan Sektor Manufaktur Yang Go
Public Di Bursa Efek Indonesia). In Simposium
Nasional Akuntansi XII. Palembang.
Erviana. (2017). Pengaruh Implementasi Sistem Informasi
Manajemen Daerah dan Kegiatan Pengendalian
Terhadap Kualitas Laporan Keuangan Pemerintah
Daerah (Survey Pada Satuan kerja Perangkat Daerah
(SKPD) Kota Palu). E Journal Katalogis, 5(4), 182–
193.
Fitriani, A. (2017). Pengaruh Komitmen Pimpinan dan
Lingkungan Pengendalian Internal Terhadap Kualitas
Laporan Keuangan (Survei Pada SKPD Provinsi
Sulawesi Tengah). E Jurnal Katalogis, 5(4), 113–122.
Retrieved from
https://media.neliti.com/media/publications/212457-
pengaruh-komitmen-pimpinan-dan-lingkunga.pdf
Ghozali, I. (2016). Aplikasi Analisis Multivariate Dengan
Program IBM SPSS 23 (VIII). Semarang: Badan
Penerbit Universitas Diponegoro.
Ijeoma, N. B., & Oghoghomeh, T. (2014). Adoption of
international public sector accounting standards in
Nigeria : Expectations , benefits and challenges.
Journal of Investment and Management, 3(1), 21–29.
https://doi.org/10.11648/j.jim.20140301.13
Jensen, & Meckling. (1976). Theory of the Firm:
Managerial Behavior, Agency Cost and Ownership
Structure. Journal of Financial Economics, 3(4), pp:
305-360.
Julita, & Susilatri. (2018). Analysis Of Factor Affecting
The Quality Of Government Financial Report
Bengkalis Regency. International Journal of Scientific
& Technology Research, 7(2), 157–164.
Kesuma, D. P., Anwar, C., & Darmansyah. (2017).
Pengaruh Good Governance, Penerapan Standar
Akuntansi Pemerintah, Sistem Pengendalian Internal
Pemerintah dan Kompentensi Aparatur Pemerintah
Terhadap Kualitas Laporan Keuangan Pemerintah Pada
Satuan Kerja Kementerian Pariwisata. Jurnal Ilmiah
WIDYA Ekonomika, 1(2), 141–146.
Kibet, A. J. (2016). Effects of Management Commitment
on Financial Performance of Private Schools : A Survey
of Selected Schools in Trans-Nzoia County, Kenya.
European Journal of Business and Management, 8(30),
1–5.
Mahlil, & Yahya, M. R. (2017). Pengaruh komitmen kepala
daerah dan pengetahuan akuntansi terhadap kualitas
laporan keuangan pemerintah daerah di provinsi aceh.
Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa Ekonomi AKuntansi
(JIMEKA), 2(2), 21–29.
Mailoor, J. H., Sondakh, J. J., & Gamaliel, H. (2017).
Pengaruh Sistem Akuntansi Pemerintahan , Budaya
Organisasi , Kinerja Aparatur Pemerintah Daerah ,
Peran APIP , Dan Sistem Pengendalian Intern
Pemerintah Terhadap Penerapan Good Governance (
Studi Empiris Di Kabupaten Kepulauan Talaud ).
Jurnal Riset Akuntansi Dan Auditing “Goodwill,” 8(2),
82–94.
Mardiasmo. (2009). Akuntabilitas Sektor Publik
(IV).
Yogyakarta: C.V Andi Offset.
Muda, I., Harahap, A. H., Erlina, Ginting, S., Maksum, A.,
& Abubakar, E. (2018). Factors of quality of financial
report of local government in Indonesia. International
Journal for Quality Research, 8(1), 73–86.
https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/
Mutiana, L., Diantimala, Y., & Zuraida. (2017). Pengaruh
sistem pengendalian intern, teknologi informasi,
kualitas sumber daya manusia dan komitmen organisasi
terhadap kualitas laporan keuangan. Jurnal Perspektif
Ekonomi Darusaslam, 3(2), 151–167.
Nelia K, M. (2015). The Effect Of Adoption Of
International Public Sector Accounting Standards On
Financial Reporting In The Public Sector In Kenya.
Onyulo, O. F. (2017). Factors Influencing Quality of
Financial Reporting in Public Sector Entities in the
Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources Kenya.
KCA UNIVERSITY.
Pasaribu, H. (2009). Pengaruh Komitmen , Persepsi dan
Penerapan Pilar Dasar Total Quality Management
terhadap Kinerja Manajerial ( Survei pada BUMN
Manufaktur di Indonesia ). Junrnal Akuntansi Dan
Keuangan, 11(2), 65–75.
Purwati, A. S. (2016). Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi
Kualitas Laporan Keuangan Pada UMKM di
Kabupaten Banyumas. Journal & Proceeding
JPFBUNSOED, 808–818.
Rachmad, A. A. (2011). Pengaruh Penerapan Corporate
Governance Berbasis Karakteristik Manajerial pada
kinerja Perusahaan Manufaktur. E-Jurnal Akuntansi,
2(3), 678–696.
Rachmawati, R. (2018). Model Struktural Hubungan
Budaya Organisasi, Kompetensi Pengguna,
Pengendalian Internal dan Kualitas Informasi
Akuntansi Pemerintah Daerah. Jurnal Ilmiah
Manajemen, VIII(1), 136–150.
Rahman, D., Hardi, & Diyanto, V. (2015). Pengaruh
Pemanfaatan Teknologi Informasi, Penerapan Sistem
Akuntansi Keuangan Daerah, Dan Penerapan Standar
Akuntansi Pemerintahan Terhadap Kualitas Laporan
Keuangan Daerah (Studi Empiris Pada SKPD Provinsi
Riau). Jom Fekon, 2(2), 1–15.
Rahmatika, D. N. (2016). Determinant Factors Influencing
The Level Of Fraud And Implication To Quality Of
Financial Reporting (Research At Local Governments
Indonesia). J A B E R, 14(14), 861–879.
S, M. B. T., Taufik, T., & Hariyani, E. (2015). Pengaruh
Good Governance, Kompetetensi Sumber Daya
Manusia dan Sistem Pengendalian Internal Terhadap
Kualitas Informasi Laporan Keuangan. Jom Fekon,
2(2), 1–14.
Sako, U., & Lantowa, F. D. (2018). Pengaruh Penerapan
Standar Akuntansi Pemerintahan Terhadap Kualitas
Penyajian Laporan Kueangan Pada Pemerintah
Kabupaten Gorontalo.
Journal of Accounting Science,
2(1), 43–54.
Silviana. (2012). Pengaruh Komitmen Kepala Daerah
Terhadap Kualitas Laporan Keuangan Pemerintah
Daerah di Provinsi Jawa Barat. In Seminar NAsional
Akuntansi & Bisnis (SNAB) (pp. 862–869).
The Effect of Implementing Internal Control System, Accounting Standards Implementation, Management Commitment to Quality
Financial Report
433

Sudarno. (2018). Analisis Peran Karyawan dalam
Hubungan Antara Dukungan Pimpinan dengan
Efektifitas SPIP dan Kualitas Laporan Keuangan.
Jurnal Akuntansi Dan Auditing, 15(1), 115–137.
Susilawati, & Riana, D. S. (2014). Standar Akuntansi
Pemerintahan dan Sistem Pengendalian Intern Sebagai
Anteseden Kualitas Laporan Keuangan Pemerintah
Daerah. STAR – Study & Accounting Research, XI(1),
15–32.
Sutaryo, & Sinaga, D. (2018). Government Internal Control
System Maturity : The Role of Internal Guidance and
External Control of Local Government in Indonesia.
Jurnal Akuntnasi Dan Investasi, 19(1), 24–35.
https://doi.org/10.18196/jai.190189
Suwanda, D. (2015). Factors Affecting Quality of Local
Government Financial Statements to Get Unqualified
Opinion (WTP) of Audit Board of the Republic of
Indonesia (BPK). Research Journal of Finance and
Accounting, 6(4), 139–157.
Syarifudin, Surasni, N. K., & Inapty, B. A. (2016).
Determinan Kualitas Laporan Keuangan dan
Implikasinya terhadap Akuntabilitas Publik (Studi
Empiris pada Inspektorat Kab. Lombok Timur,
Kabupaten Bima dan Perwakilan BPKP Provinsi NTB).
In SNA XIX Lampung. Retrieved from https://sna-
iaikapd.or.id
Tambingon, H. N., Yadiati, W., & Kewo, C. L. (2018).
Determinant Factors Influencing the Quality of
Financial Reporting Local Government in Indonesia.
International Journal of Economics and Financial
Issues, 8(2), 262–268.
Upabayu, I. P., Mahaputra, R., & Putra, I. W. (2014).
Analisis Faktor-Faktor yang Mempengaruhi Kualitas
Informasi Pelaporan Keuangan Pemerintah Daerah. E-
Jurnal Akuntansi Universitas Udayana, 8(2), 230–244.
Usman, H. (2010). Manajemen (Teori, Praktek, dan Riset
Pendidikan). Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Wisdom, O., Damilola, E., Inemesit, B., & Opeyemi, A.
(2017). Public sector accounting standards and quality
of financial reporting : A case of Ogun state
government administration in Nigeria. Business and
Management Research, 7(December), 76–81.
Yunita, T. A., Tanjung, A. R., & Anggraini, L. (2015).
Pengaruh Penerapan Standar Akuntansi Pemerintahan,
Sistem Pengendalian Internal Dan Kompetensi Staf
Akuntansi Terhadap Kualitas Laporan Keuangan
Pemerintah Daerah (Studi Pada SKPD Kota Dumai).
Jom Fekon, 2(2), 1–15.
Yusniar, Darwanis, & Abdullah, S. (2016). Pengaruh
Penerapan Sistem Akuntansi Pemerintahan dan
pengendalian Intern Terhadap Good Governance dan
Dampaknya Pada Kualitas Laporan Keuangan (Studi
Pada SKPA Pemerintah Aceh). Jurnal Magister
Akuntansi Pascasarjana Universitas Syiah Kuala, 5(2),
100–115.
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
434
