
A Propositions and Implications in Conceptualization
of Human Resource Competencies 4.0
Anggia Sari Lubis
1
, Prihatin Lumbanraja
2
, Yeni Absah
2
, and Amlys Syahputra Silalahi
2
1
Student of Doctoral Program in Management Science Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
2
Lecturer of Doctoral Program in Management Science Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Competencies, Human Resource Competencies, Human Resource Competencies 4.0, Industrial Revolution
4.0.
Abstract: The purpose of this article is to provide a new conceptualization of human resource competencies for
industry 4.0 era. The authors aim to base their new conceptualization on extensive evidence from literature
review, and synthesis of the review of literature. An extensive literature review of the extant
conceptualizations and operationalizations of human resource competencies for industry 4.0 era is first
carried out. Based on the review and synthesis of literature, a human resource competencies 4.0 with three
domain areas is conceptualized, through several propositions in the paper. The human resource managers
can now apply more specifically, any of the three dimensions areas of human resource competencies 4.0 and
understand the conditions under which a particular dimensions area is important for employees to
understand the changes caused by the industrial revolution 4.0 and adjust the competencies possessed by
these changes.
1 INTRODUCTION
The industrial revolution 4.0 provides disruption,
and changing challenges for the entire scope of the
business world. The manufacturing process is
experiencing automation and digitalization which
are increasingly narrowing the role of humans in the
production process (Hecklau et al., 2016).
Transforming the role of human resources is a major
concern both for companies and for humans
themselves (Rahardjo, 2014). Human Resources
(HR) who do not master digital literacy sooner or
later will be eliminated. Types of jobs that can be
automated include data processing, machine
running, administrative tasks and others (Institute,
2017). The development of the industrial revolution
marked by the use of massive technology, the
Internet of Things, Big Data and Artificial
Intelligence (Brijesh Sivathanu, 2018) had an impact
on the disruption of the role of human resources
within the company. As technology develops rapidly
in every aspect of human life, every organization
needs competent human resources (Kock, 2008).
Competence is a collection of human resources that
dynamically demonstrate intellectual capacity,
quality of mental attitude and capability of a person
(Correll et al., 2004). Competence is the initial
capital that must be owned by an employee to be
able to carry out work in accordance with their
duties and responsibilities (Lestariningsih, Mei
2018). Human resource competence is the main
characteristic possessed by a person that causes him
to be able to perform effectively and excel at work,
which includes a combination of: knowledge, skills,
attitudes, and personal characteristics needed to
achieve success in a job (Spencer, 2003).
Competence is defined as the ability or ability
possessed by someone in carrying out their work
(Boyatzis and Boyatzis, 2008).
In accordance with the development of the
industrial revolution, human resources must have the
capability to face job challenges that increasingly
narrow the role of humans in the company.
Competence is an absolute thing that must be owned
by the employees and the business people that are
adjusted to the demands of the times. The concept of
human resource competency 4.0 is a submission of
the concept of competency based on the
development of the industrial revolution which has
reached the stage of the industrial revolution 4.0, so
that employee competencies must be adjusted to the
demands of the development of the industrial
74
Lubis, A., Lumbanraja, P., Absah, Y. and Silalahi, A.
A Propositions and Implications in Conceptualization of Human Resource Competencies 4.0.
DOI: 10.5220/0009199200740081
In Proceedings of the 2nd Economics and Business International Conference (EBIC 2019) - Economics and Business in Industrial Revolution 4.0, pages 74-81
ISBN: 978-989-758-498-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

revolution 4.0. Human resource competency 4.0 is
the submission of the concept of competency that is
compiled based on the synthesis of literature review
and future management encouragement and the
development of competencies for businesses to deal
with Industry 4.0. Therefore the dimensions of
competencies are adjusted to develop and build
appropriate competencies for the future.
In this article, we try to conceptualize human
resource competencies 4.0 on the practice of human
resource management concepts. The concept of
human resource competence that is developing at
this time, has a very general dimension that consists
of skills, knowledge and abilities that have not been
focused on the needs of the industrial world that is
highly developed and requires flexible and
adaptative human resources who have competencies
in accordance with the development of the
revolution industry. Therefore we provide a new
conceptualization of human resource competency
constructs, which are more forward-looking, such as
integrating the practice of human resource
management concepts with knowledge, expertise
and other specific capabilities that are manifested by
human resources within the company. We first
conduct an extensive literature review of the concept
of human resource management and its derivatives.
We then carry out analysis of theoretical content and
synthesis of relevant literature to take key the
theoretical factors that underlie the construct to
derive three dimensional areas.
Based on these three dimensions, we provide a
new conceptualization of the construction of human
resource competencies. The new definition has clear
boundaries that are depicted, are more contemporary
and apply broadly, these three dimensions include:
(1) Core competencies
(2) Managerial competencies;
(3) Core value competencies;
This research has several important managerial
implications for the company / industry and human
resource department managers, in terms of looking
at the readiness of employees to face any changes
that come both from within and outside the
company, and in carrying out special training based
on the needs of the required competencies, as well in
terms of considering individual characteristics and
competencies possessed by prospective employees
during the recruitment and selection process.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 The Human Resource Management
Concept
Human resources have a very important role in
achieving company goals. In a very dynamic and
competitive business world, human resources are
increasingly showing their role in achieving
company goals. The resources of the company are
basically limited, so the company is demanded to be
able to empower and optimize its use to maintain the
company's survival. Of the various resources owned
by human resources, the company occupies a
strategic position among other resources in the
company. Human resource management is currently
moving along with the times when external shaking
conditions are an important factor that must be
considered in achieving company goals. The change
in paradigm for human resource management is
absolutely happening along with the changes faced.
Humans are the most valuable resources in the
company that must be managed professionally by
focusing on the functions of human resource
management namely the formation function,
maintenance function, motivation function and
development function (Suhariadi, 2013).
Furthermore, the challenges faced by the business
world today are influenced by the development of
globalization and the industrial revolution, which
makes the competition in the business world more
stringent, and makes aspects of the quality and
competence of human resources are very important.
At the company level, competency management for
human resources is dependent on human resource
management. Human resource management in order
to adjust competence in accordance with the
challenges of the globalization era and the
development of the industrial revolution is
absolutely necessary, and this is the responsibility of
the human resources division within a company or a
business (Adeniji, 2012).
2.2 Human Resource Competencies
Discussing human resource competencies means
discussing the characteristics of human resources in
this case is the qualified employees who can support
work operations and organizational growth. The
development of an increasingly broad competence of
human resources ensures that human resource
management plays an important role in
organizational success. Characteristics of individuals
who have the skills, knowledge and abilities that are
A Propositions and Implications in Conceptualization of Human Resource Competencies 4.0
75

used in a manner consistent with achieving the
desired goals are definitions of human resource
competencies (Azmy, 2015). Personality or personal
characteristics, ways of thinking and behavior of
people at work is a unit that forms employee
competencies in addition to knowledge and skills
that can be observed, measured and evaluated
(SUDARSO, 2015). Companies and professionals in
the HR field must be able to respond to internal and
external changes in business, by having human
resource competencies. Values, knowledge, and
abilities of employees are definitions of competence
(Ulrich et al., 2007). Employees with the right
competencies will contribute to the achievement of
company goals (Lubis, 2019).
2.3 Human Resource Competencies
4.0: Review of Literature
The basic concept of competence is one's
understanding, expertise and professional identity.
Competence is a determinant of employee
commitment to the company, employee performance
and employee satisfaction (Alamsyah Lotunani,
2014). The first step in formulating the concept of
human resource competencies 4.0 is to determine a
review of the competencies from previous studies.
The three most recent competency concepts
proposed by The RBL Group and the Ross School of
Business at the University of Michigan formulate the
Human Resource Competency Study (HRCS) into 3
dimensions: relationships, Systems & Processes and
Organization Capabilities (Mike Ulrich, 2015).
Changes that absolutely occur from within and
outside the company, caused by the challenges of
globalization and the development of the industrial
revolution requires companies to adapt. The first
industrial revolution began in the 17th century,
followed by the second industrial revolution in the
early 20th century marked by mass production
activities. The third industrial revolution was marked
by digitalization and the introduction of the internet
that made it easy for people and business processes
(Zeng, 2016). Today the business world is made
easier by the existence of robotics technology,
artificial intelligence, internet of things, big data,
automation in all fields, all of which are summarized
in the concept of the industrial revolution 4.0 (Nagy
et al., 2016).
The industrial revolution can be an opportunity
as well as a challenge for the business world. If you
return to the concept of human resource
management which states that human resources have
an important role in achieving company goals, so
that companies can survive the challenges of the
industrial revolution 4.0, human resources are
needed to be able to respond the changes that arise
and can be flexible in dealing with these changes.
Human resources must have the competencies
required to be able to face the challenges of the
industrial revolution 4.0. Furthermore, after the
competency dimension proposed by The RBL Group
and the Ross School of Business at the University of
Michigan, we will look at the competency
dimension proposed by (Hecklau et al., 2016), which
divides competencies into four dimensions namely
technical competencies, methodological
competencies, social competencies and personal
competencies. Finally, we also include the division
of competency dimensions proposed by Unesco
which divides competencies into three dimensions,
namely core competencies, managerial competencies
and core value competencies. These three
competency concepts with their dimensions and
indicators form the basis of the formulation of the
concept of human resource competencies 4.0.
The second stage is to formulate the challenges
faced by companies and human resources in facing
the industrial revolution 4.0 and determine the
competencies needed to face these challenges. The
various challenges and competencies needed in the
face of the industrial revolution 4.0 are presented in
Table 1 below.
Table 1.
No. Challenge type Required
Competencies
1. The use of
information
technology and the
increasingly high
use of coding and
networking in the
business world
(Tjandrawinata,
2016)
The ability to
understand information
technology and
networks accepts all
forms of digitization
and automation and is
able to learn coding as a
form of communication
language between
humans and com
p
uters.
2. Changes and
uncertainties in the
business world make
workers have to
work amid these
uncertainties
(YAHYA, 2018)
Work while maintaining
the quality of work and
being able to work in a
professional manner
regardless of changes
and uncertainties.
3. The 4.0 industrial
revolution caused
changes in consumer
behavior so
companies must be
able to innovate to
Employees must be
creative to produce
innovations that are able
to support companies to
innovate products and
services to adapt to
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
76
match consumer
tastes for products
and services
consumer tastes
4. To be able to
survive in the midst
of globalization and
the industrial
revolution,
companies must
collaborate with
other companies in
order to overcome
the disruption of
supply chain
management and
business processes,
because there is
cooperation to
complement the
limitations of the
company (Vieira et
al., 2013)
Synergy and
cooperation between
companies to
complement each
other's limitations must
be supported by human
resources who are also
able to carry out good
collaboration between
employees in the
company, as well as
between employees of
other companies.
Mutual communication
skills are needed so that
the collaboration
process can run well
No. Challenge type Required
Competencies
5 The borderless
world causes every
country in the world
to conduct business
activities without
interruption of
distance and time
(
Kohnová, 2018
)
Interactions that occur
between companies in
every country in the
world must be
supported by employees
who can accept cultural
diversity and master
forei
g
n lan
g
ua
g
es
6 High uncertainty
faced by the
company (Nurazwa
Ahmad, 2019)
The uncertainty faced
by companies requires
the expertise of
employees to think
critically and
analytically in order to
be able to solve
com
p
lex
p
roblems
7. Technology trends
are developing in
business (Mohamed,
2018)
The ability to increase
knowledge in line with
developments and
changes in the world of
technology associated
with the field of work
involve
d
8. Smart process,
Smart product, and
smart after sales
service are a must in
business success in
Industry 4.0 (Uygun,
2018)
Smart process, Smart
product, and smart after
sales service can be
realized with the
support of human
resources who can work
productively and focus
on achievin
g
g
oals.
9. Digital
transformation is a
must for companies
(Maksumic, 2017)
Demands for
digitalization for
companies must be
supported by employees
who are able to share
knowledge related to
changes implemented in
the company and are
able to improve work
results in a sustainable
manne
r
10. The transition from
only the use of hard
skills to a
combination of hard
skills, soft skills and
work-related
knowledge.
(Ermolaeva, 2016)
Employees must have
Confidence in attitudes
and expectations to
make standard actions
in the workplace that
use resources carefully,
attentively and in
connection with social
j
ustice.
No. Challenge type Required
Com
p
etencies
11. New Working
conditions regards to
interface and control
tasks (Sorko S. R.,
2016)
Changing working
conditions result in
increased control of
work that requires
quality and useful
decision making
ca
p
abilities
12 Resistance To
change for company
and employee
(Trstenjak, 2018)
Resistance to change is
the biggest obstacle for
the company in the
midst of very dynamic
conditions of change
and very competitive
competition. Leadership
skills are absolutely
necessary as a driver for
the success of change,
so that employees are
able to motivate
employees to want to
adapt to be flexible,
adaptative and accept
chan
g
es
3 CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
TOWARDS A NEW
CONCEPTUALIZATION DATA
Based on a review of the human resource
competencies and human resource competencies
literature 4.0, we formulated a new
conceptualization for the concept of human resource
competencies 4.0, due to the limited scope for the
concept of human resource competencies. With a
complete literature review, we formulated three
construct domains which are dimensions of human
resource competencies 4.0. The three construct
domains address issues that fill and form gaps for
the concept of human resource competencies that are
A Propositions and Implications in Conceptualization of Human Resource Competencies 4.0
77
adapted to the development of the industrial
revolution. For example the important thing in the
domain area left behind from the construct domain
of human resource competencies is having the
ability to master ICT, networking and coding skills.
Now we will discuss three domain areas from the
construct of human resource competencies from the
literature review. These aspects have been derived
from various studies in the literature on human
resource management, the concept of human
resource competencies, the concept of industry 4.0
and other related matters. We therefore place and
discuss three propositions to provide new and
expanded conceptualizations of concepts:
P1: The dimension of human resource
competencies 4.0 is core value competency which
is a competency that must be possessed in order
to achieve company goals which is the core
principles and rules which are a reference in
acting for members of the organization.
The industrial revolution 4.0 will bring changes to
the work model of employees who will certainly
utilize Information, Communication and Technology
(ICT) to the fullest, use work-related software to
support work efficiency and effectiveness, and have
the coding skills that are indispensable in working in
an era industrial revolution 4.0. Further propositions
in this study relate to the core competencies that
employees must possess that will support the
achievement of company goals. Core competencies
are the main competencies grouped in aspects of
attitudes, skills and knowledge that employees must
have in carrying out their duties and responsibilities
at work. Core competencies must describe a
balanced quality between the achievement of Hard
skills and Soft skills, then the second proposition in
this study is:
P2: Human resource competencies 4.0 requires
core competencies related to a combination of
hard skills and soft skills that can improve
aspects of adaptability and quality of work.
Considering the challenges faced by companies that
are of enormous changes coming from internal and
external companies, globalization and the
development of the industrial revolution as well as
competitive conditions that have reached the
hypercompetitive stage, therefore there is a need for
managerial competencies that guide the company to
succeed in facing these challenges. Employees must
have managerial competence which is an individual
competency concept that is more focused on the goal
of improving management performance within the
scope of the company carried out by employees,
which is a combination of activities, knowledge,
skills or attitudes as well as personal characteristics
possessed by employees. The concept of managerial
competence is more focused on the approach to
behavior and managerial personality that companies
need to support the stability and sustainability of the
company amidst the changes caused by
globalization, the development of the industrial
revolution and hypercompetitive competition
(Boyatzis and Boyatzis, 2008).
P3: Companies need managerial competence for
the success of achieving company goals, so the
managerial competence is a dimension of human
resource competencies 4.0.New definition of
Human Resource Competencies 4.0
Based on the three domain areas positioned above
from human resource competencies 4.0, we define
human resource competencies 4.0 as:
Employees' capabilities or capabilities that are
adapted to the development of the 4.0 industrial
revolution with a combination of expertise in the
fields of ICT, hard skills and soft skills that are
formulated based on future management
encouragement and competency development for
businesses to deal with Industry 4.0.
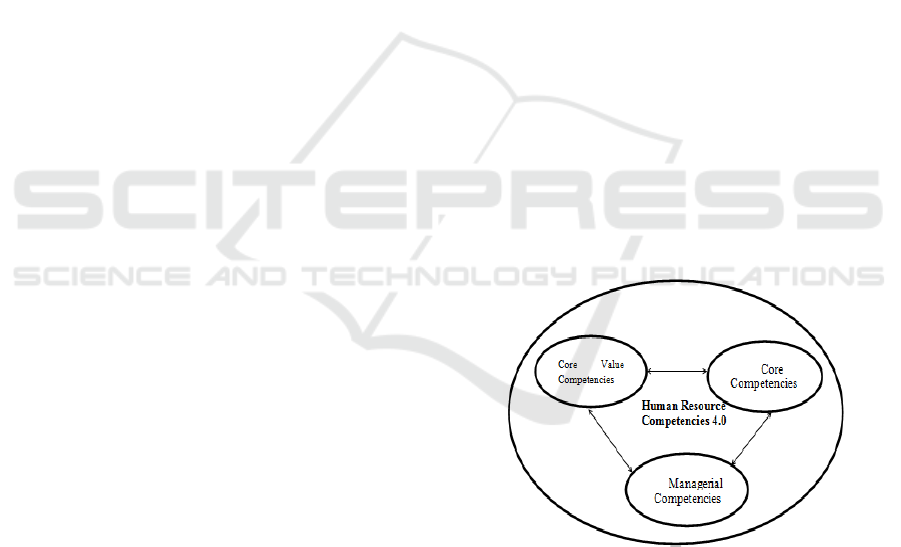
The construct of human resource competencies 4.0
has the following three domain fields. We illustrate
this construct and its domain area in Figure 1.
1. Core Value Competencies
2. Core Competencies
3. Managerial Competencies
Figure 1: Domain of human resource competencies 4.0
and its three domain areas.
4 MANAGERIAL IMPLICATIONS
CONCLUSIONS
Human resource competence is becoming
increasingly important in the ongoing changes
driven by globalization and the development of the
industrial revolution. This is because human
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
78
resource competence is an amalgamation of the
abilities, knowledge, and expertise that exists in
employees that can support the achievement of
company goals. The concept of human resource
competency 4.0 is a submission from the
development of the concept of resource competency
based on the challenges faced by companies in the
era of the industrial revolution 4.0. Three main
dimensions consisting of several indicators in the
concept of human resource competencies 4.0 can be
used as a reference by companies, HRD managers in
preparing recruitment and selection planning, as well
as training and developing employees in the
company in order to have competencies that are in
accordance with the needs and demands of work in
the revolutionary era industry 4.0. This study has
several significant managerial implications (see
Table I to see a direct comparison between
traditional conceptualizations of new orientations of
human resource competencies).
First, new conceptualizations for companies and
HR managers, three specific domain areas that are
the focus for managing and controlling employees.
Each of these three domain areas can be a useful
diagnostic tool for managers to develop strategic
human resource planning for companies, especially
in the context of recruitment and selection for
prospective employees.
Second, the three domain areas can separately
act as diagnostic tools that are useful in identifying
the specific training needs of employees. Based on
the diagnosis of the usefulness of each domain area,
design and implement improvements in accordance
with the demands of the industrial revolution era 4.0.
For example, if the results of performance appraisal
from employees indicate that employee performance
has decreased performance oriented to one of the
three domain areas, HRD managers can nurse
customized training programs. This approach is
more effective than identifying general training
inputs, or recommending the same in training
programs for all employees.
Table 1. Comparison of traditional and new definitions of
human resurce competencies, its domain areas, and its
implications
Old vs new
conceptualization
Domainareas
Implications
Competence is a
basic
characteristic that
a person has or a
combination of
characteristics
possessed by
someone who can
show superior
performance
(Spencer, 2003)
Skill
Knowledge
Ability
Superior
Performance
Employees'
capabilities or
capabilities that
are adapted to the
development of
the 4.0 industrial
revolution with a
combination of
expertise in the
fields of ICT, hard
skills and soft
skills that are
formulated based
on future
management
encouragement
and competency
development for
businesses to deal
with Industry 4.0.
(New definition
proposed in
this paper)
Core Value
Competencies
Core
Competencies
Managerial
Competencies
New
constructs
The three
different
domain
areas can
be
followed
up by
manageme
nt
Employee
Readiness
to change
Focus on
understand
ing
flexible
competenc
y
hierarchies
in
accordance
with the
developme
nt of the
industrial
revolution,
and
creating
employee
commitme
n
t
Finally, the three domain areas will be useful for
the new workforce that will enter the workforce,
namely Generation Z or final year students. Three
domain areas in the concept of human resource
competencies 4.0 will be a more comprehensive
representation of their readiness to enter the world of
work, where indicators in these three domain areas
can be used as a reference in their success in
entering the world of work. This study contributes
by conceptualizing the conceptualization of the old
domain vs. the new implication of the extent to
which Generation Z in completing and developing
the competencies that they must have for success in
A Propositions and Implications in Conceptualization of Human Resource Competencies 4.0
79

the world of work is affected by the development of
the industrial revolution.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to express my very great
appreciation to my mother, my husband and my
children for their support and encouragement
throughout my study.
I would like to express my very great
appreciation to Prof Dr. Prihatin Lumbanraja,
M.Si, Dr. Yeni Absah, M.Si, Dr. Amlys S
Silahahi (my research supervisor) of their patient
guidance, enthusiastic encouragement and useful
critiques of this research work and Their
willingness to give their time so generously has
been very much appreciated.
I would also like thank to Dr Endang Sulistya
Rini, M.Si, and Dr. Bebby Karina, M.Si for their
valuable and constructive suggestions during the
planning and development of this research work.
I would like to express my deep gratitude to
Universitas Muslim Nusantara Al Washliyah
Medan for their valuable support during my
study
REFERENCES
Akhtar, Naeem, Muhammad Tahir, and Zahra Asghar.
2016. “Impact of Social Media Marketing on
Consumer Purchase Intention.” International Review
of Social Sciences, no. October: 385–94.
Almada-Lobo, F. 2016. “The Industry 4.0 Revolution and
the Future of Manufacturing Execution Systems
(MES).” Journal of Innovation Management 3 (4): 16–
21.
Ansari, Nadia Umair, and Hanif Mohammed. 2015.
“Factors Affecting the Intent to Purchase Halal
Personal Care Products : Empirical Evidence from
Pakistan.” Int. J. Islamic Marketing and Branding 1
(2): 199–213.
Aziz, Yuhanis Abdul, and Nyen Vui Chok. 2013. “Halal
Certification , and Marketing Components in
Determining Halal Purchase Intention Among Non-
Muslims in Malaysia : A Structural Equation
Modeling Approach.” Journal of International Food &
Agribusiness Marketing 25 (1): 1–23.
https://doi.org/10.1080/08974438.2013.723997.
Baharuddin, Kasmarini, and Norliya Ahmad Kassim.
2015. “Understanding the Halal Concept and the
Importance of Information on Halal Food Business
Needed by Potential Malaysian Entrepreneurs” 5 (2):
170–80. https://doi.org/10.6007/IJARBSS/v5-i2/1476.
Borzooei, Mahdi, and Maryam Asgari. 2013. “Halal
Branding and Purchase Intention : A Brand Personality
Appeal Perspective.” International Journal of Business
and Management Invention 2 (8): 23–27.
Chen, Hui. 2012. “The Impact of Comments and
Recommendation System on Online Shopper Buying
Behaviour.” JOURNAL OF NETWORKS 7 (2): 345–
50. https://doi.org/10.4304/jnw.7.2.345-350.
Cohen, J. 1988. Statistical Power Analysis for the
Behavioral Sciences. New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum.
Hair, Joseph F. Jr., G. Tomas M. Hult, Christian M.
Ringle, and Marko Sarstedt. 2014. A Primer on Partial
Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-
SEM). United States of America: SAGE Publications.
Ireland, John. 2011. “UAE Consumer Concerns About
Halal Products.” Journal of Islamic Marketing 2 (3):
274–83. https://doi.org/10.1108/17590831111164796.
Khan, Saba Anwar, Naveed Ramzan, M Shoaib, and
Adam Mohyuddin. 2015. “Impact of Word of Mouth
on Consumer Purchase Intention.” Science
International 27 (1): 479–82.
Khaniwale, Manali. 2015. “Consumer Buying Behavior.”
International Journal of Innovation and Scientific
Research 14 (2): 278–86.
Kotler, Philip, and Kevin Lane Keller. 2012. Marketing
Management. 14th ed. New Jersey: Prentice Hall.
Lada, Suddin, Geoffrey Harvey Tanakinjal, and Hanudin
Amin. 2009. “Predicting Intention to Choose Halal
Products Using Theory of Reasoned Action.”
International Journal of Islamic AndMiddle Eastern
Finance AndManagement 2 (1): 66–76.
https://doi.org/10.1108/17538390910946276.
Laksamana, Patria. 2018. “Impact of Social Media
Marketing on Purchase Intention and Brand Loyalty :
Evidence from Indonesia ’ s Banking Industry.”
International Review of Management and Marketing 8
(1): 13–18.
Nurhasanah, Saniatun, and Happy Febrina Hariyani. 2017.
“Halal Purchase Intention on Processed Food.” Tazkia
Islamic Finance and Business Review 11 (2): 187–
209.
O’Leary, Steve, and Sheehan. 2008. Building Buzz to Beat
the Big Boys Word of Mouth Marketing for Small
Bussiness. United States of America: Praeger
Publishers.
Ringle, C. M., Wende, S., and Becker, J.M. 2015.
“SmartPLS 3.” Boenningsted: SmartPLS GmbH.
Roudposhti, Vahid Mohseni. 2018. “A New Model for
Customer Purchase Intention in E-Commerce
Recommendation Agents.” Journal of International
Studies 11: 237–53. https://doi.org/10.14254/2071-
8330.2018/11-4/17.
Salehudin, Imam, and Basuki Muhammad Mukhlish.
2012. “Pemasaran Halal : Konsep , Implikasi Dan
Temuan Di Lapangan.” In Dulu Mendengarsekarang
Bicara: Kumpulan Tulisan Ekonom Muda FEUI, 293–
305. Jakarta: Lembaga Penerbitan Fakultas Ekonomi
Universitas Indonesia.
Sharifpour, Yousef, Inda Sukati, Mohd Noor, and Azli
Bin. 2016. “The Influence of Electronic Word-of-
EBIC 2019 - Economics and Business International Conference 2019
80

Mouth on Consumers ’ Purchase The Influence of
Electronic Word-of-Mouth on Consumers ’ Purchase
Intentions in Iranian Telecommunication Industry.”
American Journal of Business, Economics and
Management 4 (1): 1–6.
Sharma, Khumar. 2018. “The Impact of Social Media
Marketing Strategies On Consumer Purchase
Intention.” Multi-Knowledge Electronic
Comprehensive Journal For Education And Science
Publications 5 (February): 172–82.
Sitalakshmi, Rajagopal, Shambavi Satapathy, Ramanan
Subhadra, and Ramanan Visvanathan. 2011. “Halal
Certification : Implication for Marketers in UAE.”
Journal of Islamic Marketing 2 (2): 138–53.
https://doi.org/10.1108/17590831111139857.
Trinh, Giang, John Dawes, and Larry Lockshin. 2009. “Do
Product Variants Appeal to Different Segments of
Buyers within a Category?” Journal of Product and
Brand Management 18 (2): 95–105.
https://doi.org/10.1108/10610420910948997.
Tuten, Tracy L. 2008. Advertising 2.0 Social Media
Marketing in a Web 2.0. Connecticut: Praeger.
Ulumi, Bahrul, Yanis Rusli, and Sri Suharmini. 2014.
Pemasaran Jasa Informasi Perpustakaan. Jakarta:
Penerbit Universitas Terbuka.
Victor, Vijay, Jose Joy Thoppan Robert, Jeyakumar
Nathan, and Fekete Farkas Maria. 2018. “Factors
Influencing Consumer Behavior and Prospective
Purchase Decisions in a Dynamic Pricing
Environment — An Exploratory Factor Analysis
Approach.” Social Science 7.
https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci7090153.
Weinberg, Tamar. 2009. The New Community Rules :
Marketing on the Social Web. California: O’Reilly.
A Propositions and Implications in Conceptualization of Human Resource Competencies 4.0
81
