
1
Anti-Adipogenic Activity of Fractions of Guazuma ulmifolia Leaf
Nuri
1,2*
, Bambang Prajogo
3
, Sukardiman
3
1
Doctoral Program of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Departement of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry Faculty of Pharmacy,
Airlangga University, Surabaya, Indonesia
2
Department of Pharmaceutical Biology, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Jember, Indonesia,
3
Department of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, Faculty of Pharmacy, Airlangga University, Surabaya, Indonesia.
Keywords : Guazuma ulmifolia leaf, Fractions, Anti-adipogenic, Preadipocytes
Abstract : This study purposed to investigate the anti-adipogenic activity of the chloroform, ethyl acetate, and residual
ethanol fractions of Guazuma ulmifolia leaf extract. The fractionation of ethanol extract was carried out
by solvent-solvent partition using chloroform and ethyl acetate. Inhibition of fractions to the
proliferation and differentiation of primary cultures of rat preadipocytes were tested to investigate the anti-
adipogenic activity. Separation of ethanol extract yielded three fractions, i.e. fraction of chloroform, fraction
of ethyl acetate, and fraction of residual ethanol. The results of anti-proliferation and anti-differentiation
activity test showed that the highest activity was demonstrated by ethyl acetate fraction, followed by
residual ethanol fraction and chloroform fraction. The highest total flavonoid content was also shown by the
fraction of ethyl acetate. The fraction of ethyl acetate showed the highest anti-adipogenic activity and the
highest total flavonoid content
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays obesity is not only seen as a
performance problem but has become a pandemic
and a major health problem resulting in increased
risk of comorbidity that contributes significantly to
mortality (Castanon, Lasselin and Capuron, 2014).
Obesity has become a major risk for diabetes,
hypertension, coronary heart disease, dyslipidemia,
and certain tumors (Pi-Sunyer, 2002). The World
Health Organization (WHO) defines obesity as an
abnormal or excessive accumulation of fat that
harms the health of human (Word Health
Organization, 2018). In fact, obesity can be
controlled by reducing the fat content of food
accompanied by an increase in physical exercise.
However, it is estimated that over 90% of people
who lose weight with diet and increase physical
exercise, within 2-5 years will return to their original
weight. Increased adipose tissue mass involves an
increase in the number of adipocytes formed from
precursor cells, which in turn occurs enlargement of
adipocyte size. The formation of the adipocytes from
precursor cells and enlargement of their size is a life
cycle of adipocyte, and treatment that can regulate
adipocyte counts and measures can be used as a
therapeutic approach to treat obesity (Rayalam,
Della-Fera, and Baile, 2008).
Flavonoids, polyphenol compounds, are widely
present in plants and are known to inhibit
proliferation in some cell cultures and have anti-
adipogenic effects on 3T3-L1 line cells. The results
of Park et al (2009) research show that luteolin
inhibits the differentiation of preadipocyte and
regulates the early stages of adipogenesis. Other
flavonoids myricetin, a flavonoid found in various
foods, can inhibit adipogenesis as indicated by
decreased intracellular lipid droplet accumulation
(Bin and Choi, 2012). Flavonoids present in Citrus
aurantium L. suppress adipogenesis by decreasing
PPARg and C/EBPa expression (Kim et al., 2012).
The anti-adipogenic effects of this 3T3-L1 cell,
coupled with anti-proliferative activity, proposes the
presumption that flavonoids may inhibit the increase
of adipocytes or signals that promote adipogenesis.
G. ulmifolia is a plant originating from tropical
America and is a plant belonging to the family
Sterculiaceae. In Indonesia, this plant commonly
called Jati belanda and traditionally has been used to
lose weight and reduce excessive fat content
(Mardisiswojo and Rajakmangunsudarso, 1985).
Nuri, ., Prajogo, B. and Sukardiman, .
Anti-Adipogenic Activity of Fractions of Guazuma ulmifolia Leaf.
DOI: 10.5220/0009845500002406
In Proceedings of BROMO Conference (BROMO 2018) - Symposium on Natural Product and Biodiversity, page 1
ISBN: 978-989-758-347-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1

2
The leaf of G. ulmifolia contain a number of
phytochemical constituents i.e. colistin, colatannins,
caffeine, tartaric acid, theobromine, xanthan gum,
catechins, kaempferol, some of procyanidin
(procyanidin B-2, B-5, and C-1), and tiliroside
(Sharma and Prasad, 2014; Departement of Health
Republic of Indonesia, 2008). Among these
compounds, namely catechins, kaempferol,
prosianidin and tiliroside including flavonoid
derivatives compounds. The presence of this
compounds gives the estimate of G. ulmifolia leaf as
anti-obesity by inhibiting adipogenesis.
In this study, the ethanolic extract of G. ulmifolia
leaf was fractionated by means of the liquid-liquid
partition using chloroform, ethyl acetate. The
obtained fractions (chloroform, ethyl acetate, and
last remaining ethanol) were tested for inhibiting the
proliferation and differentiation of rat preadipocytes.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials
Organic solvents of n-hexane, chloroform, ethyl
acetate and ethanol were in proanalytical grade
(Merck), TLC plate (Merck), collagenase type I
(Sigma), culture media DMEM, HEPES, NaHCO
3
,
biotin, D-pantothenate, FBS, Penicillin and
Streptomycin (Sigma), differentiation induction
materials insulin, dexamethasone, IBMX (Sigma)
2.2 Collection and Drying of G.
ulmifolia Leaf
Leaf of G. ulmifolia was collected from Meru Betiri
National Park with an altitude of 900 - 1,223 m asl
and an average rainfall of 2,300 mm/year in October
2016. Prior to collection, the plants were determined
in LIPI Botanical Gardens, Purwodadi, East Java.
The leaf was sorted, i.e. removed the damaged leaf
and other impurities then washed with running
water. The clean leaf was dried and then pulverized
(grounded) to powder.
2.3 Extraction and Fractionation
G. ulmifolia leaf powder weighing 800 g was
defatted with n-hexane four times (each 1000 mL).
The residue was collected, air dried, and macerated
in 70% ethanol (2000 mL) for 24 hours. This
procedure was repeated three times using the same
powdered leaf. The filtrate then concentrated by
using a rotary evaporator at 45°C under reduced
pressure to obtain a less 70% ethanol extract.
Successively, the extract was fractionated using
chloroform and ethyl acetate (3 x 350 mL of each
solvent) to obtain chloroform, ethyl acetate, and
residual 70% ethanol fraction. The fractions solvent
was completely removed under the vacuum to obtain
dry fractions and preserved in vials and kept at 4 °C
before use.
2.4 Determination of Total Flavonoid
Content
Total flavonoid content was measured by the
aluminum chloride colorimetric assay. An aliquot
(150 μL) of fractions or standard solution of
quercetin (5, 10, 20, 40, 60, 80 and 100 mg/L) was
added to 1.5 ml cuvet containing 0.4 ml of aqua
distilled water. To the cuvet was added 0.03 mL 5 %
NaNO
2
and 0.03 mL 10 % AlCl
3
. After 6 min, 0.2
mL 1 N NaOH and 0,24 of mL distilled water were
added. The solution was stirred until homogeneous,
then the absorbance was measured at 415 nm. Total
flavonoid content of fraction was expressed as mg
quercetin equivalents (QE)/g fraction. Samples were
analyzed in triplicates (Ratnadewi et al., 2018).
2.5 Preparation of Cell Culture
Preadipocytes were isolated from mice adipose
tissue aged 4-8 weeks. The visceral fat tissue was
sliced in a sterile condition and cleaned as much as
possible from surrounding tissues. The tissue was
washed with PBS and chopped into small pieces.
Chopped tissue was digested by type I of
collagenase at 37 °C for an hour. After that, the
suspension was filtered through 250 µm nylon mesh.
The suspension containing isolated cells were
centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 7 minutes, and the two
types of cells were separated. Mature adipocytes
were found at the top layer of the suspension and the
pellet at the bottom of a tube containing
preadipocytes cells. Furthermore, the pellet was
resuspended in culture medium containing FBS
10%, homogenized, and plated on plate culture, then
incubated at 37˚C, 5% CO
2
(Duarte, et al., 2012).
After two days, differentiation was induced by the
addition of induction medium ((DMEM/F12 added
by 66 mM insulin, 100 nM dexamethasone, 0.5 mM
3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine) and incubated at 37°C
in a 5% CO
2
incubator for 24 hours.
The cell culture was incubated with chloroform,
ethyl acetate, and ethanol fractions of G. ulmifolia
leaf fraction for up to 24 hours (Lin, Della-Fera, and
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
2
3
Baile, 2005). All experiments were performed at
least in triplicate at concentrations of 500 ppm.
2.6 MTT Assay
Cell proliferation was examined by MTT assay. In
brief, 20μl assay medium containing MTT was
added to each well of 96 well plates. The incubation
continued at 37 ℃ for 4 hours , adding 150 μl
DMSO to dissolved the colored formazan. The
absorbance of each sample was measured by a
microplate reader at 490 nm.
2.7 Determination of The Cells
Differentiation
After the treatment with fractions, the amount of
differentiated and non-differentiated cells were
calculated under the microscope at a 400
magnification (Hemmrich et al., 2005). Cells were
calculated at 25 fields of view. Cell differentiation
was calculated based on the number of cells
undergoing morphological changes in adult
adipocytes.
2.8 Oil-Red-O Staining
Cells were fixed in 10% formalin and washed a
moment with running tap water. After rinsed with
propylene glycol, the freshly prepared Oil-Red-O
working solution was added with agitation for 7
minutes. Then, the cells were rinsed with 85%
propylene glycol and stained with hematoxylin.
Finally, cells were washed with running tap water,
dried, and observed under the microscope at 400
magnification (Lin, Della-Fera, and Baile, 2005).
3 RESULTS
3.1 Extraction and Fractionation
The yields of all the fractions corresponding to the
initial dry leaf material are shown in Table 1. The
extractive yield varied among the solvents used.
Chloroform and ethyl acetate fractions showed less
extractive yield as compared to residual 70% ethanol
fraction.
Table 1: Fractions yield (%) of 800 g G. ulmifolia leaf
powder in the different solvent
Fractions Extractive
value (
g
)
% Yield
Chloroform
Fraction
3,61 0,45
Ethyl acetate
Fraction
5,98 0,75
Ethanol Fraction 48,41 6,05
3.2 Total Flavonoid Content
The results obtained in the estimation of flavonoid
content (Table 2) showed that all fractions had a
certain amount of total flavonoid content. The
fraction of ethyl acetate showed the highest total
flavonoid content (314,50 ±4,50 mg QE/g fraction).
The total flavonoid contents exhibited the
descending order with fractions of ethyl acetate >
chloroform > ethanol.
Table 2: Total flavonoid content of fractions
Fractions Total flavonoid content
(mg QE/g Fraction) ± SD
Chloroform
Fraction 109,92 ± 2,15
Ethyl acetate
Fraction 314,50 ± 4,50
Ethanol Fraction 10,22 ± 1,08
3.3 Anti-proliferation and Anti-
differentiation Activities of
Guazuma ulmifolia Leaf Fractions
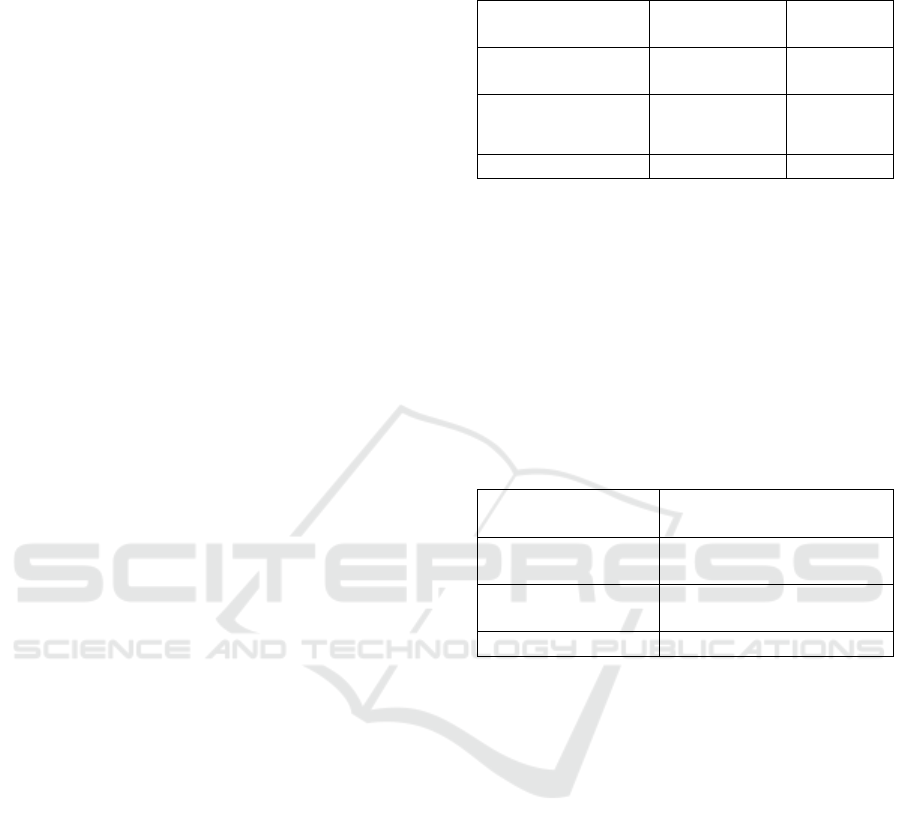
Anti-proliferation activity indicates the ability of
fractions to inhibit the proliferation of preadipocyte
cells. Anti-proliferation activity of each fraction is
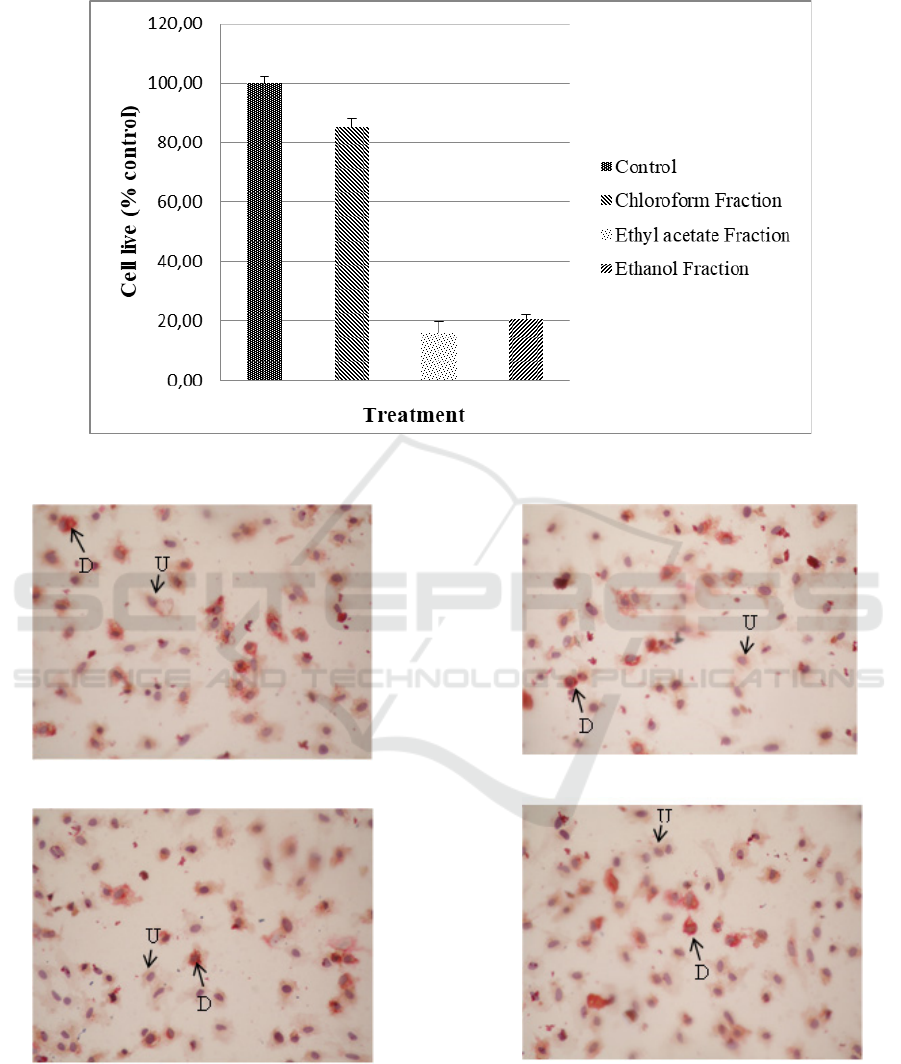
shown in Figure 1. Cell differentiation is
characterized by changes in adipocyte morphology.
Inside the cell, there is a lipid drop as shown in
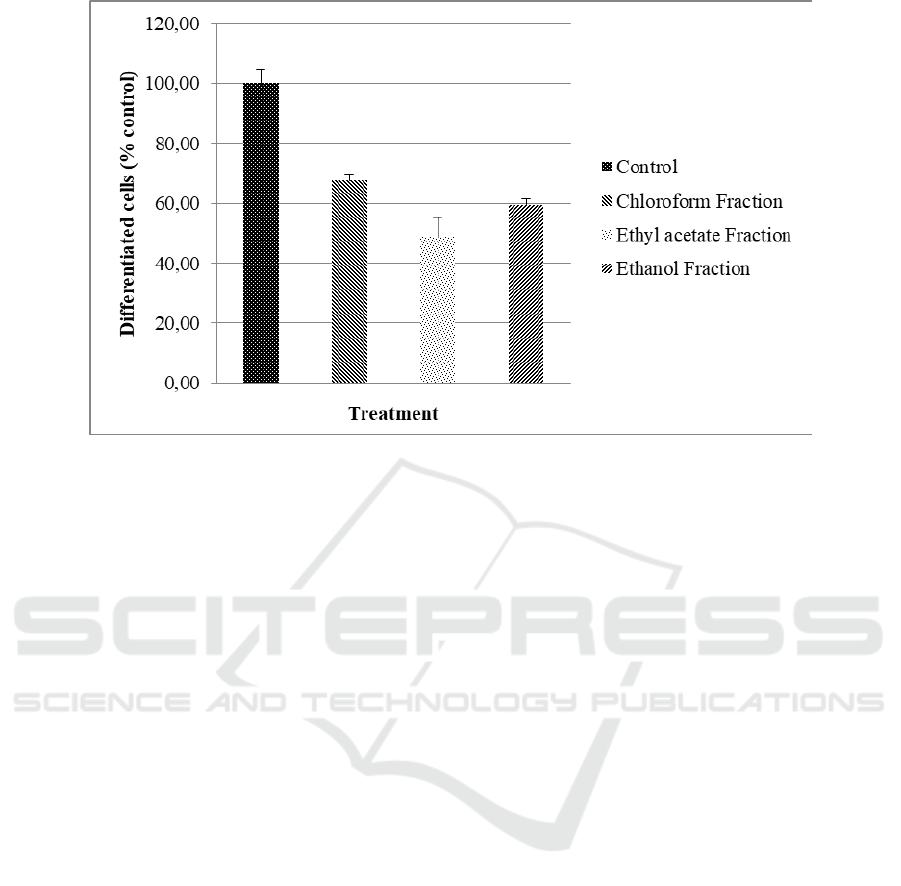
Figure 2. The anti-differentiation activity showed the
ability to inhibit preadipocyte cell changes in
adipocyte mature cells. The anti-differentiation
activity of the fractions is shown in Figure 3.
Anti-Adipogenic Activity of Fractions of Guazuma ulmifolia Leaf
3
4
Figure 1: Anti-proliferation activity of G. ulmifolia leaf fractions
Figure 2: Preadipocyte morphology after incubation with G. ulmifolia leaf fractions for 24 hours. D = Differentiated cells,
U = Undifferentiated cells
Control
Chloroform Fractio
n
Eth
y
l acetate Fractio
n
Ethanol Fractio
n
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
4
5
Figure 3: Anti-differentiation activity of G. ulmifolia leaf fractions
4 DISCUSSION
Fractionation of ethanol extract of G. ulmifolia leaf
using chloroform and ethyl acetate showed the most
yield was the residual 70% ethanol fractions (Table
1). These results indicated that most of the extracted
content was polar compounds.
The leaf of G. ulmifolia contain flavonoids, i.e.
catechins, kaempferol, procyanidin B-2, procyanidin
B-5, procyanidin C-1 and tiliroside. Numerous
studies reported that flavonoids inhibited
adipogenesis (Park et al., 2009; Bin and Choi, 2012;
Hsu and Yen, 2007; Chien et al., 2005)(5,6,15,16).
The fractionation of ethanol crude extract resulted in
fractions with different total flavonoid content. The
sequence of the fractions based on total flavonoid
content detected were ethyl acetate fraction >
chloroform fraction > ethanol fraction (Table 2).
This results indicated that flavonoids compound
which was found in the leaf of G. ulmifolia prefer to
be extracted with solvent possessing moderate
polarity degrees (semi-polar) such as ethyl acetate
and chloroform than solvents with strong polarity
(ethanol) as seen in Table 2. Based on the principle
of like dissolves like, it was thought that most
flavonoids were in the form of aglycons (Sarker,
Latif, and Gray, 2006).
Anti-proliferation activity of ethyl acetate
fraction was higher than other fractions (Figure 1).
This result was consistent with the total flavonoid
content of the ethyl acetate fraction as mentioned
above, that higher than other fractions. Other studies
have shown that flavonoid of G. ulmifolia leaf
(tiliroside) can inhibit the proliferation of T47D and
MCF7 cancers cell lines (Da’i et al., 2016).
Cells differentiation were indicated by
preadipocytes morphological changes into mature
adipocytes that were shown by the formation of fat
droplets in the adipocytes. Fat droplets can be
observed with Oil-Red-O staining. This staining has
been widely used to exhibit the differentiation of
preadipocytes to adipocytes because it is positively
correlated with the amount of lipid stored in the cell.
Hence it is used to indicate potential anti-obesity
effects of natural products (Poudel et al., 2015).
Figure 2 showed the morphology of adipocytes after
the treatment with chloroform, ethyl acetate, and
residual ethanol fractions for 24 hours. The
differentiated cells (D) were characterized by orange
lipid droplets and otherwise, these droplets were not
observed in undifferentiated cells (U). The ethyl
acetate fraction also showed the highest anti-
differentiation activity among the other fractions
(Figure 3).
In the case of anti-proliferation activity of
chloroform fraction and residual ethanol fraction,
ethanol fraction showed higher activity than the
chloroform fraction. Similarly, by anti-
differentiation activity, ethanol fraction showed
higher activity than chloroform fraction. This may
be due to only certain flavonoids that can inhibit
proliferation and differentiation of preadipocytes.
For example, ganistein may inhibit the
differentiation of preadipocytes of the 3T3-L1 cell
Anti-Adipogenic Activity of Fractions of Guazuma ulmifolia Leaf
5

6
line, but naringenin had no effect on this process
(Harmon and Harp, 2001).
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the result of above research can be
concluded that the ethyl acetate fraction contains the
highest total flavonoid contents among other
fractions. The ethyl acetate fraction also showed the
highest anti-proliferation and anti-differentiation of
rat preadipocytes.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of
interest.
REFERENCE
Bin H-S, Choi U-K, 2012. Myricetin inhibits adipogenesis
in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem
cells. Food Sci Biotechnol, 21(5):1391–6
Castanon N, Lasselin J, Capuron L, 2014.
Neuropsychiatric comorbidity in obesity: Role of
inflammatory processes. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne),14;5(May):1–9.
Chien P, Chen Y, Lu S, Sheu FUU, 2005. Dietary
flavonoids suppress adipogenesis in 3T3-L1
preadipocytes. J Food Drug Anal., 13(2):168–75.
Da’i M, Wikantyasning ER, Wahyuni AS, Kusumawati
ITD, Saifudin A, Suhendi A, 2016. Antiproliferative
properties of tiliroside from Guazuma ulmifolia lamk
on T47D and MCF7 cancer cell lines. Natl J Physiol
Pharm Pharmacol., 6(6):627–33.
Departement of Health Republic of Indonesia, 2008.
Indonesian Herbal Pharmacopoeia.: 36-9.
Duarte MS, Wei S, Paulino PVR, Du M, Jiang Z, Zan L,
Hausman GJ and Dodson MV, 2012. Isolation of
mature adipocytes and stromal vascular cells under
adverse sampling conditions. J Metab Syndr., 1(4):1–4
Harmon AW and Harp JB, 2001. Differential effects of
flavonoids on 3T3-L1 adipogenesis and lipolysis. Am
J Physiol Cell Physiol., 280:807–13.
Hemmrich K, Von Heimburg D, Cierpka K, Haydarlioglu
S, Pallua N, 2005. Optimization of the differentiation
of human preadipocytes in vitro. Differentiation.,
73(1):28–35.
Hsu CL and Yen GC, 2007. Effects of flavonoids and
phenolic acids on the inhibition of adipogenesis in
3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Agric Food Chem.,
55(21):8404–10.
Kim G, Park HJ, Woo J, Kim M, Koh P, Min W, 2012.
Citrus aurantium flavonoids inhibit adipogenesis
through the Akt signaling pathway in 3T3-L1 cells.
BMC Complement Altern Med., 12(31):1-10.
Lin J, Della-Fera MA, Baile CA, 2005. Green tea
polyphenol epigallocatechin gallate inhibits
adipogenesis and induces apoptosis in 3T3-L1
adipocytes. Obes Res., 13(6):982–90.
Mardisiswojo S, Rajakmangunsudarso H, 1985. Cabe
Puyang Warisan Nenek Moyang. Jakarta: Balai
Pustaka: 270.
Park HS, Kim SH, Kim YS, Ryu SY, Hwang JT, Yang HJ,
2009. Luteolin inhibits adipogenic differentiation by
regulating PPAR activation. BioFactors, 35(4):373–9.
Pi-Sunyer FX, 2002. The Obesity Epidemic:
Pathophysiology and consequences of obesity. Obes
Res., 10(S12):97S–104S.
Poudel B, Nepali S, Xin M, Ki HH, Kim YH, Kim DK,
2015. Flavonoids from Triticum aestivum inhibit
adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells by upregulating the insig
pathway. Mol Med Rep., 12(2):3139–45.
Ratnadewi AAI, Wahyudi LD, Rochman J, Susilowati X,
Nugraha AS, Siswoyo TA., 2018. Revealing anti-
diabetic potency of medicinal plants of Meru Betiri
National Park, Jember - Indonesia. Arab J Chem.,
(did):0–5.
Rayalam S, Della-Fera MA, Baile CA, 2008.
Phytochemicals and regulation of the adipocyte life
cycle. J Nutr Biochem., 19(11):717–26.
Sarker SD, Latif Z, Gray AI, 2006. Natural Products
Isolation. Totowa, New Jersey: Humana Press.:37.
Sharma M and Prasad SB, 2014. Evaluation of
Anthelmintic Activity of Leaves Extracts of Guazuma
tomentosa. Int J Pharmacol., 1(1):1–5.
World Health Organization, 2018. Obesity and
overweight:1–6. Available from:
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/
[Last accessed on 2018 March 8].
BROMO 2018 - Bromo Conference, Symposium on Natural Products and Biodiversity
6
