
The Influence of Customer Relationship Management Influencing
Factors on Student Loyalty using Student Satisfaction as
Mediation Variable
Dewi Murtiningsih, Wendi Usino and Joko Christian Chandra
Universitas Budi Luhur, Indonesia
Keywords: Commitment, Communication, Service Quality, Satisfaction, Loyalty
Abstract: The purpose of this research is to find out the influence of commitment, communication and service quality
on student loyalty; to find out the influence of commitment, communication, and service quality on student
satisfaction; to find out the influence of student satisfaction on student loyalty; to find out the influence of
satisfaction in mediating the influence of commitment, communication and service quality on student loyalty.
This research is an explanatory research. The number of sample used in this research is 76 students of Special
Diploma 3. Questionnaire is used as a tool to collect data from respondent, which validity and reliability will
be tested. Data is analyzed using smart PLS. Research result shows that commitment does not influence
student loyalty, communication does not influence student loyalty, service quality influences student loyalty,
commitment influences student satisfaction, communication influences student satisfaction, service quality
influences student satisfaction, student satisfaction influences loyalty, student satisfaction fully mediates the
influence of commitment on loyalty, student satisfaction fully mediates the influence of communication on
loyalty, student satisfaction partly mediates the influence of service quality on loyalty.
1 INTRODUCTION
The ability of university in applying University Tri
Dharma (three basic value: Education, Research and
Community Service) effectively, usefully and
consistently together with its other supremacies
(facilities and infrastructure, accreditation, qualified
teaching staff, foundation management, department,
achievement, working network and others) will
become the main asset to gain interest from students.
Therefore, private universities will show their
excellences so community can have their own point
of view of the university image.
Maintaining good relationship with customer is
one of the ways for company to survive in the
condition and to maintain the existing customer.
Therefore, company must be able to be aware of and
fulfill what is wanted or what is needed by the
customer quickly and accurately. This must be done
so that company can get maximum sales results, loyal
customers, and also new customers.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is
one of company’s strategies to maintain their
customers. CRM is applied to win customer’s favor
by allocating all of the existing resources in the
company in order to achieve customer satisfaction.
Customer satisfaction plays a very important role in
highly competitive industry. It is because there is a
significant difference in the loyalty of customers who
are just satisfied and very satisfied or pleased
(Lovelock & Wright, 2007). Generally company
wants the product they produce to be able to give
satisfaction for the customers in order to get loyal
customers which can be maintained for a long time.
According to the previous research conducted by
Imasari and Nursalim (2011), the result shows that
there is a significant relation between CRM variable
and customer loyalty. The research points that CRM
is able to create positive company image in the
customer’s mind. CRM strategy which is applied by
company can determine the loyalty level of customers
who are satisfied by the company performance.
Other previous research conducted by Victor et
al (2015), shows that there is significant relation
between CRM variable and customer satisfaction.
CRM strategy which is applied by the bank is able to
maintain the good relationship with its customers.
The strategy is by providing satisfying service that
fulfill the customer’s expectation.
622
Murtiningsih, D., Usino, W. and Chandra, J.
The Influence of Customer Relationship Management Influencing Factors on Student Loyalty using Student Satisfaction as Mediation Variable.
DOI: 10.5220/0008434506220627
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World (ICIB 2019), pages 622-627
ISBN: 978-989-758-408-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

In the research conducted by Ersi and Samuel
(2014), the result shows that customer satisfaction
significantly influences customer loyalty. The
researchers also explained that when satisfaction is
formed, customer loyalty will follow, because the
customer’s expectation has been fulfilled.
Meanwhile, the result of the research conducted
by Padmavathy, Balaji and Sivakumar (2012) shows
that CRM significantly and positively influences
consumer loyalty. The researchers explained that
customer loyalty is the result of CRM which is
successfully applied by company, that a good CRM
effort will be able to create a strong bond between
company and customer, and increase customer
loyalty. This is in contrary with the research result of
Smith and Chang (2010) which shows that there is no
significant relation between CRM and customer
satisfaction and loyalty.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Customer Relationship
Management
Chan (2003) defined Relationship Marketing as close
familiarization of every guest in order to create two-
way communication by managing a mutually
beneficial relationship between consumer and
company. While according to Brown and Rigby,
Reincheld, Dawson (Gaffar, 2007), CRM is a process
to gain, maintain and develop beneficial service, and
needs a clear focus on a service attribute that can
generate value for customer that will lead to their
loyalty. In conclusion, customer relationship
manajemen (CRM) is not a concept or project, but a
business strategy which purpose is to comprehend,
anticipate and manage the needs of existing and
potential customer of a organization. Robinette in
Febrianingtyas (2013) explained that there are four
factors which influence CRM; those are mutual
benefit, commitment, truth and communication.
2.2 Customer Satisfaction
Consumer satisfaction is an important role in
marketing concept and consumer research. It has been
a public opinion that if consumer is satisfied of a
certain product or brand, they tend to keep buying and
using it, and also telling other people of their
enjoyable experience in using the product. If they are
not satisfied, they tend to shift to other place, and even
tell other consumers (Olson and Peter, 2000).
Satisfaction is someone’s happiness or
disappointment which occurs because they compare
perceived performance (of a product or result) with
their expectation (Kotler and Keller, 2009).
Customer’s review of product performance depends
on many factors, especially the nature of customer
loyalty of a brand which often create a more
enjoyable perception of a product from brand that
they already consider positive.
2.3 Customer Loyalty
Customer loyalty is a manifestation and continuation
of customer satisfaction in using facility or service
provide by a company, to be their regular customers.
Therefore, the core component to keep the life
sustainability of a company for a long time is
customer loyalty (Aaydin and Ozer, 2005). Griffin
(2005) states that a loyal customer characteristics are:
repeating purchase regularly, buying between lines
product and service, showing invulnerability of
competitor promotion, giving recommendation to
others. Aydin and Ozer (2004) state that the key for
a long term company life sustainability is customer
loyalty. Kotler (1997) states that customer loyalty is
formed by customer’s positive review. While Neal
(1998) states that factors which can create customer’s
choice and loyalty is value. Thus, from those two
researchers statements above, it can be concluded that
company which pays attention on value expected by
customer will gain their loyalty in return.
3 METHODOLOGY
This research is an explanatory research. Sample of
this research is 76 students of Special Diploma 3 Budi
Luhur University Jakarta, academic year 2016/2017
and 2017/2018. Questionnaire is used in data and
information collection process. To measure each item
of the surveys we used a Likert scale of 5 points. Data
collection techniques use questionnaire that has been
tested for validity and reliability. The data analysis
technique used to answer hypothesis is Smart PLS.
The Influence of Customer Relationship Management Influencing Factors on Student Loyalty using Student Satisfaction as Mediation
Variable
623
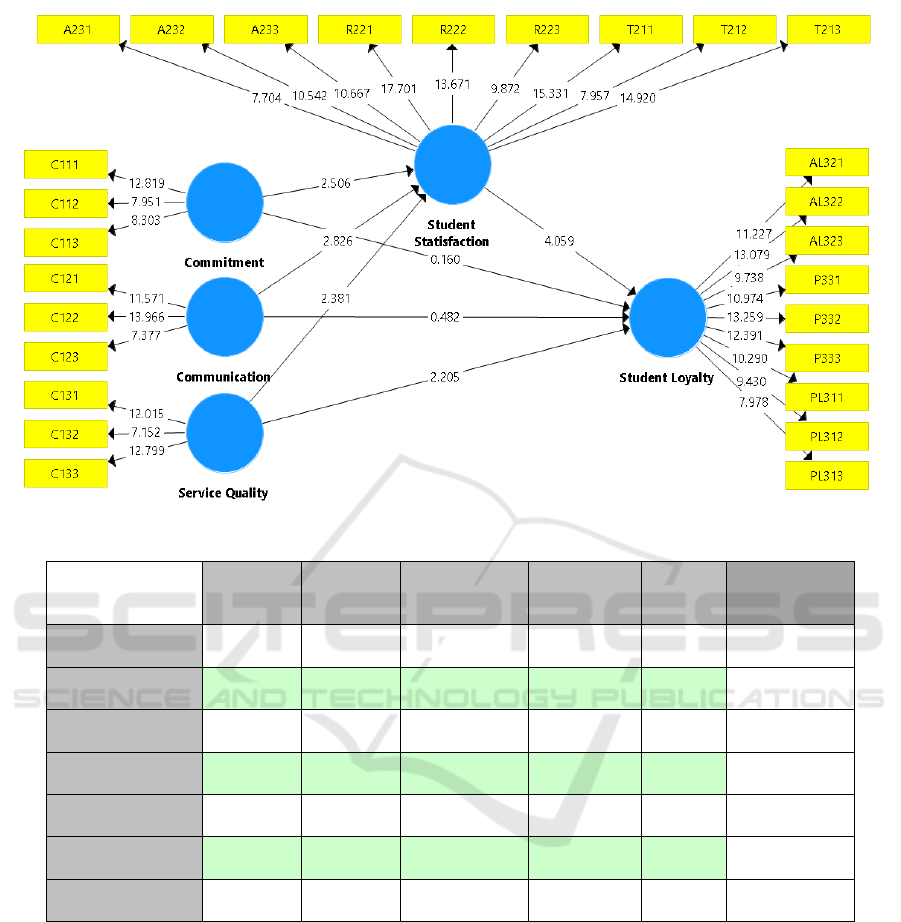
Picture 4.2: Result of PLS Algorithm Bootstrapp Structural Model Output.
Table 4.1 Path Coefficients (t-Value) Direct.
Source : Processed Data 2019
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The structural model of this research can be seen on
Picture 4.1 above.
To measure the significance of prediction model
in structural model testing, it can be seen from the t-
statistic value between independent and dependent
variable in Path Coefficient table 4.1 on PLS Output.
In PLS, the statistically test of each hypothesized
relation is done in simulation. In this case, by using
bootstrap method on the sample. The bootstrap test is
also intended to minimize research data abnormality
problem. The bootstrapping test result of PLS
analysis as follows:
Commitment Influences Loyalty
Hypothesis 1a test result shows that the relation of
commitment variable and loyalty indicates 0.874 path
coefficient value with t value 0.160. This value is
smaller than t table (1.960). The result means that
commitment does not positively and significantly
influence loyalty, which mean it does not correspond
Path
Original
Sample (O)
Sample
Mean (M)
Standard
Deviation
(STDEV)
T Statistics
(|O/STDEV|)
P Values
Remarks
Commitment ->
Student Loyalty
0.019
0.040
0.119
0.160
0.874
Insignificant
Commitment ->
Student Statisfaction
0.247
0.233
0.099
2.506
0.014
Insignificant
Communication ->
Student Loyalty
0.070
0.098
0.145
0.482
0.631
Significant
Communication ->
Student Statisfaction
0.332
0.322
0.118
2.826
0.006
Significant
Service Quality ->
Student Loyalty
0.232
0.229
0.105
2.205
0.031
Significant
Service Quality ->
Student Statisfaction
0.285
0.316
0.120
2.381
0.020
Significant
Student Statisfaction
-> Student Loyalty
0.533
0.508
0.131
4.059
0.000
Significant
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
624

with hypothesis 1a that states commitment influences
loyalty. Therefore, hypothesis 1a is rejected. This
research is not corresponding with the research
conducted by Guenzi and Pelloni (2004), and Supar
and Suasana (2017) which state that customer
relationship management influences loyalty.
Communication Influences Loyalty
Hypothesis 1b test result shows that the relation of
communication variable and loyalty indicates 0.631
path coefficient value with t value 0.482. This value
is smaller than t table (1.960). It means that
communication does not positively and significantly
influences loyalty, which mean it does not correspond
with hypothesis 1b that states communication
influences loyalty. Therefore, hypothesis 1b is
rejected. This research is not corresponding with the
research conducted by Guenzi and Pelloni (2004),
and Supar and Suasana (2017) which state that
customer relationship management influences
loyalty, and also Chan’s (2003) which states that
close familiarization of every guest creates two-way
communication by managing a mutually beneficial
relation between consumer and company.
Service Quality Influences Loyalty
Hypothesis 1c test result shows that the relation of
service quality variable indicates 0.031 path
coefficient variable with t value 2.205. This value is
bigger than t table (1.960). It means that service
quality positively and significantly influences loyalty,
which mean it corresponds with hypothesis 1c.
Therefore, hypothesis 1c is accepted. This research is
in line with the research conducted by Guenzi and
Pelloni (2004), and Supar and Suasana (2017) which
state that customer relationship management
influences loyalty, and also Lupiyoadi’s (2013) which
states that the important factor of customer
relationship management application is service
quality that can be seen from customer satisfaction
achievement; service quality of a company is the
privilege given by company to the customer to fulfill
their needs and wishes.
Commitment Influences Satisfaction
Hypothesis 2a test result shows that the relation of
commitment variable and satisfaction indicates 0.014
path coefficient value with t value 2.506. This value
is bigger than t table (1.960). It means that
commitment positively and significantly influences
satisfaction, which mean it corresponds with
hypothesis 2a that states commitment influences
satisfaction. Therefore, hypothesis 2a is accepted.
This research is in line with the research conducted
by Victor et al., (2015) and Padmavathy, Balaji and
Sivakumar (2012) which show that customer
relationship management significantly influences
consumer satisfaction.
Communication Influences Satisfaction
Hypothesis 2b test result shows that the relation of
communication variable on satisfaction indicates
0.006 path coefficient value with t value 2.826. This
value is bigger than t table (1.960). It means that
communication positively and significantly
influences satisfaction, which mean it corresponds
with hypothesis 2b that states communication
influences satisfaction. Therefore, hypothesis 2b is
accepted. This research is in line with the research
conducted by Victor et al., (2015) and Padmavathy,
Balaji and Sivakumar (2012) which show that
customer relationship management significantly
influences consumer satisfaction.
Service Quality Influences Satisfaction
Hypothesis 2c test result shows that the relation of
service quality variable on satisfaction indicates
0.020 path coefficient value with t value 2.381. This
value is bigger than t table (1.960). It means that
service quality positively and significantly influences
satisfaction, which mean it corresponds with
hypothesis 2c that states service quality influences
satisfaction. Therefore, hypothesis 2c is accepted.
This research is in line with the research conducted
by Victor et al., (2015) and Padmavathy, Balaji and
Sivakumar (2012) which shows that customer
relationship management significantly influences
consumer satisfaction, and Lupiyoadi’s (2013) which
states that the important factor of customer
relationship management application is service
quality that can be seen from customer satisfaction
achievement.
Satisfaction Influences Loyalty
Hypothesis 3 test result shows that the relation of
satisfaction variable on loyalty indicates 0.000 path
coefficient value with t value 4.059. This value is
bigger than t table (1.960). It means that satisfaction
positively and significantly influences loyalty, which
mean it correspond with hypothesis 3 that states
satisfaction influences loyalty. Therefore, hypothesis
3 is accepted. This research is in line with the research
conducted by Ersi and Samuel (2014), and Iriandi
(2005) which states that customer satisfaction
significantly influences customer loyalty.
The Influence of Customer Relationship Management Influencing Factors on Student Loyalty using Student Satisfaction as Mediation
Variable
625
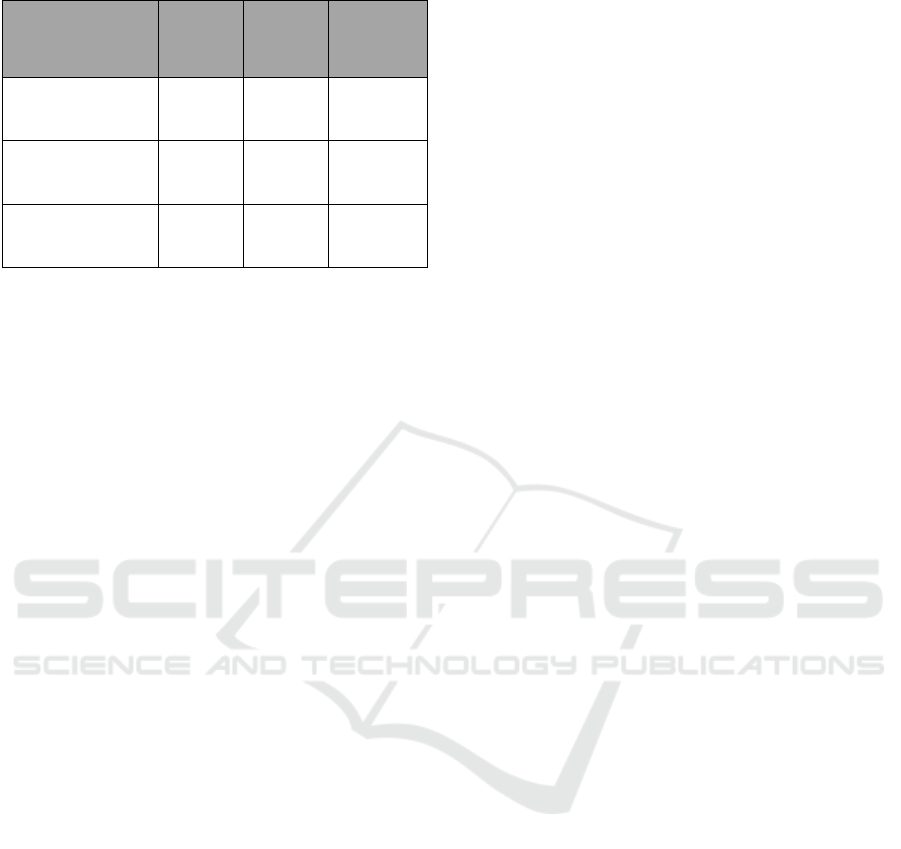
Table 4.2: Sobel Test.
Source: SmartPLS output
Satisfaction Mediates the Influence of Customer
Relationship Management on Loyalty
The purpose of hypothesis 4 testing is to examine the
indirect influence of customer relationship
management variable on loyalty through satisfaction.
The mediation influence test is conducted using Sobel
formula. The test on the mediation influence between
intervening variable and dependent variable is
conducted using calculation of Sobel formula. The
result of mediation test using Sobel test to find out
whether satisfaction truly mediates or not, can be seen
on Table 4.2 above :
Based on Table 4.2 above, it can be concluded that
satisfaction mediates the influence of commitment on
loyalty and it is shown by 0.033 P value and 2.132 t
statistic (these numbers are above the value of T table
1.99), which means significant. Meanwhile, the role
of satisfaction variable as mediation variable can be
seen from the direct influence of commitment on
loyalty which is insignificant. It is proven by the P
value 0.874. This result proves that satisfaction plays
role as full mediation variable because commitment
does not directly influence loyalty, while satisfaction
variable indirectly and significantly mediates the
influence of commitment on loyalty.
In the testing of the role of satisfaction in
mediating the influence of communication on loyalty,
it can be seen that the direct influence of
communication on loyalty is insignificant because the
P value (0.631) is bigger than P table (0.05). It means
that the direct influence is insignificant. Meanwhile,
the indirect influence of communication on loyalty
through satisfaction is significant because P value
(0.020) is smaller than P table (2.319). This research
result shows that satisfaction plays role as full
mediation variable, because in direct influence
communication does not influence loyalty, while
through mediation role the influence is significant.
The role of satisfaction in mediating the influence
of service quality on loyalty is significant, with P
value 0.040 and T table 2.053. In the testing of direct
influence of service quality on loyalty, the influence
is significant. This result means that satisfaction plays
role as partial mediation variable, because in the
direct influence, service quality significantly
influences loyalty, while in indirect influence,
satisfaction significantly mediates the influence of
service quality on loyalty.
From the testing above, it can be concluded that
satisfaction plays role as variable that mediates the
influence of customer relationship management
factors on loyalty. Therefore, hypothesis 4 is
accepted. From the hypothesis test using Sobel
formula, it can be seen that satisfaction plays role as
mediation variable. This research result corresponds
with the research conducted by Caruana (2002),
Iskandar (2015) and Iriandi (2015).
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the previous analysis and discussion,
therefore it can be concluded that: The first
hypothesis test result shows that there is direct and
positive relation between commitment and loyalty,
communication and loyalty, and service quality and
loyalty. The second hypothesis test result shows that
there is direct and positive relation between
commitment’s influence on satisfaction,
communication’s influence on satisfaction, and
service quality’s influence on satisfaction. The third
hypothesis test result shows that there is a direct and
positive relation between satisfaction and loyalty. The
fourth hypothesis test result shows that satisfaction
mediates the influence of customer relationship
management on loyalty.
Suggestion for further research is to conduct pre-
sampling questionnaire test since there are still dual
indicators (one indicator that can measure two
variables) in this research. The source of sample in
this research is taken only from one institution,
therefore for further research, it is suggested to use
more samples by expanding the number of
institutions which used as research object. This
research is conducted on service institution,
specifically university. Further research needs to
conduct such research on different population, for
instance service company, trading and manufacturing
sector or other financial institutions, except banking
institution. The analysis tool used in this research is
SEM-PLS, further research is suggested to use other
analysis tool, such as SEM-AMOS, SPSS and others.
Path
T Statistic
(>1.99)
P Values
(<0.05)
Remarks
Commitment ->
Student Statisfaction
-> Student Loyalty
2.132
0.033
Significant
Communication ->
Student Statisfaction
-> Student Loyalty
2.319
0.020
Significant
Service Quality ->
Student Statisfaction
-> Student Loyalty
2.053
0.040
Significant
ICIB 2019 - The 2nd International Conference on Inclusive Business in the Changing World
626

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank the research institution for the
support that the research activities can be carried out
properly.
REFERENCES
Aydin, Serkan, and Ozer, Gokhan. 2005. The
Analysis of Antecedents of Customer Loyalty in
the Turkish Mobile Telecommunication Market.
European Journal of Marketing, 39(7/8):910-925.
Aydin, Serkan, and Ozer, Gokhan. 2005. National
Customer Satisfaction Indices : An Implementation in
the Turkish Mobile Telephone Market. Marketing
Intellegence & Planning, 23(5):486-504.
Aydin, Serkan, and Ozer, Gokhan. 2005. Customer Loyalty
and the Effect of Switching Costs as a Moderator
Variable : A Case in the Turkish Mobile Phone Market.
Marketing Intellegence & Planning, 23(1):89-103.
Caruana, 2002. Service loyalty: The effects of service
quality and the mediating role of customer satisfaction.
European Journal of Marketing, Vol. 36 Iss: 7/8,
pp.811 – 828.
Chan, Syafruddin.2003. Relationship Marketing : Inovasi
pemasaran yang menbuat pelanggan Bertekuk lutut.
Jakarta : Pt. Granmedia Pustaka Utama.
Ersi, Dzikiryati Yuni dan Semuel, Hatane. 2014. Analysis
CRM, kepuasan pelanggan dan loyalitas produk UKM
berbasis bahan baku terigu di Jawa Timur. Jurnal
Manajemen Pemasaran, 8(1): 1 8. Diakses pada tanggal
9 April 2015 dari http://jurnalpemasaran.
petra.ac.id/index.php/ mar/article/view/19093/18714.
Febrianingtyas, Media., Zainul Arifin., Dahlan Fanani.
2014. Pengaruh Customer Relationship Management
Terhadap Kepuasan Dan Loyalitas (Survey pada
Nasabah Bank Jawa Timur Cabang Gedung Inbis
Malang). Jurnal Administrasi Bisnis (JAB) Vol. 9 No.
2.
Gaffar, V. 2007. CRM dan MPR Hotel (Customer
Relationship Management and Marketing Public
Relation). Alfabeta. Bandung.
Guenzi, Paolo; Pelloni, Ottavia. 2004. The impact of
interpersonal relationships on customer satisfaction and
loyalty to the service provider. Department of
marketing, Scuola di Direzione Aziendale, Universita
Commerciale Luigi Bocconi, Milano, Italy.
Griffin, Jill. 2005. Customer Loyalty: Menumbuhkan dan
Mempertahankan Kesetiaan Pelanggan. Jakarta :
Erlangga.
Imasari, K. dan Nursalin, K. K. 2011. Pengaruh Customer
Relationship Managementterhadap Loyalitas
Pelanggan pada PT BCA Tbk. Jurnal Fakultas
Ekonomi Universitas Kristen Maranatha. Vol 10 (03),
183-192.
Iriandini, A. P. 2015. Pengaruh Customer Relationship
Management terhadap Kepuasan dan Loyalitas
Pelanggan. Jurnal Administrasi Bisnis, Vol 23 (2), 1-8.
Iskandar, Priasmoro 2015. Pengaruh Kualitas Pelayanan
Terhadap Loyalitas Pelanggan Melalui Kepuasan
Sebagai Variabel Intervening pada Pengguna Jasa
Transportasi PT. Tara Megah Muliatama (Taksi Gemah
Ripah) di Kota Bandung. e-Proceeding of
Management. 2 (3), 3953-3960.
Kotler, Philip. 1997. Dasar-Dasar Pemasaran – Principles
of Marketing. Edisi VII. Jakarta.
Kotler , Philip and Kevin Lane Keller. 2009. Management
pemasaran. Edisi 13 jilid 1.Dialihbahasakan oleh Bob
Sabran, MM. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Lovelock, Christopher H. dan Wright, Lauren K. 2007.
Manajemen Pemasaran Jasa. Dialihbahasakan oleh
Agus Widyantoro. Jakarta: PT Indeks.
Lupiyoadi, Rambat. 2013. Manajemen Pemasaran Jasa.
Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Neal, William D. 1998. Satisfaction is Nice, but Value
Drives Loyalty, Journal of Marketing Research.
Olson, Jerry C & Peter, J. Paul. 1999. Consumer Behavior,
Perilakukonsumen dan Strategi Pemasaran. Jilid
kedua, Edisi Keempat. Terjemahan Damos Sihombing
dan Peter Remy Yossi Pasla. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Padmavathy, Balaji, and Sivakumar. 2012. Measuring
Effectiveness Of Customer Relationship management
In Indian Retail Banks. International Journal of Bank
Marketing, 30 (4), 246-266.
Smith, M and Chang. 2010. Improving customer outcomes
through the implementation of customer relationship
management Evidence from Taiwan. Asian Review of
Accounting, 18(3), 260-285.
Supar, Dewa Ayu Wina Ariyunita dan Suasana, I Gusti
Agung Ketut Gede. 2012. Peran Kepuasan Pelanggan
Dalam Memediasi Pengaruh Customer Relationship
Management Terhadap Loyalitas Pelanggan. E-Jurnal
Manajemen Unud, Vol. 6, No. 3, 2017: 1534-1563.
ISSN : 2302-8912.
Victor, Christian, Rotinsulu J.P, Jacky S.B. Sumarauw.
2015. Pengaruh Customer Relationship Management
dan Kepercayaan terhadap Kepuasan serta
Dampaknya terhadap Loyalitas Konsumen. Jurnal
EMBA Universitas Sam Ratulangi Manado.Vol 3 (2),
671-683.
The Influence of Customer Relationship Management Influencing Factors on Student Loyalty using Student Satisfaction as Mediation
Variable
627
