
Urban Social Changes: The Problem of Redefining the Urban
Neighbourhood for Developing Country Context
Agustinus Adib Abadi
1
a
and Adithya Rizky Isnandya
2
1
SAPPD, Institut Teknologi Bandung, Jln Ganesha 10, Bandung 40132, Indonesia
2
Institut Teknologi Bandung, Jln Ganesha 10, Bandung 40132, Indonesia
Keywords: neighbourhood, urban community, Society 5.0, social change, Bandung
Abstract: Neighbourhoods are a universal condition of human settlement that can be found in all periods, in all cultures
and urban contexts. But many researchers find difficulties in defining the term neighbourhood as it is dynamic
and multi-dimension term. To understand neighbourhoods as it is crucial to understand neighbourhood
dynamic characteristics in which social changes with its factors is considered as the most important reason
for the changes. The continuous social changes have taken us into the information society whereby
information has gradually controlled people by providing different interaction patterns. Those situations seem
to have opportunity to meet condition of futuristic a human-cantered society 5.0. Achieving highly integrates
cyberspace and physical space, however, is difficult as the people will challenge issues to present a future
neighbourhood model. By way of socio-spatial based concept, neighbourhood model is supposed to create
communities that can meet all their necessary within walking distances. Even so, the consequences of urban
social changes will modify socio spatial characteristic as the neighbourhood substance. The paper attempts to
identify the impact of urban social mobility in the developing country context to its neighbourhood function.
Analysing the socio-spatial mobility pattern and characteristic is expected to identify the potential model of a
future urban neighbourhood. The case study of Bandung, Indonesia shows that the changes of urban socio
behavioural due to the introduction of IoT culture still have a significant role in maintaining the idea of
traditional neighbourhoods and have some positive aspects of adapting to future better neighbourhood.
1 INTRODUCTION
Neighbourhoods have been the focus of concern of
city planners, architects, and urban designers for a
long time It is an influential idea and has occupied a
well-entrenched place in the minds of theoreticians
and practitioners for many years. However, a close
analysis of its meaning reveals an extremely elusive
concept whose substantive characteristics ebb and
flow over time. The meanings attached to the idea are
continually being disassembled, shuffled, and
reassembled according to the circumstances (Galster,
2019).
And Talen (2019) affirms that urban
neighbourhoods as socio-spatial units in modern
planning has fundamentally changed when
urbanization process diminish the need for a local
urban existence. Urban life became less about a
localized-relationships, but more about movement
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0031-3627
and freedom, and neighbourhood was redefined
accordingly. Freed from the requirement of
proximity, a social connection that required physical
contact, and daily life based on walking, the notion of
a neighbourhood became open to broader
interpretation. And by the time the neighbourhood
slowly and continuously changes unstoppable until
this time.
At this time, we have entered the era of
information. A period in which its society so-called
Society 4.0., is characterized by a fusion of
technologies that distorts the lines between the
physical, digital, and biological spheres (Moraes and
Lepikson, 2017). However, there is still no common
understanding upon the definition, but it is
undoubtedly that nowadays life is such a result of the
horizontal expansion of IT. However, to be defined
entirely the Society requires a combination between
technology and institution that change people
Abadi, A. A. and Isnandya, A. R.
Urban Social Changes: The Problem of Redefining the Urban Neighbourhood for Developing Country Context.
DOI: 10.5220/0013056800002836
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 10th Architecture Research and Design Conference (AR+DC 2019), pages 65-73
ISBN: 978-989-758-767-2; ISSN: 3051-7079
Proceedings Copyright © 2025 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
65

mindset. Thus, it is a serious issue affecting political
and economic stability and even the survival of
humankind. Indeed, the changes in society mindset
will become more noticeable and accelerated in the
future due to the transformations of technology,
economic, and geo-politic.
Taking into account the development process of
human society, it is forecasted that in the future,
people life’s aspects will relate to the IT’s innovation,
and this stage is so-called the Internet of Things (IoT).
In this era, it seems that all of the social systems are
interrelated by smart devices. As a consequence many
human life activities will depend on intelligence
devices. Urban life problems such as city parking,
traffic lights control, and even toll collection services,
have been operated by smart machines. By now,
digital technologies and data science are used to
weave the very fabric of sociality and to shape
societies (Moraes and Lepikson, 2017).
The proposed idea of Society 5.0 - as a rational
continuation of Society 4.0 - by the Japanese
government has indicated the future of smart
technology. Keidanren or Japan Business Federation
Report (2016) defines it as a human-centered society
that balances economic advancement, and resolving
social problems with a system that highly integrates
cyberspace and physical space. In this society, the
potential smart devices are becoming a part of the
mainstream electronics culture, and people are
adopting smart devices into their homes faster than
ever. Of course, not all activities can be substituted by
smart technology, but at least they will be more social
works and activities that will be replaced by them.
Compared to Society 4.0, the 5.0 one stresses its role
to deal with social problem solving as it was not
adequately provided in the Society 4.0, although it
was expected.
The idea of Society 5.0 is perceived will
significantly change the current community life. As it
conceptualized the Society 5.0 will achieve a high
degree of convergence between cyberspace (virtual
space) and physical space (real space). However,
people, things, and systems are all connected in
cyberspace, and optimal results obtained by AI
exceeding the capabilities of humans are fed back to
physical space. This process brings new value to
society in ways not previously possible. Achieving
such a society, however, will not be without its
difficulties of challenging to manage economic and
physical issues to establish a future model community
and its neighbourhood.
According to the proposal, human interest will be
put in the centre of community life and place
supportive AI and robots. This idea exactly is
different from the new life situation where a priority
has been placed generally on social, economic, and
organizational systems. These changes enable
humans to undertake daily heavy work and tasks that
they are not particularly good at, through the creation
of new social value and organizational system. In the
future, society will incorporate advanced
technologies in diverse industries and social activities
and foster innovation to create new value.
The creation of new values will be certainly
followed by socio-behavioral changes. The use of
smart devices will primarily generate alternation of
activities’ patterns, and relationships of persons and
their communities that are different from those in
which they engaged in some time before. Thus, new
value of smart devices will increasingly modify the
way people work, nurture a family, educate their
children, govern them, and seek ultimate meaning in
life. If these processes happen, then in one time, there
will be new human culture, and it means that the
behavioral changes as a function of social mobility
has occurred. However, the cultural transformation
will not be processed globally, instead, it will depend
on many local conditions that play fundamental role
in the development of local socio-cultural values
(Betancur and Smith, 2016).
Logically local socio-cultural value will play
essential role in transforming the character of
neighbourhood. In that context, the neighbourhood is
considered as an alternative concept to deal with
urban housing and settlement problems. The concept
considers urban community as a critical element to
achieve a better quality of living environments as the
idea inwardly focused on neighbourhood cell from
the greater urban context. Thus, in explaining
neighbourhoods, it is very crucial to consider locality
and process as significant aspects.
Due to the globalization process, the idea of
human-centered society has continuously inspired
developing countries people. It, however, has to face
a particularly different situations when it deals with
current urban social changes in the Indonesian
context. And the circumstances will be more
complicated as Indonesia is facing challenges of
managing urban social changes toward a human-
focused society. Nowadays, the influence of smart
technology development has been part of Indonesian
urban community life. People in the city of Bandung,
for instance, are already very familiar with such smart
devices to fulfill their daily life demands and services.
The question then to what extent multidimensional
urban social changes as the consequences of the
society 5.0 idea introduction will modify the current
AR+DC 2019 - Architecture Research and Design Conference
66

physical spaces character and function of an urban
neighbourhood.
This paper is aims to observe the correlation
between social changes and urban neighbourhood
socio-function as to the reference of society 5.0. In
more detail, it expects to explore the possibility of
neighbourhood socio-spatial transformation
concerning such multidimensional urban community
change. In the end this paper will explain problems of
re-defining the neighbourhood concept in the context
of developing countries. For the purpose, it takes a
look at Bandung city with its housing and settlement
development to represent of dynamic problems of an
urban neighbourhood in developing countries,
especially Indonesia
2 THEORY AND RESEARCH
METHODS
2.1 Research Theory
The unique term of neighbourhood, in fact, can be
found in so many places all around the world. In the
Indonesian context, neighbourhood is used to entitle
rukun warga as it is described in Bahasa and Javanese
language (Talen, 2019). Although, as living space, it
can be recognized by all of its inhabitants, but it is
hard to describe the term. However, the importance
of the neighbourhood is undeniable. As it is pointed
out in some places throughout early 20th century, that
neighbourhoods maintained to hold meaning and
relevance despite technological changes.
There are so many descriptions on it that illustrate
neighbourhood as such a multi-dimensions entity.
Gold (2002) summaries that there are four approaches
to study the neighbourhoods through the ecological
neighbourhood, neighbourhood resources, symbolic
and subcultural neighbourhood. In addition,
neighbourhood also has several functions, for
instance, as a source of mutual aid, center for
impersonal influence, some functions arena for
interaction, the base for formal and informal
organizations, reference group, and status arena.
The typical neighbourhood has physical, social, and
political aspects with processes in between their
correlation. In a comprehensive and simple way,
Betancur and Smith (2016) explain neighbourhood as
real space with its cultural meaning that derived from
the imagination which transforms symbols and
images into meaningful place. While from the
sociologist’ viewpoint, Gold (2002) adds very
important insight that neighbourhoods are critical part
for such a comprehensive understanding of urban life.
Moreover, Timms (2010) stresses that the
neighbourhood is a locally based social system that is
part of urban society. At that point he also explains
that neighbourhood represents an area, its inhabitants,
relationship between inhabitants, the friendship
between inhabitants. He also says that the cultural
dimension of the neighbourhood is reflected by the
values of the population concerned. It indicates that
the community plays an important role in the
neighbourhood life. Betancur and Smith (2016) also
list some indicators of neighbourhood related to
community life such as social status, income,
ethnicity, educational background, family size,
housing status, security, and social cohesiveness.
Those indicators then will intrinsically interact with
other features of public services, physical
environment, and economy to fabricate the real
neighbourhood.
The importance of community as primary agent of
social change processes in the neighbourhood has
been concerned some writers. According to Franklin
(2006) the parameters of community have been even
more resistant to exposition than those of homes. The
community has been linked to the more explicitly
physical dimension of neighbourhood, and together
this concept has been underpinned numerous
government-endorsed model for development and
regenerations. It was also underlined that Howard’s
idea of neighbourhood unit has the function to foster
good relations and a sense of community.
In relation to the urban community, it is essential to
consider upon their socio-economic characteristics.
Downs (1981) concludes that the socioeconomic
status of urban neighbourhoods can change over time
due to multiple processes. Some of these processes
operate at the urban level, which causes
neighbourhoods to change relative to one another
within the urban area. These processes can generate
changes in the distribution of socioeconomic
characteristics of the population in an urban area,
which can translate into neighbourhood change.
As neighbourhood encompasses socio-cultural
aspects, therefore, it is subject to change aligned with
such socio-behavioral changes. The influence of
social changes on the dynamic’s neighbourhood life
is pointed out by Talen (2019) by describing that the
history of systematic urban expansion is often a
history of growth by neighbourhood. It is to indicate
that the ideal place for discussing neighbourhood
issues is in the local or urban level.
Social changes itself can be summarized as the
process that refers to the transformation of the social
Urban Social Changes: The Problem of Redefining the Urban Neighbourhood for Developing Country Context
67

order in the community by making adjustments and
variations to social institutions, behavior, and
relations. It involves social evolution where
the society makes amendments to traditional societal
norms leading to the necessary change (Jack and
Akujobi, 2017).
Concerning the global human society development
stage, it is clear that the information era has globally
and inevitably introduced all types of social changes.
The current use of smart gadgets for shopping,
ordering, servicing has started to alter the pattern of
social activities, functional spaces as well as social
values, mainly in the urban area.
Franklin (2006) illustrates and mentions that along
with globalization, society has affected all areas of
life, including economy, social relationship, built
environment, and pattern of living. Reasonably as the
physical dimension of neighbourhood is the product
of cultural processes. This reversible process that
involves structure, agency, and representation layers
can be simple framework to understand how the
cultural and social process will works as an engine for
built environment creation.
In more detail, the structure level includes culture and
society that consist of social-spatial and conceptual
processes which inhere in a particular culture. The
introduction of the information era certainly will alter
the relation and spatial concept of the agency that
consists of constituent elements of institution and
organization; individuals; as well as people. The
neighbourhood then can be perceived as a
communicative action result of agents that transform
social structure and express individual and
organizational value. However, the process is
reversible one, so, it is likely that in a certain time the
neighbourhood’s physical dimension will influence
behavior or social changes etc.
To identify the changes Downs (1981) proposed
common measures. The measure relies on the relative
positions of the neighbourhoods within the city
context, exclude the effect of overall growth or
decline and confound the impacts of urban positional
exchanges with the effect of an increase in inequality.
By using the standard practices, it is impossible to
estimate the effects of structural processes on
neighbourhoods. It is also impossible to
systematically compare processes of neighbourhood
change across cities, while accounting for the ideal
conditions in neighbourhoods.
In the context of Indonesia, the issues of defining
neighbourhood closely relate to the character of urban
housing. Based on the housing process, there are two
main categories: formal and informal development.
The informal settlement, in fact, is the majority in the
Indonesian urban landscape. This informal category
seems to become the clearest example of the process
of physical neighbourhood alternation due to socio-
cultural changes. In contrast, the formal process
creates neighbourhood following the standard
process of new housing development that meets
conditions of SNI 03-1733-2004 on The Guideline for
Urban Housing Development.
According to it, a neighbourhood unit - rukun warga
(RW), is a component of kelurahan or urban village
that inhabited about 2500 peoples and consists of
about 8-10 hamlet or rukun tetangga (RT). The
guideline also put on attention on public facilities and
infrastructure fulfillment that indeed will depend on
the number and characteristic of the inhabitant. In
addition, the housing development must fulfill all
requirements of administrative, technical, and
ecological aspects. The development must provide
public facilities, and infrastructure to support and
enhance economic, social, and cultural social
activities. In addition, the neighbourhood planning
and design have to meet universal design criteria that
allow all people in all limited physical condition to
access all public facilities.
2.2 Method
Researches on neighbourhood include interest in
structural issues (such as income, demography, and
housing) and social issues (such as social networks
and relationships, a sense of collective efficacy, daily
patterns of activity, norms, and behaviors). Data on
structural and social issues can be generated through
observation, surveys, interviews, and other means,
but some data are already available. Research in
neighbourhoods often seeks to explore residents’
perceptions and experiences or effects of social
changes to spatial function of the neighbourhood.
To approach the issues, this research chooses
exploratory to work in the interface between social
and technical aspects. The study deals with
community characteristics and their perception
concerning the physical and spatial condition of their
neighbourhood. To respond to such complicated
issues the research was conducted using mixed-
method that is a combination of quantitative and
qualitative methods (Creswell, 2003). From the
correlation study on community perceptions towards
the introduction of public services and
neighbourhoods socio-spatial function, it is expected
to identify the issue of defining the urban
neighbourhood.
To examine the research subject, two Kelurahan in
Bandung that represents urban neighbourhood’s
AR+DC 2019 - Architecture Research and Design Conference
68

development processes and illustrates the urban
socio-economic differences in Indonesia in relation to
their engagement with technological change on
public services provision is used.
Data was collected from 2018-2019 by distributing
questionnaires and field surveys. The closed-ended
questions using 1-5 likert scale by using purposive
non-random sampling involved 178 respondents for
all two urban villages with a confidence level of 95%.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 The Case Studies
This research is conducted at Kelurahan Sukaluyu
and Kelurahan Antapani Tengah in the city of
Bandung, West Java (Figure 1). The cases were
selected by considering regional characteristics
differences that represent the practices of the
neighbourhood concept in Bandung residential
development.
Figure 1. Location of neighbourhoods’ case studies
Source: Research Data, 2018
Based on its Detail of Spatial Planning), kelurahan
Sukaluyu and Antapani Tengah are designated
similarly as a residential zone. Kelurahan Sukaluyu
consists of 11 RW with a population of 18,913 people
and a total area of 71.58 ha. Meanwhile, Kelurahan
Antapani Tengah slightly has different character in
term of its development process. Indeed, most of the
area in this kelurahan is lodged by formal housing of
Griya Bumi Antapani established by Perumnas. The
total area of the Kelurahan Antapani Tengah is about
93 ha and occupied 7,128 people.
3.2 Findings
The two kelurahans (urban villages) are inhabited
majority by Sundanese (68.5%). Moreover, 69% of
houses are occupied by owners, and the rest is rented.
Meanwhile, most of the residents have educational
background of high school level (31%) with their
employment (34%) is “others.” This other category
represents informal workers (odd jobs), students, as
well as homemakers. The data also reveals that some
57% were residents who had lived in their house for
more than 20 years.
The observation indicates that the physical boundary
of RW is defined by some streets in different
hierarchies (secondary, collector, and local streets) as
well as natural features (river). In addition, each RW
has social facilities such as elementary school or
kindergarten, mosque, community health center, mini
market, open space. However, their conditions and
availabilities differ according to people though they
are in the same kelurahan. In general, those public
facilities have played a significant role in
neighbourhood social interaction (Table 1.).
Playground, kindergarten, and elementary school are
considered as potential meeting places. Indeed, more
than 50% of respondents stated that these facilities
often generate people interaction. Mosque, actually
becomes the most place for interaction. But,
recreational areas and community health centers are
not considered as potential community places.
Table 1. Potential Spaces for Interaction
The data (Table 2.) also shows that the residents of
kelurahan Antapani Tengah tend to go out of their
neighbourhood to fulfill their public services and
facilities demands in compare to the Sukaluyu’s
community who strongly prefers to use public
facilities within their neighbourhood. Some residents
Variables
Kelurahan Sukaluyu
QD D A QA SA
Playground 0% 10% 39% 19% 4%
Shops 0% 10% 44% 36% 10%
Schools (Kg/
El.Sc)
0% 1% 11%
57% 16%
Place of Worship 0% 0% 31% 38% 30%
Recreation place 9% 39% 28% 23% 1%
Polyclinic 28% 62% 9% 1% 0%
Field 0% 8% 42% 39% 7%
Notes: SA (Strongly Agree), QA (Quite Agree), A (Agree), D (
D
Variables
Kelurahan Antapani Tengah
QD D A QA SA
Playground 0% 14% 61% 24% 1%
Shops 0% 3% 36% 49% 12%
Schools (Kg/
El.Sc)
0% 7%
61% 25% 7%
Place of Worship 0% 1% 30% 46% 23%
Recreation place 0% 1% 42% 53% 4%
Polyclinic 0% 22% 48% 27% 3%
Field 0% 0% 46% 44% 10%
Urban Social Changes: The Problem of Redefining the Urban Neighbourhood for Developing Country Context
69
of those two kelurahan are willing to go outside their
neighbourhoods to get better school quality and
health services. Some residents considered that their
schools and health services are not good enough to
accommodate their relatively high demands. For
monthly domestic shopping, many people also prefer
to buy their needs at supermarkets or markets outside
their neighbourhood though it is quite far. In fact, they
consider shopping as recreational activities since they
could go to other places for family entertainment
afterwards.
Table 2. Social Interaction Locations
In addition, the study displays that residents of both
kelurahans have a good quality of social interaction
and sense of community although with different
quality levels. The data indicates that the level of
social interaction and sense of community at
kelurahan Sukaluyu in general is lower than that of
situation at kelurahan Antapani Tengah, and, more
than 50% of respondents agree to upon that matters
(Table 3).
Table 3 also shows positive responses upon smart
technology in providing community services with
some differences levels to it. The residents of
Kelurahan Antapani Tengah consider getting
advantages from the presence of an online
transportation system. Most of the respondents agree
to the significance of smart technology applications
for daily live services. However, despite its high
consumption, the smart system does not entirely
replace the conventional public transportation yet.
Some residents still use traditional urban transport for
a relatively short distance.
Some others are still hesitated to use the facilities or
not using it frequently as they still do not know how
to use the application, especially for the elders. In
addition, the introduction of transportation
application does not seem to affect the security level
of the neighbourhood; however several residents
annoyed by the online drivers who gather in particular
spot in their neighbourhood.s
Table 3. Neighborhood Characteristics and Mobility
Regarding social changes, the data denotes that
kelurahan Sukaluyu and Antapani Tengah have a
relatively similar level of housing occupancy rate.
This situation describes one of importance condition
for communicative action in the neighbourhoods. In
those two kelurahans, the housing vacancy level
generally is considered at a low rate (below 5%) and
in fact, most of them are at very low level (less than
2%) with vacant period is less than three months. That
figure indicates that social mobility in that
neighbourhood is low. However, kelurahan Antapani
Tengah is considered more stable than the other one.
The people in and out at kelurahan Sukalyu are
relatively high as it is about 9-12% of their
population, while in kelurahan Antapani Tengah is
only about 2-5% (Table 4).
Table 4. Social changes
Meanwhile, the correlation analysis between related
factors to the use of smart technology in the society
to access public services – especially online
transportation - indicates various results. In general,
it shows the significant correlation of socio-economic
factors and the utilization of smart technology. The
housing types indeed play an important role on the
perception of kelurahan Sukaluyu’s community
towards smart technology applications for public
services but not for another one. In contrast, age and
housing tenure have a central position for the
perception of kelurahan Antapani Tengah’s
community. However, all correlations in two
kelurahan show no high rate correlations (close to
Variables
Kelurahan Sukaluyu Kelurahan Antapani Tengah
Inside The
N
eighborhoo
d
Outside The
N
eighborhoo
d
Inside The
N
eighborhood
Outside The
N
eighborhoo
d
Children play 88% 7% 45% 55%
Shop for daily needs 87% 13% 52% 48%
Children's school 38% 57% 49% 51%
Worship 99% 1% 45% 55%
Interaction with residents 84% 16% 42% 58%
Health Treatment 33% 67% 45% 55%
Exercise 71% 29% 45% 55%
Variables
Kelurahan Sukaluyu Kelurahan Antapani Tengah
SA QA A D QD SA QA A D QD
Ease of meeting other
people
17% 25%
32% 22% 4% 12% 35% 45% 7% 1%
Having a new friend 24% 29% 42% 4% - 10% 36% 51% 3% -
Get to know many people
through children
10% 23%
26% 27%
14
%
2% 16% 44% 32% 6%
Friends in neighborhood
are part of daily activities
17%
28% 28% 19% 8% 7% 29% 52% 12% -
Meet friends usually in
public spaces
10% 31%
39% 16% 4% 1% 18% 62% 19% -
Participate in social
activities
18% 22%
37% 21% 2% 11% 24% 62% 3% -
OL transportation apps in
fulfilling demand
27% 28%
31% 6% 8% 22% 38% 40% - -
OL transportation reduces
dependency on public one
15% 12%
50% 18% 5% 6% 20% 27% 37% 10%
OL transportation affect
security negatively
1% 0
5% 15%
78
%
0 0
16% 59% 25%
OL Transportation apps
fulfilling daily needs
54% 22% 22% 1% 1% 16% 36% 43% 5% -
Notes: SA (Strongly Agree), QA (Quite Agree), A (Agree), D (Disagree), QD (Quite Disagree)
Variables
Kelurahan Sukaluyu Kelurahan Antapani Tengah
No. of resident
perceive vacant
houses’ rate
No. of resident
perceive rate new
residents in/out
No. of resident
perceive vacant
houses’ rate
No. of resident
perceive rate new
residents in /out
Ver
y
low
(
< 2%
)
55% 21% 43% 43%
Low
(
3-5%
)
22% 24% 39% 39%
Hi
g
h
(
9-12%
)
17% 41% 3% 3%
AR+DC 2019 - Architecture Research and Design Conference
70

1.00 or -1.00) as they are on average about 0.2 to 0.4
with positive or negative correlation.
The correlation model also has several significant
factors that indicate the differences between those
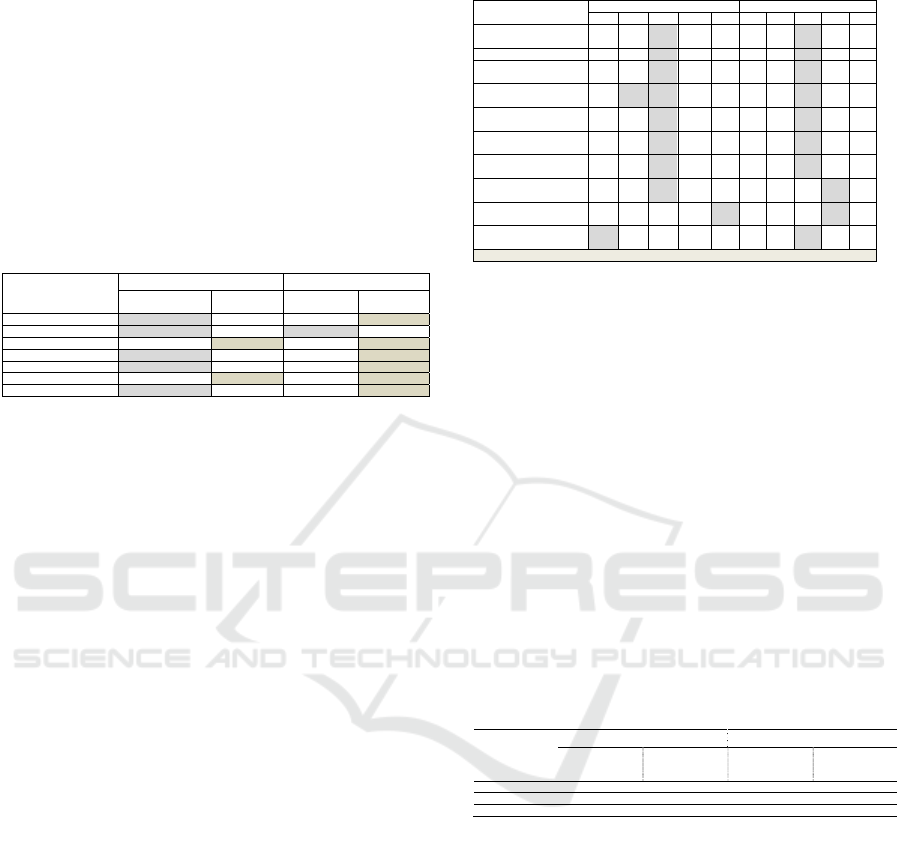
two kelurahan’s characteristics (Table 5). For
kelurahan Sukaluyu some parameters indicate its
significance, but, its correlations between factors are
at low rate (around 0.32 to -0.33), mainly the
perception on the role of online transportation in
altering urban transport services. Similarly, for
kelurahan Antapani Tengah correlation is at level
around 0.252 to 0.283 and -0.246 to -0.360 with 2-
tailed sig. <0.01.
Table 5. Society Perception Factors Correlation
3.3 Discussion
The objective of this study is to understand the
problem of redefining neighbourhood concept in
developing countries in the perspective of Society
5.0. As the Society 5.0 is futuristic concept therefore
it is required to predict the possibility of
neighbourhood spatial function alternation due to the
socio-cultural changes as the introduction of smart
technology in the primary concern of the Society. The
picture is clear that there will be new values in the
future as the result of the Internet of Thing (IoT). This
socio-cultural value is established by the uses of the
internet to connect all people, to free people from
burdensome works, to integrate people, things, and
systems in cyberspace. The question then to what
extent these value changes will deliver new
distinctive behavior patterns that makes spatial and
functional impacts to their neighbourhood?
According to Franklin (2006) such a built
environment form is the result of long and
complicated transformation of social, spatial, and
conceptual processes to produce communicative
actions. The recent socio-cultural characteristics of
the two kelurahan communities show the social
dynamic patterns of modification towards their
acceptance on the quality of public services that lead
to socio-behavioral changes.
As the principal neighbourhood’s component,
the communities of kelurahan Sukaluyu and
Antapani Tengah tend to be in the dynamics change
process. The high rate of movement residents at these
two kelurahan shows their capacity to adapt to
changes. However, their shallow housing vacancy
rate (less than 2%) displays that they are a very
established neighbourhood. This stability seems in
coincidence with their level of social interaction and
sense of community. This is critical cultural factors to
support social system and social processes as a basis
for organizing principles of society that affect both
social systems and in turn, spatial arrangements. This
condition is in accordance to social relationship level
in both kelurahans that have created such strong
social bonding and sense of community.
Although most of them consider certain facilities as
potential interaction spaces, but, the community at
kelurahan Antapani Tengah seems more adaptive to
responds to any public facilities insufficiency. Indeed
minimum public facilities have been stated at the
Urban Housing Development Guideline, but, it looks
that the existing regulation unable to deal with such
dynamic community changes. Hence it has raised the
gradual adaptation of ways of life and associated
artifacts in which people choose to find public
facilities outside their neighbourhood. This trend
illustrates the adaptive character of dynamic, flexible
as well as better-off people at kelurahan Antapani
Tengah. However all communities in those two
kelurahans still considered the importance of
strengthening the local community. This is a cultural
viewpoint that meets to traditional or local value in
Indonesia.
Upon the introduction of smart technology,
people of those two kelurahan respond in different
ways. It seems that socioeconomic plays a potential
role in influencing the neighbourhood change. For
Antapani residents, there is interesting hint that the
usage of the application to fulfill transportation
services needs shows a positive correlation with
education level. It is indicated that in the future, along
with the increase of human development index as
well as social prosperity, the prospect of the uses of
smart technology in society life is very encouraging.
However, there are also negative correlations shown
between the dependence on public transportation with
age and duration of living. This socio-cultural
problem indeed will resolve naturally by the changing
generation in the future.
While for Sukaluyu residents, some socio-
economic variables such as housing ownership and
education level have a significant correlation with
perception on the reduction of public transportation
Variables
Kelurahan Sukaluyu Kelurahan Antapani Tengah
1 2 4 5 7 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 11
9
OL fulfill
demand
0.18 0.16 0.20
0.23 -0.03 0.28
**
0.03
0.27
**
-0.07
0.0
4
0.0
2
1.00
10
Ol reduces depend
on public
0.28 0.25 0.23 0.32 -0.16 0.28
**
0.21
*
0.15 -0.25
*
-
0.36
**
0.2
3
*
0.02
11
OL put negative
security
-0.04 -0.04 0.11 0.18 0.02 0.18
0.25
*
-
0.0
1
0.04
-
0.1
6
0.1
1
-0.08 1.00
12
Ol fulfill daily
needs
0.01 0.07 0.10 0.03
-0.33 0.04 0.10
0.1
3
-0.23
*
-
0.0
8
0.0
6
0.48
**
-0.23
*
Notes : (1) Housing type/size (2) House land area (4) Ethnicity (5) Education level (6) Age (7) Education level (8)
House tenure status
Urban Social Changes: The Problem of Redefining the Urban Neighbourhood for Developing Country Context
71

dependency. The analysis shows a positive
correlation between those variables, on moderate
coefficient correlation, 0.28 and 0.32. It means the
more affluent and higher the education level of a
household and its members, the slighter the
dependency on online transportation, and vice versa.
It is indeed such a logical situation in which the
wealthy people really depend on public transport
services in the socio- cultural context of Indonesia.
Moreover, nowadays, the use of smart devices
and technology has altered the pattern of urban social
life. It has changed the way of communication, fulfill
demand, as well as organize and manage daily jobs
and duties. It can be seen in the neighbourhood
surrounding how fast the phone box disappears as
required public facilities from community life. To
date, it is a common urban phenomenon, that all
family members gather around the dining table but
they busy with each gadget and have no
communication between other family members.
This personal lifestyle is also revealed in their
activities as a part of a community. Although the
analysis shows various correlation rates, but, most
people use online transportation services to help them
to fulfill their daily life needs and services. The
application of Gojek and Grab, for instance, is not
only to provide transportation services but also
already various services such as delivery, shop, food,
health, cleaning, and many others that make easier
and more efficient life in urban area. This
technological acceptance, indeed, has gradually
changed social value and culture. These services
apparently will reduce the uses of a private car that
has been many urban people’s wishes. In simple case,
if this trend going well then there will be socio-
functional decrease in urban neighbourhood as the
decline of private car ownership.
4 CONCLUSION
The established neighbourhood concept indeed is
relevant in the changing socio-cultural context of
Indonesia, especially in Bandung city. The study
shows the existence of neighbourhoods’ culture in
Kelurahan Antapani Tengah and Sukaluyu. The study
also reveals the correlation between heterogeneous
with good inhabitants’ social cohesion in the mid of
dramatic cultural changes as the consequence of
technological expansion.
The introduction of smart technology as the society
5.0’s foundation indeed has altered the socio-cultural
values of the community in developing countries such
as Indonesia. In a certain extent, the introduction of
new technological values has changed the urban
societal behavior pattern mainly in fulfilling daily
services. The decrease of mobility will alter the
spatial function of the human environment. The
positive responses toward the use of smart
technologies indicate the openness of urban
community to the new social value, and predictably it
would put an impact on the neighbourhood spatial
function. It seems that spatial function modification
will follow the values alternation in terms of sizes,
types, and number. However, transformation
processes will depend on inhabitants’ socioeconomic
conditions.
Regarding the future shape of neighbourhood, urban
behavioral changes are significant indicators in
relation to popularity of smart technology use in
providing community services in last seven years.
Many people in Bandung now can obtain and fulfill
their needs such as foods, transportation (car or
motor), ticket, shopping, bill as well as package and
many more only by using application on the phone
cell. This trend has gradually change community
behavior in their daily activities. However, in
speculating about the future, the same contextual
approach can be adopted as has been done for the
contemporary situation. Undoubtedly the parameters
of space provide an important context, but it is
perhaps in the trajectory of the social system and
social processes. Some new neighbourhood design
concepts may emerge primarily based on cultural and
social change, but more direct processes have been
gradually done in the informal urban neighbourhood
influenced by socio-spatial changes in relation to the
introduction of IoT culture in the Indonesian urban
society.
Indeed, not all people use smart technology, for some
reasons, it means that the institution of social values
will proceed slowly and diverges. However, by
considering their socio-cultural condition, it seems
that new social value will play an influential role in
transforming the neighbourhood spatial function. Its
role will depend on local Indonesian culture to control
and direct the social value developments. Therefore,
more attention must be paid on neighbourhood
planning, especially in the very urban area as it will
play a critical role on maintaining the integration of
its community
AR+DC 2019 - Architecture Research and Design Conference
72

REFERENCES
Betancur, John J and Janet L. Smith. 2016.Claiming
neighbourhood. New Ways of Understanding Urban
Change. University of Illinois Press. Urbana, Chicago,
and Springfiled.
Creswell, John W. 2014. Research Design. Qualitative,
Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. Sage.
Los Angeles.
Downs, Anthony. 1981. Neighborhod and Urban
Development. Brooking Institution. Washington DC.
Franklin, Bridget. 2006. Housing Transformation. Shaping
the Space of 21
st
century living. Routledge. New York
Galster, George C. 2019. Making Our neighbourhood,
making Our Selves. University of Chicago Press.
Chicago and London.
Gold, Harry. 2002. Urban Life and Society. Prentice Hall.
New Jersey.
Moraes, E. Cardoso and Lepikson, H.A. 2017. Industry 4.0
and its impacts on society. Proceedings of the
International Conference on Industrial Engineering
and Operations Management, p 729-735. Bogota,
Colombia, October 25-26, 2017
Talen, Emily. 2019. neighbourhood. Oxford University
Press. New York.
Timms, DWG. 2010. The Urban Mosaic. Towards a Theory
of Residential Differentiation. Cambridge University
Press. Cambridge.
Jack, Jackson TCB and Theofilus C Akujobi. 2017. Social
Change and Social Problems. In Abasiekong, E.M,
Sibiri, E.A, Ekpenyong, N.S (eds.) Major Themes in
Sociology: An Introductory Text. pp 491-526. Benin
City, Mase Perfect Prints.
------------. 2004.SNI 03-1733-2004 Tata cara perencanaan
perumahan di perkotaan. Bandan Standard nasional.
Urban Social Changes: The Problem of Redefining the Urban Neighbourhood for Developing Country Context
73
