
Analysis of the Information System with Ward & Peppard
Method
f
or the Strate
g
ic Business Plan of the Colle
g
e
Lilik Sugiarto
1
and Widada
1
1
STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta, Veteran street, Notosuman, Singopuran, Kartasura, Sukoharjo, Central Java, Indonesia
Keywords: information, systems, analysis, strategy, bussines, plan, development.
Abstract: Every university has a vision of the mission to be achieved, one of the achievements of the vision is to
produce graduates in accordance with the vision and slogan of the college itself. The vision's benchmark
performance reflects the development strategy of information systems and information technology that
applies to the college itself. The development of information technology is based on the vision STMIK
Cipta Darma Surakarta. The basic idea that requires an analysis of information systems that can later be
used for the development of information systems STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta. The methods used to
analyze strategic information systems in this study are Ward & Peppard methods, SWOT analysis, value
chain analysis, PEST analysis and five-force model analysis. The results of the review will show strategic
business planning, information system and information technology strategy. Management strategy as one of
the components that support the achievement of the STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta..
1 INTRODUCTION
The role of information technology in education
today plays a very important role. The rapid
development of this technology requires that the
world of education always adapts to the evolution of
information technology to improve the quality and
the realization of the vision of every educational
world in college. Today, information technology has
changed the paradigm of society through the use of
information technology to easily perform all
activities anytime, anywhere, This is with the
support of both hardware and software tools and the
proliferation of providers or providers of Internet
services are becoming increasingly prevalent with
low costs.
The information system is now a part that cannot be
separated from the life of modern people. In the
current age of globalization, information systems
play an important role in various aspects of life.
Information systems have very positive effects on
many things, including: Assistance in decision-
making, increasing efficiency and productivity,
supporting work and learning activities, and even
improving people's quality of life. The role of
information systems will increase with the
development of the era and become the fundamental
element in life.
The role of information and communication
technology in the educational world is also huge,
especially in terms of supporting the teaching and
learning process and the efficiency of academic and
administrative jobs (Rahmawati, 2013). Universities
as one of the educational institutions should be able
to use information systems to support various
activities. The introduction of information systems at
universities will have a very positive impact and is
expected to result in high efficiency and productivity
in academic and administrative areas. In addition,
with the implementation and adaptation of
information systems, it is also expected that the
university will be able to continue to compete in the
arena of competition in the educational (Jogiyanto,
2006).
Information and communication technology
(ICT) has grown in line with the evolution of human
civilization, which works in all areas. STMIK Cipta
Darma Surakarta is one of the private universities in
the city of Surakarta. College Computer in JL
Veterans Notosuman Singopuran Kartasura has
played an active role in the use of information
systems and information technology for lectures and
learning activities and management of campus
operations. The STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta in
3036
Sugiarto, L. and Widada, .
Analysis of the Information System with Ward Peppard Method for the Strategic Business Plan of the College.
DOI: 10.5220/0009946330363042
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Recent Innovations (ICRI 2018), pages 3036-3042
ISBN: 978-989-758-458-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
the development of information technology has not
achieved its goals optimally, system strategy of IS /
IT, personnel and budget problem. This is reflected
in the non-integrated information system in each
academic service.
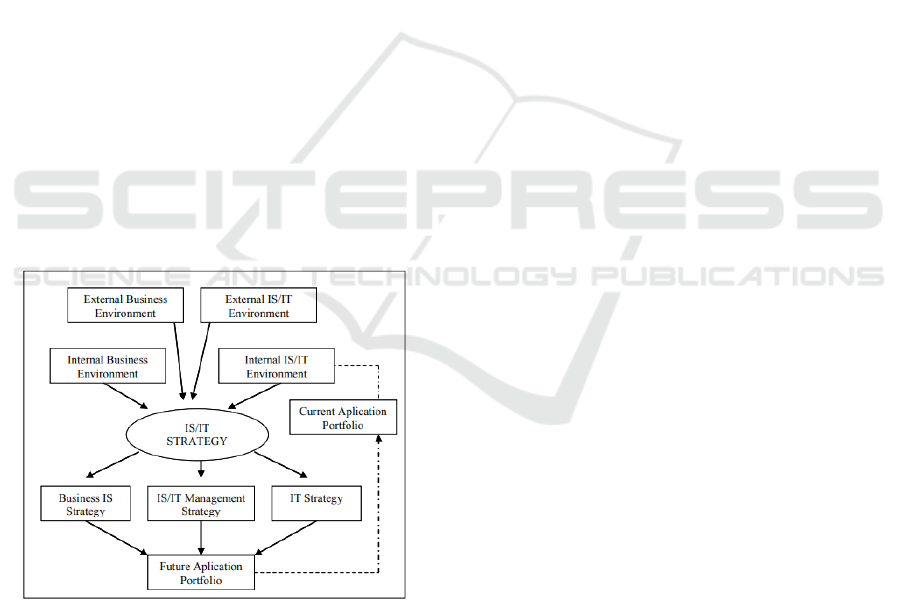
2 STRATEGIC PLANNING IS/IT
VERSION WARD & PEPPARD
2002
In this study, there are several phases of input,
analysis of the internal business environment,
analysis of the external business environment,
analysis of the internal IS / IT environment, analysis
of the external IS / IT environment. For the phases
IT Business Strategy, IT Strategy and Management
Strategy IS / IT uses different techniques / analysis
methods such as value chain analysis, SWOT
analysis, PEST analysis model, five-forces model
analysis and McFarlan Strategic Grid Analysis.
To conduct this study in need of data collection
through technology (observation, interview and
questionnaire), analysis of the business environment,
environment of IS / IT and IT / planning, and end
result, the information system is planned (Septiana,
2017; Setiawan and Ilman, 2012; Wedhasmara,
2009; Riyanto, 2007).
Figure 1: Strategic Planning SI/TI Version Ward&Peppard
2002 (Septiana, 2017)
3 ANALYSIS
In order to formulate the strategy of the information
system, one has to use an analysis method whose
subsequent result of the analysis will be used as a
basic reference of the determination of the strategy
of the information system strategy at STMIK Cipta
Darma Surakarta after some step analysis
.
3.1 Internal Business Environment
Analysis: Using SWOT
The feasibility analysis uses a SWOT analysis.
There are four aspects to consider: strength,
weakness, opportunities and risks (Johnson and
Scholes, 1984).
3.1.1 Strength
In carrying out the feasibility study, the strength
element used by STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta in
the development of the information and technology
system is described as follows:
a. Support from the leadership, which is with the
policy and willingness to develop the
information system, while the leadership policy
in the form of commitment leader STMIK
Cipta Darma Surakarta, support, develop
information and communication technology as
a means of supporting campus activities.
b. Availability of Information Technology
Infrastructure in the Form of Internet Network
with Fiber Optic Fiber Main Backbone.
c. The availability of human resources included in
the UPT work item, supported by the subunit
portion of the information system, the
Administration, Technical Support, and
Network Scope sections.
d. The geographic location of the STMIK Cipta
Darma Surakarta campus is strategically
supported by the availability of multiple ISPs
that deploy fiber backbones.
e. The level of user request of student services,
faculty and information technology service
employees is quite high.
3.1.2 Weakness
Some weaknesses in the process of developing
information systems are as follows:
a. The lack of a standard reference in the
development and application of information
technology in the future, which is sustainable.
b. The organizational structure of information and
communication technology is still not
synergistic, which in its subunit is often turned
into other subunits.
Analysis of the Information System with Ward Peppard Method for the Strategic Business Plan of the College
3037
c. The lack of clear recruitment / recruitment for
the continuous support of information
technology.
d. The possibilities for the development of
information and communication technology are
still very limited.
e. The lack of HR skills development / rarely is
included in education in information
technology.
f. Not yet comparable number of institutions that
support information technology to both faculty,
staff and students.
3.1.3 Opportunity
a. The extent of development in the field of
technology and communication, especially in
education and government.
b. The growing demand for information
technology in various fields, both because of
the trend and the need for rapid data access and
the era of disclosure of information.
c. The lack of educational institutions, which
include the certification of information
technology at international and national level.
d. The existence of open source, which can be
used and developed cost-effectively
3.1.4 Threat
a. The increasingly intense university competition
in Surakarta in the development of information
technology.
b. The rapid development of technology has a
rapid impact on the depth of a technology.
3.1.5 Strategic Formula STMIK Cipta
Darma Surakarta:
a. Developing strengths and optimizing
opportunities (S-O):
Increasing budget allocations for ICT
development in supporting academic activities,
working with senior high school to provide
STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta with new
undergraduates, creating qualified graduates
through computer literacy, and improving
university quality to obtain / enhance
accreditation of the study program.
b. Development of Power to Overcome Threats
(S-T):
Recruitment prospective scholar with rigorous
selection, so that the needs of trained personnel
in the market can be met with competence in
various skills, improve the quality of facilities
and infrastructure, to create qualified graduates
who can reduce the competition for new
admissions, and regular evaluation of the
Syllabus tailored to the needs of the market.
c. Minimize vulnerabilities to take advantage of
opportunities (W-O):
Increase the competence of human resources
through training, recruitment lecturer with
expertise in the IT field, improving the
competence of teachers with training at home
and abroad through the state scholarship
program and cooperation with related
institutions to improve the performance,
facilities and infrastructure.
d. Minimize weaknesses to avoid threats (W-T):
Collaborate with other institutions or
universities to share knowledge on the
development of ICT applications, establish
collaborations with government agencies and
other institutions in conducting personnel
research, and collaborate with related
institutions on scholarship programs for faculty
and scholar
.
3.2 Internal Enterprise Environmental
Analysis: Using the Value Chain
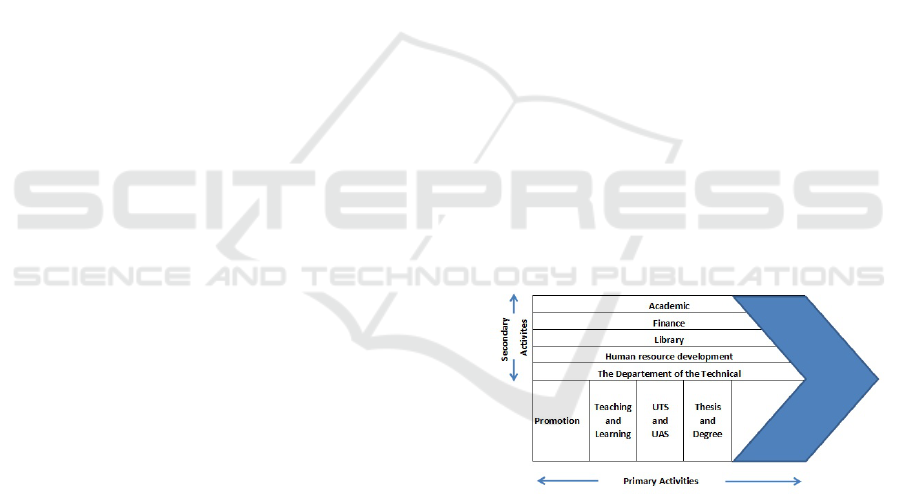
Figure 2. Framework value chain
3.2.1 Secondary Activities
Academic activities in universities meant here are
academic and student administration activities. All
academic and student activities must be managed in
a good administration.
a. Finance
Financial activities cover all activities of the finance
department in ensuring the smooth operation of
higher education because all operational activities
generate substantial funding needs. The finance
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
3038

department realizes the budget based on the priority
scale.
b. Library
Library activities are activities in order to ensure the
provision and provision of information services to
support education. The library section must
guarantee the availability of libraries that support the
teaching and learning process. The library is
provided in the form of physical and library libraries
that can be accessed online.
c. d. Human Resource Development
Human resource development activities are human
resource management activities. This activity
includes the procurement and development of
lecturers and education personnel. The Human
Resources Development Section must be able to
primarily guarantee the ratio of the number of
lecturers and students in accordance with
government regulations. The number of education
personnel must be sufficient for the smooth
operation of higher education. Development of
lecturer and education staff competencies to improve
the quality of education services provided by
students. Finally, it is hoped that graduates will be
increasingly qualified in the future.
d. The Department of The Technical
The activities of the technical department are the
activities of managing the infrastructure and
facilities of universities. The activities of the
technical department include, among other things,
managing inventory items, supplying electricity and
internet as well as college communication
equipment. The department is also responsible for
preparing classes and laboratories used for teaching
and learning. This is important in order to ensure the
comfort of students in studying.
3.2.2 Primary Activities
STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta has an annual
agenda that includes promotion and acceptance of
new students, teaching and learning processes, UTS
and UAS, theses and degrees. The explanation is as
follows:
a. Promotion
Promotional activities become the main activity
every year. The goal is to get prospective new
students. Promotional activities carried out included
socialization to schools and cooperating, promotion
of using billboards in strategic streets, and brochure
printing.
b. Admission of new students
The new student admission activity is an objective
selection of prospective students who will study in
college. A number of assessment instruments are
made in order to ensure objectivity of valuation.
Students are input that will later be processed in the
college to be output or graduates. The hope is that
with good input, it will produce good output as well.
c. Teaching and learning process
The activity of the teaching and learning process is
the activity of processing students into graduates
who have the competencies needed by the world of
work. The curriculum must always be updated to
suit the needs of the workforce.
d. UTS and UAS
UTS means the Mid-Semester Examination and
UAS means the Final Semester Examination. The
two activities were carried out in order to test the
competence of students after taking courses in the
curriculum of each study program. The form of UAS
and UTS can be in the form of written and unwritten
exams according to the subject competency
requirements.
e. Thesis and degree
The thesis activity is an activity to do the final
project while studying in college. After students pass
the thesis examination, each graduate will get a
degree according to the level of education. Currently
STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta provides three
diploma and undergraduate education programs.
3.3 External Business Environment
Analysis: Using PEST
a. Politic
The Indonesian government policy in the form
of the Law on the National Education System
and the Minister of Research and Technology
Regulations has a direct impact, one of which
is the formation of the curriculum. STMIK
Cipta Darma Surakarta must adjust to these
regulations and harmonize with its vision and
mission. The education budget which reaches
30% of the total state budget and expenditure
shows that education has a strategic position in
improving the nation's progress.
b. Economies
Indonesia's economy has always grown from
year to year. This shows an increase in demand
for goods and services both nationally and
locally. Universities as education service
providers must be able to take advantage of
these opportunities, including STMIK Cipta
Darma Surakarta. Public interest in continuing
his education at the University is getting
bigger. The existence of scholarships from the
government and national companies will also
increase interest in continuing education in
universities.
Analysis of the Information System with Ward Peppard Method for the Strategic Business Plan of the College
3039

c. Social Cultural
STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta has become a
"brand" in the community and has become one
of the universities that have basic expertise in
multimedia. People prefer products or services
that are recognized for their reliability. STMIK
Cipta Darma Surakarta must improve its multi-
media "brand" among the community so that it
is always the choice of the people. In this case
STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta has formed a
brand to become "STMIK CDS".
d. Technology
Technological developments, especially
information and communication technology
(ICT) have been so rapid. Today's technology
is the backbone of the university. Universities
can be considered as the main institutions, so
that good design must be in place to ensure that
ICT facilities can be used to their full potential.
The government in this case always encourages
increased use of ICT facilities in universities.
3.4 External Business Environment
Analysis: Use Five Force Model
a. Thread new Competitor
The growth of similar universities on a local
scale may not always occur every year, but on
a national scale it is possible. STMIK Cipta
Darma Surakarta must always be careful and
pay attention to the growth of similar new
universities.
b. Thread Product or Subtitution Service
Currently there are around 68 products that are
the same as the products produced by STMIK
Cipta Darma Surakarta at a regional scale.
Therefore, the STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta
product in terms of its study program must be
completely different from its competitors so
that it can be the choice of the community. This
is a challenge for study program managers in
the STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta
environment. In line with the development of
ICT the use of e-learning and various ICT
facilities can also support STMIK Cipta Darma
Surakarta products.
c. Strength Customers
STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta acknowledges
that to get student satisfaction requires a very
expensive investment for the sake of its future
sustainability. Good service and a pleasant
learning process are expected to be a living and
continuous advertisement. Besides that the
timeliness of graduation and the waiting period
of graduates in getting a short job is a
benchmark for student satisfaction.
d. Strength Supplier
In the Surakarta Residency, there are about 200
high school or vocational school prospects to
continue their studies, this is reflected in the
participation of graduates who enroll in state
university entrance exams reaching more than
25,000 participants. This opportunity must be
utilized as much as possible by STMIK Cipta
Darma Surakarta. This amount from year to
year is relatively always experiencing an
increase although not too much.
e. College of one kind Competition
Currently, STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta has
approximately 40 competitors who provide
similar education at the regional scale and 10
competitors at the local scale of Surakarta. The
value of higher education accreditation must be
increased continuously in order to win the
competition with similar universities at the
local and regional levels.
Future competitors of STMIK Cipta Darma
Surakarta can be mapped with the Analysis of
the Five Model Strengths of STMIK Cipta
Darma Surakarta can be seen in the following
figure:
Figure 3: Five Force Model Analysis
3.5 Current State IS / IT STMIK Cipta
Darma Surakarta with McFarlan
Grid
Based on the results of the internal IS / IT
analysis, applications existing today in STMIK Cipta
Darma Surakarta using McFarlan Matrix can then be
mapped as follows:
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
3040
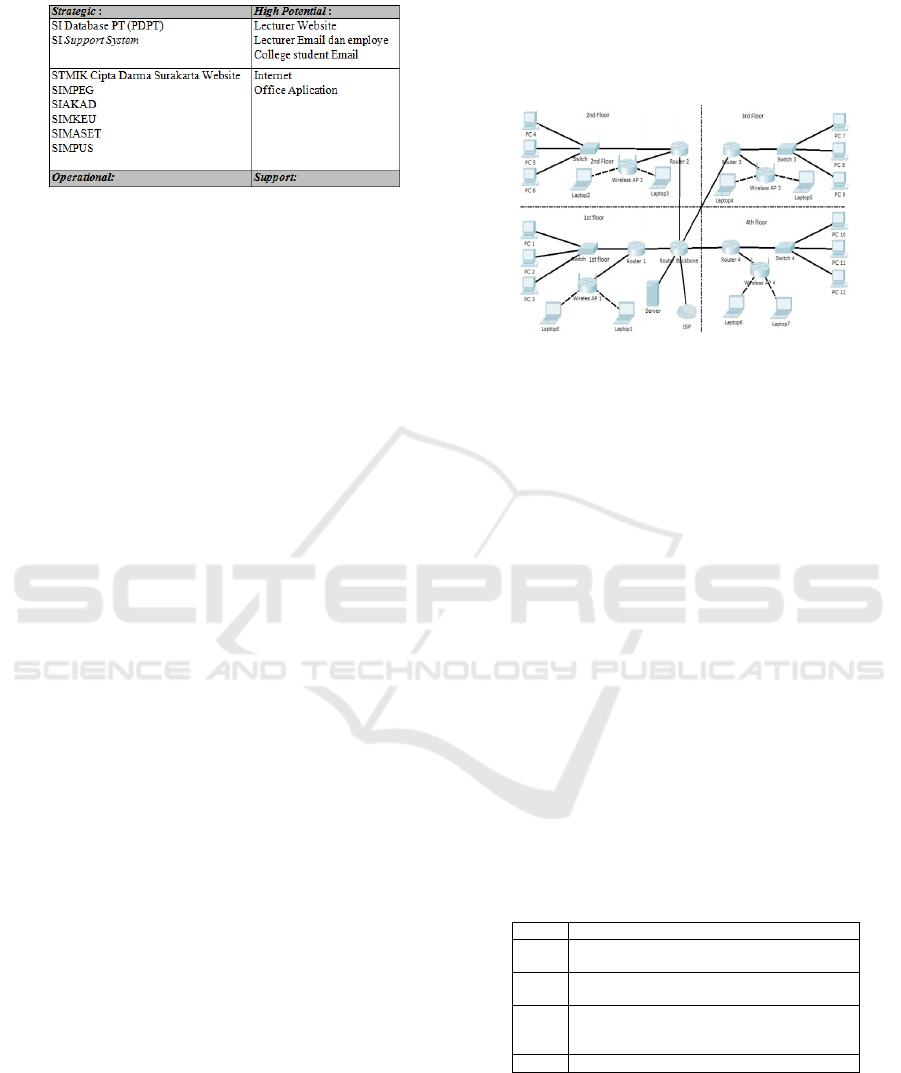
Table 1: Mcfarland Grid
The strategic column contains information
systems that are highly susceptible to the
sustainability of institutional business
processes. Key operational, ie systems that are
currently running
.
3.5.1 Internal Environmental Analysis IS/IT
STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta
a.
Hardware Technology and Specifications
used to support learning, management, and
decision-support in STMIK Cipta Darma
Surakarta are as follows: The existing network
infrastructure consists of server, router, client,
switch, and access point. Media transmission
for data communication wired and radio.
Networks (LAN) that exist on each floor are
connected online through the ISP's Internet
network
.
b.
Software , Software is an element that is
important because almost every line of college
services use device software ditetu especially
college with the field of information
technology. As technology advances rapidly, it
will affect the changing needs of the software
.
c.
Operating System Technology In order to
support the system of teaching and learning of
legal operating system software, STMIK
strives to collaborate with certain operating
system vendors, and for some software needs
that are supported by open source software,
such as LINUX
.
d. Infrastructure technology to integrate data
services STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta, which
is divided into four floors with the architecture
Local Area Network (LAN). For client
connections that use wireless (wireless) LAN
technology with Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol (DHCP). In view of the greater
distance, integrated information system
solutions use a technology architecture often
called Wide Area Network (WAN). Some
things to consider when choosing infrastructure
solutions include: bandwidth, technology, IP-
based support, easy configuration and
maintenance, low cost, and security. The
network architecture for four floors, executed
as shown below.
Figure 4 Network Architecture
Based on the analyzes carried out with some of
the above analyzes, some strategies in the field of
information systems can be introduced. These
strategies include business strategy, information
technology strategy, and information systems
management strategy. Here are the details of the
strategies that result from data collection and
analysis.
3.6 Business Strategy
Business system strategy is a strategy of using
information system to achieve STMIK Cipta Darma
Surakarta vision. This business strategy should
support the use of information systems in the
environment STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta.
Strategies based on the conditions in STMIK Cipta
Darma Surakarta and the analyzes performed.
Strategies for realizing an effective and efficient
information system, which refers to some of the
analyzes performed, are shown in the following
table.
Table 2: Business Strategy
NO Business Strategy
1
Maximize the use of existing information
systems for administration and teaching.
2
The use of information systems in accordance
with the task of each section.
3
Provision of information systems that can
support the work and business processes
STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta.
4 Providing a user-friendly information system..
3.7 Information Technology Strategy
Information technology strategy is a strategy in the
management of the IT infrastructure to support the
information system. Good infrastructure
Analysis of the Information System with Ward Peppard Method for the Strategic Business Plan of the College
3041
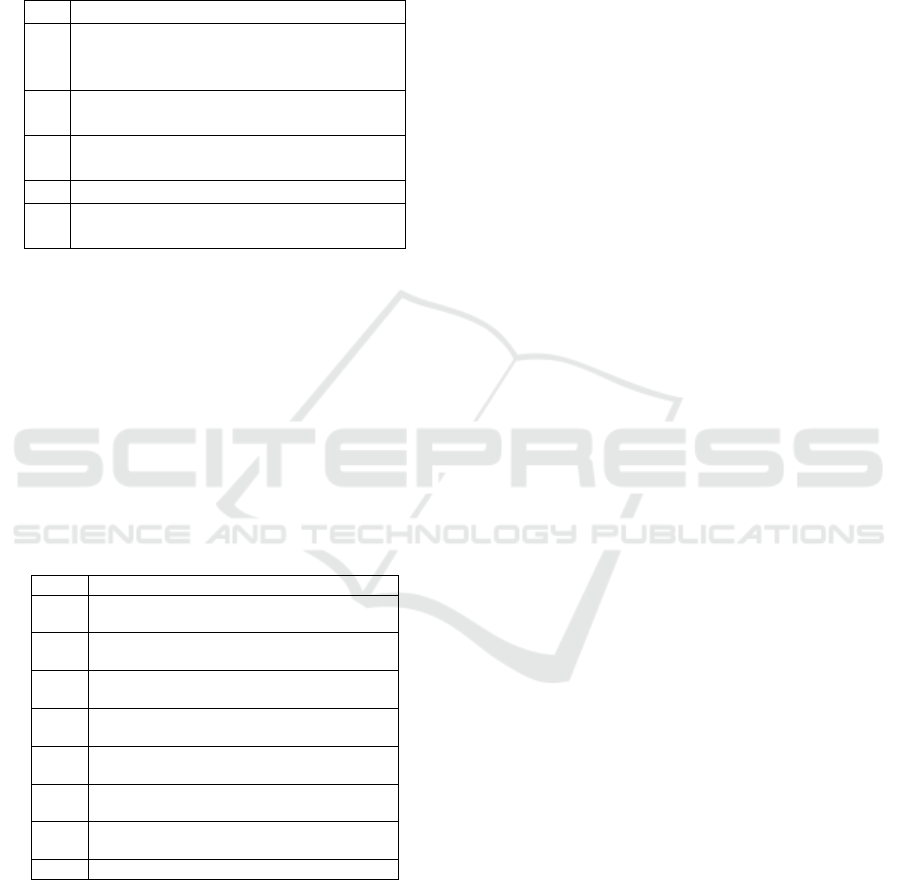
management is expected to support maximum
existing information systems.
Strategies for implementing an effective and
efficient information system that points to an
analysis performed are shown in the following table.
Tabel 3: Information Technology strategy
NO INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY STRATEGY
1
Procurement of hardware or other devices that
support the STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta
business process.
2
Perform routine checks on existing equipment or
information systems.
3
Make improvements if faults in the device or
information system occur.
4 The presence of maintenance documents.
5
Discontinuation of the use of Internet or hosting
in the area STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta.
3.8 Management Strategy IS/IT
Management Strategy IS / IT is a strategy to
support IS / IT applied in the environment STMIK
Cipta Darma Surakarta. This strategy is applied
when information systems / information technology
already exists or is in use.
Strategies that can be implemented to realize the
management of IS / IT are effective and efficient,
referring to some of the analyzes performed, which
are presented below.
Table 4: Management Strategy IS/IT
NO MANAGEMENT STRATEGY IS/IT
1
Disseminating information systems that are
new or existing.
2
Conducting training for information systems
in related fields.
3
Create instructions for using the information
system.
4
Generate reports on the use and development
of information systems.
5
Perform the task distribution or users of
information systems precisely and clearly.
6
Always update the evolution of information
technology.
7
Create an information system development
team
8 Cooperation with IT companies
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the discussion that has been described, a
study results from several aspects with the following
conclusions:
This analysis uses SWOT analysis techniques,
PEST, Five Force Model. The analysis of the
external side of the company is used to see the state
of the universities in the face of the college
competition. The approach using the SWOT analysis
technique led to a pro-factor analysis of S-W-O-T
and then some of these factors to a SWOT college
matrix analysis with 4 strategies, ie SO-ST-WO-WT
strategy. Approach using PEST analysis, looking at
results in terms of political conditions, economic
conditions, social conditions and technological
developments. The five-force model analysis
examines universities with multiple component
factors, namely, newcomer components, suppliers,
customers, replacement services, and competitors
Analysis of the internal college business using
the approach with Value Chain Analysis to map the
entire process of work occurring within the
organization into two categories of activities, the
primary activity and secondary activities. Analysis
describing the activities of the college business with
value-chain technique, which includes primary
activities and supporting activities of the universities
STMIK Cipta Darma Surakarta
REFERENCES
Jogiyanto, H.M, 2006, Sistem Informasi Strategik Untuk
Keunggulan Kompetitif, Yogyakarta: Andi.
Johnson, G., Scholes, K., 1984, Exploring Corporate
Strategy, Singapore: PHI.
Rahmawati, Amri, F., 2013, Perencanaan Strategi Sistem,
Teknologi dan Manajemen Informasi Dalam
Meningkatkan Daya Saing Sekolah dan Kompetensi
Lulusan, Seminar Nasional Aplikasi Teknologi
Informasi (SNATI).
Riyanto, B., 2007, Perencanaan Strategis Sistem Informasi
Pada Lembaga Pemerintah Non Departemen: Studi
Kasus Lembaga Penerbangan Dan Antariksa
Nasional, Tesis, Program Studi Teknologi Informasi,
Magister Teknologi Informasi, Universitas Indonesia,
Jakarta.
Septiana, Y., 2017, Perencanaan Strategis Sistem
Informasi Dengan Pendekatan ward and Peppard
Model, Jurnal Wawasan Ilmiah, Vol. 8, No. 1.
Setiawan, A., Ilman, B., 2012, Perencanaan Strategik
Sistem Informasi Pada Perusahaan Penerbitan
Dengan Metode Ward and Preppard: Studi Kasus
Pada Penerbit Rekayasa Sains Bandung, Jurnal
Manajemen Teknologi, Vol. 11, No. 3
Wedhasmara, A., 2009, Langkah-Langkah Perencanaan
Strategis Sistem Informasi Dengan Menggunakan
Metode Ward and Peppard , Jurnal Sistem Informasi
(JSI), Vol. 1, No. 1.
ICRI 2018 - International Conference Recent Innovation
3042
