
Infusion of e-Procurement at Indonesian Local Government
Willy Abdillah
1
and Desiana Rosman
2
1
Lecturer at Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Bengkulu, Indonesia
2
Student of Magister Management Program, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Bengkulu, Indonesia
Keywords: Problem-focus adaptation, emotion-focus adaptation, IS infusion, e-procurement (SPSE), and local government.
Abstract: This study examines information system (IS) Infusion Model of e-Procurement at City Government of
Bengkulu. This study uses 68 e-Procurement's users distributed by self-administered questionnaire. Data
examined using Partial Least Square (PLS) technique. The results show that the opportunity appraisal, threat
appraisal, and secondary appraisal have an important role in improving problem-focused adaptation and
emotional-focused adaptation. However, only opportunity appraisals have an important role in promoting
problem-focused adaptation. Also, only problem-focused adaptation predict IS infusion. Implication for
stakeholder and further research are discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
E-government system has several advantages in
implementing transparent, efficient and effective public
services. Government-based information technology
(IT) system, can provide affordable services and
expand access information easily for community. One
of the Indonesian government's efforts to create public
transparency is President Instruction (Inpres) No.
3/2003 about Policies and National Strategies
Development of e-Government. The real example of e-
government is e-procurement.
Implementation of e-procurement begins with the
issuance of Presidential Regulation No. 106/2007
about the Establishment of Government Procurement
Policy Institution (LKPP) who develops and
formulates government procurement policies. The
concrete manifestation of such good practice is the
Regulation of LKPP No. 2/2010 about Electronic
Procurement Services which conveys that Local
Government shall establish an e-Procurement system
(LPSE) to facilitate Procurement Officer (ULP) in
implementing electronic procurement.
Moreover, the high corruption cases around goods
and services procurement (PBJ) of government
institutions motivate the importance of e-procurement.
Indonesia Procurement Watch states that 70 percent of
corruption cases are sourced from the PBJ domain,
both at the central and regional levels. The variation
of cases are bribery, procurement of goods and
services in the state administration, misuse of
budgets and levies in public services, and licensing
and money laundering cases (Corruption Eradication
Commission [KPK], 2017) (see Table 1).
Table 1 . Data of Corruption Handling by Type of Case Year 2004-2017 (March 31, 2017)
Cases 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
Procurement 2 12 8 14 18 16 16 10 8 9 15 14 14 7
Licensing 0 0 5 1 3 1 0 0 0 3 5 1 1 1
Bribery 0 7 2 4 13 12 19 25 34 50 20 38 79 16
Charges 0 0 7 2 3 0 0 0 0 1 6 1 1 0
Misappropriation
of budget
0 0 5 3 10 8 5 4 3 0 4 2 1 1
Money
Laundering
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 7 5 1 3 2
Blocking the
KPK Process
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 3 0 0 0
Amount 2 19 27 24 47 37 40 39 49 70 58 57 99 27
Source: Anti Corruption Clearing House (ACCH)-KPK, May 30, 2017
Abdillah, W. and Rosman, D.
Infusion of e-Procurement at Indonesian Local Government.
DOI: 10.5220/0009948431353142
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2018), pages 3135-3142
ISBN: 978-989-758-458-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
3135

In addition, the results of the Indonesian Corruption
Watch (ICW) study with the Potential Fraud Analysis
(PFA) method, found the highest potential for fraud of
Local Governments are Bengkulu Province (15.4
points), South Sumatera (15.1 points), followed by
Central Kalimantan, North Kalimantan and Lampung
(www.pedomanbengkulu.com, 2017). Thus, it is
important to investigate e-procurement
implementation by Indonesian local government.
2 METHODS
Implementation of reliable e-procurement system must
fulfill six pillars, namely people, process, technology,
strategy, governance and organizational interface.
Unfortunately, the development of human resource
competencies at Indonesia Local Government is not as
extensive as technology and rules (KPK, 2017). Then,
the digital divide issues becomes main challenge in the
infusion of e-procurement (Nightisabha, 2010), such as
unwished IS usage (Jogiyanto and Abdillah, 2011).
Therefore, it needs guidance in using IS, such as
ability to adapt an IT events (Tyre and Orlikowski,
1994; Orlikowski, 1996; Beaudry and Pinsonneault,
2005; Fadel, 2012). Coping Theory is a relevant
concept to explain user behavior and adaptation
outcomes. The conceptual model called coping models
of user adaptation or CMUA (Beaudry and
Pinsonneault, 2005; Lazarus and Folkman, 1984).
Previous empirical studies have examined the
CMUA model (Fadel, 2012; Sigalotang et al., 2014;
Astriana et al. study, 2015). However, there are limited
studies to examine CMUA model in context of local
government institution. Thus, CMUA model are
relevant to re-examined in the context of the use of
similar mandatory systems, such as in e-procurement
systems. This study examines the CMUA model in the
context of e-procurement system at Indonesian local
government institution.
The fundamental premise of CMUA is the
introduction of a technology or a modification of an
existing technology that can bring perceived new
changes (Louis and Sutton, 1991) and improve
disturbances in organizations (Lyytinen and Rose,
2003). By defining user adaptation as a coping
problem, it can be learned various kinds of user
responses including how users can restore emotional
stability, modify tasks, reinvest, and adapt technology,
or even reject it.
The process of coping can be done through two
processes that constantly affects each others (Lazarus
and Folkman, 1984). Both processes include process of
assessing the consequences of an event that will result
in a primary appraisal. Furthermore, individuals will
take different actions to address the situation based on
the results of the appraisal, called coping efforts.
Individuals will combine cognitive and behavioral
efforts, both of which are also categorized as problem-
focused or emotion-focused (Folkman, 1992; Lazarus
and Folkman, 1984; Stone, et al., 1992).
Opportunity appraisal is an appraisal of perceived
IT events to have positive consequences. While
problem-focused adaptation is directed to handle
issues related to IT activities directly by adapting
themselves, adapting their work, and adapting the
technology. Furthermore, emotional-focused
adaptations are oriented towards oneself and lead to
a change in one's perceptions resulting from the
consequences of an IT event or to reduce emotional
tension.
The CMUA model concludes that an IT event
assessed as an opportunity tends to effect on
problem-focused adaptation and emotional-focused
adaptation behavior (Beaudry and Pinsonneault,
2005). Primary appraisal is a situation where the
consequences perceived from technological event
information rated as an opportunity, effects on
benefits satisficing, which is the less adaptation
problem-focused efforts were minimal and limited
(Lazarus and Folkman, 1984). Challenge appraisal
which is also a characteristic of positive judgment
has a significant effect on problem-focused and
emotion-focused adaptation (Fadel, 2012). Thus,
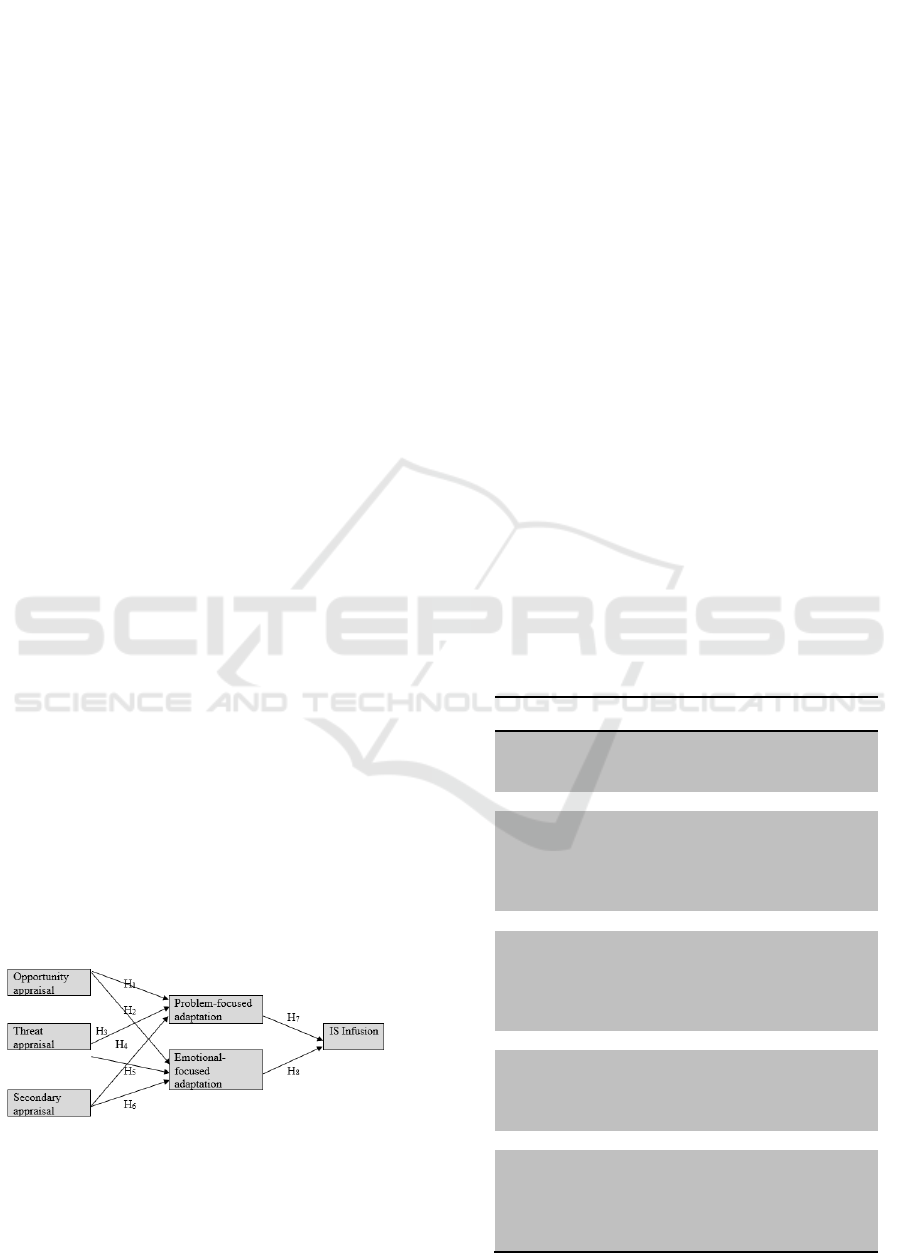
hypothesis 1 and hypothesis 2 are as follows:
H1 : Opportunity appraisal has a positive effect
on problem-focused adaptation.
H2 : Opportunity appraisal has a positive effect
on emotional-focused adaptation.
Threat appraisal is an appraisal of IT events
that are perceived to have negative consequences.
Based on the CMUA model, Beaudry and
Pinsonneault (2005) also concluded that when
individuals assess the event of IT as a threat, their
efforts will be largely oriented to reduce emotional
distress and reduce the perceived negative
consequences associated with the event. Thus, this
research formulates hypothesis 3 and hypothesis 4 as
follows:
H3 : Threat appraisal has negative effect on
problem-focused adaptation.
H4 : Threat appraisal has positive effect on
emotional-focused adaptation.
Secondary Appraisal is user appraisal on how
much control they have on IT event options for their
adaptation to the specific resources available to
them. In Coping's study, it shows that problem-
focused adaptation attempts to effect when an
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
3136
individual feels that he or she can do something to
change his or her situation, while emotionally-
focused adaptation has shown an effect when
individual feel he or she has little or no control
(Beaudry and Pinsonneault, 2005). This is what
underlies hypothesis 5 and hypothesis 6 proposed as
follows:
H5 : Secondary appraisal has positive effect on
problem-focused adaptation.
H6 : Secondary appraisal has negative effect on
emotional-focused adaptation.
Problem-focused adaptation is directed to address
issues related to IT events by adapting themselves,
their work, and IT. CMUA model predicts users
with problem-focused adaptations will more easily
achieve effective and efficient results in IS
utilization. The empirical results by Fadel (2012)
support the model and find problem-focused
adaptation behavior to be a single strong predictor of
IS infusion. This is in line with the empirical results
by Sigalotang, et al. (2014) which found a
significant positive effect problem-focused
adaptation on IS infusion. Thus, this research
proposes hypothesis 7 as follows.
H7 : Problem-Focused adaptation effects IS
infusion.
Emotionally-focused adaptation orients toward
individual itself and leads to changes in one's
perception as a result of the consequences of the IT
event to reduce emotional tension. Emotion-focused
adaptations minimize consequences of IT events,
selective attention, positive comparisons (Lazarus
and Folkman, 1984), and passive acceptance (Tyre
and Orlikowski, 1994). Empirical results of
Sigalotang, et al. (2014) found positive effect of
emotional-focused adaptation on IS infusion. Thus,
hypothesis 8 is formulated as follows.
H8 : Emotionally-focused adaptation has
positive effect on IS infusion.
Figure 1 presents the proposed model tested in this
study.
Figure 1 . Research model (Source:Adapted from Beaudry
and Pinsonneault (2005), Fadel (2011), Fadel (2012) and
Astriana, et al. (2015))
3 METHODS
This research is quantitative with survey
questionnaire as the instrument of data collection.
All constructs measured using 5 Likert scales from
strongly disagree to strongly agree. The population is e-
procurement users of City Government of Bengkulu
Province, which are The Committee Procurement and
Vendors. All of vendors were selected as sample.
Primary data collected by self-administered
questionnaires during January-May 2018. All data were
tested using the Partial Least Square (PLS) method.
Testing phase consists of evaluation of measurement
model for construct validity and reliability, and
evaluation of structural model for hypothesis testing.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
68 Respondents in this study are individuals who are
active users of SPSE or who use the e-procurement
application of LPSE Bengkulu City Government
who served as a procurement committee of goods
and services or members of the working group
Procurement Unit (ULP) and winner vendor in e-
tendering of Bengkulu City Government Year
Budget 2017.
Table 2. The Characteristics of Respondents
Category Number of
Respondents
Percentage
(%)
Gender
Male
Female
54
14
79
21
Number of Respondents 68 100
Last education
High Education
Diploma
Undergraduate
Postgraduate
9
3
50
6
13
4
74
9
Number of Respondents 68 100
Age
25-30 Years
31-35 Years
36-40 Years
> 40 Years
12
20
13
23
18
29
19
34
Number of Respondents 68 100
Position
The working group of the
procurement services unit
(ULP)
Vendor of goods/services
17
51
25
75
Number of Respondents 68 100
Period of using SPSE
< 1 Year
1-3 Years
4-6 Years
> 6 Years
3
21
31
13
4
31
46
19
Infusion of e-Procurement at Indonesian Local Government
3137

Number of Respondents 68 100
Conduct SPSE Socialization
Yes
Never
57
11
84
16
Number of Respondents 68 100
Frequency of SPSE
Socialization
1x
> 1x
49
19
67
33
Number of Respondents 68 100
Source: Own elaboration, 2018
Based on Table 2, it can be seen that the
respondents are mostly male. This indicates that the
heavy workload and pressure of various parties in the
scope of work of the procurement process of
government goods and services require the respondents
to have a high intensity that causes women often feel
reluctant for a career in the procurement of government
goods and services. Also, this condition is caused by
the characteristics of work are more technical that
requires more technical capabilities owned by men.
Respondent's education indicates that the
respondent who is responsible for the operation of
SPSE application has adequate formal education.
Education is closely related to the abilities and skills
possessed by the respondent as a stock to be able to run
the job well. While the age of respondents shows the
majority of respondents in the productive age category
so that the respondents tendency more familiar and
responsive to new technology.
The use of SPSE shows that most of the
respondents have long worked as procurement
committee or vendor so that there is enough experience
level in SPSE context. This is also supported by the
majority of respondents (84%) have followed the
socialization, although the majority only one time.
Measurement Model Results
Measurement model is used to test the validity of the
construct and the reliability of the research instrument
(Abdillah and Jogiyanto, 2015).
Table 3. Output of Measurement Model
Variables AVE Composite
Reliability
R-Square
Emotional-
Focused
Adaptation
0,614 0,889 0,461
Problem-Focused
Adaptation
0,700 0,845 0,362
IS Infusion 0,702 0,823 0,217
Threat Appraisal 0,525 0,921
Opportunity
Appraisal
0,582 0,864
Secondary
Appraisal
0,618 0,874
Source: SmartPLS Output, own elaboration, 2018
After elimination of the PK1, PS4, AM6, AM7,
AE1, AE3, AE4, AE5, AE7, AE3, AE4, AE5, AE5,
AE7, AE3, and IS3 indicators, all variables have
sufficient convergent validity (see Table 3).
Table 4. Cross Value Indicators with Constructions in Model
Indicator Emotional-
Focused
Adaptation
Problem-
Focused
Adaptation
IS
Infusion
Threat
Appraisal
Opportunity
Appraisal
Secondary
Appraisal
AE10 0.914 0.049 -0.124 0.586 -0,227 -0.352
AE12 0.690 0.006 -0.096 0.537 -0.155 -0,019
AE2 0.572 0.248 0.029 0.407 -0,095 -0.153
AE6
0.538 0.124 0.084 0.221 0.055 -0.164
AE8 0.864 0.037 0.078 0.427 -0,053 -0.154
AE9
0.903 0.211 0.124 0.511 0.004 -0,251
AM1 -0.038 0.614 0.185 0.059 0.404 -0.024
AM2 0.049
0.799 0.353 0.061 0.486 0.237
AM3 0.202 0.760 0.371 0.063 0.309 0.096
AM4 0.185
0.774 0.295 0.042 0.301 0.029
AM5 0.125 0.657 0.431 -0,055 0.438 0.060
IS1 0.016 0,500
0.910 -0,170 0.570 0.208
IS2 -0,026 0.319 0.851 -0.179 0.583 0.309
IS4 0.063 0.141
0.549 0.024 0.345 0.339
PA1 0.591 0.095 -0,040 0.843 -0.260 0.082
PA2 0.340 0.075 -0.069
0.705 -0.291 0.150
PA3 0.465 0.028 -0.177 0.870 -0,230 -0.002
PA4 0.555 0.162 -0.105
0.897 -0.192 -0.109
PA5 0.537 -0.184 -0.338 0.856 -0.370 -0.123
PK2 -0.039 0.449 0.558 -0.261
0.804 0.263
PK3 -0.152 0.460 0.493 -0.207 0.804 0.317
PK4 0.003 0.424 0.587 -0,300
0.805 0.338
PK5 -0.177 0.381 0.387 -0,227 0.718 0.131
PS1 -0.148 0.105 0.482 -0,057 0.425
0.699
PS2 -0.298 0.116 0.137 -0.006 0.207 0.938
PS3 -0.097 0.068 0.283 0.048 0.299
0.858
Source: SmartPLS Output , own elaboration, 2018
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
3138

Table 4 shows that all values of cross-loading
indicators are higher in constructs than cross loading in
other constructs. It can be concluded that the model has
sufficient discriminant validity. Additionally to
construct validity test, validation of measurement
model, reliability testing is done by Composite
reliability method. The results in Table 3 show that all
constructs are reliable with the criterion of reliability
test value> 0.7.
Structural Model Results
Hypothesis testing in this study using inner model with
95% confidence level and error analysis (α) = 5%. The
test was performed using bootstrapping method in
SmartPLS 3.2.7 software to obtain path coefficients
(β). Based on the coefficient value of each path in
Table 5, four hypotheses are accepted.
Table 5. Structural Model Results
Path Original
Sample
T-
Statistics
P
Value
Conclusion
PK AM 0,661 6,209 0,000 Accepted
PK AE 0,198 1,043 0,298 Rejected
PA AM 0,251 1,656 0,098 Rejected
PA AE 0,667 2,605 0,009 Accepted
PS AM -0,099 0,657 0,511 Rejected
PS AE -0,312 2,302 0,022 Accepted
AM IS 0,471 4,611 0,000 Accepted
AE IS -0,057 0,346 0,729 Rejected
Source: SmartPLS Output , Data Processing, 2017
This study found that opportunity appraisal
positively affects the problem-focused adaptation. This
finding indicates that the ability of the SPSE system to
provide positive consequences, such as supporting user
tasks. Internet-based SPSE system causes faster process
and delivery of information in the form of aanwijzing
media and online clarification can be accelerating
response to questions and clarification
of auctions.
SPSE placement also reduces user and vendor fees for
goods or services because the auction requirement of
hard copy is only requested to the winner at the end of
the auction process.
According to CMUA, users are first involved in a
primary appraisal when users assess whether an IT
event is an opportunity or a threat. IS becomes an
opportunity appraisal arising from belief that the IS will
bring positive consequences (Beaudry and
Pinsonneault, 2005). If users view the IS positively,
then the users will conduct an adaptive behavior
attempt to deal with the situation, by anticipating the
need to learn new skills, overcoming difficulties, and
adapt to working procedures.
Adaptive users behavior to face situation due to the
implementation of this SPSE system is a problem-
focused adaptation effort. The problem-focused
adaptation behavior aims to manage disturbing events
by altering the external aspects of situations such as
environmental stress, constraints, resources, or
procedures (Lazarus and Folkman, 1984). Efforts made
procurement committee and vendor transform external
aspects of situation due to SPSE implementation to
realize user’s expected benefits of IS, for example,
attempts to change work adapted habits to the
procedures that must be done in following e-
procurement. Thus this problem-focused adaptation
behavior can lead actions to improve efficiency and
effectiveness in using IS, which tend to affect the user's
performance positively.
The result also show that no positive effect of
opportunity appraisal on emotion-focused adaptation.
This result indicates that users who evaluate a positive
SPSE will not require drastic adaptive responses, such
as less engagement either restoring emotional stability
or altering the environment. Emotion-focused
adaptation behavior is carried out through positive
reappraisal by means of users having to accept the
SPSE system as an opportunity to gain a better profit
when compared to the manual system. User adaptation
efforts are directed at restoring to emotional stability
and reducing the tensions caused by IT events, tending
to ask for social support from spouses or family
members. This situation indicates that users have
limited control of SPSE as mandatory system, with less
choice and necessity to understand procedures in
operating SPSE electronically. Otherwise, users are
less likely to agree with the consequences of
implementing the SPSE system and reduce their
involvement in work.
This result does not support Coping Theory
(Lazarus and Folkman, 1984; Fadel, 2012).
Combination of problems and effort to cope with user’s
emotions depends on the appraisal of the situation due
to the implementation of the SPSE. Logically,
positively assessed events are more likely to require
problem-focused adaptation rather than emotional-
focused adaptations because there is no threat to
emotional stability. These results indicate that SPSE’s
rating system does not affect emotional-focused
adaptations, which mean that if the system are
qualified, then users will use the system continuously
(Seddon and Kiew, 1996). Referring to that opinion, it
is very important to maintain and improve the quality
of SPSE so that users are not reluctant to interact with
SPSE. Thus it is expected that improvements made to
the quality of the SPSE will be able to improve
emotionally focused adaptation users of SPSE System.
Infusion of e-Procurement at Indonesian Local Government
3139

This research also found threat opportunity has
no effect on problem-focus adaptation. It indicates
that average users are productive, experienced and
have participated in SPSE socialization. This means
that the capabilities of the SPSE users will be able to
overcome the perceived negative consequences
associated with IT events. However, a problem-
focused adaptation can address issues related to IT
activities directly, such as developing new standards
of behavior, increasing interest in using IT, and
seeking training for self-improvement.
According to Fadel and Brown (2010), threat
perceptions are strongly influenced by the extent to
which users perceive IS to be difficult to use. This
means that LPSE can reduce threat perception by
ensuring support to help users to cope with IS
problems. In addition, it should periodically monitor
system and coordinate with developers in Central
LKPP to anticipate the existence of anomalies and
various threats. It is thus expected that efforts to
overcome difficulties in the use of the SPSE system
will affect problem-focused adaptation efforts.
The study also found a threat appraisal has a
positive effect on emotion-focused adaptation. User’s
perceived SPSE has several advantages in the process
of procurement such as ease of use, save the cost of
procurement administration and cost of use of
consumables (e.g. stationery), and speed up the
procurement process. However, users also feel the
application of the SPSE system as a threat when certain
parties want to take advantage of the SPSE system for a
particular interest. Therefore, LPSE should fostere
employees’s responsibilities for managing the SPSE
through clear procedures of recruitment, transfer and
dismissal, training, and paying attention to unsatisfied
employees with the organization which may lead to
negative actions.
This study also found that secondary appraisal had
no positive effect on the problem-focused adaptation.
It indicates that users generally had sufficient IT
capabilities but insufficient ability to perform tasks
related to electronic auctions, starting from registration,
procurement documents, and uploading bidding
documents. This finding also indicates users have job
autonomy in but less control on technology features
and functions of e-procurement as mandatory
system.
Furthermore, this study found a negative effect of
secondary appraisal on emotional-focused adaptation.
Procurement committees and vendor are not able to
deny the existence of a dilemma in the procurement
process that will affect their emotions. Thus, bidding in
the auction must be ensured in accordance with
requirements as outlined in the auction document as a
specification or technical requirement. In order to
achieve these objectives, it must be ensured that the
vendor will be able to complete the work according to
the contract, such as vendors should have appropriate
experience, financial and personnel capabilities
adequate, so that work can be done according to the
contract. Both technical requirements and qualification
requirements must be equally fulfilled.
Furthermore, this study found that problem-focused
adaptation has positive effect on IS infusion. It
indicates that users maturity level (e.g. experience) are
considered as capability in managing disturbing events
due to SPSE implementation by changing the external
aspects, such as environmental stresses, obstacles,
resources, or procedures. This finding supports
Coping Theory which shows the form of user
adaptation as a problem-solving in response to
disturbing events occurring in the environment
(Lazarus and Folkman, 1984). The CMUA model
predicts users who have problem-focused adaptations
will more easily achieve effective and efficient results
on deep system utilization.
Finally, this study found that emotion-focused
adaptation has no effect on IS infusion. It indicates that
even though users perceive dissatisfied regarding to
technically disadvantage of e-procurement as
mandatory system, users are quite capable to adapt the
IT events consequences by attempting to reduce
emotional tensions. User initiates efforts by soliciting
moral support from colleagues, family members and
superiors, further motivating oneself with positive
thinking towards e-procurement (Davis, 1989). Thus, it
is important to improve user’s perceived benefits of e-
procurement by increasing user’s emotion-focused
adaptation.
5 CONCLUSION
This study found that opportunity appraisal, threat
appraisal, and secondary appraisal have an important
role in improving problem-focused adaptation and
emotional-focused adaptation. However, only
opportunity appraisal has an important role in
improving problem-focused adaptation. Furthermore,
both problems-focused and emotion-focused adaptation
play important role in increasing IS infusion. Problem-
focused adaptation is the most dominant variable in
influencing IS infusion. These findings are meaningful
when problem-focused adaptation and emotion-focused
adaptation improved, it will increase e-procurement
infusion. Theoretically, this study confirms the role of
the CMUA model and Coping Theory in explaining the
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
3140

IS infusion process in the context of local government
organizations.
Practically, these findings underscore the need
for stakeholders to continuously develop user
capabilities (problem-focus adaptation) for handling
technical disturbances and optimize organizational
control through separation of duties and
responsibilities. Also, regarding to security issues,
Local governments should involve users in IS
development process due to improve users’s ownership
and provide sufficient job autonomy.
Methodologically, further researches need to be
expand generalization in the context of other
Government agencies, such as ministries and
Institutions. Also, nonprobabilistic sampling need to be
deepen the research context by exploring the research
subjects better.
REFERENCES
Abdillah, Willy & Jogiyanto, HM (2015). Partial Least
Square (PLS): Alternative Structural Equation
Modeling (SEM) in Business Research . Yogyakarta:
CV Andi Offset (Andi Publisher).
Anti-Corruption Clearing House (ACCH) KPK (2017,
May 30). Retrieved from
http://acch.kpk.go.id/id/statistik/tindak-pidana-
korupsi/ .
Arumsari, Totok, Iswahyudi, Mucharor, & Akib. (2017,
September 12). Audit of Electronic Auction
Implementation in Procurement of Government Goods
and Services. Retrieved from
http://www.bpkp.go.id/investigation/berita/read/ 13521/0/
AUDIT-ON-IMPLEMENTATION-ELECTRONIC-
AUCTION-IN-PROCUREMENT-GOODS-AND-
GOVERNMENT SERVICES .
Astriana. (2015). Influence Appraisal of Infusion Accounting
IS Accrual Based Through User Adaptation Behavior at
State Administration Institution. Journal of State
Administration, Vol. 21, No. 2, Pg. 70-78.
Astriana, Pontoh, GT & Syamsuddin. (2015). Influence
Appraisal of Infusion Accounting IS Accrual Based
Through User Adaptation Behavior . National Seminar
on Indonesian IS (SESINDO) 2-3 November 2015 , p.
47-54.
Beaudry, A. & Pinsonneault, A. (2000). IT and Individual
Performance: A Coping Based Model of the
Appropriation Process. In Proceedings of ASACIFSAM ,
Canada, Page. 1-11.
Beaudry, A. & Pinsonneault, A. (2005). Understanding User
Responses to IT: A Coping Model of User Adaptation.
Journal of MIS Quarterly , Vol. 29, No. 3, Pg. 493-524.
Bengkulu Province Highest Potential Corruption
Procurement of Goods and Services. (2017, May 30).
Retrieved from
http://pedomanbengkulu.com/2017/05/provinsi
bengkulutertinggipotensi
korupsipengadaanbadandanjasa /.
Cooper, RB & Zmud, RW (1990). IT Implementation
Research: A Technological Diffusion Approach .
Management Science, Vol. 36, No. 2, Pg. 123-139.
Corruption Eradication Commission (KPK). (2017 , May 6 ).
6 Pillars of Building a Capable Procurement System.
Retrieved from
http://kpk.go.id/id/berita/bloggingactivities/16396veryupo
ningthewebsite.
Eder, LB & Igbaria, M. (2001). Determinants of Intranet
Diffusion and Infusion . Omega, Vol. 29, No. 3, Pg. 233-
242.
Electronic Procurement (SPSE) Version 4. (2017, September
12) . Retrieved from
http://www.pengadaan.web.id/2015/02/pengadaan-
secara-elektronik-spse-versi-4.html.
Fadel, KJ & Brown, SA (2010). ISs Appraisal and Coping:
The Role of User Perceptions. Communications of the
Association for ISs , p. 107-126.
Fadel, KJ (2011). User Adaptation and Infusion of ISs.
Journal of Computer ISs , Spring , Page. 1-10.
Fadel, KJ (2012). The Role of Appraisal in Adapting to
ISs. Journal of Organizational and End User
Computing , Page. 18-40.
Folkman, S. (1992). Making the Case for Coping, in
Personal Coping: Theory, Research, and Application .
BN Carpenter (Ed.), Praeger, Westport, CT, Page. 31-
46.
Folkman, S., & Lazarus, RS (1980). An Analysis of
Coping in a Middle-Aged Community Sample. Journal
Health Social Behavior , Vol. 21, p. 219-239.
Head Regulation of LKPP Electronic Procurement
Service, Number 2, (2010).
Head of LKPP Regulations E-Tendering Procedure,
Number 1, (2011).
Instruction of the President of the Republic of Indonesia
National Policies and Strategies for the Development
of E-Government, Number 3, (2003).
Instruction of the President of the Republic of Indonesia
Corruption Prevention and Eradication of 2012,
Number 17, (2011).
Jogiyanto, HM (2007). Behavioral IS (edition I).
Yogyakarta: CV. Andi Offset (Andi Publisher).
Jogiyanto, HM & Abdillah, Willy. (2011). IT Governance
System . Yogyakarta: CV. Andi Offset (Andi
Publisher).
Lazarus, RS & Folkman, S. (1984). Stress, Appraisal, and
Coping . New York: Springer Publishing Company.
Louis, MR, & Sutton, RI (1991). Switching Cognitive Gears:
From Habits of Mind to Active Thinking. Human
Relations , Vol. 44, p. 55-76.
LPSE Institute for Procurement of Goods and Services
(LPSE-LKPP). (2017, May 5). Retrieved from
https://lpse.lkpp.go.id/eproc4/publik/about us.
Lyytinen, K. & Rose, GM (2003). The Disruptive Nature of
IT Innovations: The Case of Internet Computing in
Systems Development Organizations. MIS Quarterly ,
Vol. 27, No. 4, Pg. 557-596.
Infusion of e-Procurement at Indonesian Local Government
3141

Nightisabha, IA (2010). Perception of Users of Procurement
of Goods/Services at City Government of Yogyakarta on
Implementation of E-Procurement System . Thesis of
Sebelas Maret University, Surakarta .
Orlikowski, WJ (1996). Improvising Organizational
Transformation Over Time: A Situated Change
Perspective . IS Research, Vol. 7, No. 1, Pg. 63-92.
Presidential Instruction of the Republic of Indonesia
Acceleration of Procurement of Goods and Services
(PBJ) through Electronic (E-Procurement), Number 1,
(2015).
Presidential Instruction of the Republic of Indonesia
Acceleration of the Implementation of National
Strategic Project, Number 1, (2016).
Regulation of the President of the Republic of Indonesia
Government Goods/Service Procurement Policies
Agency, Number 106, (2007).
Regulation of the President of the Republic of Indonesia
Procurement of Government Goods / Services, Number
54, (2010).
Regulation of the President of the Republic of Indonesia
Fourth Amendment of Presidential Regulation Number
54 Year 2010 concerning Procurement of Government
Goods / Services Number 04, (2015).
Seddon, PB & Kiew, MY (1996). A Partial Test and
Development of the DeLone and McLean Model of IS
Success. Australian Journal of IS , Vol. 4, No. 1, Pg.
90-109.
Sigalotang, WA, Pontoh, GT & Damayanti, RA (2014).
Infusion Mediation IS on the Influence of IS
Utilization on Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Users Performance . National Seminar on Accounting
17 Mataram, Lombok . .
Stone, AA, Kennedy-Moore, E., Newman, MG,
Greenberg, M. & Neale, JM (1992). Conceptual and
Methodological Issues in Current Coping Appraisals .
in Personal Coping: Theory, Research, and
Application, BN Carpenter (Ed.), Praeger, Westport,
CT, Page. 15-29.
Suwastika, P. (2017, May 6). E-Procurement Budget Savings.
Retrieved from http://ppm-manajemen.ac.id/blog/artikel-
manajemen-10/post/eprocurement-perhemat-budget-353 .
Tyre, MJ & Orlikowski, WJ ( 1994 ). Windows of
Opportunity: Temporal Patterns of Technological
Adaptation in Organizations . Organization Science , p.
98-118.
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
3142
