
The Interdependence of Stock Market among Malaysia
and Selected Middle East Countries: Financial
Innovation of Islamic Stock Index
Erlie Sharina Kamisan, Rafidah Othman, Beni Widarman Yus Kelana,
Theresa C. F. Ho, and Mohd Khairuddin Ramliy
Azman Hashim International Business School, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Malaysia
Abstract. This article is publish to review the interdependence of stock market
among Malaysia and selected Middle East countries (Jordan, United Arab
Emirates, Bahrain and Qatar). Throughout the year, there are many researches
and studies conducted on stock market. Majority of the studies come out with the
conclusion that most of the stock market around the world has linkages and
interdependence. However, there still lack of study in the context of Islamic stock
market interdependencies that explore the linkage between volatility of returns in
selective Middle East market. Hence, in this article, the study is to focus on the
level of international equity market interdependence between Malaysia and
selected Middle East country. The study will conduct based on the daily data of
the stock indices from January 2008 until December 2018. The results from the
study will be useful for the policy maker in regulating the market especially for
financial innovative, and to investors and speculators to beat the both markets.
Keywords: Islamic Stock Market∙Middle East Country∙Financial Stock
Innovative
1 Introduction
Malaysia is among of the top countries that fastening their economic growth through
their successful open market activities in the South East Asia. A good diplomatic
strategy and relationship with many countries around the world makes Malaysia as one
of the best country to have a good platform for an investment. There are many industries
that well develop in Malaysia, as a part of that, Malaysia stock market is one of the
industry that playing an important role in Malaysia’s financial sector which
subsequently helping in boosting the sustainability of the economy. Unfortunately, a
tough condition in 1997 Asian Financial crisis had brought Malaysia facing to the worst
recession from devalued of Ringgit currency. According to (Azman-Saini, W.N.W.
and Habibullah, M.S. and Law, Siong Hook and Dayang-Afizzah, 2007), during this
tough condition, the fall of composite index of Kuala Lumpur Stock Exchange (KLSE)
gives such impactful to financial sectors and this situation as a consequences leads to
stock return decrease. Going through the hard situation in 1997, it shows that stock
market play as an important role in boosting Malaysia’s financial sector. According to
(Nandha & Hammoudeh, 2007) , 1997 crisis had giving a worst impact to Asia Pacific
region countries and after the decades a crisis in 2008 happen again. Thus, this will be
898
Kamisan, E., Othman, R., Kelana, B., Ho, T. and Ramliy, M.
The Interdependence of Stock Market among Malaysia and Selected Middle East Countries: Financial Innovation of Islamic Stock Index.
DOI: 10.5220/0010609000002900
In Proceedings of the 20th Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics, Management and Accounting (MIICEMA 2019), pages 898-903
ISBN: 978-989-758-582-1; ISSN: 2655-9064
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
an attractive point to propose this study in order to know the situation of capital market
especially Islamic capital market from 2008 to 2018. Throughout the year, there are
many researches and studies have been conducted regarding the stock market. Majority
of the studies come out with the conclusion that most of the stock market around the
world has linkages and interdependence. However, there still less study in the context
of Islamic stock market interdependencies that explore the linkage between volatility
of returns in selective Middle East market (Bouri & Yahchouchi, 2014) Hence, in this
paper, the study is to focus on the level of international equity market interdependence
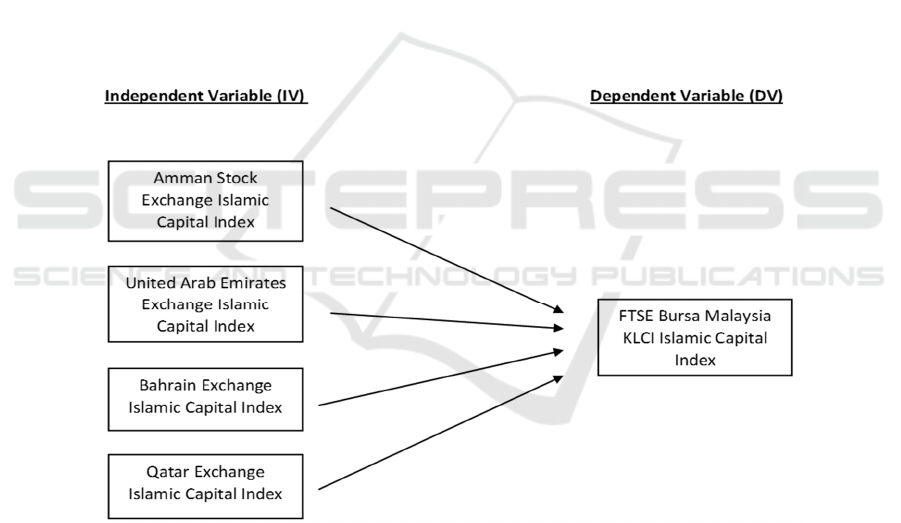
among Malaysia and selected Middle East country (Jordan, United Arab Emirates,
Bahrain and Qatar) for Islamic capital index in a decade emphasizing during recent
economic financial crisis. The interesting in study it will investigates the existence of
equity Islamic market relationship among the Middle East country, i.e. Jordan, United
Arab Emirates, Bahrain and Qatar to the Malaysia stock market in term of Islamic stock
index during a past 10 decades from 1st January 2008 until 31st December 2018. Since
these five (5) countries are Islamic countries, we expected that there will be an
association and relationship between the stock market among this countries in term of
Islamic capital index as shown in the proposed research framework in Figure 1. The
findings is predicted to give a good platform for investors in order to expand their
investment especially in the Islamic stock market over the Middle East countries and
Malaysia.
Fig.1. Proposed Research Framework.
2 Institutional Background of the Islamic Stock Indices in Middle
East and South East
MENA stock market is having a small equity market and not well developed, thus need
The Interdependence of Stock Market among Malaysia and Selected Middle East Countries: Financial Innovation of Islamic Stock Index
899

their countries itself to improve their development on their stock market. A research
conducted on this market, however, the result showed this market is less liquidity than
other world financial market. In addition, the short selling was still remains illegal
(Bouri & Yahchouchi, 2014). Moreover, this market also show weak form efficiency
due to poor quality information and low competition (Lagoarde-Segot & Lucey, 2008).
Besides, MENA countries have different function than those developed counterparts.
Their market consequently have relatively common economic, institutional, regulatory,
political and cultural links which at some extent, the industrial organization found in
MENA markets is also quite different from that in developed economies (Assaf, 2009)
. Furthermore, the MENA capital markets also are less developed than the Asian or
Latin American emerging markets (Bouri & Yahchouchi, 2014) but MENA market
offer portfolio and fund managers outstanding diversification benefits (Neaime, 2012).
According to Floros, (2011), little investors know about the existing of the dynamic
relationships between the prices of Middle East stock markets although empirical
research generally suggests that national mature stock and futures markets move
together. Besides, previous research that focusing on the integration of stock markets
in MENA nations with those in the rest of the world is limited. Based on (Neaime,
2002) that using the Engle-Granger (1987) co-integration approach, test for the
integration of MENA markets with world stock markets over the period 1990 to 2000
shows there is a weak integration among the MENA markets (Morocco, Egypt, Jordan
and Turkey), however, among developed market the result reveals there is strong
integration between MENA markets and developed markets (U.S., U.K. and
France).The studies of (Paskelian, Nguyen, & Jones, 2013) also find similar results as
(Neaime, 2002). Besides, research that focuses on the integration of stock markets
within the MENA region with each other and the rest of the world is limited.
3 Gap and Issue of Islamic Stock Index
Jamaani & Roca, (2015) stated that developing market experience well growth over the
last few decades. Nikkinen, Omran, Sahlström, & Äijö, (2008) reports, incident of
September 11 that attacks New York, USA have largest impact to the world stock
market. However, Middle East and North Africa financial markets had only a minor
effect towards the incident. In the Middle East countries, the market itself can be
characterised as a market with low liquidity, small market and less information for the
investors (Haque, Hassan, Maroney, & Sackley, 2004). Based on the research and study
by Elango and Hussein (2008), there is less study conducted in the Middle East towards
the market efficiency, even it has but only produce the fragmented results. Even though
market at Middle East still not well develop compared to the other markets and regions,
but they still offer an outstanding diversification benefits to the investors (Henry &
Springborg, 2010). In this study, the main research gap is reflected with empirical
studies in terms of interdependence of Islamic stock indices around the world. Previous
researchers found there is still less study in the context of Islamic stock market
interdependencies that explore the relationship between volatility of returns in selective
Middle East market and south East Asia countries. In addition, the data used in previous
study are limited to the conventional stock markets located in US and Europe, even it
has study conducting on Islamic stock index but the empirical is more concentrating on
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
900

the post-economic crisis period analysis.Therefore, in this study we want to explore
more the association and interdependence of selected Middle East Islamic stock index
towards Kuala Lumpur FTSE Bursa Islamic stock indices focusing on global financial
crisis period. For this reason, this study examine the relationship of the Middle East
stock markets and whether these markets are weak-form efficient and have bad effect
towards Malaysian stock market especially in Islamic stock indices during 1
st
January
2008 until 31
st
December 2018. The question is about whether is there any significant
relationship between selected Middle East countries Islamic stock market to the
Malaysia Islamic stock market.
4 Conclusion
The main objective of this study is to investigate the level of international equity market
interdependence among Malaysia and selected Middle East country, i.e. Jordan, United
Arab Emirates, Bahrain and Qatar in term of Islamic stock index. Based on the previous
study by Miniaoui, Sayani, & Chaibi, (2015), which indicates the performance on the
Islamic and conventional indices of the GCC countries. The findings shows the GCC
Islamic index exhibits similar attributes of the conventional indices in all the periods of
analysis in 2008. In fact, the results show that the GCC Islamic index has similar risk
profile as its conventional counterparts. This support the findings of association
between Islamic and conventional stock index in selected Middle East stock market and
Malaysia stock market which shows the weak correlation. Research by Girard &
Hassan, (2009) found that Islamic and conventional groups of FTSE are integrated.
Research that used a multivariate co-integration analysis also emphasized that both
types of indices have similar return to risk and diversification benefits. Moreover,
Islamic indices have the same level of efficiency as conventional ones. In terms of co-
integration analysis, Islamic indices of Dow Jones and S&P have no co-integrating
relations with their respective benchmarks, which suggests the existence of long-run
diversification opportunities (El Khamlichi, Sarkar, Arouri, & Teulon, 2014). Based on
the previous study it is proven that Islamic and conventional stock indices are
interdependence and have linkage to each other. Referring to the efficient market
hypothesis (EMH) theory, information transmission in the international market
transactions can give the impact on the stock market performance especially for those
countries that is interdependent. The investor and speculator should aware of this
situation as anything happen to Qatar conventional stock exchange will affect the other
countries stock exchange. Besides, the new information that comes from Qatar will
have a linkage towards Malaysia, Jordan and UAE stock exchange. In addition,
information transmission that happen between those countries will help the speculator
to predict the market movement of the equity market to gain some profit.
5 Research Limitation and Recommendation
In order to keep the study comprehensive some limitations had to be made. First of all,
the data used in this study are limited only to the stock market of Malaysia and selected
Middle East country, i.e. Jordan, United Arab Emirates, Bahrain and Qatar in term of
The Interdependence of Stock Market among Malaysia and Selected Middle East Countries: Financial Innovation of Islamic Stock Index
901

Islamic and conventional stock index. Even though in the Middle East have many of
Islamic countries but all of them is not equally developed. Due to this problem, the
research only limit into a certain number of countries. There are also insufficient
references can be used for this study since most of the related research was been done
on Europe and US market. Since this dissertation is using stock indexes as tool to
investigate the relationship between stock market indices, a comprehensive index has
to be available. By browsing the Data stream, the study tried to find the stock markets
for each country. From this research, it is found that Islamic stock indices are quite hard
to find due to the stock market are still at the early stage. Based on the chosen markets
and the timeframe, Islamic stock index for those country in Middle East are very
limited. As consequences, the best timeframe for the data available is only for 10 years.
This limitation may be criticized, however this research have found previous research
by Miniaoui et al., (2015), that also studied the linkage between the selected countries
which we consider to strengthen our argument.
Acknowledgements: This article was supported by Lecturer of Faculty Business
Management, UTM and main author express her thanks for all lecturers, for all
continuous encouragement, invaluable suggestions, patient guidance and supporting
with kindness, sympathy and academic enthusiasm. All forceful comments and
meticulous directions were a constant source of inspiration to this research that
immensely improved the quality of this project paper.
References
Assaf, A. (2009). Extreme observations and risk assessment in the equity markets of MENA
region: Tail measures and Value-at-Risk. International Review of Financial Analysis.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2009.03.007
Azman-Saini, W.N.W. and Habibullah, M.S. and Law, Siong Hook and Dayang-Afizzah, A.
(2007). Stock prices, exchange rates and causality in Malaysia: a note. The ICFAI Journal of
Financial Economics.
Bouri, E. I., & Yahchouchi, G. (2014). Do return and volatility traverse the Middle Eastern and
North African (MENA) stock markets borders? Journal of Economic Studies.
https://doi.org/10.1108/JES-02-2012-0020
El Khamlichi, A., Sarkar, K., Arouri, M., & Teulon, F. (2014). Are Islamic equity indices more
efficient than their conventional counterparts? Evidence from major global index families.
Journal of Applied Business Research. https://doi.org/10.19030/jabr.v30i4.8660
Floros, C. (2011). Dynamic relationships between Middle East stock markets. International
Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management. https://doi.org/10.1108
/17538391111166467
Girard, E. C., & Hassan, M. K. (2009). Is There a Cost to Faith-Based Investing: Evidence from
FTSE Islamic Indices . The Journal of Investing. https://doi.org/10.3905/joi.2008. 17.4.112
Haque, M., Hassan, M. K., Maroney, N., & Sackley, W. H. (2004). An empirical examination of
stability, predictability and volatility of Middle Eastern and African emerging stock markets.
Review of Middle East Economics and Finance. https://doi.org/10.1080/
14753680410001685669
Henry, C. M., & Springborg, R. (2010). Globalization and the politics of development in the
Middle East, second edition. Globalization and the Politics of Development in the Middle
East, Second Edition. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511778162
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
902

Jamaani, F., & Roca, E. (2015). Are the regional Gulf stock markets weak-form efficient as single
stock markets and as a regional stock market? Research in International Business and
Finance. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ribaf.2014.09.001
Lagoarde-Segot, T., & Lucey, B. M. (2008). Efficiency in emerging markets-Evidence from the
MENA region. Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intfin.2006.06.003
Miniaoui, H., Sayani, H., & Chaibi, A. (2015). The impact of financial crisis on Islamic and
conventional indices of the GCC countries. Journal of Applied Business Research.
Nandha, M., & Hammoudeh, S. (2007). Systematic risk, and oil price and exchange rate
sensitivities in Asia-Pacific stock markets. Research in International Business and Finance.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ribaf.2006.09.001
Neaime, S. (2002). Liberalization and Financial Integration of MENA Stock Markets * Simon
Neaime Department of Economics / Institute of Financial Economics American University
of Beirut I . Introduction. ERF’s 9th Annual Conference on Finance and Banking.
Neaime, S. (2012). The global financial crisis, financial linkages and correlations in returns and
volatilities in emerging MENA stock markets. Emerging Markets Review.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ememar.2012.01.006
Nikkinen, J., Omran, M. M., Sahlström, P., & Äijö, J. (2008). Stock returns and volatility
following the September 11 attacks: Evidence from 53 equity markets. International Review
of Financial Analysis. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.irfa.2006.12.002
Paskelian, O. G., Nguyen, C. V., & Jones, K. (2013). Did financial market integration really
happen in MENA region? - An analysis. Journal of Economic Cooperation and Development.
The Interdependence of Stock Market among Malaysia and Selected Middle East Countries: Financial Innovation of Islamic Stock Index
903
