
Relationship between Demographic Characteristics and Incidence of
Violence in Children in Malang City, East Java Indonesia
Aini Alifatin*, Thathit Manon, Dini Kurniawati, Tutik Sulistyowati, Erna Retna Rahadjeng, and
Dyah Worowirastri Ekowati
University of Muhammadiyah Malang
Jalan Bendungan Sutami 118 A Malang 65145 East Java, Indonesia
Keywords: Demographic characteristics, violence on children, anticipation.
Abstract: Cases of violence against children in Indonesia several years have increased by very sharp. Results of Survey
Year 2013 by KPP-PA, in cooperation with the Ministry of Social Affairs and CPM, find happening to
increase the number of children who experienced violence either sexually, physically, or emotionally.
National Commission of Children Protection data in 2013 are available there were 1620 cases of violence
against children: 490 (30%) physical violence, 313 (19%) emotional abuse, 817 (51%) sexual violence.
Several actually could be more significant again. The various background behind the violence was much to
do research. The purpose of this study was to determine the relationship between demographic characteristics
and the incidence of violence in children. The study design used a correlation description where the study
population was school-age children grades 3, 4, 5, and 6 in Muhammadiyah Elementary Schools in Malang.
Simple Random Sampling obtained 3 47 samples. The process of processing data through editing, coding,
scoring, and tabulating, then tested with Chi-Square. Based on data analysis, the results are obtained: based
on gender, several siblings, parents' marital status, parents' last education, and parents' work, influence the
occurrence of violence with a p-value of 0.0 2 0 - 0.0 48 (ρ <0.05). So it can be interpreted that there is a
relationship between demographic characteristics and the incidence of violence in children. The study
concludes that demographic characteristics are the originators of violent incidents.
1 INTRODUCTION
Indonesia is in condition department emergency
child. Cases of violence against children in Indonesia
several years have increased by very sharp. Results of
Survey of Violence Against Children In 2013
conducted by KPP-PA in cooperation with the
Ministry of Social Affairs and CPM find the group
aged 18-24 years, showed to 1 of 2 men and 1 out of
6 women at least experiencing any of the violence of
sexual, physical or emotional. Based on
National
Commission of Children Protection data in 2013, there
were 1620 cases of violence against children: 490
(30%) physical violence, 313 (19%) emotional abuse,
817 (51%) sexual violence. The data mentioned
above are the data regarding cases that revealed by
the police, the number of actual cases that are not or
have not been exposed to so much bigger again
Children are the next generation of the nation.
Children are a family investment; however, the
condition becomes a hope for the future. A child,
whatever the conditions, requires the same attention
as other children, lots of love, and affection. Young
children need to be carried, invited to play, kissed,
cuddled, fed, and lulled to sleep. As they grow,
children need to play, have friends, and go to school,
just like other children. The lack of access to get a
playroom like this will affect the optimization of the
growth and development of children in society
(Momon S, 2008). If the child does not get proper care
during his growth and development, then the child
cannot grow and develop optimally so that the
nation's successor is born physically, mentally,
intellectually, socially, and spiritually.
The impact of the abuse treatment on children
would cause trauma and leave the growth and
development abnormalities that will affect later
adulthood. Proved that when these perpetrators of
violence not only do the mature, proven by the data
of the Directorate General of Corrections,
Kemenkumham the month August, 2014 Son of the
Conflict with the Law include: The number of
Alifatin, A., Manon, T., Kurniawati, D., Sulistyowati, T., Retna Rahadjeng, E. and Worowirastri Ekowati, D.
Relationship between Demographic Characteristics and Incidence of Violence in Children in Malang City, East Java Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0009143502450251
In Proceedings of the 2nd Health Science International Conference (HSIC 2019), pages 245-251
ISBN: 978-989-758-462-6
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
245

custody of children as many as 1,441 children,
consisting of children of men as many as 1,409
children and children of women as many as 32
children. Several inmates of children as many as
3,154 children, consisting of children of men as many
as 3,096 children and children of women as many as
58 children. Furthermore, regard this raises the
question correctly, whether the prison is a place that
is good and true for the process of education, growth,
and development of the child?
Many parentings consciously or unconsciously
put parents as an authoritarian figure, sole rule maker,
threatening, punishing when children make mistakes.
As a result, children become afraid, reluctant, or dare
not tell stories openly about what they want or
experience. Children who often get violence, both
from the closest people and strangers, often at the
same time receive threats and prohibitions not to
convey to others. The phenomenon of the iceberg in
cases of sexual violence also occurred because the
victims did not dare to report, or the only one
reported, but behind them, there were 6 victims even
more who did not report.
Various factors underlying the occurrence of
violence have been widely studied. Lack of social
control is the originator of the neglect of violence
against children. Children who get punishment from
parents is considered something familiar between
children and parents. Neighbors or anyone who will
not report the sentence as violent unless the child dies
or is seriously injured. The relationship between
children and adults behaves like a social hierarchy in
the community. Children should not argue what is
done by their parents. Father punishes children;
teachers punish students, make the child as being that
much lower and not enter who has the right and the
will.
Oppressive economic and political structures have
given birth to a violent subculture. Due to economic
pressures, parents experience prolonged stress. He
became compassionate. He gets angry easily.
Physical fatigue does not allow him to joke with
children. Emotional violence, verbal abuse, physical
violence occurs. Parents can force children to do
heavy work or sell their children to prostitution agents
because of economic pressures.
Doctor Tabatabaei, a media expert in Iran, once
wrote that childhood is one of the stages of the age of
a human being, who has his own needs and capacities.
Soft souls and physical children do not have the
readiness to be confronted with conflicts and
problems experienced by adults. Neil Postman, an
American writer, also wrote that if there were no
boundaries between the world of children and the
world of adults, there would be no more so-called
childhood. Children are not adults in mini size. They
need support, support, and protection from "adult"
actors: family, community, government, and country.
Protection of children must be all activities to
guarantee and protect children and their rights so that
they can live, grow, develop, and participate
optimally following human dignity and dignity, and
receive protection from violence and discrimination,
as stated in Law No. 35 Th.2014 on Amendment of
Law No.23 Th. 2002 on Child Protection. Necessary
efforts to explore a variety Characteristic that can be
behind the violence on children so that can be
obtained openness child when getting abuse, whether
physical, emotional, and sexual, so that all the
behavior of the potentially abusive child and various
incidents in children can be anticipated.
The research question is what the correlation
between demographic characteristics and the
incidence of violence in children is? The objective is
identifying data about the shape, and the background
behind the sociological, children get violent,
identifying the frequency of violence on children, to
analyze the relationship characteristic of the
incidence of child abuse
2 METHODS
The design of this study was a correlative descriptive
study, in which the research variables of respondents'
characteristics were correlated with the variable of
violence on children. The population in the study of
this were student SD Muhammadiyah derby Malang
grade 3, 4, 5, and 6, which were taken by random and
obtained 347 respondents of SD Muhammadiyah 1,
5, 6, and 9 the city of Malang, East Java, Indonesia.
The research was carried out in each SD
Muhammadiyah, namely 1, 5, 6, and 9 from the date
of 1 November until 15 December 2017. The process
of collection of data was done, by the way,
distributing questionnaires on each student in each
class at a different time. After the questionnaires were
distributed, the researcher read the questions and
explain the purpose of each question were listed on
the questionnaire. For students’ grades three and four,
the researchers provide explanations one by one on
each question that exists in the questionnaire as
attached because of the level of understanding of
children who still need assistance. The univariate test
in this study included age and sex. The bivariate test
in this study was to determine the relationship
between respondents' characteristics and the
HSIC 2019 - The Health Science International Conference
246

incidence of violence. The statistical test used in this
study is the Chi-Square (X 2) test.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Demographic Characteristics of the
Respondent
Table 1, shows that the majority of respondents who
often get violence are male sex (56%), and the results
of the chi-square test in table 1, shows that there is a
significant relationship between sex and the incidence
of violence, with P-value: 0.02 (α <0.05). Gelles
Richard J. declared Inheritance of violence between
generations (Intergenerational Transmission of
violence), that child will learn the behavior of the
violence of the parents, and when it grew into
adulthood, they commit acts of violence to her in any
case (RJ Gelles, 2006).
Table 1: Respondent Characteristics by Gender
Gender F %
Male 153 44%
Female 194 44%
Total 347 100%
Table 2: Respondent Characteristics by Age
Ages F Percentage
Year 8 47 14%
Year 9 81 23%
Year 10 109 31%
Year 11 72 21%
Year 12 28 8%
Year 13 10 3%
Total 347 100%
Figure 2 shows that the majority of respondents
aged 10 years (31%) followed by the age of 9 years
(23%) and the age of 11 years (21%) and the age of
the other — Chi-Square test results in Table 1. The
show is no relationship between character age on the
incidence of violence. It is pointed to the right number
of violence at the level of the school base is very high.
It has probably happened because the parents do not
understand the development and needs of the child as
well as his ability with age so that parents treat
children is wrong (Radja et al., 2016)
Table 3: Respondent Characteristics by School Level
School Level F %
Level 3 71 20%
Level 4 103 30%
Level 5 93 27%
Level 6 80 23%
347 100%
In Table 3, it is explained that the majority of
respondents were Grade 4 respondents (30%)
followed by Grade 5 (27%), Grade 6 (23%), and
Grade 3 Primary Schools (20%). Chi-square test
results showed no relation, which exhibited
significantly between levels of classes with the
incidence of violence with p-value 0.0625 (α> 0.05).
It is pointed to the right number of violence at the
level of the school base is very high. It has probably
happened because the parents do not understand the
development and needs of the child as well as the
ability to appropriate age so that the parents treat the
child is wrong. (Radja et al., 2016)
3.2 Information Sociology Data
Data sociology that is presented in the form;
frequency tabulation based on the number of siblings,
the order of children to what, the marital status of
parents, the level of education of fathers and mothers,
and the work of fathers and mothers.
Figure 1: Respondent Characyeristic by Siblings
Based on Figure 1, the frequency of respondents
is based on the number of siblings, ranging from
single children to three siblings, which is 23-30%.
The chi-square test results in table 1 show that there
is a significant relationship between the number of
siblings and the incidence of violence, with a p-value
of 0.0431 (α <0.05). Total brother helped determine
the burden of economic family, so that the potential
of the occurrence of violence, but the number of
families also can be a source of power which is
23%
30%
26%
8%
6%
2%
1%
3%
1%
Respondent Characteristics by
Siblings
1
2
3
4
5
Relationship between Demographic Characteristics and Incidence of Violence in Children in Malang City, East Java Indonesia
247
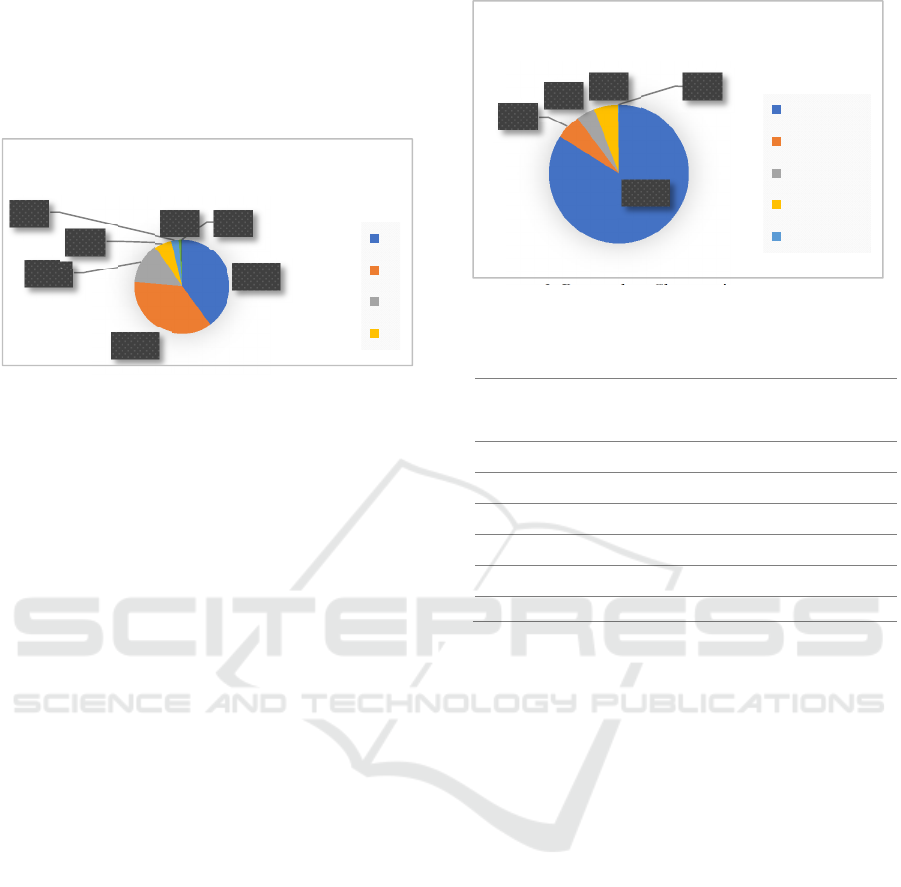
excellent for improving the economy of the family.
Acts of violence also occur in the middle class and
wealthy families. However, many of the family was
inadequate for several reasons. (R. Gelles & Perlman,
2012).
Figure 2: Respondent Characteristic by Number of
Siblings
Based on Figure 2, the majority of respondents
ranked 1-3 children. Chi-Square test results, showing
not there is a relationship that significant between the
orders of the child in the family with the incidence of
violence, with a P-value: 0.110 (α> 0.05). Stress
caused by various social conditions increases the risk
of violence against children in the family. The
conditions of these include unemployment, illness,
poor housing condition, a larger than average family
size, the presence of a new baby, a disabled person at
home (RJ Gelles, 1989).
In Figure 3, the majority of respondents came
from the wedding; those parents were intact (64%).
Chi-Square test results showed there is a relationship
that significant between the status of marriage the
parents with the incidence of violence, with a P-value:
0.03 (α <0.05). One older single more allows
committing acts of violence against children
compared with the parent intact. Apart from that,
families where nice husband or wife to dominate in
the making decision important, such as where housed
live, work what that would be taken, if family have
children, and some of the decisions the other, has the
level of violence against children are much higher
compared with families that conjugal same the same
shall be liable on decisions such (RJ Gelles, 1989).
Figure 3: Respondent Characteristic by Marital Status
Table 4: Respondent Characteristics by Parents Educational
Level
Educational Level Fathers'
Educational
Level
Mothers'
Educational
Level
Unschooled 2% 4%
Elementary School 9% 7%
Secondary School 9% 8%
High School 37% 33%
Tertiary 43% 48%
100% 100%
Table 4 shows the tabulated frequency of
respondents based on parents' educational level, with
the highest percentage of last education being High
School and Tertiary. Chi-Square test results showed
that there was a significant relationship between
parental education and violent incidents, with P
values of 0.03 and 0.04 (α <0.05). Low education and
attention to the elderly, as well as the lack of
knowledge of how to educate children the right, will
have an impact on the behavior of the parents to
provide care to children. Education and income of the
parents are low is one of the factors that can trigger
happens level of violence that is experienced by the
child. Hope the parents were too high without
knowing the limitations of the child and view the
parents that the child is the right to belong to the
parents or the assets of the economy led to the parents
do not know the needs and abilities of children, so the
parents are always imposing its will against children
(Mary, 2017).
3.3 Cross Tabulation between Violence
and Respondent Demographic Data
In the tabulation cross this, the data on violence are
classified into there and not the violence, which tests
the hypothesis performed with the Chi-Square test on
40%
36%
14%
6%
3%
1% 0%
Respondent Characteristics by
Number of Siblings
1
2
3
4
84%
6%
4%
6% 0%
Respondent Characteristics by
Marital Status
Married
Divorce
Remarried
Deceased
Polygamy
HSIC 2019 - The Health Science International Conference
248

each variable. In the test chi-square, in each cell is not
found their cell frequency is 0 (zero) or the frequency
expectation of less than 5 (five), so the analysis
followed by the Chi-Square test.
Table 5: Crosstab relationship between demographic characteristics and violent incidents.
Characteristics Demography Violence
Yes No Total P-value
Gender Man 161 33 194 00.02
Woman 107 46 153
Total Score 268 79 347
Class School Level 3 63 8 71 0,4527778
4 86 17 103
5 72 21 93
6 47 33 80
Total Score 268 79 347
Ages 8 41 6 47 0,1395833
9 74 7 81
10 83 26 109
11 45 27 72
12 20 8 28
13 5 5 10
Total Score 268 79 347
Child order 1 122 15 137 0,0763889
2 103 22 125
3 24 24 48
> 3 19 18 37
Total Score 268 79 347
Number of siblings 1 58 21 79 0,2993056
2 68 32 100
3 74 14 88
> 3 68 12 80
Total Score 268 79 347
Wedding status Married 242 46 288 00.03
Divorce 22 33 55
Total Score 268 79 347
Parents educational level Unschooled 45 12 57 0.048
Elementary school 16 6 22
Middle school 16 8 24
High school 88 22 110
Tertiary 113 31 144
Total Score 268 79 347
Mother education status Unschooled 44 8 52 0.033
Elementary school 20 6 26
Middle school 17 9 26
High school 79 33 112
Tertiary 108 23 131
Total Score 268 79 347
Father’s Employment status Work 195 54 249 0.044
Unemploy 73 25 98
Total Score 268 79 347
Mothers’ Employment
status
Work 183 49 232 0.023
Unemploy 85 30 115
Total Score 268 79 347
Based on Table 5, indicate that the demographic
Characteristic who have a relationship that is
significant to the incidence of violence is
Characteristic demographic types of sex, number of
Relationship between Demographic Characteristics and Incidence of Violence in Children in Malang City, East Java Indonesia
249

siblings, the status of marriage the parents, the level
of education the parents, and the work of the parents.
Score p-value at the seventh Characteristic of
respondents is between 0.02- 0048, which means that
the numbers are much smaller than the level of error
(α <0.05), while the class, the age of the child, the
position of the child to not there is a relationship that
is significant to the occurrence of violence. A score
of P-value of 0.0652 to 0.201, which means that the
numbers are more substantial than the level of error
(Α> 0.05).
Demographics characteristics that influence the
occurrence of violence on children is a kind of sex,
several siblings, the status of marriage the parents, the
status of education, and the status of the work the
parents. Children who get punishment from parents is
considered something familiar between children and
parents. The relationship between children and adults
behaves like a social hierarchy in the community.
Children should not argue what is done by their
parents.
Father punishes children; teachers punish
students, make the child as being that much lower and
not enter who has the right and the will. Oppressive
economic and political structures have given birth to
a violent subculture. Due to economic pressures,
parents experience prolonged stress. He became
compassionate. He gets angry easily. Physical fatigue
does not allow him to joke with children. Emotional
violence, verbal abuse, physical violence, and sexual
violence occur (Midwifery & Midwifery, 2015).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Demographics characteristics of the child influence
the occurrence of violence. A character who has a
relationship that is significant to the incidence of
violence on children is a kind of sex, some siblings,
the status of marriage the parents, the status of
education, and the status of the work the parents.
Boys get more violence than girls. The number of
members of the family is significant to trigger the
occurrence of violence for dealing with stress due to
the crush of the economy, although the magnitude of
the number of members of the family also can be a
source of power humans are useful in the economy of
the family. Character other co-related to the incidence
of violence is the status of marriage, the parents, the
status of education and employment status, where
everything can be geared to the stability of the
economy and an understanding of the patterns of
custody of the child. Children should not argue what
is done by their parents. Father punishes children;
teachers punish students, make the child as being that
much lower and not enter who has the right and the
will. Due to economic pressures, parents experience
prolonged stress. He became compassionate. He gets
angry easily. Physical fatigue does not allow him to
joke with children. Emotional violence, verbal abuse,
physical violence, and sexual violence occur.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Special thank you very devoted to the entire head of
SD Muhammadiyah Malang 1, 5, 6, and 9, as well as
the Chairman of the Institute for Studies and
Empowerment of Women and Children University of
Muhammadiyah Malang who has been allowing
doing research and support both morally and
materials. Thanks also delivered on LP3A team who
have worked hard to help the distribution of the
questionnaire, and the contribution of the role and
input.
REFERENCES
Achie Sudiarti Luhulima, S.H., M. . (2000). Pemahaman
Bentuk-Bentuk Tindak Kekerasan Terhadap
Perempuan Dan Alternatif Pemecahannya. Universitas
Indonesia. https://doi.org/10.14238/sp11.2.2009.136-
41
Cattaneo, C., Gibelli, D., & Ruspa, M. (2014). Sexual
Abuse. In Handbook of Forensic Medicine.
https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118570654.ch36
Child Welfare Information Gateway. (2011). Definitions of
Child Abuse and Neglect. State Statutes.
de Jong, R., Alink, L., Bijleveld, C., Finkenauer, C., &
Hendriks, J. (2015). Transition to adulthood of child
sexual abuse victims. Aggression and Violent
Behavior. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2015.04.012
Gelles, R. J. (1980). Violence in the Family: A Review of
Research in the Seventies. Journal of Marriage and the
Family. https://doi.org/10.2307/351830
Gelles, R. J. (1989). Child Abuse And Violence In Single
Parent Families: Parent Absence and Economic
Deprivation. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1939-0025.1989.tb02738.x
Gelles, R. J. (2006). Child Maltreatment and Foster Care.
Gender Issues. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03186788
Gelles, R., & Perlman, S. (2012). Estimated annual cost of
child abuse and neglect. Prevent Child Abuse America.
Humaira B, D., Rohmah, N., Rifanda, N., Novitasari, K.,
Diena H, U., & Nuqul, F. L. (2015). Kekerasan Seksual
Padaanak: Telaah Relasi Pelaku Korban Dan
Kerentanan Pada Anak. Psikoislamika : Jurnal
Psikologi Dan Psikologi Islam.
https://doi.org/10.18860/psi.v12i2.6398
Kebidanan, P., & Kebidanan, A. (2015). Faktor-Faktor
Yang Berhubungan Dengan Perilaku Orang Tua Dalam
HSIC 2019 - The Health Science International Conference
250

Melakukan Kekerasan Verbal Terhadap Anak Usia Pra
- Sekolah Yuni Fitriana, Kurniasari Pratiwi, Andina
Vita Sutanto. 14(1), 81–93.
Levin, T. L., Berdon, W. E., Cassell, I., & Blitman, N. M.
(2003). Thoracolumbar fracture with listhesis - An
uncommon manifestation of child abuse. Pediatric
Radiology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-002-0857-6
Martono, N. (2014). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif Analisis
Isi dan Anlisis Data Sekunder. Edisi Revis I2.
Maryam, S. (2017). Gambaran Pendapatan Orang Tua dan
Kekerasan pada Anak dalam Keluarga di Gampong
Geulanggang Teungoh Kecamatan Kota Juang
Kabupaten Bireuen. Psikodimensia.
https://doi.org/10.24167/psiko.v16i1.902
Moore, E., Gaskin, C., & Indig, D. (2013). Childhood
maltreatment and post-traumatic stress disorder among
incarcerated young offenders. Child Abuse and
Neglect. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2013.07.012
Radja, R. D., Kaunang, T. M. D., & Dundu, A. E. (2016).
Gambaran kekerasan pada anak sekolah dasar di
Kecamatan Malalayang Kota Manado. 4.
Rianawati, R. (2015). Perlindungan Hukum Terhadap
Kekerasan pada Anak. Raheema.
https://doi.org/10.24260/raheema.v2i1.164
sugiyono. (2016). metode penelitian pendidikan (kuantitatif
kualitatif dan R & D). Bandung: Alfabeta.
https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200409-1267OC
Sujarweni, V. W. (2014). SPSS untuk Penelitian. In SPSS
untuk Penelitian.
Walby, S., Hay, A., & Soothill, K. (1983). The Social
Construction of Rape. Theory, Culture & Society.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0263276483002001008
Relationship between Demographic Characteristics and Incidence of Violence in Children in Malang City, East Java Indonesia
251
