
Relationship between Methods of Training, Trainer and Management
Support towards Effective Training
Wan Maziah Wan Ab. Razak, Syahrul Nadwani Abdul Rahman, Zalinawati Abdullah, Ahmad Ismail
Mohd Anuar, Najah Lukman
Universiti Teknologi MARA (Terengganu), Sura Hujung, 23000 Dungun, Terengganu,
Keywords: Effective Training, Training Methods, Trainer’s Characteristics and Management Support.
Abstract: The research was conducted to study the factors that contribute to the effective training among academic
staff of a higher learning institution. This research had focused only on the general types of training
provided by department of Training unit to all the lecturers such as important training like basic teaching
and learning workshop, research training, writing workshop, ICT Training, e-Learning and etc. By
constructing a hypothetical research model to investigate the relationship of three moderating variables on
the training participants (independent variables) towards the effective training (dependent variable), a
survey questionnaire had been distributed to employees in that university who had attended training
programs. Sampling that had been used in which approximately 200 lecturers in the campus will become the
subject of the study. The respondents will be all of the permanent staff. The researchers used correlation test
in order to measure the degree of relationship between two variables, testing the significance of the variable
by using the Reliability Test, Correlation and Regression Analysis and Multiple Regression Analysis. From
all these statistical analysis, the researchers had clearly able to indicate that the main contribution factor is
management support that contribute strongly towards the effective training followed by training method and
trainer’s caharacteristics. There were siginificant relationships between all the identifiable independent
variables with the main variable of the study.
1 INTRODUCTION
The research was conducted to study the factors that
contribute to the effective training among academic
staff in one of a higher learning institution. This
research focused only on the general types of
training provided by departments Training units to
all the academicians such as important training like
basic teaching and learning workshop, research
training, writing workshop, ICT Training, e-
Learning and etc.
From this research, the relationship among all
factors that contribute towards the training provided
for the academic staff had been found out. Besides,
it is also to investigate the effectiveness of training.
Sampling that been used in which 168 lecturers in
the campus had become the subject of the study. The
respondents were all the permanent academicians in
the campus.
Hopefully, after implementing this study it will
help the organization to improve their training. Thus,
to enhance the quality of training. The findings of
this study can be in considered as continuous
improvement on training in the organization. The
top management would have another insight and
knowledge of the impact of implementation of
training practices on their employees. Moreover, the
results of the study would be of significant value to
organization that could use them as a useful
reference to provide efficient training for the staff.
Training is one of the most pervasive methods
for enhancing the productivity of individuals and
communicating organizational goals to new
personnel. It is a learning process that involves the
acquisition of knowledge, sharpening of skills,
concepts, rules, or changing of attitudes and
behaviors to enhance the performance of employees.
Refer to Mondy & Neo (2006), training designed to
provide learners with knowledge and skills needed
for their present jobs to achieve organizational goals.
But from our observation, the trainings were still not
effective maybe because of certain factors that might
be contribute to. These can be seen from the training
396
Ab. Razak, W., Abdul Rahman, S., Abdullah, Z., Mohd. Anuar, A. and Lukman, N.
Relationship between Methods of Training, Trainer and Management Support towards Effective Training.
DOI: 10.5220/0009206203960403
In Proceedings of the 2nd Economics and Business International Conference (EBIC 2019) - Economics and Business in Industrial Revolution 4.0, pages 396-403
ISBN: 978-989-758-498-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

or programmes organized, not all of the participants
could adapt or having changed after the training.
Most companies are committed to total quality
invest heavily in training and education. Training
plans should be based upon job skill requirements
and strategic initiatives of the company (Evans and
Lindsay, 2002). We could see that the management
has allocated a big amount of budget just for the
lecturer’s training but it’s better if they could come
out with something that maybe to analyze whether
the training is worth or not or maybe has given a big
impact or not to the lecturers.
Salas, Burke, Bowers and Wilson (2001; cited in
Lee, 2007) thus asserted that training evaluation
helps to determine whether the training has been
effectively on the job. This was emphasized by
Grensing-Pophal (2004; cited in Lee, 2007) that it is
important to assess training effectiveness and that
training effectiveness should be tied in with actual
work performance. So, for our research, we could
see which factors that will contribute importantly
towards the effectiveness of training in the
university.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
Refer to Mondy & Neo (2006), training designed to
provide learners with knowledge and skills needed
for their present jobs to achieve organizational goals.
But from our observation, the trainings for lecturers
are still not effective maybe because of certain
factors that might be contribute to. These can be
seen from the training or programmes organized, not
all of the participants could adapt or having changed
after the training.
Most companies are committed to total quality
invest heavily in training and education. Training
plans should be based upon job skill requirements
and strategic initiatives of the company (Evans and
Lindsay, 2002). We could see that the management
has allocated a big amount of budget just for the
lecturer’s training but it’s better if they could come
out with something that maybe to analyze whether
the training is worth or not or maybe has given a big
impact or not to the lecturers. Salas, Burke, Bowers
and Wilson (2001; cited in Lee, 2007) thus asserted
that training evaluation helps to determine whether
the training has been effectively on the job. This was
emphasized by Grensing-Pophal (2004; cited in Lee,
2007) that it is important to assess training
effectiveness and that training effectiveness should
be tied in with actual work performance. So, for our
research, we could see which factors that will
contribute importantly towards the effectiveness of
training in the university.
3 RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
The objectives of this study is to examine as follows:
1) The investigate the relationship between
three factors (training methods, trainer and
management support) towards the effective
training.
2) To identify the most influence variable
towards effective training.
4 LITERATURE REVIEW
Effective Training
Human Resource Management is concerned with the
planning, acquisition, training & developing human
beings for getting the desired objectives & goals set
by the organization. The employees have to be
transformed according to the organizations' & global
needs. This is done through an organized activity
called Training. Training and development is
defined by Dessler (2008) as a process that utilizes
various methods to provide new and existing
employees with the skills they need to perform the
job.
Mulder (2001), in his research describe a model
of evaluation of customer satisfaction about training
programs. The model is developed and implemented
for an association of training companies. The model
is aimed at determining the quality of training
programs as perceived by project managers from the
organizations that purchased in company training
programs from the training companies. The results
show that this model is confirmed for two categories
of projects. The first category is the projects that
were aimed at achieving learning results and the
second category is changed job performance
respectively.
In order to recognize the effectiveness of the
training, organization should also give their attention
on how to develop an effective training evaluation.
Several characteristics of effective training
evaluation were described by Burrow and
Berardinelli (2003) in their research Systematic
performance improvement – refining the space
between learning and results such as it must be
objective and directed at important outcomes, it
should identify the important elements of the
training program (refer to the training method), the
Relationship between Methods of Training, Trainer and Management Support towards Effective Training
397

evaluation should match the organizational
philosophy, and last but not least the evaluation
procedures should be reasonable and focus on both
the outcomes and the process.
Contributing Factors Towards the Effective
Training
Related to the contribution factors towards training
effectiveness, three factors to be considered are
management support, training methods and trainer.
These factors are frequently mentioned in the
literature.
1. Training Methods
According to Noe (2010), management support
refer to the degree to which trainees’ managers
(i) emphasize the importance of attending
training programs and (ii) stress the application
of training content to the job. Management as
well as managers can communicate expectations
to trainees by providing the encouragement and
resources needed to apply training on the job.
2. Trainer’s Characteristics
Lawson (1998), stated that the trainer act as
facilitator in a training program where they
played two roles. First role is, they were standing
in front of a group and presenting information.
The second role is they were facilitating
discussion and interaction among trainees. Each
requires a different set of skills. She also stated
that facilitation skills are particularly critical for
processing activities which will pertain to the
effectiveness of the training.
Wise and Ezell (2003) provided four major
criteria whether training program is effective or
not. Effective training should be learner focused,
demonstrate productive behavior and effective
life skills, inspires and motivates, and also
celebrate personal and group achievements.
3. Management Support
Nevertheless, training program’s developer must
take into account the method of training program
that best suit to the adult learning theory.
Malcolm Knowles’s Andragogy (Knowles,
Holton, and Swanson, 2000) is most frequently
associated with adult learning theory. Andragogy
is based on the following assumptions (a) adult
learners bring life experiences to the learning
process that should be acknowledge, (b) adults
need to know why they need to learn something,
and how it is relevant to their lives, (c)
experiential, hands-on learning is effective with
adult learners, (d) adult approach learning as
problem-solving, (e) adults learn best with the
topic is of immediate value to them in their lives.
To top that up, Wise and Ezell (2003)
provided four major criteria whether training
program is effective or not. Effective training
should be learner focused, demonstrate
productive behavior and effective life skills,
inspires and motivates, and also celebrate
personal and group achievements.
5 METHODOLOGY AND
RESEARCH DESIGN
5.1 Research Concept
The type of this research is quantitative research
method and it is used to support the earlier findings
and serve as measure to find the best factors among
all independent variables towards the effectiveness
of training. Quantitative analysis also will be
explained as a major method adopted which is by
using survey method. Through this quantitative
method, the primary data is obtained by distributing
questionnaires to the respondents. The researchers
had chosen this method because it is the easiest
method to be used and could get accurate data from
respondens.
5.2 Research Design
Research design is a framework for conducting the
research project, which describes the procedures
necessary for obtaining the information to form or
solve problems (Malhotra et al., 2008). The
researchers used descriptive study in order to
investigate the effective training among
academicians. According to Uma Sekaran (2006),
descriptive study is undertaken in order to ascertain
and be able to describe the characteristics of
variables of interest in a situation such as to describe
the characteristics of academicians from every
faculties as for example the age, education level,
grade of position, as well as types of training
preferred and etc. Besides, descriptive study is also
undertaken to understand the characteristics of
organizations that follow certain common practices.
For example, the training department of UiTM
Terengganu has put certain measurement for the
staff to achieve the number of training attended per
year.
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
398
5.3 Unit of Analysis
The academicians involved in this study which only
consists of permanent staff. It will only cover the
area of training that they experienced provided by
top management either by the unit of training or any
program inside or outside of the university.
5.4 Data Collection Method
Primary Data
Self-administered questionnaires had been chosen by
the researchers because the information can be
collected immediately, able to motivate respondents
and also have chances to 100% responses from the
respondents. The researchers also distributed
questionnaires to the respondents but still needed
assistance in getting the right number of
respondents.
5.5 Sample Design
A sample of 168 respondents were successfully
obtained from all permanent lecturers within three
months. Sample design involves the procedures of
choosing the right individuals, objects or events that
can provide accurate answer to solve the research
problem (Sekaran, 2003). In order to obtain
representative data for study, there are five steps
need to be followed consisting of defining target
population, determining the sampling frame,
designating sampling techniques, determining
sample size and execution of the sampling process
(Malhotra et al., 2008).
5.5.1 Population
The population of this study is all the permanent
academicians at one higher learning institution in
Terengganu. At the time, the campus has about 340
permanent academicians.
5.5.2 Sampling Frame and Technique
The sampling frame is a tool that represents the
element of target population. It is the list of direction
for identifying the targeted population. From this
study, the researchers have taken the sampling frame
from the list of academicians obtained from the
Academic Department. The probability and stratified
sampling was used in order to collect data for this
study, which is from ten faculties in the university,
there were ten questionnaires were distributed for
each of the faculties.
5.5.3 Sampling Size
Sampling size is the quality of the element that
included in this study. Sekaran (2010), suggested
using Krecjie and Morgan (1970) table for
determining the sample size for a population size.
Thus, for this research, the sample size was about
200 academicians as respondents. However, the
questionnaires collected were only 168 samples
from all of the ten faculties.
5.5.4 Framework
The framework of this study can be described as to
investigate the relationship among all variables with
the dependent variable.
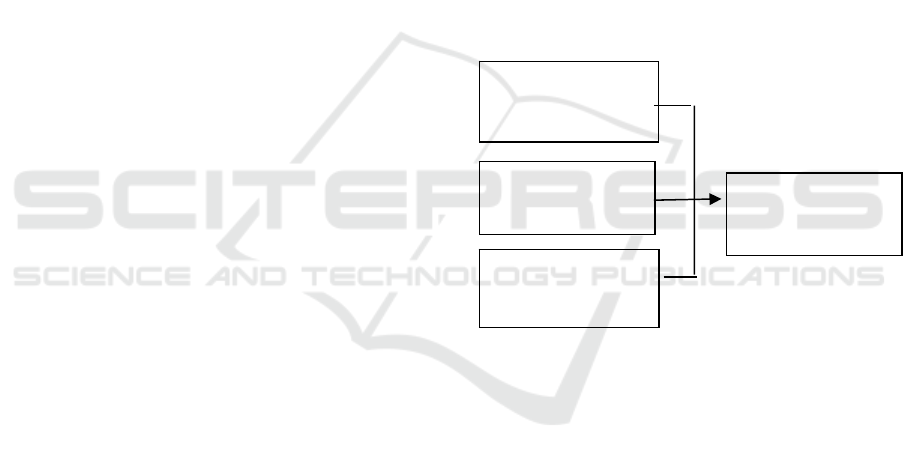
5.6 Research Framework
Independent Dependent
Variables (IV) Variable (DV)
Figure 1: Research framework
The independent variables are the factors that may
contribute to the dependent variable,which is
effectiveness of training. The independent variables
consist of training methods, trainer’s characteristics
and also management support.
5.7 Scale Development
5.7.1 Operationalization
Likert Scale has been used because it represented
whether respondents agreed or not on the three
factors contribute to the effectiveness of training
among lecturers. The scale comprises of 1- Strongly
Disagree, 2- Disagree, 3- Fair, 4- Agree, 5- Strongly
Agree and also to see whether any of independent
variables are not applicable to the lecturers ; NA-
Not Applicable.
Training Methods
Management
su
pp
or
t
Traine
r
’s
Characteristics
Management
Support
Effective
Training
Relationship between Methods of Training, Trainer and Management Support towards Effective Training
399
5.7.2 Questionnaires
The questionnaire contained two sections: the first
section was designed to gather information about
samples’ personal, demographic, and their responds
towards the number of training attended and
specification of training preferred, and etc. The
profile of the sample’s characteristics is shown in
Table 2.
In the second section of the questionnaire, the
respondents were asked to indicate on a five-point
Likert Scale towards four parts ;consists of ; one part
of effectiveness of training and another three parts
on independent variables questions such as training
methods, trainer’s characteristics and management
support.
The results had been analyzed through Statistical
Package for the Social Science (SPSS) 13.0. The
types of data analysed used were Reliability Testing,
Frequencies, Correlation and Regression Analysis
and Multiple Regression Analysis.
6 FINDINGS AND DATA
ANALYSIS
6.1 Reliability Test
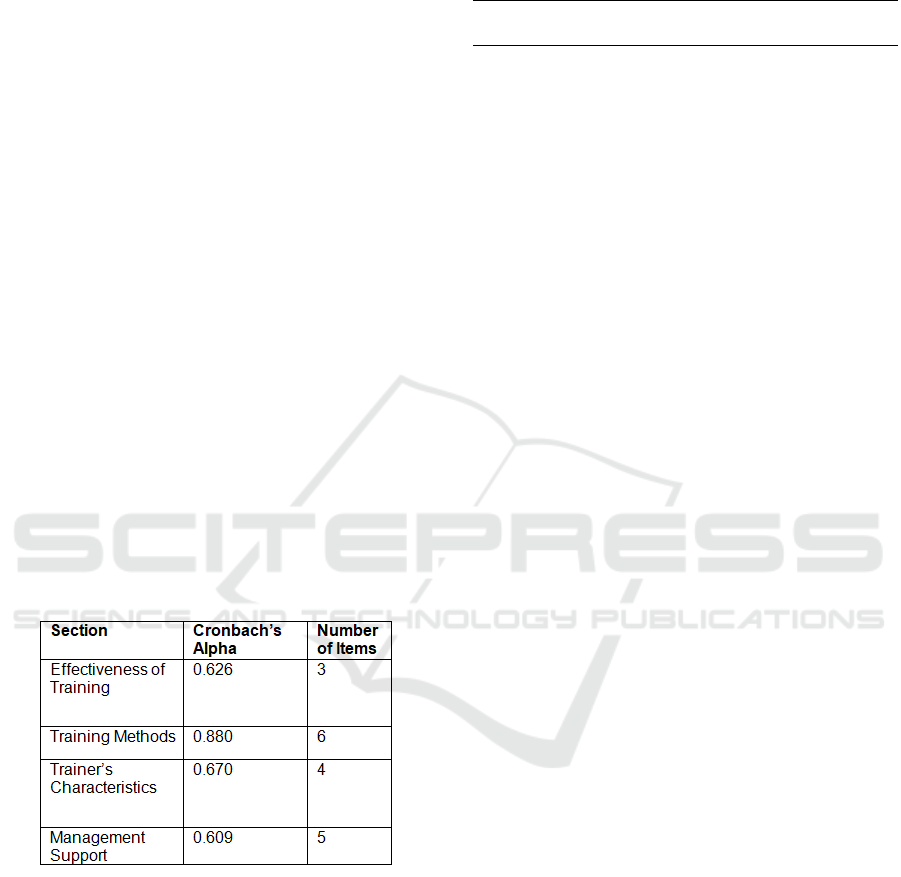
Table 1: Reliability Statistics
Analysis of this study is shown in Table 1 above.
Most of the sections, training method was felt in
good of association which cronbach’s alpha value is
0.880. Then, trainer’s characteristics and
management support were felt in moderate of
association which alpha value among 0.6 to < 0.7.
The dependent variable for this study which is
effectiveness of training is in moderate of
association with result of cronbach’s alpha 0.626.
6.2 Frequencies Analysis
Table 2: Frequencies Table
Profile Frequency
Percent
(%)
Education
Bachelor Degree 22 13.1
Masters Degree 143 85.1
PHD 3 1.8
Race
Malay 166 98.8
Chinese 2 1.2
Indian 0 0
Others 0 0
Number of Training Attended
1-5 17 10.1
6-10 71 42.3
11-15 53 31.5
More than 16 25 15.1
Working Experience
1-5years 136 81.0
6-10years 17 10.1
11-15years 12 7.1
16years and above 2 1.2
Among the demographic profile or respondents
discussed are education level, race, number of
training attended and the year of working
experienced.
From the above table, it can be seen that most of
the respondents have Masters Degree certificate
which out of 168 respondents, there are 143
respondents hold that certificated with 85.1%. Its
follow by 22 respondents with Bachelor Degree
level and 13.1% respondents hold Bachelor Degree
level. Lastly, 3 respondents have PHD level and
1.8% respondents hold PHD level.
There are four categories of race stated in the
researcher where it is Malay, Chinese, Indian and
others. Refer to the result; we can see that Malay is
the highest respond to the researcher’s study, with
166 respondents at the 98.8% score. 2 respondents
from Chinese with 1.2%, and there is no respondents
from Indian and others.
The respondents who attended 6-10 time get the
highest score where 42.3% out of 71 respondents.
The respondents who attended 11-15 time are at the
second level with 53 respondents that are 31.5% and
followed by 15.1% from 25 respondents who
attended more than 16 time and 17 of respondents
who attended 1-5 time is at the fourth level with
score 10.1%.
The majority respondents from working
experience at 1-5 years given the highest score that
are 81.0% out of 136 respondents. It followed 17
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
400
respondents from working experience at 6-10 years
with the score is 10.1%. There are 12 respondents
from working experience at 11-15 years given 7.1%
and the last is 2 respondents from working
experience at 16 years and above given 1.2%.
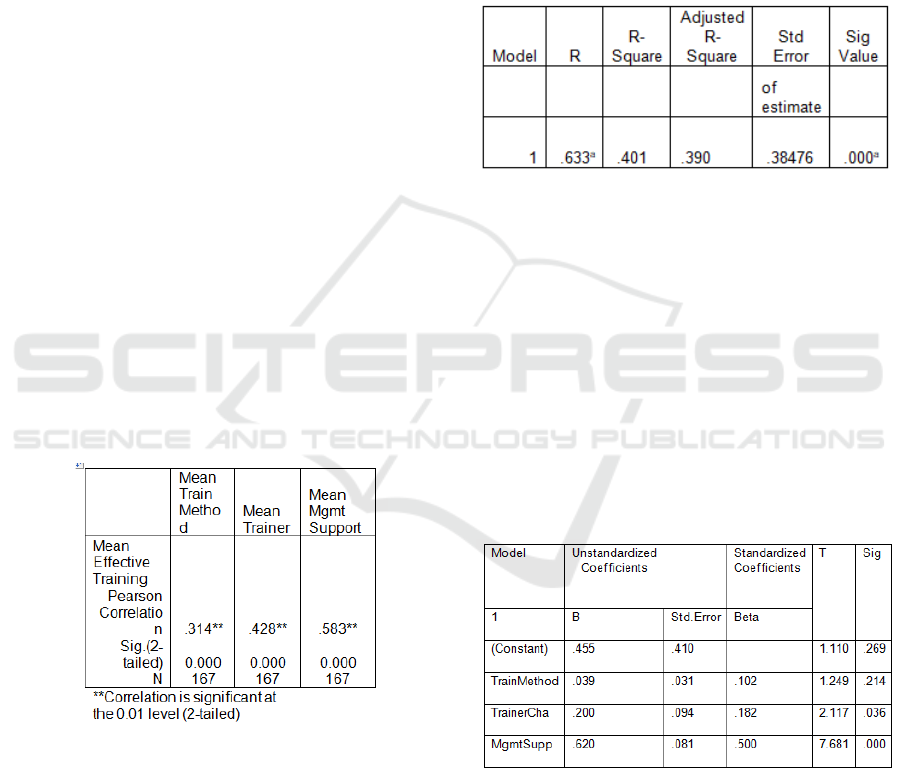
6.3 Pearson Correlation
As indicated in the Table 3, it shows that there were
siginificant relationships between all the identifiable
independent variables with the main variable of the
study. All the three independents were significant at
0.01 significant level (p>0.01). However, the
strength of the relationship differs for certain
variables. Significant positive relationships exist
between training method and effective training and
the strength of correlation is moderate. The result of
correlation between these variable is 0.314 and the
significant 0.000 level (r=0.31 4,p<0.000). Better
relationship appears to exist between trainer’s
characteristics and effective training among
academicians, and the strength is moderate. The
result of correlation between variables was 0.428
and significant at 0.000 level (r=0.428,p<0.000).
Lastly is management support and effectiveness of
training, it shown much stronger relationship among
these two variables which is the correlation was
0.583 and the siginificant 0.000 level
(r=0.583,p<0.000).
Table 3: Correlation Analysis
6.4 Multiple Regression Analysis
The result of the regression analysis was shown as
table 4. A summary of Multiple Regression for all
the effectiveness of training factors (training
method, trainer’s characteristics and management
support) towards dependent variable (effectiveness
of training) is displayed in table 4.
The multiple correlation coefficient (R), using all
the predictors simultaneously is 0.633 and Adjusted
R-Square is 39.0 meaning that 39.0 percent of the
variance in the effective training among
academicians can be predicted from the training
method, trainer’s characteristics and management
support. Note that the adjusted R-Square is lower
than the R-Square (40.1%). This is related with the
number of variables in this research. Furthermore, F
shows 36.412 and is statistically significant
(Sig.V=0.000).
Table 4: Summary of the Investigated Variables
Further analysis through regression, produced
standardized measures (Beta Weights) of the
strength of each dimension’s association with
effective training among academicians. Among the
three independent variables, management support (β
= .500, p<.000) was the main contributor factor
towards the effective training among academicians.
The training method variable (β= .102, p<0.214) and
the trainer’s characteristics variable (β=.182,
p<.036), it seemed that these variables less
contribute compared to management support in
predicting the factor that may contribute strongly to
the effective training among academicians.
Table 5: Multiple Linear Regression
7 CONCLUSION &
RECOMMENDATIONS
The study has revealed that top management support
plays important role and it stands as the most
important factor among other two factors in order to
Relationship between Methods of Training, Trainer and Management Support towards Effective Training
401

ensure the training provided for academicians will
be effective and successful. This factor is mostly
significant towards the effective training as the
results shown very impressively in multiple linear
regression and pearson correlation.
Trainer’s characteristics can be a moderate factor
that might contribute to the effective training, maybe
it is not chosen as important factor by the
respondents compared to the support by top
management and the method of training used.
Whereby, training method also can be considered as
having potential to become important factor towards
the effective training for the academicians in
university as the result was moderate in multiple
linear regression analysis. Otherwise, there is a lot of
other factors that may contribute in order to get
effectiveness of training, such as the environmental
factors, training facilities and perhaps motivation
among academicians could be added as one of the
factors that will give better impact on the
effectiveness of training in the university. These are
some recommendations that maybe can be used for
future direction.
For management support:
Involve management in course design
Apparently, developers often ask management for
information during the needs assessment phase, but
then less so during actual design. To ensure the
effectiveness of the training in the future, developers
should invite the management personnel to provide
some ideas and their views so that their input can be
included as part of training improvement towards
creating real-world scenarios and simulations, case
studies, as well as the what-ifs situations. This will
support their understanding of what the course will
and won’t cover, and develop their vested interest in
seeing the training succeed (Bozarth, 2010). By
doing so, management will be able to increase their
understanding of what benefits can be gained by
their employees those attending the the training
program. besides, management also will know
whether the training program be able to solve
employee's problems or not.
For trainers:
Trainer's behavior
Trainer's behavior throughout the session influences
trainees participation. trainer's behavior in terms of
their nonverbal and verbal communication whether
straightforward or subtle that communicated without
trainer's awareness may have powerful impact
towards trainees involvement and participation
during training session. sometimes, trainers don't
have to speak loudly to gain trainees' attention. what
trainers need to do just to improve their nonverbal
communication. such powerful nonverbal
communication techniques to encourage trainees'
participation as suggested by Lawson (1998) are:
Eye contact. be attentive to making eye contact
with all participants.
Head nodding. nod your head to show
understanding and to encourage participants to
continue.
Posture. avoid defensive postures such as folded
arms.
Body movement. avoid distracting movements
such as too much walking or pacing.
Smile. concentrate on smiling with both mouth and
eyes to encourage and relax the group.
REFERENCES
Burrow, J. and Berardinelli, P. (2003). Systematic
performance improvement: Refining the space
between learning and results. Journal of Workplace
Learning, 15(1), 6-13.
Bozarth, J. (2010). From Analysis to Evaluation: Tools,
Tips, and Techniques for Trainers. San Francisco:
Pfeiffer.
Dessler, G. (2008). Human Resource Management (11
th
ed.). New Jersey, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Evans, J. R. and Lindsay, W. M. (2002). The
Management and Control of Quality. USA: South
Western.
Grensing-Pophal, L. (2004). A sumforall reasons: A way
to reduce administrative headaches and cut costs when
relocating employees is to give them a lump sum--one
check upfront--to cover some or all of their expenses.
In Lee, K. L. (Ed.), Evaluating the effectiveness of a
conceptual skill training: A quasi-experimental
approach (pp.4). The Malaysia University of Science:
Dissertation.
Knowles, M. S., Holton, E. F., & Swanson, R. H. (2000).
The adult learner: The Definitive Classic in Adult
Education and Human Resource Development.
Houston, Texas: Gulf Professional Publishing Co.
Lawson, K. (1998). Involving your audience: Make it
active. Needham Heights, MA: Allyn and Bacon.
Mondy, R. W. and Noe, R. M. (2006). Human Resource
Management. Texas: Prentice Hall.
Mulder, M. (2001). Customer satisfaction with training
programs. Journal of European Industrial Training,
25(6), 321-331.
Noe, R. A. (2010). Employee training and development
(5
th
ed.). New York, NY: Mc Graw Hill.
Salas, E., Burke, C. S., Bowers, C. A. & Wilson, K. A.
(2001). Team training in the skies: Does Crew
resource management (CRM) training work? In Lee,
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
402

K. L. (Ed.), Evaluating the effectiveness of a
conceptual skill training: A quasi-experimental
approach (pp.4). The Malaysia University of Science:
Dissertation.
Sekaran, U. and Bougie, R. (2010). Research Methods for
Business: A Skill Building Approach, New York: John
Wiley & Son Ltd.
Wise, D. and Ezell, P. (2003). Characteristics of effective
training: Developing a model to motivate action
Retrieved June 30, 2010, from
http://www.joe.org/joe/2033april/a5.php
Relationship between Methods of Training, Trainer and Management Support towards Effective Training
403
