
The Mammary Histopathology Depiction of Female Mice Induced by
Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteria after Scaevola Taccada Extract
Administration
Nurul Aini Siagian
1
, Mutiara Dwi Yanti
1
Andayani Boang Manalu
1
, Putri Ayu Yessy Ariescha
1
,
Firdaus Fahdi
2
, Prihantono
3
1
Midwifery Faculty, Institut Kesehatan Deli Husada Delitua
2
Pharmacy Faculty, Institut Kesehatan Deli Husada Delitua
3
Department of Oncology, Medical Faculty of Universitas Hasasanuddin Makassar
Keywords: Histopathology, Scaevola Taccada, Staphylococcus Aureus
Abstract: The public is concerned about chemical-based anti-inflammatory drug usage, so it is an indication to find an
anti-inflammatory drug made from herbal plants, one of them is from the Scaevola taccada (Gaertn.) Roxb.
This research was conducted by finding out the histopathological depiction of female mice (Gaertn.) Roxb.
induced by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria after the administration of Scaevola taccada (Gaertn.) Roxb.
Samples were divided into two groups, namely the control and treatment group. The control group was
given by antibiotic amoxicillin 9.59 mg/kg bb, while the treatment group was given by antibiotic
amoxicillin 9.59 mg/kg bb plus Scaevola taccada extract 400 mg/kg bb, an anti-inflammatory determination
is done by the formation of artificial inflammation or mastitis with the induction of staphylococcus aureus
bacteria in mammary parts of rats.
1 INTRODUCTION
Inflammation is a protective response toward tissue
injury caused by physical trauma, chemicals,
damage, or microbiological substances. Anti-
inflammatory drugs are a class of drugs that have
analgesic (pain relief), antipyretic (heat-reducing),
and anti-inflammatory properties. This drug is
relatively safe if it is used by at the appropriate
dosage. But concerns will arise if it is consumed in
high doses or long term because it will cause side
effects such as liver poisoning, digestive tract
disorders, kidney disorders and others (Sitti Amirah
Rahmawati, Safriani Rahman, 2014).
Staphylococcus aureus is a major pathogen in
humans that causes various clinical infections. At
present, staphylococcus aureus is also used to
diagnose mastitis known as "infectious mastitis"
which is being applied to describe acute case
conditions. Staphylococcus aureus can express a
variety of surface proteins that can play key role in
the infection process because it can promote
bacterial adhesion to host cells and tissues, as well
as obtain important nutrients and avoid immune
responses (Contreras and Rodríguez, 2017)
(Yagdiran et al., 2016) (Habib et al., 2015) (Cells,
2019).
Clinical infection caused by staphylococcus
aureus is likely to have a general or even serious
impact. It can be seen from antimicrobial resistance
increasing even clinical disease is also increasing
due to staphylococcus aureus bacteria (Tong et al.,
2015). Mastitis is an inflammatory disease of the
breast. Staphylococcus aureus is the most dominant
bacterium that is often found by inflamed breasts, in
other studies saying that the mammary glands
sinuses and epithelial cells were damaged due to
staphylococcus aureus bacteria (Chen et al., 2014).
According to WHO 2013, many health cares of
medicinal plants have been used by preventing or
treating certain diseases. Because of the efficacy and
availability and also affordable prices so that the
demand for herbal medicines that use natural
ingredients continues to increase. There are millions
of people in major regions of developing countries
covering from 70 to 80 percent of health care needs
in the world population (Essien et al., 2017).
604
Siagian, N., Yanti, M., Manalu, A., Ariescha, P., Fahdi, F. and Prihantono, .
The Mammary Histopathology Depiction of Female Mice Induced by Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteria after Scaevola Taccada Extract Administration.
DOI: 10.5220/0010015306040610
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology (ICHIMAT 2019), pages 604-610
ISBN: 978-989-758-460-2
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Scaevola taccada (Geartn.) Roxb. is trusted by
the public for treating digestive, anti-tumor, and
anti-inflammatory problems. The fruit can be used
as juice to overcome menstrual problems and
ringworm. The roots are also commonly used by
people as a treatment for dysentery, syphilis, and
beriberi. The Decoction of the leaves and bark can
prevent tachycardia, this plant can also reduce the
frequency of heartbeats, slow the pulse and stimulate
the heart to contract normally, anti-inflammatory,
anti-fungal, anti-bacterial and cough medicine
(Mejin, 2009) ( Chandran and Arunachalam, 2015)
(Review and Scavola, 2017).
According to research conducted (Suthiwong,
Thongsri, and Yenjai, 2016), there is strong
antifungal activation found in the content of
Scaevola taccada (Geartn.) Roxb. Scaevola taccada
(Geartn.) Roxb. has also been used as
dermatological aid in Hawaii. A mixture of root bark
crushed with salt is used by curing skin diseases. In
Indonesia, the roots are used as an antidote when
consuming poisonous fish and crabs. Scaevola
taccada is reported by having chemical constituents
from alkaloids, flavonoids, lipids, terpenoids,
glycosides, and saponins (Mejin, 2009) (Chandran
and Arunachalam, 2015).
Previous research on chemical component
groups found in diethyl ether fraction of Scaevola
taccada (Gaertn.) Roxb. was Flavonoid group with a
wavelength of 239.50 nm and had hydroxy,
aromatic, ketone, alkyl group and supported by spot
spotting after spraying with benedict reagents and
Antimony (III) Chloride reagents. The research
results also support traditional plants used for the
treatment of several diseases and inflammatory
conditions (Rachmat Kosman, 2012).
In this case, the researchers concluded by
utilizing the Scaevola taccada (Gaertn.) Roxb. to
reduce inflammation caused by staphylococcus
aureus bacteria), so it needs to be re-tested whether
there is an effect of the Scaevola taccada (Gaertn.)
Roxb. on inflammation that occurs in mammary
bacteria induced by female mice induced by
staphylococcus aureus bacteria.
2 METHOD
This research was experimental research by using
the post-test only controls group design. The study
was conducted at Biopharmaca Laboratory and
Biology Pharmacy Laboratory of UIN Makassar and
for the adaptation of mice to the end of the treatment
at Hasanuddin University animal laboratory.
Subjects in this study were twelve strains Sprague
Dawley mice with the body-weight of 200-250
grams, divided into control and treatment groups.
The main ingredients were amoxicillin and Scaevola
taccada extract. Other materials were cotton alcohol,
10% formalin buffer solution, and container pots,
injection syringes, tissue, light microscopes, glass
objects, microtomes, water baths, and glass covers.
Mouse cages are plastic tubs covered by wire and
given sawdust and place to eat and drink.
The sample of this study was divided into two
groups. The control group was induced by
staphylococcus aureus (0.2 ml x 108 ml/CFU), and
they are given amoxicillin antibiotics at a dose of
9.59 mg/ml/ 250 gram bb of mice for five days.
While the treatment group induced by
staphylococcus aureus (0.2 ml x 108 ml/CFU), it
was given amoxicillin antibiotics at a dose of 9.59
mg/ml/ 250 gram bb of mice for five days and
Scaevola taccada extracts at dose of 400 mg/ml/kg
bb of mice for five days. Then on the 6
th
day, the
mice in euthanasia were taken and the mammary
part and examined for processing and making the
histopathological preparations.
The material was the Scaevola taccada plant
obtained from Watang Suppa Village, Suppa
District, Pinrang Regency. They are cleaned from
the dirt attached by using flowing water and then cut
the sample into small pieces. They are dried to
contain water content below 10%. Scaevola taccada
was sieved with a mesh size of 40 so that a smooth
Simplicia sample was obtained. After that, the
sample is ready to be extracted by maceration
method. Extraction by the maceration method used
70% ethanol solvent. First, the sample is moistened
with 70% ethanol until fully submerged for 15
minutes. After that, it is sufficient again to be two
liters with 70% ethanol at the temperature room for
3 x 24 hours while occasionally stirring. Macerate is
then filtered and the pulp is macerated again. The
extract obtained then evaporated by using a rotary
evaporator until it thickens, then dried with the help
of a water bath. The extract obtained is then
evaporated by using a rotary evaporator until it
thickens, and then dried with the help of the water
bath. The resulting viscous extract is inserted into
porcelain vial and weighed the extract weight.
Furthermore, the dose is converted to obtain a dose
of 400 mg/kg bb.
Then, staphylococcus aureus cultured was
planted in BHIB medium and incubated for 18-24
hours at 37° C in an incubator. Then the bacteria
were planted on NA (Nutrient Agar) medium and re-
incubated for 18-24 hours at 37° C. After bacterial
The Mammary Histopathology Depiction of Female Mice Induced by Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteria after Scaevola Taccada Extract
Administration
605

incubation, do gram staining. Biochemical tests were
carried out by NA colonies for staphylococcus
aureus by planting on DNAse agar medium and then
mannitol salt agar, then doing bacitracin and
Novobiocin tests followed by catalase coagulase
test. Then it was re-incubated for 18-24 hours with a
temperature of 37° C. The bacteria that grew on
biochemical tests were matched with the
identification table of staphylococcus aureus
bacteria. To make bacterial samples that were
injected into mice by making suspension in a
physiological NaCl solution as much as 10 ml mixed
with golden yellow S. aureus bacterial colony with
turbidity level of Mc Farlan 2 x 108 CFU. The
accuracy of the Mc Farland turbidity level is
measured by the Densi check tool.
Adaptationofanimal
Scaevolataccada Extractsacevolataccada
Histopathologicaltestmikroskopik Givingextracts
Figure 1. Research Scheme
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The identification results of alkaloid compounds,
flavonoids, steroids/triterpenoid, saponins and
tannins groups in sea leaves (Scaevola taccada
(Gaertn.) Roxb. extracts showed positive results (+)
which means that there are alkaloid compounds,
flavonoids, steroids/triterpenoid, saponins and
tannins in Scaevola taccada (Gaertn.) Roxb).
extracts.
Flavonoid compounds are found in almost all
parts of plants including the outer bark, leaves, fruit,
and roots. Flavonoids are also natural compounds
that have potential as antioxidants that can
counteract free radicals that play a role in the
generation of degenerative diseases through the
mechanism of damage to the immune system, lipid
oxidation, and protein (Aminah, Tomayahu, and
Abidin, 2017).
Scaevola taccada plant used in this study is only
part of the leaf. The Scaevola taccada leaf can be
used as an anti-inflammatory because it contains
several compounds. One of them is the flavonoid
compound.
In this study, the Scaevola taccada leaves were
obtained from the coast of Watang Suppa Village,
South Sulawesi. Scaevola taccada leaves must be
cleaned of dirt that attaches to the leaves so as not to
interfere with the extraction process. Next, the
Scaevola taccada leaves cut into small pieces to
facilitate the drying process. The dried leaves are
extracted.
Extraction is a technique used to extract
compounds in the plant. The extraction technique
used in this study was the maceration technique
because the maceration technique is the simplest
extraction technique that is the easiest to do.
Maceration is done by using three times
recapitulation for 70% ethanol sailor for 24 hours
after the extraction process of liquid extract is
evaporated using a rotavator to obtain thick green
and dark extracts.
The subjects were 12 female Sprague Dawley
mice that were adapted by seven days at Hasanuddin
University animal laboratory, which met the
inclusion criteria. The results of the
histopathological study of female mammary mice
induced by bacterium Staphylococcus aureus after
Scaevola taccada (Gaertn.) Roxb. extract
administration by comparing with the control group
were only given antibiotics.
According to figure 3, it can be seen in the group
that only has not been given antibiotics. There are
many inflammatory cells in milk glands and
connective tissue, while after being given
amoxicillin, the inflammation antibiotics appear to
be reduced but still appear in some cells. However,
In Figure 4, inflammation cells can be seen before
antibiotic amoxicillin administration and Scaevola
taccada extracts, there are many inflammation cells
in milk glands and connective tissue after antibiotic
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
606
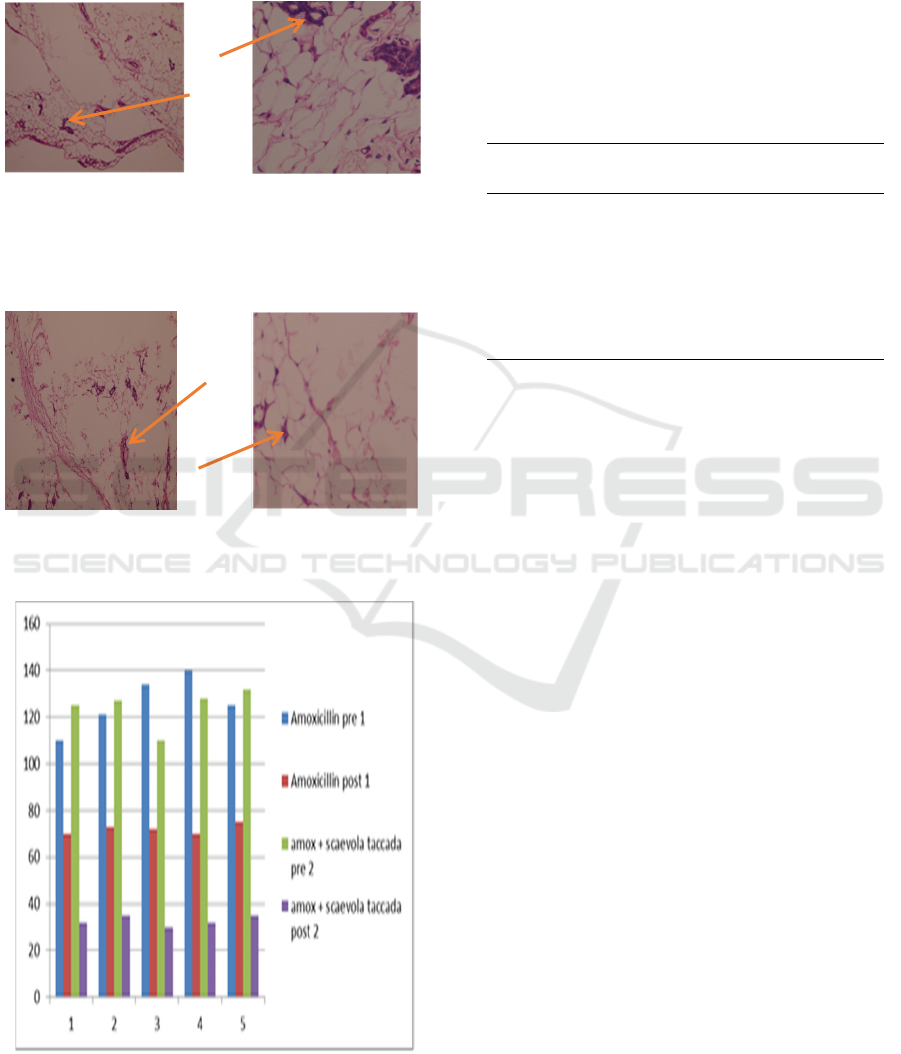
treatment and extra Scaevola taccada inflammation
cells are reduced by only visible inflammation cells
in the connective tissue section.
Pre Post
Figure 2: Microscopic features in mammary mice control
group
Pre Post
Figure 3: Microscopic features in the mammary mice
treatment group
Figure 4: Inflammation Number Diagram
Table 1 shows that the average number of
inflammation in the control group was 54,000 while
in the treatment group was 91,600 with a mean
difference of 37.6. It meant that the treatment group,
namely the group was given by the Scaevola taccada
extract (Gaertn.) Roxb. was more influential in
reducing inflammation cells than the control group
that was only given amoxicillin.
Table 1: Histopathological examination results of mice
induced by Staphylococcus Aureus who were given by
treatment
Group Mean±SD
Mean
Deviation
P-
value
Control
(Amoxicil
lin)
54.000 ±
11.916
37.6
0.001
Treatment
(Amoxicil
lin+
Scaevola
Taccada)
91.600 ±
6.804
0.000
Inflammation is a localized protective response
caused by tissue damage or injury that functions to
destroy the agent and causes injury. It is
characterized by pain, heat, redness, swelling, and
loss of function. Inflammation is divided into two
namely acute inflammation that lasts quickly or
briefly, and chronic inflammation that occurs
repeatedly (Willianto and Wijayahadi, 2016).
The inflammation mechanism in the body which
is commonly called inflammation is an immune
response that maintains tissue homeostasis in the
body and allows the body to survive during the
process of injury or infection. Inflammation is also
normal and healthy body processes that are usually
produced by several disorders or various diseases
from the body's localized response to the general
response. So it can be concluded that inflammation
is the body's first reaction when injury and infection
occur in a person's body. Inflammation can be
treated with various types of anti-inflammatory
agents that are effective and safe to help treat or
reduce inflammation which is called agents (Ganesh
et al., 2014).
The occurrence of mastitis begins with an
increase in pressure in the duct (ASI channel) due to
stasis of ASI. If the milk is not removed
immediately, there is excessive alveoli tension and
causes the epithelial cells that produce milk to
become flat and depressed so that the connective
tissue permeability increases. Some components
(mainly immune proteins and sodium) from plasma
enter the breast milk and subsequently into the
The Mammary Histopathology Depiction of Female Mice Induced by Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteria after Scaevola Taccada Extract
Administration
607

tissues around cells so that it triggers an immune
response. Untreated ASI stasis results in an
inflammatory response and tissue damage making it
easier for breast infections (IDAI, 2013, Tristandi &
Nariyah 2019).
There are several ways the entry of germs into
the breast is through the lactiferous ducts into the
secretion lobes, through cracked nipples to the
lymph glands around the duct (periductal) or through
hematogenous (blood vessel) spread. The most
frequent organisms are Staphylococcus aureus,
Escherichia coli, and Streptococcus. (IDAI, 2013).
Mastitis treatment and prevention depend on
antibiotics usage. So, the abuse of antibiotics can
lead to antibiotic resistance. So it is necessary to
develop treatment strategies with natural ingredients
that have been widely used by various countries in
the world, which can reduce the risk of drug usage
which is made by chemicals (Cheng et al., 2019).
In another study stated that the treatment of
mastitis both infectious and non-infectious with
antibiotics can provide rapid resolution.
Erythromycin is considered the drug of choice
because it has high efficacy, low cost, and has a low
risk of inducing bacterial resistance. Handling of
mastitis using antibiotic therapy with breast
cleansing is more effective for relieving symptoms
quickly compared to only giving antibiotic therapy
(Kamal et al, 2012, Jahanfar et al, 2013).
Antibiotics have often used the treatment of
mastitis. The World Health Organization also says
the use of antibiotics is too excessive. But the
correct use of antibiotics is also a wise treatment of
mastitis. Ask for non-pharmacological assistance in
mastitis such as giving a hot compress to the breast
to help relieve swelling and pain, Allow breast milk
to reduce swelling (Yu Z et al., 2018).
Scaevola taccada (Geartn.) Roxb. is a species of
plant that lives in coastal shrubs scattered throughout
the coastal regions of the Pacific Ocean and Hindia
(Ando et al., 2014). In general, Scaevola taccada
(Geartn.) Roxb. has been used by the community as
traditional medicine, among others, it is used for the
treatment of digestive problems, anti-tumor, anti-
inflammatory, menstrual complaints, ringworm,
dysentery, syphilis, beriberi and others (Chandran
and Arunachalam, 2015).
Phytochemical screening is conducted to
determine the content of any secondary metabolites
contained in these plants. From the results of
phytochemical screening, it can be concluded that
what compounds can provide anti-inflammatory
activity. As screening results of phytochemicals that
have been carried out at UIN Makasar
pharmaceutical biology laboratory toward Scaevola
taccada (Geartn.) Roxb. plant, there are flavonoid
compounds, alkaloids, saponins, terpenoids, and
tannins. It is in line with previous research that the
content of Scaevola taccada (Geartn.) Roxb. is an
alkaloid, flavonoid, Scaevola, and saponin (Rachmat
Kosman, 2012) (Chandran and Arunachalam, 2015).
Traditional medicinal plants have enormous
potential as the development of antimicrobial drugs.
Many studies have described the antibacterial
properties of traditional medicinal plant extracts
isolated from traditional medicinal plants (Ilanko
and Cock, 2019).
The Scaevola taccada plant is a large shrub,
reaching 3-4 meters long which is typical in coastal
areas where it grows very close to a splash of open
seawater, usually on sandy soil or graveled soils.
The leaves widen upwards containing water
measuring 20 cm long and surrounded by bunches of
edges. The color is yellowish-green and shiny, the
edges are curved and the leaf surface is waxy. It
looks attractive with a yellowish-green color. The
fruits and flowers are white. Scaevola taccada
blooms throughout the year and the flowers have a
pleasant shape so they are called pleasure flowers or
beak flowers. The fruit floats in the sea and is spread
by ocean waves, this shrub becomes a new
pioneering plant on the sand edge of tropical waters
(Whiffin, et al. 2010, Chandran, et al. 2013).
Figure 5: The Scaevola Taccada Plant
One of Scaevola taccada (Geartn.) Roxb. extract
content is a flavonoid compound. Various
nutraceutical applications, pharmaceuticals,
cosmetic medicines use flavonoids as indispensable
components. This is due to the anti-inflammatory,
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
608

antimutagenic and anti-carcinogenic properties
contained therein to modulate the function of the
cellular enzyme kuci (Panche, Diwan, and Chandra,
2016).
Products produced from arachidonic acid
metabolism are one of the inflammation causes.
Through phospholipase, cells have been activated by
mechanical, chemical, or physical stimuli which as a
way to release arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is
also an unsaturated fatty acid with 20 carbon atoms.
There are two main pathways in the metabolic
process of arachidonic acid, namely cyclooxygenase
by synthesizing prostaglandins as well as
thromboxane and lipoxygenase which synthesize
leukotriene and lipoxin (Arfan, 2016).
In particular, the flavonoid content is also able to
stop the formation and release substances that cause
inflammation due to allergic reactions. The
compounds included in the flavonoid group have
different effects on inflammation. Anti-
inflammatory mechanism carried out by flavonoids
can go through several pathways, namely inhibiting
the activity of COX enzyme and lipoxygenase
directly which causes inhibition of prostaglandin and
leukotriene biosynthesis which is the final product of
COX and lipoxygenase pathways (Nijveldt RJ, Nood
EV, Hoorn DEV, Boelens PG, Norren KV, 2001)
(Panche, Diwan and Chandra, 2016).
Previous research that said that the anti-
inflammatory effect of Scaevola taccada (Geartn.)
Roxb. extract was evaluated using various methods
by using mice experimental animals. The results
support traditional Scaevola taccada (Geartn.) Roxb.
plant usage in several inflammatory conditions
(Mejin, 2009) (Chandran and Arunachalam, 2015)
(Rachmat Kosman, 2012) (Rahmawati et al., 2014)
(Umrah, 2018).
Complementary therapy of saponin compounds
can modulate the immune system that mediated by
cell systems to increase antibody production.
Saponin does not only has a stimulating effect on
certain components of immunity but also it affects
several non-specific immune reactions such as
inflammation, as well as tannin compounds that
function as antibacterial (Iqbal et al., 2007).
Thus the presence of complementary therapy of
Scaevola taccada (Gaertn.) Roxb. extract) can help
heal inflammation caused by staphylococcus aureus
bacteria at a dose of 400 mg/kg bb.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results and discussion, it can be
concluded that the administration of amoxicillin and
Scaevola taccada (Gaertn.) Roxb. extracts are better
able to reduce inflammation cells in female
mammary mammals induced by staphylococcus
aureus at dose of 400 mg/kg bb compared to groups
that are only given amoxicillin with mean deviation
of 37.6 /kg.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research was supported by Health Institute of
Deli Husada Deli Tua, Health Institute of Medistra
Lubuk Pakam, Sembiring Hospital Foundation, and
Grand Medistra Hospital Foundation. Indonesia
REFERENCES
R. et al. 2014. Test of Antioxidant Activity Leaves of
Scaevola Taccada (Gaertn.) Roxb. Using Dpph (1, 1-
Diphenyl-2-Picrylhydrazyl), International Research
Journal of Pharmacy, 5(3), pp. 159–162. doi:
10.7897/2230-8407.050333.
Ando, H. et al. .2014. Development of Microsatellite
Markers for the Coastal Shrub Scaevola taccada
(Goodeniaceae), Applications in Plant Sciences, 2(5),
p. 1300094.doi: 10.3732/apps.1300094.
Cheng, W. N., Jeong, C. H., Seo, H. G., & Han, S. G.
.2019. Moringa Extract Attenuates Inflammatory
Responses and Increases Gene Expression of Casein in
Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells. Animals : an open
access journal from MDPI, 9(7), 391.
doi:10.3390/ani9070391
Chandran, A. and Arunachalam, G. 2015. Evaluation of In
vivo Anticancer Activity of Scaevola taccada Roxb
against Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma in Swiss Albino
Mice. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and
Research 7(9), pp. 626–632.
Chandran A,. & G. Arunahalam. 2013. Study Of Anti-
Inflammatory Activity Of Scaevola Taccada Roxb
Extracts. International Journal Of Phytoparmacology
2013. E-ISSN 0975-9328
Chen, F. et al. 2014. Role of sortase A in the pathogenesis
of Staphylococcus aureus -induced mastitis in mice,
351, pp. 95–103.doi: 10.1111/1574-6968.12354.
Cheng et al. 2019. Moringa Extract Attenuates
Inflammatory Responses and Increases Gene
Expression of Casein in Bovine Mammary Epithelial
Cells, Animals, 9(7), p. 391. doi: 10.3390/ani9070391.
Contreras, G. A. and Rodríguez, J. M. 2017. Mastitis :
Comparative Etiology and Epidemiology. J Mammary
The Mammary Histopathology Depiction of Female Mice Induced by Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteria after Scaevola Taccada Extract
Administration
609

Gland Biol Neoplasia. (September 2011). doi:
10.1007/s10911-011-9234-0.
Diana M. Bond. Jonathan M. Morris, and Natasha
Nassar.2017. Study protocol: evaluation of the
probiotic . Lactobacillus Fermentum CECT5716 for
the prevention of mastitis in breasfeeding women: a
rendomised controlled trial.,Bond et al. BmC
Pregnancy and Childbirth.17:148
Essien, A. Di.et al. 2017. Antimicrobial and toxicological
evaluation of ethanol leaf extract of Salacia
lehmbachii’, Interdisciplinary Toxicology, 10(4), pp.
163–167. doi: 10.1515/intox-2017-0023.
Ganesh, S. et al. 2014. A review on some plants having
anti-inflammatory activity, The Journal of
Phytopharmacology, 3(3), pp. 214–221. Available at:
www.phytopharmajournal.com.
Habib, F. et al. 2015. Morphological and Cultural
Characterization of Staphylococcus Aureus Isolated
from Different Animal Species. Journal of Applied
Environmental and Biological Sciences, 5(2), pp. 15–
26.Availableat:https://www.researchgate.net/publicati
on/273778041_Morphological_and_Cultural_Characte
rization_of_Staphylococcus_Aureus_Isolated_from_D
ifferent_Animal_Species.
Ilanko, A. and Cock, I. E. 2019. The interactive
antimicrobial activity of conventional antibiotics and
Petalostigma spp. extracts against bacterial triggers of
some autoimmune inflammatory diseases,
Pharmacognosy Journal, 11(2), pp. 292–309. doi:
10.5530/pj.2019.11.45.
IDAI. 2013. Mastitis : Pencegahan dan Penanganan,
Indonesian Pediatric Society, Jakarta. Www.
Idai.Or.Id
Iqbal, R. Z. et al. 2007. Adjuvant effects of saponins on
animal immune responses. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B,
8(3), pp. 153–161.doi: 10.1631/jzus.2007.B0153.
Jahanfar S Et.Al. .2013. Antibiotics For Mastitis In
Breastfee Antibiotics For Mastitis In Breastfeeding
Women (Review). Cochrane Library.
Kamal, Et. Al. 2012. Management Of Lactational Mastitis
And Breast Abscesses; Review Of Current Knowladge
And Practice. Review Article.
Mejin, M. .2009. Isolation , Structural Elucidation and
Antibacterial Activity of the Chemical Constituents of
Scaevola Spinesces, A Thesis submitted to the
University of Adalaide in Fulfillment of the
Requirement for The Degree of Master of Science
5005.
Tristanti I, Nasriyah. 2019. Mastitis (Literaur Review).
Jurnal Ilmu Keperawatan dan Kebidanan Vol 10 No 2
Hal. 330-337
Nijveldt RJ, Nood EV, Hoorn DEV, Boelens PG, Norren
KV, L. P. 2001. Flavonoids: a Review of Probable
Mechanisms of Action and Potential Applications, Am
J Clin Nutr, 74(4), p. 418.
Panche, A. N., Diwan, A. D. and Chandra, S. R. 2016.
Flavonoids: an overview, Journal of Nutritional
Science, 5. doi: 10.1017/jns.2016.41.
Rachmat Kosman, K. T. 2012. Isolasi dan Identifikasi
Golongan Senyawa Kimia Fraksi Dietil Eter Daun
Beruwas Laut (Scaevola taccada (Gaertn.)Roxb) Asal
Kabupaten Pinrang (Sulawesi Selatan), 4(2), pp. 219–
227.
Review, L. and Scavola, O. F. 2017. World Journal of
Pharmaceutical Research, 6(11), pp. 251–258. doi:
10.20959/wjpr201711-9578.
Sitti Amirah Rahmawati, Safriani Rahman, F. A. 2014. Uji
Efek Antiinflamasi Ekstrak N-Heksan Daun Beruwas
Laut (Scaevola Taccada (Gaertn.) Roxb) Pada Mencit
Jantan (Mus Musculus) Yang Diinduksi Dengan
Karagen Sitti, as-Syifaa, 6(2), pp. 198–205.
Suriati, I., Mardiana, A.,Nurul, A. S., Prihantono. 2019.
The Effect Of Pagoda Leaf Extract (Clerodendrum
Paniculatum L) On The IL-10 Level In Mammae Of
Female Rats Strain (Sprague Dawley) Induced With
Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteria. Qanun Medika
Jurnal Kedokteran FK UM Surabaya.Vol 3, No 1.
Suthiwong, J., Thongsri, Y. and Yenjai, C. 2016. A new
furanocoumarin from the fruits of Scaevola taccada
and antifungal activity against Pythium insidiosum’
Natural Product Research, 6419(May). doi:
10.1080/14786419.2016.1188100.
Tong, S. Y. C. et al. 2015. Staphylococcus aureus
Infections : Epidemiology , Pathophysiology , Clinical
Manifestations , and Management, Clin Microbiol Rev
28(3), pp. 603–661. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00134-14.
Umrah, A. S. 2018. The Effectiveness of Scaevola tacada
Extract (Gaertn roxb) on the Level of Cytokine IL-10
of Strain Sprague dawly (Female Laboratory Rats)
Induced by the Staphylococcus Aureus Bactera’,
Qanun Medika - Medical Journal Faculty of Medicine
Muhammadiyah Surabaya, 2(2). doi:
10.30651/jqm.v2i2.1732.
Willianto, H. C. and Wijayahadi, N. 2016. Pengaruh
Pemberian Ramuan Ekstrak Produk X Sebagai
Analgesik Pada Mencit, Jurnal Kedokteran
Diponegoro, 5(4), pp. 972–981.
Whiffin V. S., Van Paassen L. A., Harkes M. P. .2007..
Microbial Carbonate Precipitation As A Soil
Improvement Technique. Geomicrobiol. J. 24, 417–
423.10.1080/01490450701436505
Yagdiran, Y. et al. 2016. Staphylococcus aureus and
Lipopolysaccharide Modulate Gene Expressions of
Drug Transporters in Mouse Mammary Epithelial
Cells Correlation to Inflammatory Biomarkers. The
PLOS ONE pp. 1–16.doi:
10.1371/journal.pone.0161346.
Yu Z. et Al.2018. High_Risk Factors for Suppurative
Mastitis in Lactating Women, Med sci Monit:
24:4192-4197
ICHIMAT 2019 - International Conference on Health Informatics and Medical Application Technology
610
