Effects of Population, Consumption and Exports on
Economic Growth in Indonesia Period of 2005-2017
Ali Sandy Hasibuan
1
1
Student of Post Graduated Program, Universitas Negeri Medan, Medan -Indonesia
Keywords: Population, Consumption, Exports, Economic Growth
Abstract: The aim of this paper is to analyse the effect of population, consumption and exports on economic growth in
Indonesia. This study uses time series data in the period 2005-2017 obtained from the Badan Pusat Statistik
(BPS) and Bank Indonesia (BI). This study uses multiple linear regression analysis using Eviews 10. The
simultaneous test results show that population, consumption and exports have a significant influence on
economic growth in Indonesia. The partial test results show that the population variable has a significant
influence on economic growth in Indonesia, the consumption variable also has a significant influence on
economic growth in Indonesia and the export variable also has a significant influence on economic growth in
Indonesia.
1 INTRODUCTION
Economic development is a series of businesses and
policies carried out by the government of a country or
region to improve people's welfare. From the point of
view of economics, development is defined as an
effort to increase the growth of income per capita
faster than the rate of population growth (Todaro,
2011).
Economic development is a multidimensional
process which means that economic development has
interrelated relationships and influences among the
factors that produce economic growth. Development
and economic growth have interrelated relations
where development will encourage economic growth
and economic growth can facilitate the economic
development process itself.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a benchmark
for the success of a country's development. from GDP
data, the value of a country's economic growth can be
determined, and economic growth is defined as the
rate of increase in income per capita (Sukirno, 1981).
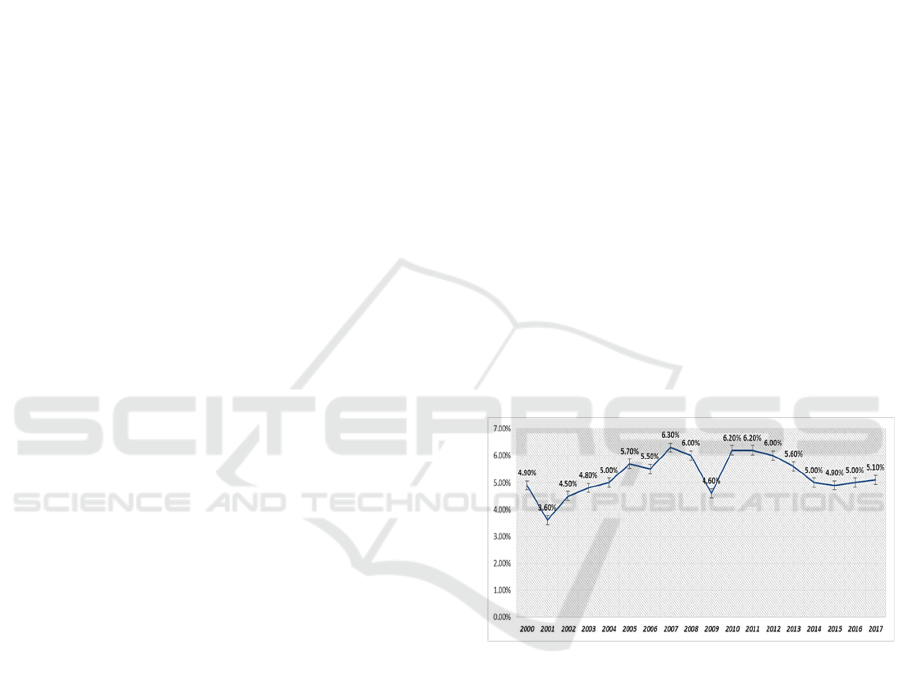
Figure 1: Economic Growth in Indonesia
(source : bps)
Figure 1. describes the graph of economic growth in
Indonesia in the period 2000 to 2017. Based on the
picture, it can be seen that the condition of economic
growth has fluctuated from year to year. The lowest
growth conditions existed in 2001 around 3.60% and
the highest condition of Indonesia's economic growth
was in 2007 at 6.30%.
In recent years, the percentage of Indonesia's
economic growth has decreased. Then experienced a
slight increase in 2017 where in the previous year
Indonesia's economic growth of 5.00% rose to 5.10%.
This change in economic growth is certainly
influenced by variable variables supporting economic
growth.
594
Hasibuan, A.
Effects of Population, Consumption and Exports on Economic Growth in Indonesia Period of 2005-2017.
DOI: 10.5220/0009508705940601
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 594-601
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Theoretical economic growth is influenced by
population (human resources), natural resources,
physical capital, and human capital (Mankiw, 2009).
As one of the factors that influence economic growth,
the main role of the population is in terms of
providing labor. Moreover, the population with
superior quality of human capital will be a more
productive workforce. Indonesia as a country with a
large population is expected to be able to take
advantage of the abundance of the population as a
driving force for economic growth.
Conceptually, the population affects the output of
the economy. High economic output can be obtained
from the production of goods and services carried out
by residents. The more population, a country will be
able to produce more goods and services, which
means it can consume more goods and services. This
will further encourage economic growth (Thuku et al,
2013).
Output is usually measured by Gross Domestic
Product (GDP). Gross Domestic Product shows the
total value of final goods and services produced by all
economic units. Economic growth occurs when an
economy is able to increase GDP from the previous
period.
On the other hand, Keynesian theory states that
national income growth is determined by the amount
of consumption expenditure, government
expenditure, investment and net exports. To increase
economic growth as measured by increasing national
income, an increase in consumption demand, demand
for government expenditure, investment demand, and
demand is needed. export and import. The
implementation of both concepts and theories
(Classical and Keynesian) can be used to calculate
economic growth both on a national scale and at the
scale of regional macroeconomics.
According to Salvator (1990), it implies that
exports are one of the engines of economic growth in
its study showing that exports are one of the main
factors for developing countries to increase their
economic growth. Increased exports by developing
countries can drive output and economic growth.
The impact of population, consumption and
exports in their influence on economic growth in
Indonesia still has to be studied. Thus, the process of
improving the country's economy on a macro level
can be achieved and felt by all communities in
particular. From the description above, the author is
interested in conducting research with the title "
Effects of Population, Consumption and Exports on
Economic Growth in Indonesia Period of 2005-2017"
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 Population
According to the Badan Pusat Statistik (BPS),
population are all people who are domiciled in the
geographical area of Indonesia for 6 months or more
and / or those who live less than 6 months but aim to
settle. According to Maltus (in Lincolin Arsyad,
2010) that the general tendency of the population of a
country to grow according to a series of
measurements is to double every 30-40 years.
Meanwhile, at the same time, due to the decreasing
yield of the land production factor, the food supply
only grows according to the arithmetical series.
Because the growth of the food supply cannot keep
pace with the very fast and high population growth,
per capita income (in the farming community is
defined as per capita food production) will tend to fall
to very low, which causes the population to never
stabilize, or only slightly above the subsiten level
Population growth is a dynamic balance between
two forces that increase or decrease the population.
The development of the population will be influenced
by the number of babies born but simultaneously will
also be reduced by the number of deaths that can
occur in all age groups. In the spatial context of
population mobility also affects changes in
population, where immigration will increase the
population and emigration will reduce the population
in a region.
In the theory of growth according to Kuznet prior
to the era of growth, the economic activities of the
population were concentrated from the extractive
primary sectors, namely agriculture, fisheries and
mining. The process of economic growth has since
been characterized by a diversification of sectoral
activities with the growth of various types and types
of industries (Djojohadikusumo, 2004).
2.2 National Consumption
Household consumption expenditure is one of the
macroeconomic variables. A person's consumption
expenditure is part of the income spent. If the
consumption expenditure of all people in a country is
added up, then the result is the consumption
expenditure of the country concerned.
In macro terms, public consumption expenditure
is directly proportional to national income. The
greater the income, the greater the consumption
expenditure. The comparison of the size of the
additional consumption expenditure to income is
called Marginal Propensity to Consume: MPC. In
societies whose economic life is relatively unstable,
their MPC numbers are relatively large, while their
MPS numbers are relatively small, meaning that if
they get additional income, most of the additional
Effects of Population, Consumption and Exports on Economic Growth in Indonesia Period of 2005-2017
595

income will be allocated for consumption. This is the
opposite to the people whose economic life is
relatively more established. According to Rahardja
(2001: 45), consumption expenditure consists of
government consumption and public consumption.
Some of the reasons underlying the level of
consumption of the community or household are:
a. Household consumption expenditure has the
largest position in total aggregate expenditure.
b. Household consumption is endogenous in the
sense that the amount of household consumption
is related to other factors that are considered to
influence it. Therefore we can compile economic
models and theories that produce an
understanding of the relationship between the
level of consumption and other factors that
influence it. The theory and model is known as the
consumption model theory which has proven to be
beneficial for macroeconomic managers.
c. The rapid development of society has resulted in
the behavior of consumption behavior also
changing rapidly. This is another reason that
contains a study of household consumption
remains relevant
2.3 Export
According to Curry (2001), exports are goods and
services sold to foreign countries to be exchanged for
other goods (products, money). The export process is
an action taken to issue goods or commodities from
within the country to enter them into other countries.
The development of exports from a country is not
only determined by the factors of comparative
advantage but also by factors of competitive
advantage. The essence of the competitive advantage
paradigm is the superiority of a country in global
competition in addition to being determined by
comparative advantage (classical theories and H-O) it
has and also because of protection or assistance from
government facilities, also determined by its
competitive advantage. Competitive advantage is not
only owned by a country, but also owned by
companies in that country individually or in groups.
17 Another difference with comparative advantage is
that competitive advantage is more dynamic with
changes, such as technology and human resources
(Tambunan, 2001).
2.4 Economic Growth
In general, economic growth is defined as increasing
the ability of an economy to produce goods and
services. Economic growth shows the extent to which
economic activity will generate additional income for
the community in a given period. Because basically
economic activity is a process of using production
factors to produce output, then this process will in
turn result in a return of service to the factors of
production owned by the community. With the
economic growth, it is expected that people's income
as the owner of production factors will also increase
(Sukirno, 2006: 423).
According to Kuznets economic growth is a long-
term increase in the ability of a country to provide
more and more types of economic goods to its
population; this ability grows according to
technological progress, and institutional and
ideological adjustments that are needed (Jingan,
2010: 57).
Thus it can be concluded that economic growth is
a development in economic activity characterized by
an increase in the output of goods and services which
impacts on the increase in per capita income.
Economic growth is an increase in the output of
society caused by the increasing number of
production factors used in the production process,
without any change in "technology" production itself,
for example output increases caused by the growth of
capital stock or the addition of production factors
without changes in production technology the old one
(Arsyad, 2010: 96).
2.5 Effect of Population on Economic Growth
The economic growth rate can be attributed to the rate
of population growth because in principle economic
growth must be enjoyed by the population. The
number of residents needs to be considered because
besides being a subject, the population is also an
object of development. Changes that have been made
in the aspect of population will affect the
development process and the objectives to be
achieved.
In the view of classical economists there are four
factors that influence economic growth, namely the
number of people, the amount of stock of capital
goods, the area of land and natural wealth, and the
level of technology used even though realizing that
economic growth depends to many factors. But
classical economists focus on the influence of
population growth on economic growth. In their
growth theory, it is assumed that the area of land and
natural wealth are fixed in number and the level of
technology has not changed. Based on this example,
it is further analyzed how the influence of population
growth on the level of national production and
income (Sukirno, 2010: 433).
According to classical economics, the law of
additional yields that are increasingly scarce will
affect economic growth. This means that economic
growth will not continue. At the beginning, if the
population is small and natural wealth is relatively
excessive, the rate of return on capital from the
investment made is high. Then entrepreneurs will get
a big profit. This will get new investment and
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
596

economic growth materialized. Such circumstances
will not continue. If the population is too much, the
first thing will decrease the level of economic activity
because the productivity of each population has
become negative (Sukirno, 2010: 433).
2.6 Effect of National Consumption on
Economic Growth
Household consumption expenditure is the value of
expenditures made by households to buy various
types of needs in a given year. The income received
by households will be used to buy food, clothing,
transportation services, pay for children's education,
pay rent for houses and buy vehicles. These items are
purchased by households to meet their needs.
(Sukirno, 2010).
Household consumption decisions are influenced
by overall long-term and short-term behavior. Long-
term household consumption decisions are important
because of their role in economic growth. As for
short-term analysis, the role is important in
determining aggregate demand. Consumption is two-
thirds of GDP.
Keynes had an absolute consumption theory
called the Keynesian Theory (Absolute Income
Hypothesis). Keynes argues that the amount of
household consumption depends on the income
generated. The comparison between the amount of
consumption and income is called Keynes as
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC). This MPC
is used to measure that the greater the income owned,
then the level of household consumption is also high,
and vice versa.
2.7 Effect of Exports on Economic Growth
Export is an international trade process that aims to
gain profits so that each country will benefit from the
occurrence of international trade, this occurs because
the specialization of each country is different so that
international trade will occur so that efficiency and
specialization will occur in each country. In other
words, cost comparative emphasizes that comparative
advantage will be achieved if a country produces an
item that requires fewer hours of labor than other
countries so that production efficiency occurs.
The important function of the export component
of foreign trade is that the state gains and gains
national income, which in turn increases the amount
of output and the rate of economic growth. With a
higher level of output the vicious circle of poverty can
be broken and economic development can be
improved (Jhingan, 2000). Exports play an important
role in the economic activities of a country. Exports
will generate foreign exchange which will be used to
finance the import of raw materials and capital goods
needed in the production process which will form
added value. According to Salvator (1990), it implies
that exports are one of the engines of economic
growth in its study showing that exports are one of the
main factors for developing countries to increase their
economic growth. Increased exports by developing
countries can drive output and economic growth.
2.8 Previous Research
The results of the research by Darma Rika
Swaramarinda entitled (2011) "The Effects of
Consumption Expenditures and Government
Investment on Economic Growth in Indonesia". The
results of the study show that government
consumption expenditure and investment expenditure
have a positive effect on economic growth, there is a
positive relationship between the expenditure of
government consumption and economic growth in the
study period.
The research results of Dian Purnamasari entitled
(2015) "Population and Economic Growth: A New
Empirical Explanation". The results of the research
show that the Estimated Results indicate that
population density has a negative effect on the
accumulation of human capital and the accumulation
of human capital has a positive effect on output. This
study concludes that a large population will have a
positive effect on economic output if the population
has superior quality of human capital. This means that
the positive influence of population density on output
occurs when high population densities encourage the
accumulation of human resources.
The research results of Christiawan Eka Arianto,
et al, entitled (2015) "Influence of Population and
Unemployment Rate on Economic Growth of Jember
Regency". The results of the study show that from the
results of the analysis carried out, conclusions can be
drawn on the partial test (t test), it is known that the
number of residents has a positive and significant
influence on economic growth. While unemployment
has a positive but not significant influence on
economic growth in Jember Regency.
The research results of Dian Fristia Alfiyanto
entitled (2014) "analysis of the influence of
population, labor, education level and government
expenditure on economic growth in grobogan district
in 1990-2012". The results showed that population,
labor, government expenditure had a significant
effect on gross regional domestic product (RGDP)
while the education level did not have a significant
effect on gross regional domestic product (RGDP).
The results of Ismadiyanti Purwaning Astuti's
research, Fitri Juniwati Ayuningtyas entitled (2018)
"the influence of exports and imports on economic
growth in Indonesia from 2000-2016". The results
showed that exports had a positive influence on
economic growth..
Effects of Population, Consumption and Exports on Economic Growth in Indonesia Period of 2005-2017
597
Ari Muliyanta Ginting's research results entitled
(2017) "analysis of the effect of exports on
Indonesia's economic growth 2001-2015". The
results showed that exports had a positive and
statistically significant influence on economic growth
in Indonesia..
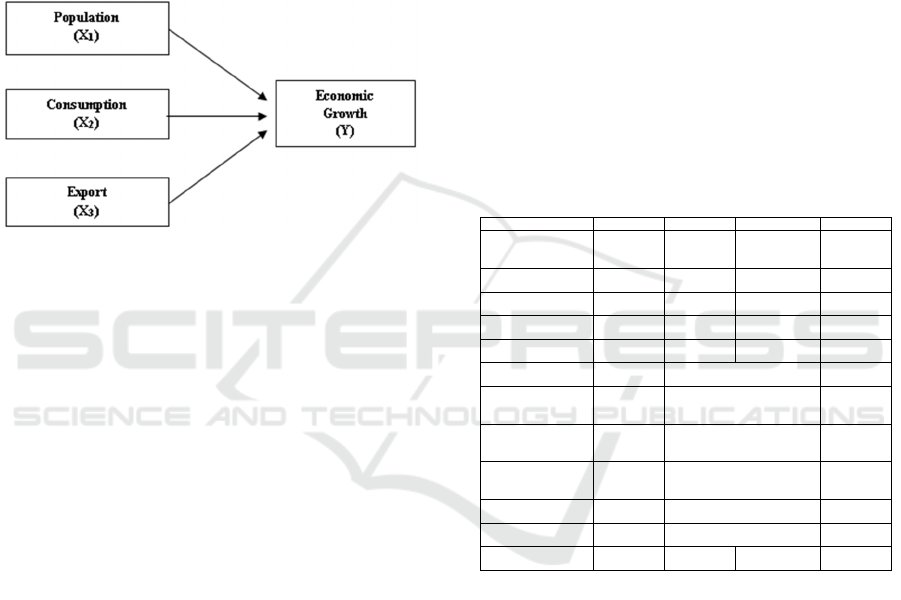
2.9 Framework of Thinking
Based on the explanation of the theory and previous
research, the framework of this research can be
described as follows:
Figure 2: Framework of thinking
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This research was conducted in North Sumatra
Province. The data used in this study are secondary
data based on periodic data series (time series) from
2005 - 2017 obtained from the Central Statistics
Agency. The analysis technique used in this study is
quantitative analysis techniques.
In this study the independent variables were
Population (X1), Consumption (X2) and Export (X3)
in Indonesia in 2005 - 2017. Whereas the dependent
variable was Indonesian Economic Growth in 2005 -
2017. The analysis tools used were analysis multiple
linear. The regression equation is as follows:
Y = β
0
+ β1 LogX1 + β
2
LogX
2
+ β3 LogX3+ μi
Description:
Y = Economic Growth
X1 = Population
X2 = Consumption
X2 = Export
β0 = Constanta
β1, β2, β3 = Regression coefficient
μi = Error term
This analysis aims to determine the Effect of
Population, Consumption and Exports on Economic
Growth in Indonesia from 2005 - 2017. In this
analysis using the program Eviews 10 assistance
which aims to see the effect of independent variables
on the dependent variable.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Estimation Results
Multiple regression analysis is a method used to
determine the possible forms of relationships between
variables, namely the independent variable and the
dependent variable together with the help of the
program Eviews 10, the following results are
obtained:
Table 1: Results of Multiple Regression Estimates
Dependent Variable: LOG_PDBG
Method: Least Squares
Sample: 2005 2017
Included observations: 13
Variable
Coefficien
t
Std. Erro
r
t
-Statistic Prob.
C -25.35258 1.680960 -15.08220 0.0000
LOG_POP 4.463171 0.212204 21.03250 0.0000
LOG_CONS 0.038451 0.025361 1.516129 0.0163
LOG_EX 0.043944 0.017869 2.459256 0.0362
R-squared 0.999823 Mean dependent va
r
12.33389
Adjusted R-
squared 0.999764 S.D. dependent va
r
0.092011
S.E. of
regression 0.001414 Akaike info criterion -10.03659
Sum squared
resid 1.80E-05 Schwarz criterion -9.862760
Log likelihoo
d
69.23784 Hannan-Quinn criter. -10.07232
F-statistic 16925.10 Durbin-Watson sta
t
1.497590
Prob(F-statistic) 0.000000
Source : Eviews output
From the table of estimation results, the regression
equation in this study is made as follows:
Log_PDBG = -25.3525 + 4.4631*Log_POP +
0.0384*Log_CONS + 0.0439*Log_EX
From the above equation, the results that can be
explained are as follows:
1. Constant value of –25,352, meaning that if the
value of the Population, consumption and export
value is 0, then the economic growth decreases by
25,352%.
2. Value of β1 = 4,463, meaning that if the variable
Total Population increases by 1% while the
Consumption and Export variables remain then
economic growth has increased by 4,463% Signs
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
598
(+) indicate there is a unidirectional relationship
between population and economic growth. If the
population increases, economic growth will rise.
3. Value of β2 = 0.038, meaning if the Consumption
variable is 1% while the variable Total Population
and Exports is fixed then economic growth
increases by 0.038%. The sign (+) shows that
there is a direct relationship between consumption
and economic growth. If consumption rises,
economic growth will rise.
4. Value of β3 = 0.044, meaning that if the Export
variable is 1% while the variable Population and
Consumption is fixed then economic growth
increases by 0.044%. The (+) sign indicates a
unidirectional relationship between exports and
economic growth. If exports rise, economic
growth will rise.
4.2 Classic Assumption Test
Multicollinearity
Aim to find out whether there is a significant
correlation between fellow independent variables.
Table 2: Multicollinearity test
LOG_POP LOG_CONS LOG_EX
LOG_POP 1.00000 0.79570 0.74349
LOG_CONS 0.79570 1.00000 0.75509
LOG_EX 0.74349 0.75509 1.00000
Source : Eviews output
From the table above it can be seen that there are
no variables that have a greater value (>) 0.8. so it can
be concluded that there is no multicollinearity in the
regression model.
Serial Correlation (Autocorrelation)
To detect the presence or absence of serial correlation
in the research model. This study uses the Lagrange
Multiplier test (LM Test) to detect the presence or
absence of autocorrelation. From the results of testing
the data obtained the results of the Prob -obs * R-
square value of 0.3580> 0.05. so that it can be said
that there is no autocorrelation in the regression
model
Table 3: Autocorrelation test (LM Test)
Breusch-Godfrey Serial Correlation LM
Test:
F-statistic 0.656926 Prob. F(2,7) 0.5477
Obs*R-square
d
2.054411
Prob. Chi-
Square(2) 0.3580
Source : Eviews output
Normality
From the results of testing the above data obtained
results with a Probability value> α or 0.502220> 0.05.
so it can be concluded that the data used in this study
has a normal distribution and passes the normality
test.
0
1
2
3
4
-0.002 -0.001 0.000 0.001
Series: Residuals
Sample 2005 2017
Observations 13
Mean 2.39e-15
Median 0.000130
Maximum 0.001358
Minimum -0.002088
Std. Dev. 0.001225
Skewness -0.580251
Kurtosis 1.906295
Jarque-Bera 1.377436
Probability
0.502220
Figure 3: Normality test
Heteroscedasticity
To see the presence or absence of heteroscedasticity
can be done by the White Heteroscedasticity test on
Eviews by looking at the value of Prob Value –obs *
R-square contained in the output table.
Tabel 4. Heteroskedasticity test
Heteroskedasticity Test: White
F-statistic 3.3511 Prob. F(5,7) 0.0731
Obs*R-s
q
uare
d
9.1693
Prob. Chi-
S
q
uare
(
5
)
0.1025
Scaled ex
p
lained SS 1.9914
Prob. Chi-
S
q
uare
(
5
)
0.8503
Source : Eviews output
From the table above, it can be seen the value of
Prob Value –obs * R-square of 0.1025> 0.05. it can
be said that there is no heteroscedasticity in the
regression equation model.
4.3 Hypothesis Testing
t Test
The t test is used to test the independent variables on
the dependent variable partially. From the results of
testing the data obtained the value of Prob (t-statistic)
<α that is equal to 0.0000 <0.05 for the variable
Population. Thus the variable population has a
positive and significant influence on economic
growth in Indonesia. So, the higher the population,
the higher the economic growth in Indonesia.
The value of the Prob (t-statistic) consumption
variable is 0.0163 <0.05. With the Prob value (t-
statistic) it shows that the consumption variable has a
positive and significant influence on economic
growth. So, the higher the consumption of the
Effects of Population, Consumption and Exports on Economic Growth in Indonesia Period of 2005-2017
599

community, the higher the economic growth in
Indonesia.
The value of the Prob (t-statistic) export variable
is 0.0362 <0.05. With the Prob value (t-statistic) it
shows that the export variable has a positive and
significant influence on economic growth. So, the
higher the export of the community, the higher the
economic growth in Indonesia.
F Test
The F test is used to test the relationship of
independent variables to the dependent variable
simultaneously. From the results of testing the data
obtained the value of Prob (F-Statistics) <α is equal
to 0.000000 <0.05. Then the three independent
variables, namely the population, consumption and
export together influence economic growth in
Indonesia.
Coefficient of Determination (R2)
The coefficient of determination is used to see how
much influence the independent variables have on the
dependent variable. The coefficient of determination
is determined by the value of adjusted R-Square.
Based on the estimation results obtained the value of
R-Squared is 0.999823. This shows that the variable
population, consumption and export are able to
explain the variable of economic growth of 99.98%.
While the remaining 0.02% is influenced by other
variables not used in this study.
5 CONCLUSIONS
5.1 Conclusions
Based on the results of the analysis and discussion
that has been conducted, the conclusions can be taken
as follows:
1. The population has a positive and significant
effect on economic growth in Indonesia
2. Consumption has a positive and significant effect
on economic growth in Indonesia
3. Exports have a positive and significant effect on
economic growth in Indonesia
4. Population, national consumption and export
simultaneously have a positive and significant
effect on economic growth in Indonesia
5.2 Suggest
Based on the results of the discussion and
conclusions, the suggestions that the author needs to
describe are as follows:
1. Population, export consumption is able to explain
the variable Economic Growth of 99.98% So that
in taking government policy it is necessary to pay
attention to other variables not examined.
2. For researchers interested in conducting studies in
the same field, they should add a time span of
research and other variables not used in the study.
REFERENCES
Alfiyanto, Dian Fristia (2014) ‘Analisis Pengaruh Jumlah
Penduduk, Tenaga Kerja, Tingkat Pendidikan dan
Pengeluaran Pemerintah Terhadap Pertumbuhan
Ekonomi Di Kabupaten Grobogan Tahun 1990-
2012’, Electronic Theses and Dissertation
Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta. Available at:
http://eprints.ums.ac.id/30661/
Arianto, Christiawan Eka (2015) ‘Pengaruh Jumlah
Penduduk Dan Angka Pengangguran Terhadap
Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Kabupaten Jember’,
Universitas Jember Digital Repository. Available at:
http://repository.unej.ac.id/handle/123456789/63990
Arsyad, Lincolin (2010) Pengantar Perencanaan
Pembangunan. Media Widya Mandala: Yogyakarta
Djojohadikusumo, Sumitro. (1994) Perkembangan
Pemikiran Ekonomi: Dasar Teori Ekonomi
Pertumbuhan Dan Ekonomi Pembangunan. Pt
Pustaka Lp3es Indonesia: Jakarta.
Jhingan, M.L (2010) Ekonomi Pembangunan Dan
Perencanaan. PT. Rajagrafindo Persada: Jakarta.
Mankiw, N. Gregory (2006) Makroekonomi. Erlangga:
Jakarta.
Purnamasari, Dian (2015) ‘Penduduk Dan Pertumbuhan
Ekonomi: Sebuah Penjelasan Empiris Baru’,
Dipenegoro University Institutional Repository.
Available at: http://eprints.undip.ac.id/45748/
Astuti, Ismadiyanti Purwaning dan Fitri Juniwati
Ayuningtyas (2018) ‘Pengaruh Ekspor Dan Impor
Terhadap Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Di Indonesia’,
Jurnal Ekonomi dan Studi Pembangunan, 19(1), pp.
1-10. Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.18196/jesp.
0.0.3836
Rahardja, Pratama (2008) Pengantar Ilmu Ekonomi
(Mikroekonomi Dan Makroekonomi), Edisi Ketiga.
Fakultas Ekonomi. Universitas Indonesia
Swaramarinda, Darma Rika (2011) ‘Pengaruh Pengeluran
Konsumsi Dan Investasi Pemerintah Terhadap
Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Di Indonesia’, Jurnal Ilmiah
Ekonosains, 9(2), pp. 95-105. Availlable at:
https://doi.org/10.21009/econosains.0092.01
Sukirno (2006) Makroekonomi: Teori Pengantar. Penerbit
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
600

Pt. Raja Grafindo Persada: Jakarta..
Todaro, Michael (2011) Pembangunan Ekonomi Dunia
Ketiga Erlangga: Jakarta.
Effects of Population, Consumption and Exports on Economic Growth in Indonesia Period of 2005-2017
601
