
Synthesis of Cross-linked Breadfruit Starch (Artocarpus communis)
using Epichlorohydrin
Cut Fatimah Zuhra
1,2*
, Mimpin Ginting
1
and Desi Sonya Siregar
1
,
1
Departement of Chemistry, Faculty Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan,
North Sumatera , Indonesia
2
Pusat Unggulan Iptek Kitosan dan Material Maju
Keywords: Breadfruit Starch, Epichlorohydrin, Cross-linked Starch, Degree of Substitution.
Abstract: Synthesis of cross-linked starch has been successfully carried out by crosslinking reaction between breadfruit
starch (Artocarpus communis) and epichlorohydrin with variation of epichlorohydrin 1%; 2%; and 3 %. The
result of cross-linked starch was characterized by FT-IR spectrophotometer and the degree of Substitution
(DS). The formation of cross-linked starch was confirmed by FT-IR spectra data with the appearance of
stretching vibrational of C-O-C at 1018.41-1242.16 cm
-1
. The value of DS for variations of epichlorohydrin
1%; 2%; 3% are 0.0552; 0.0701; 0.0613, respectively. The cross-linked starch with variation 2% of
epichlorohydrin has the highest DS and then it was characterized using SEM and determined the swelling
degree. The results of the swelling degree test with a variation of absorption time of 6 hours, 24 hours, 36
hours, 72 hours were 0.9925%, 1.4611%, 1.8054%, 2.0049%, 3.0124%, respectively.
1 INTRODUCTION
Starch is one of important source of food ingredients.
Starch can be found in grains, tubers and fruit from
plant which has shape like granules (Sauyana, 2014).
The application of starch as a raw material for
industry is very broad, including in the food, textile,
cosmetics and paper industries. The need of starch
tends to increase both for domestic consumption and
exports. Considering the need of starch is quite large,
many reseacher were interested to find the alternative
source of starch from other crops other than the
source of starch as well as we know such as cassava,
potatoes and corn (Hartati and Prana, 2003).
Breadfruit is one source of starch and intensively
cultivated in Indonesia. Breadfruit has high
carbohydrates contain so that breadfruit is a
promising source of starch. The isolation starch from
breadfruit produced 18.5g/100g which have 98.86%
of purity with amylose and amylopectin content of
27.68% and 72.32%, respectively (Rincón and
Padilla, 2004).
Natural starches such as tapioca, corn starch, sago
have problems if used as raw material for food and
non-food industries. If we cooked starch takes a long
time (until it needs high energy), also the pasta that is
formed hard and not clear. Besides that it is too sticky.
These constraints cause natural starch to have limited
use in the industry. Even though the source and
production of starch in our country is very abundant,
which consists of cassava starch, sago starch, rice
starch, and many other sources of starch that have not
been produced commercially. The development of
technology in the field of starch processing, starch
can be modified according to the properties that we
needed (Zuhra, et al, 2018).
Modified starch is starch that hydroxyl group has
been altered through a reaction or by modifying its
original structure. Pati is given certain treatment with
the aim of producing better properties to improve the
previous properties so that they can be used in
accordance with industrial needs (Wijayatiningrum,
2009).
Crosslinking method is one of method to modify
starch. The principle of this method is the way to
replace the OH group of starch and replaced it with
other functional group such as an ether, ester, or
phosphate group (Stevens, 1989). The advantages of
using crosslinking method can produce starch with
lower swelling capacity, furthermore its impact to
strengthen starch granules and make the starch more
resistant to acidic and hot media so that it does not
218
Zuhra, C., Ginting, M. and Siregar, D.
Synthesis of Cross-linked Breadfruit Starch (Artocarpus communis) using Epichlorohydrin.
DOI: 10.5220/0008878902180222
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Chemical Science and Technology Innovation (ICOCSTI 2019), pages 218-222
ISBN: 978-989-758-415-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

break easily during heating process. In addition,
crosslinking methods can improve texture and
viscosity of starch. However, this method has
disadvantages such as decreasing of the solubility,
precipitation, volume and stability of starch (Raina et
al., 2006).
The crosslinking of carboxymethyl starch from
rice was made by reaction between rice starch and
epichlorohydrin at concentrations (0.1-15% w/w).
The crosslinking reaction of carboxymethylation
directly using methanol as a solvent, the degree of
carboxymethylation substitution was between 0.24-
0.26 w/w with lower the content of amylose. The
resultof SEM showed a small changes on the surface
of the granule. Absorption of water volume and
swelling capacity of crosslinked starch increased
significantly as a result of modification
(Kittipongpatana and Kittipongpatana, 2013).
Original (unmodified) rice starch has rarely use in
industrial processes so modification of starch is
needed to reach the standard of food products. Rice
starch is cross-linked with epichlorohydrin with
various different concentrations (0.5%, 0.7%, 0.9% w
/ w, based on dry weight). Hydrolyzed rice starch by
α-amylase and hydrolyzed rice cross-linked starch
showed that the degree of amylase hydrolysis is
lower than hydrolyzed rice starch (Xiao et al., 2012).
The crosslinking agent used in this study were
epichlorohydrin. Epichlorohydrin is the best of
crosslinking agent if we compared to other monomers
such as POCl
3
and Sodium Trimetaphospate (STMP)
because its has small molecular weight (Rodríguez
and Nunez, 2008). The crosslinking bond that formed
between carbohydrate and epichlorohydrin generaly
were ether which bridges or connects of two hydroxyl
groups or more glucose units from starch molecules
(Wurzburg, 2010).
Based on the background, the researcher is
interested to synthesis cross-linked starch by
crosslinking reaction betweeen starch that isolated
from breadfruit and various concentration of
epichlorohydrin.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials and Equipment
Breadfruit starch is isolated from ripe breadfruit.
Chemical used, which is sodium carboxymethyl
cellulose and aluminum sulfate octadecahydrate are
purchased from Merck & Co.
2.1.1 Material
The materials used in this study are: Starch
Breadfruit, Epichlorohydrin, NaOH, HCl, NaCl,
Aquadest, Phenolphtalein Indicator.
2.1.2 Equipment
The tools used in this study were: FT-IR Shimadzu
Spectrophotometer, Scanning Electron Microscope
Hitachi, Blender, Desiccator, Analytical Balance,
Oven Blower, Burette, Beaker Glass, Pumpkin
Measure, Measuring Cup, Hotplate Stirer, Universal
Indicator, Funnel, Desiccator , Magnetic stirrer, Statif
and clamp.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Isolation of Starch from Breadfruit
Breadfruit was peeled, cut into small piece, and then
washed using water to remove the gum and other
impurities. The resulted breadfruit was added with
enough water and then mashed using a blender.
Furthermore, the result was then pricipitated after
filtered using gauze. The precipitation was washed
frequently until the washed water waste was
transparent. The obtained starch was dried in the oven
at 45
0
C for 24 hours. This step aims to prevent starch
becoming charred and gelatinized. Crude starch was
then milled and sieved with a size of 115 mesh
(Merdikasari et al., 2009). Finally, the starch was
analyzed using FT-IR and SEM.
2.2.2 Synthesis of the Cross-linked Starch
Synthesis of cross-linked starch was carried out based
on the (Xiao et al., 2012) method with a slight
modification, namely crosslinking of starch with
epichlorohydrin. 30 gram of breadfruit were mixed
with 45 ml aquadest until a suspension was formed
and then 3 grams of NaCl, 1% epichlorohydrin was
added successively and stirred. The mixture was
made into pH = 10 by dripping 1 M NaOH while
stirring and then stirred for 3 hours at 30
o
C.
Subsequently, the starch pulp obtained was
neutralized to pH 6.0-6.5 with 1 M HCl and washed
thoroughly. The starch was dried at 45
0
C for 24 hours.
Crude crosslinked starch was milled and sifted. The
same procedure was carried out for variation 2% and
3% Epichlorohydrin. Finally, the cross-linked starch
were analyzed using FT-IR and SEM, and also
determined the degree of substitution (DS) and the
degree of swelling capacity.
Synthesis of Cross-linked Breadfruit Starch (Artocarpus communis) using Epichlorohydrin
219
2.3 Characterization
2.3.1 Determination the Degree of
Substitution (DS)
The Degree of Substitution (DS) of cross-linked
starch was determined by titration method. Weighed
as much as 0.1 grams of starch, dissolved in 5 mL
NaOH 0.5 N and stirred for 30 minutes. Then 3 drops
of phenolphthalein indicator were added and titrated
with 0.5 N HCl until it reached the equivalent point.
2.3.2 Determination of Swelling Capacity
The degree of swelling capacity determined by
(Zuhra, et al, 2018) method, the starch were weighed
at 2-3 grams, then placed on a dry cup whose weight
was known, then stored in a desiccator which had
been saturated with K2SO4 or KCl solution and
observed weight gain. Samples were weighed over a
period of 6, 12, 24 48, 72 hours.
2.3.3 Fourier Transform Infra Red (FT-IR)
Spectroscopy
The Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra were
recorded with Shimadzu-IR Pretige 21 Spectrometer
were recorded in the transmittance mode in region
400-4000 cm
-1
at 16 cm
-1
resolution. Samples were
mixed with KBr powder and examined using IR
spectrometers.
2.3.4 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
The morphology of the surface of samples were
discovered by using Scanning electron microscope
(SEM) Hitachi and operated at 20 kV. Sample were
recorded at magnification between 1000 to 10000
times their original sizes.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Isolation of Breadfruit Starch
The result of isolation of breadfruit starch
(Artocarpus communis) from 10 kg of breadfruit was
obtained as much as 680 g (6.8%) mass of starch. The
data of FTIR spectrum of fruitbread starch displayed
in Figure 3.1. the characteristic vibrations that
confirm of breadfruit starch appeared at the wave
number area 3387cm
-1
; 2931 cm
-1
; 1643 cm
-1
; 1157
cm
-1
. The broad and intense peak at 3387 cm
-1
attributed to O-H stretching vibration and the peak at
2931 cm
-1
corresponded to C-H stretching and also
the peak at 1157 cm
-1
indicated as C-O-C functional
group.
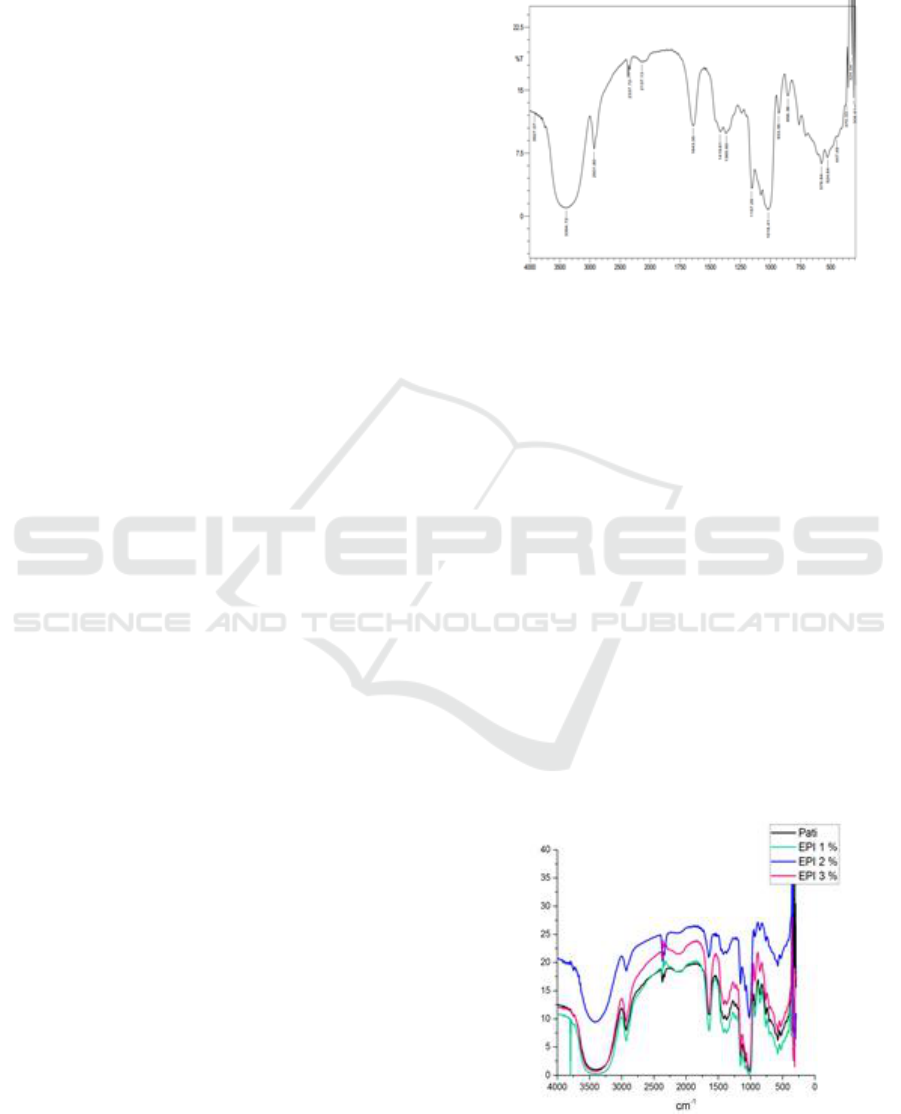
Figure 1: FTIR Spectrum of Breadfruit Fruit Starch.
3.2 Synthesis of Cross-Linked Starch
The cross-linked starch was obtained by crosslinking
reaction between starch and epichlorohydrin with
addition of NaOH as catalysts. The data of FTIR
spectrum of cross-linked starch displayed in Figure
3.2. The formation of cross-linked starch with
variation 1%,2%,3% of epichlorohydrin was showed
by FT-IR spectra data with appearance of the range
wave number at 3000-3500 cm
-1
, 1630-1650 cm
-1
,
1010-1160 cm
-1
.
The increasing variation weight of
epichlorohydrin reduced the intensity of vibration
peak at 3387 cm
-1
and the appearance of a vibration
peak in the area at 1018 -1242 cm
-1
corresponded to
C-O-C functional group. The peak at 1018 cm
-1
showed intramolecular hydrogen bonds, it was
confirmed with breadfruit starch peak at 1018 - 1242
cm
-1
more intense than cross-linked starch. This
implied that hydrogen bonds have been severed (Xiao
et al., 2012).
Figure 2: FTIR spectrum of cross-linked starch with various
concentration of epichlorohydrin (1%, 2%, 3%).
ICOCSTI 2019 - International Conference on Chemical Science and Technology Innovation
220
3.3 Degree of Substitution
In this study, the DS was obtained with ranged from
0.0552 - 0.0701 that can be seen in Table 3.1. The
cross-linked starch with addition 2% of
epichlorohydrin was the highest DS. In process of the
preparation of cross-linked starch influenced by the
number of crosslinking agents used and the length of
reaction time. In this study, the more epichlorohydrin
used, so that the more clusters can replace the OH
group. This is caused by the lenght of contact time
between epichlorohydrin and breadfruit starch. The
longer of contact time can weaken the hydrogen
bonds in starch. But the addition of 3%
epichlorohydrin, did not show improvement of the
DS but a decline of the DS if it was compared with
the value of the DS of cross-linked starch with
addition 2% of epichlorohydrin (Zuhra, et al, 2018).
Tabel 1: The value of DS of cross-linked starch with
various concentration of epichlorohydrin.
Concentration
% DS
DS
Epiklorohidrin 1%
0,33
0,0552
Epiklorohidrin 2 %
0,415
0,0701
Epiklorohidrin 3%
0,365
0,0613
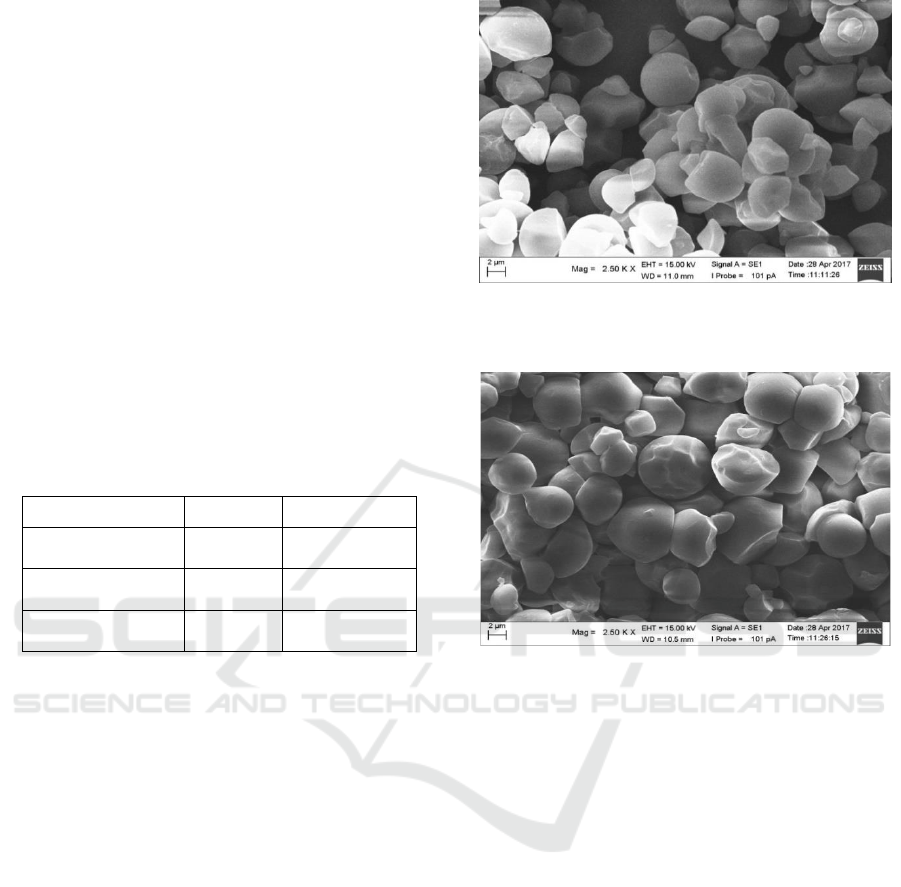
3.4 The Morphology Analysis
SEM analysis was performed to investigate the
surface morphology of the breadfruit starch and the
cross-linked starch with magnification 2500 times
that can be seen in Figure 3.3 and 3.4. In this research,
the SEM test only observed for the cross-linked starch
with addition 2% of epichlorohydrin that has the
higest value of DS. The shape of breadfruit starch and
cross-linked starch are both in the form of granules
but they have a little difference which is the surface
granule of breadfruit starch the surface of the granule
is more finer and the distance between the granules is
more tenuous while in the surface granule of cross-
linked starch is more coarse and the distance is more
tightly. This showed that the addition of
epichlorohydrin affects the shape of starch granules
(Zuhra et al., 2004).
Figure 3: The surface morphology of breadfruit starch with
magnification 2000x.
Figure 4: The surface morphology of cross-linked starch
with magnification 2000x.
3.5 Degree of Swelling Capacity
In this study, the determination degree of swelling
capacity was performed to breadfruit starch and the
cross-linked starch with addition 2% of
epichlorohydrin that has the highest value of DS. Its
can be seen in Table 3.2. The results showed that the
percentage of swelling capacity increased along with
the rising absorption time. Furthermore, the swelling
capacity decreased if it compared to breadfruit starch,
This is caused by crosslinking that are formed
between amylose molecules in starch granules, and
then causing swelling to be limited. This is also
influenced by the presence of cavities in the starch
that is formed by crosslinking reaction, so that water
molecules will be trapped to the cavity.
Synthesis of Cross-linked Breadfruit Starch (Artocarpus communis) using Epichlorohydrin
221

Table 2: Swelling capacity of breadfruit starch and cross-
linked starch.
Time
(hour)
W absorption (%)
Breadfruit starch
Cross-linked
starch
6
1.4842
0,9925
12
2.3358
1.4611
24
3.0032
1.8054
48
4.4974
2.0049
72
6.5195
3.0124
4 CONCLUSIONS
Synthesis of cross-linked starch has been
successfully carried out by crosslinking reaction
between breadfruit starch (Artocarpus communis)
and epichlorohydrin that were confirmed based on
FTIR spectrum. The FT-IR spectrum of cross-linked
starch showed C-O-C group that appears at wave
numbers 1018.41-1242.16 cm
-1
. The cross-linked
starch with addition 2% of epichlorohydrin were the
optimum condition that resulting the highest degree
of substitution at 0.0701%. The measurement of
degree of substitution from epichlorohydrin 1%; 2%;
3% were 0.0552%; 0.0701%; 0.0613%, respectively.
The SEM analysis of cross-linked starch is more
coarse and the distance between granules is more
tightly. Swelling capacity at absorption time of 6, 12,
24, 48, and 72 hours are 0.9925%; 1.4611%;
1.8054%; 2.0049%; 3.0124%, respectively.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Author would like to thank to Universitas Sumatera
Urara has facilitated all equipment until this journal
has been published successfully.
REFERENCES
Kittipongpatana, O.S., Kittipongpatana, N., 2013.
Physicochemical, in vitro digestibility and functional
properties of carboxymethyl rice starch cross-linked
with epichlorohydrin. Food Chem.
Merdikasari, Nurdjanah, S., Yulian, N., Lintang, N., 2009.
Amilografi Pasta Pati Sukun Termodifikasi
Menggunakan Sodium Tripolifosfat. Teknol. Ind. dan
Has. Pertan. 14, 173–177.
Raina, C.S., Singh, S., Bawa, A.S., Saxena, D.C., 2006.
Some characteristics of acetylated, cross-linked and
dual modified Indian rice starches. Eur. Food Res.
Technol.
Rincón, A.M., Padilla, F.C., 2004. Physicochemical
properties of Venezuelan breadfruit (Artocarpus altilis)
starch. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr.
Rodríguez, M., Nunez, S., 2008. Structural and rheological
characteristics of cross-linked banana starch with
different cross-linking agents. mexico 3–4.
Sauyana, Y., 2014. Produksi pati asetat dengan
menggunakan pati sagu nanokristalin. Dep.
IlmuPertanian FTP, IPB.
Wijayatiningrum, F.N.U.R., 2009. Makalah Seminar
Penelitian Modifikasi Cassava Starch Dengan Proses
Oksidasi Sodium Hypoclorite Untuk Industri Kertas,
Kimia, Jurusan Teknik Teknik, Fakultas Diponegoro,
Universitas Sudharto.
Wurzburg, O., 2010. Modified Starches. In: Food
Polysaccharides and Their Applications.
Xiao, H., Lin, Q., Liu, G.Q., 2012. Effect of cross-linking
and enzymatic hydrolysis composite modification on
the properties of rice starches. Molecules.
Zuhra, C.F., Ginting, M., Syufiatun, A., 2004. Modifikasi
Pati Sukun Dengan Metode Ikat Silang Menggunakan
Trinatrium Trimetafosfat. Chem. Nat. Acta 4, 142–146.
ICOCSTI 2019 - International Conference on Chemical Science and Technology Innovation
222
