
The Influence of Content Marketing and CRM toward
Brand Image and Brand Loyalty
Barkah Barkah
1
, Wenny Pebrianti
1
and Runi Virzia Mutari
2
1
Faculty of Economic and Business, Universitas Tanjungpura, Indonesia
2
PT. Astra International Tbk, Kanwil Kalimantan Barat, Indonesia
runivirzia@gmail.com
Abstract. Content marketing appears to be one of many social media marketing
strategies to engage customers. On the other hand, with a lot of options customers
are able to pick, it is quite a challenge for a brand to keep their customers to be
loyal. Hence, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) becomes one of the
powerful tools to maintain a beneficial and long lasting relationship with
customers. The sample of this study consists of 100 respondents . The data were
processed using SPSS 17 and analyzed with path analysis method. It is found that
content marketing doesn’t have a significant influence towards brand loyalty, but
it does significantly influence the brand image. CRM has a significant influence
towards both brand image and brand loyalty, and on the other hand brand image
does have a significant influence on brand loyalty.
Keywords: Brand Image ꞏ Brand Loyalty ꞏ Content Marketing ꞏ CRM
1 Introduction
The existence of internet is also generating the development of e-commerce industry.
In Indonesia, based on the Economic Census 2016 conducted by Central Bureau od
Statistic, within the year of 2006 to 2016 there are 26,2 million e-commerce operated
in the country. As customers become indecisive in terms of choosing which brand they
want to buy products from due to technological advances they have nowadays, brand
loyalty is what a company that runs its business in such competitive market sought to
achieve. However, brand loyalty has a different definition of consumer loyalty, making
these two variables cannot be mixed together. According to Saeed (2013), brand loyalty
is a dedication of the customer to the brand to purchase it over and over again despite
the influence of different marketing efforts of the competitors or other brands that may
cause switching behavior.
There are a lot of ways for a company to build its brand image in order to gain
brand loyalty. Advertisement and sales promotion might be the top two of it. As we
know, social media usage is very common in today’s world as a part of technological
development invented from time to time. According to Telegraph’s article in 2015, the
average person has at least five social media accounts and spends at least 1 hour and 40
minutes browsing them every day. Indonesia is a country with the total population is
around 255 million, and the active internet users takes up to 72.7 million people. Based
on this fact, social media is definitely holding a role as the best tools for marketers to
Barkah, B., Pebrianti, W. and Mutari, R.
The Influence of Content Marketing and CRM toward Brand Image and Brand Loyalty.
DOI: 10.5220/0010528300002900
In Proceedings of the 20th Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics, Management and Accounting (MIICEMA 2019), pages 711-724
ISBN: 978-989-758-582-1; ISSN: 2655-9064
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
711

do the sales promotion. Content marketing heavily involves social media (Murdock,
2014).
Content marketing is the process of developing and sharing relevant, valuable, and
engaging content to target audience with the goal of acquiring new customers or
increasing business from existing customers (Maksymiw, 2014). Creating an attractive
content can bond relationship between brand and customer (Bunpis & Haron, 2013)
because content marketing can drive awareness and lead engagement with opportunity
to compensate traditional strategy (Bowden, 2009). In this information-driven era,
customers request for factual and useful information to aid them in decision making
process, because customers today know they have rights to choose what information to
receive, in what kind of format that information is in and whether to believe the content
(Hipwell & Reeves, 2013).
Delivering valuable content might help a company to attract new customers, but
keeping the old ones is just as important in order to gain the brand loyalty. Customer
relationship management (CRM) is a comprehensive approach for creating,
maintaining and expanding customer relationships (Anderson & Kerr, 2002). Content
marketing implications might lure customers to be more engaged with a brand, but
CRM is the tool to keeping them and growing a depth relationship with the brand itself.
CRM can be the single strongest weapon a manager has to ensure the customers become
and remain loyal (Anderson & Kerr, 2002).
Content marketing is not really new in the marketing world itself, however, the
digital era has turned it upside down. If in the 80s content marketing was spread from
magazine to magazine, now the platform is becoming more viral and able to reach just
anyone as the company wish. CRM is also not a new thing because it is widely known
how important it is to build a strong bond with customers. However, the combination
of both might resulting to an ultimate brand loyalty from customers, as the brand image
will also probably get an impact.
In this study, researcher takes Zalora Indonesia to scrutinize whether the content
marketing and CRM will have a significant impact in building a brand loyalty. Zalora
Indonesia, a part of Zalora Group, is an online fashion store that established in 2012. In
fact, Zalora Indonesia is becoming one of the most popular fashion online store in the
country with more than 70,000 newsletter subscribers. Offering free shipping cost
across the country, Zalora Indonesia is apparently successful in winning Indonesia’s
fashion lovers.
As it is previously mentioned, the purpose of content marketing is to engage more
customers with a different kind of promotion than the traditional advertising. When
customers get engaged, they will be loyal in the brand even if there are a lot of similar
brands trying to offer a good proposal (Bunpis, 2013). The combination of content
marketing and a well-managed customer relationship might will not only engaged more
customers, but keeping them loyal with the brand.
2 Literature Review
It is crucial for the companies to have good content marketing to attract more customers
to visit their page, follow the update news and finally repeat the purchase (Ahmad,
Musa & Harun, 2015). Content marketing allows a firm to create rich, attractive,
personalized message for its targeted audience, in order to form desired image in their
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
712

minds (O’Reilly, 2014). It is also will help a firm to build the brand image because
content marketing efforts focus on what people perceived as being wrong with the brand
and polish the messages the company sends to its leads, shareholders, customers, and
followers (Millard, 2016).
2.1 Content Marketing
As content marketing means delivering valuable content, providing valuable
information to customer will create brand loyalty and purchases in the future (Hakala,
Svensson & Vince, 2012). However, the relationship can be seen explicitly through
the impact of content marketing on customer brand engagement. A study conducted in
2013 by Bunpis and Haron analyzed how content marketing can affect customer brand
engagement and ultimately leads to some sort of loyalty. The valuable content can make
trust and consumer confidence, and influence the perception and purchase intent of
consumers (Bunpis & Haron, 2013). Bowden (2009) urges that customer brand
engagement is psychological basic to push consumers become increasingly loyal to a
brand, which added by Bunpis and Haron (2013) that the brand engagement through
content marketing will add a level of commitment and trust which lead to repeated
purchasing behavior and brand loyalty.
2.2 Customer Rekationship Management
A study conducted by Brahmasari and Panjaitan (2016) on how CRM can influence
brand image of Indonesian National Army Level II Hospitals, shows that CRM has a
significant influence on brand image. This finding is supported by a study conducted
by Lingavel (2015), as it found a great influence from CRM towards brand equity.
Brand equity has five underlying dimensions, including brand performance, brand
value, trustworthiness, commitment, and brand image (Lingavel, 2015). CRM help in
monitoring a real-time customer insight, allows businesses to manage the language of
marketplace and ensure their values align with the targeted customers and ultimately
makes customers feel involved (CRM Compass, 2015). Therefore, CRM is able to
create exceptionally positive customer experience that also able to form an image in
customer’s mind. The relationship between CRM and brand image also can be
explained by a statement proposed by Nyadzayo & Khajehzadeh (2016) that said a
positive brand image is expected to strengthen the effects of service quality, satisfaction
and value on customer loyalty via CRM quality.
Wali, Wright and Uduma (2015) revealed that CRM has strong impacts on brand
loyalty. If a firm established a close relationship with its customers, it would enable
them to understand when customers taste and want has taken a new direction in order
to meet their expectations, resulting a positive brand loyalty behavior. Implementations
of CRM practices can impact on customers’ ability to get committed with the brand.
One of the objectives of CRM process is to build customers profitability and loyalty via
a bonded relationship between the business and its customers (Reinartz & Kumar,
2006). Eventually, customers will return and repeatedly purchase the products, spend
more time with the brand, and become more loyal towards the brand (Balaji, 2015).
The Influence of Content Marketing and CRM toward Brand Image and Brand Loyalty
713

2.3 Brand Image
Brand Images is believed to have an immense influence on consumer satisfaction and
brand loyalty (Saeed et al., 2013). A study by Stocchi, Driesener & Nenycz-Thiel
(2015) urges that the existence of a positive relationship between brand image and
brand usage is one of the earliest empirical patterns documented, and has commonly
been used to justify a positive impact of brand image on brand loyalty. Brand image, as
it is automatically formed in consumers’ mind, is actually the objective and mental
feedback of the consumers when they purchase a product (Natarajan & Sudha, 2016),
therefore a positive brand image will be able to enhance the brand value of organization.
2.4 Brand Loyalty
American Marketing Association described brand loyalty as the situation in which
consumer generally buys the same manufacturer-originated product or service
repeatedly over time rather than buying from multiple suppliers within the category. It
reflects a customer’s commitment to remain in a relationship for a long period of time
with a brand (So, Andrew & Yap, 2013). Brand loyalty leads to certain marketing
advantages such as reduced marketing costs, more new customers and greater trade
leverage (Algesheimer et al., 2005). Thus, because of this reason, it is something very
essential for every firm to have their brands with loyalty from customers
The role of brand image itself is to give consumers overall values of products and
lure them to have the intention of purchase again and againthis theory clarifies the
relationship between brand image and brand loyalty, because according to Natarajan &
Sudha (2016) brand loyalty comes as a stepping stone that makes consumers to express
their belief and trust over a specific brand to be bought again and again. Therefore the
hypothesis can be proposed as follows:
H1 : Content marketing has a positive impact on brand image.
H2: Content marketing has a positive impact on brand loyalty.
H3: Customer Relationship Management has a positive impact on brand image.
H4: Customer relationship management has a positive impact on brand loyalty.
H5: Brand image has a positive impact on brand loyalty.
3 Methodology
3.1 Research Design
The aim of this study is to analyze the influential variables of brand loyalty using a
causal research design. Causal research, also known as explanatory research, is type of
research that investigates the cause-and-effect relationships (Brains et al., 2011).
Dependent, Independent and the mediator variable in this research are Brand Loyalty
(Y2). Content Marketing (X1) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) (X2)
Brand Image (Y1). Likert scale used in this research.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
714

3.2 Data Collected
This research used questionnaire to collect the primary data, distributed directly to the
selected respondents, and in online form to be distributed through some social media
messenger platform such as LINE, WhatsApp, Facebook, and Twitter.
3.3 Population and Sample
Population is the citizen of Pontianak that have purchased products from Zalora
Indonesia repeatedly, sample is a finite part of a statistical population whose properties
are studied to gain information about the whole (Webster, 1985). In this research, the
sampling method that used is non-probability sampling, characteristic is that samples
are selected based on the subjective judgement of the researcher. The sampling
technique used is purposive sampling, In order to determine the minimal sample size
from the unknown number, it can be found by using the following formula (Lemeshow
et al., 1990):
𝑛
𝑍
𝑃1 𝑃
𝑑
Whereby:
n : number of sample
Z : number of standard error, which is 95% = 1,96 with P = 0.5
d : confidence interval (precision), which is 10%
3.4 Validity and Reliability Test
The data collected for this research analyzed with SPSS (Statistical Package for the
Social Science) Software. Validity tries to asses whether a measure of a concept really
measures that concept, that is, the extent to which the concept measurer the thing it was
designed to measure (Singh, 2007). Reliability test shows stability of instruments in
describing the symptoms. In this research, the reliability test will be conducted with
SPSS Software and equipped with Cronbach Alpha ().Cronbach Alpha () is a
statistic that generally used as a measure of internal consistency or reliability of a
psychometric instrument like Likert data (Sumedi, 2016). A constructed item will be
considered reliable if it has Cronbach Alpha () higher than (>) 0.60.
3.5 Classical Assumption Test
Classical assumption test is the assumption that must be met in the linear analysis based
on ordinary least squares (OLS). The classical assumption test used are normality,
multicollinearity, heteroscedasticity, and linearity.
3.6 Path Analysis
The method used in analyzing the data collected is path analysis. In this research
particularly, the path model is set to hypothesized causal relation among variables,
The Influence of Content Marketing and CRM toward Brand Image and Brand Loyalty
715

which how Content Marketing (X1) and Customer Relationship Management (X2)
influence Brand Loyalty (Y2) through Brand Image (Y1) as mediator.
Fig. 1. Path Analysis Model.
Information :
X1 : Content Marketing, X2: Customer Relationship Management, Y1 :
Brand Image, Y2: Brand Loyalty
The coefficient of determination used to see the effect of the independent variable (X)
on the mediator variable (Y1) and dependent (Y2). R
2
helps in assessing the goodness
of fit of a regression equation. It is widely accepted in the social and psychological
applications that an R
2
of above 75 per cent is very good; between 50–75 percent is
good; between 25–50 percent is fair and below 25 per cent is poor and in the given case,
we can term the model to be good (Singh, 2007). T test is used to determine whether
each of the independent variables individually significant influence on the dependent
variable. In condition; if t
value
> t
table,
so it is significant, there is the influence of the
independent variables. Otherwise, if t
value
< t
table,
so it is not significant. The formula
below are used:
𝑡𝑟
√
𝑛2
√
1𝑟
Whereby:
t = t count, r = Correlation Coefficient, n = Number of data
4 Result and Discussion
4.1 Result
Content marketing and customer relationship management influence the brand image.
The F
value
is 47.128. Meanwhile, with calculating the df1 (k-1 = 3-1 = 2) and df2 (n-k =
100-2 = 98) with the level of significance is 0,05, the F
table
is 3.090. This means the
F
value
is higher than (>) the F
table
. Thus, it can be concluded that the independent
variables that include content marketing and customer relationship management
simultaneously impact brand image..
Content marketing, customer relationship management, and brand imaget influence
brand loyalty. It can be seen that the F
value
is 26.912. Meanwhile, with calculating the
df1 (k-1 = 4-1 = 3) and df2 (n-k = 100-3 = 97) with the level of significance is 0,05, the
F
table
is 2.70. This means the F
value
is higher than (>) the F
table
. Thus, it can be concluded
X1
X2
Y1 Y2
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
716
that the independent variables that include content marketing, customer relationship
management, and brand image influence brand loyalty.
The calculated value of R is 0,702 which means it is quite close to 1. Thus, it can
be concluded that content marketing, customer relationship management, and brand
image have a very strong relationship. Meanwhile, the value of R square is 0,493. This
means that both content marketing and customer relationship management have an
influence toward brand image as much as 49,3%. The other 50,7% is influenced by
other factors.
The result of the test with interverning variable, the value of R is 0,676, which is
close to 1. This means, the relationship between content marketing, customer
relationship management, brand image, and brand loyalty as variables is very strong.
Meanwhile, the value of R square is 0,457, which means the independent variables
(content marketing, customer relationship management, brand image) have an
influence toward the dependent variable (brand loyalty) as much as 45,7% and the other
54,3% is influenced by other factors.
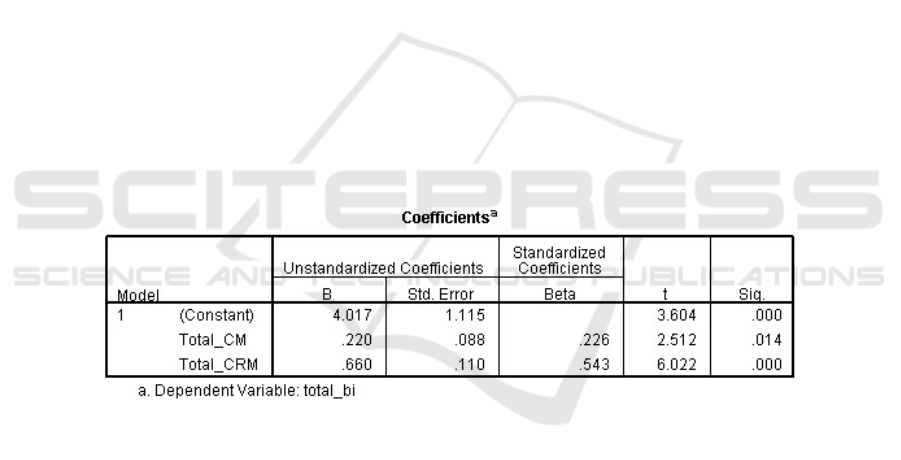
The multiple linear regression 1
st
model from the result shown in the Table 1 is:
Y2 = b1X1 + b2X2 + e
Y2 = 0,226X1 + 0,543X2 + e
Description:
Y2 : dependent variable (brand loyalty), X1: Independent Variable 1 (Content
Marketing),
X2 : Independent Variable 2 (Customer Relationship Management), b1, b2 :
Standardized Coefficents, e: Error.
Table 1. Multiple Linear Regression Model Test Result without Interverning Variable.
Source: primary processing data, 2017
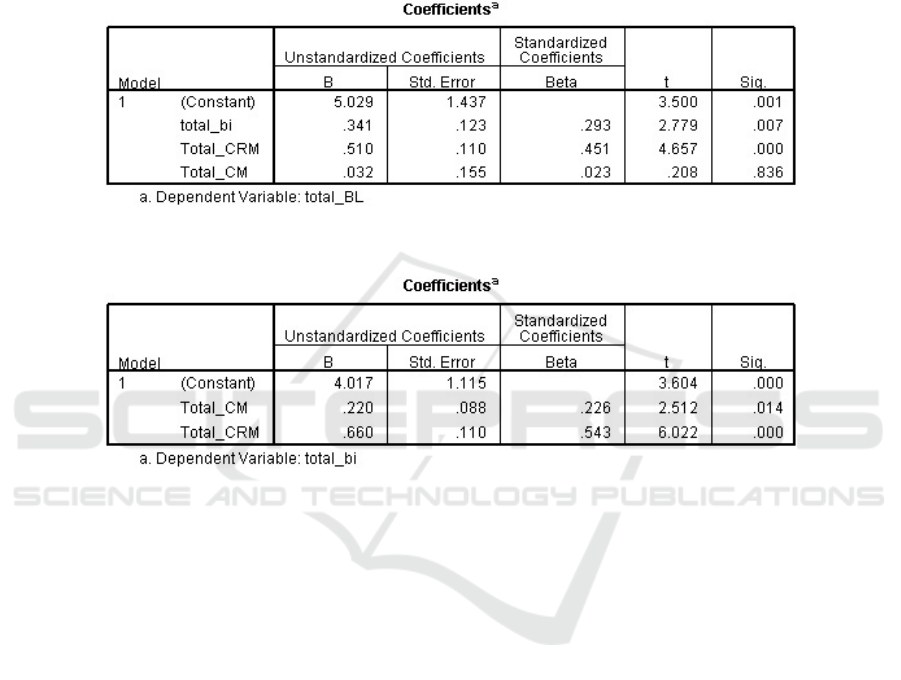
The multiple linear regression 1
st
model from the result shown in the Table 2 is:
Y2 = b1X1 + b2X2 + b3Y1 e
Y2 = 0,023X1 + 0,451X2 + 0,293Y1 + e
Description:
Y1: Mediating Vairable (Brand Image), X1: Independent Variable 1 (Content
Marketing), X2: Independent Variable 2 (Customer Relationship Management), b1,
b2 : Standardized Coefficents, e: Error
This test is used to determine whether each of the independent variables individually
significant influence on the dependent variable. In condition; if t
value
> t
table,
so it is
significant, there is the influence of the independent variables. Otherwise, if t
value
< t
table,
so it is not significant. It can also be done by comparing the significant value to the
The Influence of Content Marketing and CRM toward Brand Image and Brand Loyalty
717
value of = 5%. The first t test is performed to examine the effect of content marketing
(X1) and customer relationship management (X2) on brand image (Y1), with the
hypothesis as follows:
H
1
: content marketing has a significant impact on brand image.
H
2
: customer relationship management has a significant impact on brand image.
Table 2. Multiple Linear Regression Model Test Result with Interverning Variable.
Source: primary processing data, 2017
Table 3. T-Test Result without Interverning Variable.
Source: primary processing data, 2017
Table shows the result of the processed data using SPSS 17. It shows that the t value
Content Marketing (X1) on Brand Image (Y1) is 2,512, which is higher than (>) the t
table 1,988. Then, the significant level is in the amount of 0,014 which means it is less
than (<) 0,05. It can be concluded that the effect is quite significant. Thus, Hypothesis
1 is accepted.Meanwhile, it is also shows the t value of Customer Relationship
Management (X2) on Brand Image (Y1) is 6,022 that is higher than (>) the t table 1,988.
The significant level is seen as much as 0,000 which is clearly less than (<) 0,05. Then
it is can be said that the effect is also significant. Thus, Hypothesis 2 is accepted. The
second t test is performed to examine the effect of content marketing (X1), customer
relationship management (X2), brand image (Y1) on brand loyalty (Y2), with the
hypothesis as follows:
H
3
: content marketing has a significant impact on brand loyalty.
H
4
: customer relationship management has a significant impact on brand loyalty
H
5
: brand Image has a significant impact on brand loyalty.
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
718
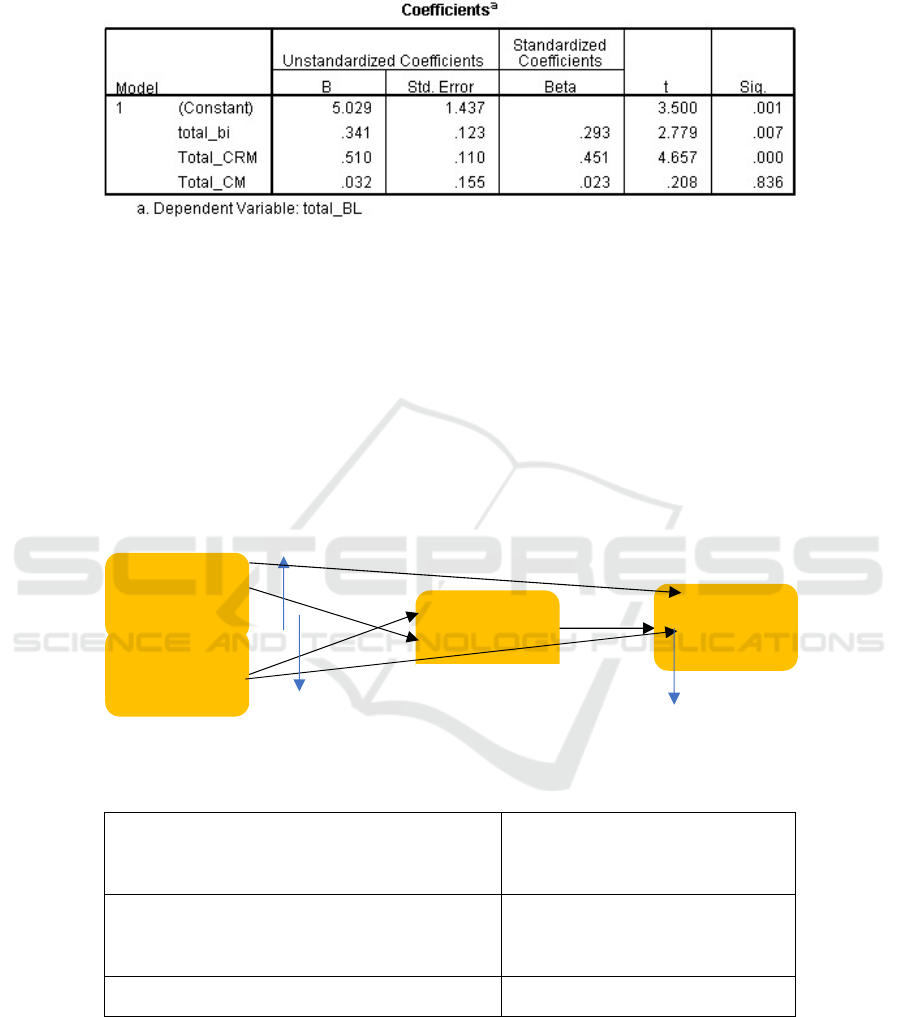
Table 4. T-Test Result with Interverning Variable.
Source: primary processing data, 2017
The t value of content marketing (X1) on brand loyalty (Y2) is 0,208. The t value seems
to be less than (<) the t table which is 1,988. The significant value is as much as 0,836,
which is higher than (>) 0,05. Thus, it can be said that the effect is not significant, and
therefore the H
0
of Hypothesis 3 is rejected. On the other hand, Table 4 shows the t
value of customer relationship management (X2) on brand loyalty (Y2) which is in the
amount of 4,657. The t value for those variables are higher than (>) the t table which is
1,988. The significant value of customer relationship management (X2) on brand
loyalty (Y2) is 0,000. This value is less than (<) 0,05. Thus, it can be concluded as the
effect is quite significant and the Hypothesis 4 is accepted. Brand image (Y1) on brand
loyalty (Y2) shows a t value as much as 2,779 which is higher than (>) the t value 1,988.
The significant value of those variables is as much as 0,007 which is less than (<) 0,05.
Thus, it can be said that the effect is significant and the Hypothesis 5 is accepted.
Source: primary processing data
Fig. 2. Path Diagram.
Table 5. Recapitulation Test Result of Path Analysis.
Direct effect from X1 to Y2
Indirect effect from X1 to Y1 to Y2
Total influence from X1 to Y2
0,023
(0,226 x 0,293) = 0,066
0,023 + 0,066 = 0,089
Direct effect from X2 to Y2
Indirect effect from X2 to Y1 to Y2
Total influence from X1 to Y2
0,451
(0,543 x 0,293) = 0,129
0,451 + 0,129 = 0,580
Direct influence from Y1 to Y2
0,293
Source: primary sourcing data, 2017
ρX
1
Y
1
= 0,226
Content
Marketing
CRM
Brand
Image
Brand
Loyalty
ρX
1
Y
2
= 0,023
ρX
2
Y
2
= 0,451
ρY
1
Y
2
= 0,293
ρX
2
Y
1
= 0,543
The Influence of Content Marketing and CRM toward Brand Image and Brand Loyalty
719

It can be seen that all of the independent variables (content marketing and customer
relationship management) have a positive relationship with the dependent variable
(brand loyalty). It can be interpreted as when there is an increase of X1 , there will be
an increase of Y2 with the assumption other independent variables are constant. When
there is an increase of X2 , there will be an increase of Y2 with the assumption other
independent variables are constant.
4.2 Discussion
The variable content marketing’s influence on brand loyalty has been tested. The result
comes out as not significant. Content marketing has a role to engage potential customers
through social media platform, in order for them to be interested in getting involved
with the brand. Content marketing taps into the first two stages of the buying process
by raising awareness of solutions and educating consumers about a product they may
have never considered before (Steimle, Forbes, 2014). Hence, content marketing’s role
for a brand is only to attract the customers, not keeping the old customers to be loyal.
However, the processed data shows there is a significant influence of content
marketing towards brand image. The respondents of this study are active social media
users who the majority of them had been stumbled upon the content Zalora Indonesia
shared through its social media platform. According to Pulizzi (2013), today’s content
marketing heavily involves social media because those networks are vital to the success
of content marketing efforts. Delivering valuable content, the practice of content
marketing will allow firms to build deep engagement with their customers. Thus, it can
be said that the content Zalora Indonesia has been delivered to its social media followers
have successfully and heavily shaped its brand image as the leading online fashion
store.
There are many ample research on how CRM affect the image of a brand. CRM has
been known as a powerful tool to create a positive experience for customers and form
an image in customers’ mind. This research has tested the variable CRM’s influence on
brand image using SPSS 17, and the result is there is a significant influence. This
research shows that the majority of the respondents agree on the constructed items to
test the variable CRM. Zalora Indonesia, as an online fashion store, has multiple ways
in maintaing the relationship with its customers in order for them to have a positive
experience with the brand.
A study conducted by Wali, Wright and Uduma (2015) proposed that if a firm
established a close relationship with its customers, it would enable them to understand
when customers taste and want has taken a new direction in order to meet their
expectations, resulting a positive brand loyalty behavior. With the result shows in this
study the variable CRM has been tested to have a significant influence and positive
impact on brand loyalty. As a tool to build an in depth relationship with customers, if
CRM done right it could gain a loyalty towards the brand from customers.
Brand image seems to have a strong influence towards brand loyalty. This finding
is supported by a previous research by Saeed, et al. (2013) that confirmed there is a
positive relationship between brand image and brand loyalty. According to numerous
marketing and psychology literatures, researchers believe that brand image can be
viewed as a set of relative localization, identical quality guaranteeing and the function
attribute of the product and service which make consumers reflect their self-image and
which help make purchase decisions (Aghekyan-Simonian et al., 2012). Zalora
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
720

Indonesia has been maintaining its image as an online fashion store offering premium
quality products for people who love fashion.
5 Conclusion
Based on those findings, the processed data also showing a few results that can be
concluded as Content marketing has a significant influence on brand image. The t test
result shows the significant value is higher than the . Content marketing does not have
a significant influence on brand loyalty, as the t test result shows significant value of
the independent variable is higher than the . Customer relationship management has
a significant influence on brand image by which the significant value shown on the t
test result comes out higher than the .Customer relationship management has a
significant influence on brand loyalty. The significant value of the independent variable
shown on the t test result appears to be higher than the . Brand image has a significant
influence towards brand loyalty. Brand image’s significant value comes out to be
higher.
References
Ahmad, N. S., Musa, R. & Harun, M. H. M.. The impact of social media content marketing
(SMCM) towards brand health. Procedia Economics and Finance. 37. 331-336 (2015)
American Marketing Association. (n.d.). In Marketing Dictionary. Retrieved from
https://www.ama.org/resources/pages/dictionary.aspx?dLetter=B
Anderson, K. & Kerr, C. (2002). Customer Relationship Management. New York, USA:
McGraw Hill Education
Batra, R. & Homer, P. (2004). The Situational Impact of Brand Image Beliefs. Journal of
Consumer Psychology. 14(3). 318-330
Boateng, H. & Okoe, A. (2015). Consumers’ Attitude Towards Social Media Advertising and
Their Behavioural Responses: The Moderating Role of Corporate Reputation. Journal of
Research in Interactive Marketing. 9(4). 299-312.
Brahmasari, I. A. & Panjaitan, H. (2016). The Influence of Service Quality, and Customer
Relationship Management (CRM) of Patient Satisfaction, Brand Image, Trust, and Patient
Loyalty on Indonesian National Army Level II Hospitals. International Journal of Business
and Management Invention. 5(5), 30-44.
Brettel, M. & Spilker-Attig, A. (2010). Online advertising effectiveness: a cross-cultural
comparison. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing. 4(3). 176-196
Brown, M. (2012, August 10). Understanding Gender and Ecommerce. PFS. Retrieved from:
http://www.pfsweb.com/blog/understanding-gender-and-ecommerce/
Bunpis, L. & Haron, M. S. (2014). The Influence of Content Marketing on Customer Brand
Engagement Towards Online Herbal Cosmetic Store in Thailand. Universiti Utara Malaysia
Repository, HB Economic Theory 2014.
Chinomona, R. (2016). Brand Communication, Brand Image and Brand Trust As Antecedents
Of Brand Loyalty in Gauteng Province of South Africa. African Journal of Economic and
Management Studies. 7(1), 124-139.
Conner, C. (2013, March 4). The ‘8 Great’ Challenges Every Business Faces (And How To
Master Them All). Forbes. Retrived from https://www.forbes.com/sites/cheryl
snappconner/2013/03/04/the-8-great-challenges-every-business-faces-and-how-to-master-
them-all/#18dc6c103891
The Influence of Content Marketing and CRM toward Brand Image and Brand Loyalty
721

Content Marketing Association. (n.d.). In Why Use Content Marketing?. Retrieved from
http://the-cma.com/about-us/why-use-content-marketing/
Durrani, B., et al. (2015). Impact of Brand Image on Buying Behaviour Among Teenagers.
European Scientific Journal. 11(5). 155-168
Ernst, H., et al. (2010). Customer Relationship Management and Company Performance ―The
Mediating Role of New Product Performance. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science.
39. 290-306
Georgieva, A. & Djoukanova, A. (2014). Content Marketing: New Opportunities for Building
Strong Brands Online. (Unpublished Master Thesis). Lund University, Sweden.
Ghazian, A., Hossaini, M. H. & Farsijani, H. (2016). The effect of customer relationship
management and its significant relationship by customers’ reactions in LG Company.
Procedia Economics and Finance. 36. 42-50
Ghozali, I. (2013). Aplikasi Analisis Multirative dengan SPSS. Semarang: Badan Penerbit
Universitas Dipenogero.
Gittings, C.(2002). The Advertising Handbook. New York: USA: Routledge
Goor, M. (2012). “Instamarketing”: A Content Analysis Into Marketing on Instagram.
(Unpublished Master Thesis). Universiteit van Amsterdam, Netherlands.
Glantz, A. & Slinker, K. (1990). Primer of Applied Regression and Analysis of Variance. New
York, USA: McGraw Hill Education
Graeff, T. (1997). Consumption Situations and The Effects of Brand Image on Consumers’ Brand
Evaluation. Journal of Psychology & Marketing. 14(1). 49-70
Harden, L. & Heyman, B. (2009). Digital Engagement: Internet Marketing that Captures
Customers and Builds Intense Brand Loyalty. New York, USA: AMACOM (American
Management Association)
Harrison, K. (2017, March 10). Want To Win At Content Marketing? Become An Expert In Your
Field. Forbes. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/kateharrison/2017/03/ 10/want-
to-win-at-content-marketing-become-an-expert-in-your-field/#30a9ae0d7237
Huber-Carol, H., et al. (2002). Goodness-of-Fit Tests and Model Validity. New York, USA:
Springer Science Business Media
Kestenbaum, R. (2017, June 14). This is How Millenials Shop. Forbes. Retrieved from:
https://www.forbes.com/sites/richardkestenbaum/2017/06/14/this-is-how-millennials-shop/
#1921ec85244c
Kort, P., et al. (2015). Brand Image and Brand Dilution in The Fashion Industry. Automatica. 42.
1363-1370
Lingavel, D. (2015). Impact of customer relationship management on brand equity: private
hospitals in Jaffna. European Journal of Business and Management. 7(4). 69-79
Llopis, G. (2014, August 11). 8 Ways Content Marketing Catapults Your Brand Relevancy.
Forbes. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/glennllopis/2014/08/11/7-ways-
content-marketing-catapults-your-brand-relevancy/#37d210dccd98
McPheat, S. (2011). Developing An Internet Marketing Strategy. Telluride, Colorado, USA:
Ventus Publishing
Melnyk, V. & Bijmolt, T. (2015). The Effects of Introducing and Terminating Loyalty Programs.
European Journal of Marketing. 49(3/4). 398-419
Millard, T. (2016, December 19). How to Design a Content Marketing Strategy to Fix a Brand’s
Image. Target Marketing Magazine. Retrieved from http://www.targetmarket
ingmag.com/article/how-to-design-a-content-marketing-strategy-t
o-fix-a-brands-image/all/
Miroshnichenko, A. (2014). Content marketing: how companies are turning into media, case
studies. Human as Media. Retrieved from http://human-as-media.com/2014/11/16/content-
marketing-how-companies-are-turning-into-media/
Moisescu, O. & Allen, B. (2010). The Relationship Between The Dimensions Of Brand Loyalty,
An Empirical Investigation Among Romanian Urban Consumers. Management & Marketing
Challenges for Knowledge Society. 5(4). 83-98
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
722

Morrison, S. & Crane, F. (2007). Building the service brand by creating and managing an
emotional brand experience. Journal of Brand Management. 14(5). 410-421
Natarajan, R. (2016). A relationship between brand image and brand loyalty (a study with
reference to FMCG consumers in Vellore District). EPRA International Journal of Economic
and Business Review. 4(5). 139-145
NewsCred. (2014). The Millennial Mind: How Content Drives Brand LoyaltyA Quantitative
Research Study Conducted by NewsCred in 2014. US: NewsCred Press.
Nyadzayo, M. & Khajehzadeh, S. (2015). The Antecedents of Customer Loyalty: A Moderated
Meditation Model of Customer Relationship Management Quality And Brand Image. Journal
of Retailing and Consumer Services. 30. 262-270.
Odongo, I. (2016). Content Marketing: Using It Effectively for Brand Strategy and Customer
Relationship Management. Advences in Social Sciences Research Journal. 3(12), 52-61.
Page, V. (2017, March 15). The Psychology Behind Why People Buy Luxury Goods.
Investopedia. Retrieved from http://www.investopedia.com/articles/personal-
finance/091115/psychology-behind-why-people-buy-luxury-goods.asp
Pajunen, J. & O’Dell, S. (1997). The Butterfly Customer: Capturing The Loyalty of Today’s
Elusive Consumer. Toronto, Canada: J. Wiley & Sons
Pappu, R. & Quester, P. (2016). How Does Brand Innovativeness Affect Brand Loyalty?.
European Journal of Marketing. 50(1/2). 2-28
Paris, D. L., Bahari, M. & Iahad, N. A. (2015). Exploring implementation factors influencing
business-to-customer (B2C) e-commerce. American Scientific Publishers. 21(5). 1455-1459
Peng, J., et al. (2014). Effects on online advertising on automobile sales. Management Decision.
52(5). 834-851
Pulizzi, J. (2013). Epic Content Marketing: How to Tell A Different Story, Break Through The
Clutter, and Win More Customers by Marketing Less. New York, USA: McGraw Hill
Education
Ranjbarian, B., Sanayei, A. & Kaboli, M. (2012). An Analysis of Brand Image, Perceived
Quality, Customer Satisfaction and Re-Purchase Intention in Iranian Department Stores.
International Journal of Business and Management. 7(6). 40-48
Rodriguez, M. & Honeycutt, E. (2011). Customer Relationship Management (CRM)’s Impact on
B to B Sales Professionals’ Collaboration and Sales Performance. Journal of Business-to-
Business Marketing. 18(4). 335-356
Saeed, R., Lodhi, R. N., Mehmood, A., Ishfaque, U., Dustgeer, F., Sami, A., Mahmood, Z., &
Ahmad, M. (2013). Effect of Brand Image on Brand Loyalty and Role of Customer
Satisfaction In It. Wolrd Applied Sciences Journal. 26(10), 1364-1370.
Sasmita, J. & Suki, N. M. (2015). Young consumers’ insights on brand equity: effects of brand
association, brand loyalty, brand awareness, and brand image. International Journal of Retail
& Distribution Management. 43(3). 276-292
Soares, M. & Pinho, J. C. (2014). Advertising in online social networks: the role of perceived
enjoyment and social influence. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing. 8(3). 245-263
Statista. (2017). Outlook Report: Fashion Trends, Insights & Top Players. The Statistics Portal.
Retrieved from https://www.statista.com/outlook/244/120/fashion/indonesia #takeaway
Steimle, J. (2014, September 19). What is Content Marketing?. Forbes. Retrieved from
https://www.forbes.com/sites/joshsteimle/2014/09/19/what-is-content-marketing/#4a2c0c0
910b9
Stokes, R. (2014). eMarketing: The Essential Guide to Marketing in A Digital World 5th Edition.
Cape Town: Quirk eMarketing (Pty)
Thornhill M., Xie K. & Lee Y. (2017). Social Media Advertising in A Competitive Market:
Effects of Earned and Owned Exposures on Brand Purchase. Journal of Hospitality and
Tourism Technology. 8(1). 19-39.
Top Brand Award. (2016). Top Brand Index 2016 Fase 2: Kategori Retail. Top Brand Award
Wali, A. F., Wright, L. T., & Uduma I. A. (2015). Customer Relationship Management for Brand
Commitment and Brand Loyalty. British Journal of Marketing Studies. 3(4), 45-58.
The Influence of Content Marketing and CRM toward Brand Image and Brand Loyalty
723

Wang, Y. & Feng, H. (2012). Customer relattionship management capabilities: measurement,
antecedents and consequences. Management Decision. 50(1). 115-129
Wilinski, E. (2016, September 20). Building Brand Loyalty with Content Marketing. The Content
Bureau. Retrieved from http://contentbureau.com/blog/beyond-the-style-guide/ building-
brand-loyalty-with-content-marketing
Wong, A. & Yazdanifard, R. (2015). The review of content marketing as a new trend in marketing
practices. International Journal of Management, Accounting and Economics. 2(9). 1055-
1064
Zvavahera, P. & Chigora, F. (2015). Attitudinal and Behavioural Loyalty: Zimbabwe Tourism
Brand Performance Ascendancy. Business and Management Horizons. 3(2). 52-59
MIICEMA 2019 - Malaysia Indonesia International Conference on Economics Management and Accounting
724
