
Evaluation the Effectiveness of Audit Design and Implementation in
Sub-cycle Procurement Information System: Case Study in PT. X
Rynaldo Jeremy Hamonangan
Magister Akuntansi, Pascasarjana Universitas Indonesia, Jl. Salemba Raya Nomor 4, Jakarta
Keywords: Effectiveness, Audit Design, Audit Implementation, COBIT 5, 3 Lines of Defense
Abstract: This research is based on the problem found in procurement sub-cycle information system that is access
violation, delay and wrong in decision making and lots of goods and services are excluded from cost
recovery calculation by government. This research is aim to evaluate the effectiveness of audit design and
implementation in sub-cycle procurement information system. This research is qualitative research. This
research method is case study. The research subject was PT. X (oil and gas company) and Department
Internal Audit and Compliance as an analysis unit. The sample was audit program in 2017. Research
instrument are interview and documentation. The result showed that audit design is not effective but audit
implementation is effective. The audit design is not effective because the same problem often occurs even
though internal auditor has conducted an audit and provide recommendation that has been implement by
management. Therefore, audit program cannot effect achievement of internal auditor objective that is to add
value and improve organization process to accelerate achievement of company objective (strategic,
operations, reporting and compliance). The main cause of the ineffective audit design is internal auditor not
perform all role according to COBIT 5 framework and doing the wrong role according to 3 lines of defense
framework, so that, internal auditor cannot identify the significant risk and root of problem. Therefore, this
research provides the design of internal auditor role that complied with COBIT 5 and 3 lines of defense
framework and 7 audit program design to eliminate the problem of procurement sub-cycle information
system in PT. X.
1 INTRODUCTION
Oil and gas industry has a lot of risk that is blowout
and oil spill, expensive investment but uncertainty of
existence of oil and gas, and numerous regulations.
Especially in Indonesia, regulations depend on
contract between government and oil and gas
company. Many oil and gas company in Indonesia
hold product sharing contract with type cost
recovery. As consequence, oil and gas company
should make work program and budget and wait
authorization for expenditure documents from
government to begin buy goods and services. If the
oil and gas company not complied with government
regulations, all goods and services that has been buy
will exclude from cost recovery calculation.
The main factor of risk above is procurement
mechanism and human skill and capability who is
part of information system. Many oil and gas
company use information technology and
application (like SAP) in procurement process.
Therefore, auditor should keep up with development
of information system in order to evaluate reliability
of communication networks competently (Weber,
1999:17). But in real, from a lot of instrument
provide by framework, auditor only use maturity
level to audit the information system because
easiness (Zhang and Fever, 2013:395). According to
Gordon (1998:103), one of factor that affected
blowout in oil and gas industry is organization that is
control, planning/ organization, and audit procedure.
PT. X has many problems in procurement sub-
cycle. The problem is KPPU give sanction to PT.X
for jack-up drilling service, empty goods and
services while needed, a lot of goods and services
are excluded from cost recovery calculation, human
error, access violation on AFE Account, WBS
master, budget and recording expense, access AFE
that has been closed, not all of committee member
1108
Hamonangan, R.
Evaluation the Effectiveness of Audit Design and Implementation in Sub-cycle Procurement Information System: Case Study in PT. X.
DOI: 10.5220/0009505411081113
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 1108-1113
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

sign WP&B, access violation in making invoice, and
record asset that there is no physical existence. This
problem has been identified by internal auditor and
audit has been performed. Internal auditor has given
recommendation and management has been doing
the recommendation. But the same problem always
occurs in next interim and next year.
2 METHODOLOGY
This research is qualitative research and the method
applied in this research was case study with mixed
method approached. According to Creswell in
Sugiyono (2017:404) mixed methods research is an
approach to inquiry that combines or associated both
qualitative quantitative forms of research. It involves
philosophical assumptions the use of quantitative
and qualitative approaches, and the mixing of both
approached in a study. Subject in this research was
PT. X (oil and gas company) with Department
Internal Audit and Compliance as an analysis unit.
The sample was audit program in 2017. The research
instrument was interview and documentation.
In this research to analyze the conformity of
internal auditor role with COBIT 5 framework were
use RACI chart from COBIT 5 framework and to
analyze the conformity of internal auditor role with
3 lines of defense framework were use 3 lines of
defense framework. To evaluate the effectivity of
audit design, this research divided the evaluation
into 2 categories effectiveness of audit design that is
effectivity based on criteria and effectivity based on
the effect.
Effectivity based on criteria refers criteria from
Sawyer (2006:235) and Information System Audit
and Control Association (ISACA) (2016:7, 13-15) as
an indicator and effectivity based on effect of audit
program is refers to 4 organization objective
(strategic, operations, reporting and compliance)
according to Pickett (2005:13-14) and the 4 effect of
audit information system according to Weber
(1999:11) as an indicator. To evaluate the effectivity
of audit implementation will perform with compare
all working paper with audit design (audit program).
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
From research that has been conducted, the result
show that internal auditor has been doing 2 from 4
roles in COBIT 5 framework that is responsible (R)
and accountable (A). But internal auditor not doing
another role that is consulted (C) and informed (I).
Internal auditor never showed his existence as a
place for management get advice and for discuss
about problem that faced by management.
Therefore, internal auditor always faced as
investigator by management. The second result is
internal auditor not complied with 3 lines of defense
framework because internal auditor actively
involved in making internal control system (1st line)
and risk management (2nd line).
For the main objective in this research that is
evaluate the effectiveness design and
implementation of audit in procurement sub-cycle
information system, this research will spread into
evaluate audit design and evaluate audit
implementation. The third result that is audit design
is complied with all criteria in Sawyer and ISACA
(effective in criteria) but not help internal auditor to
fulfil internal audit objective that is to accelerate
achievement of organization objective (strategic,
operations, reporting and compliance) so that audit
design not effective in effect/ result.
However, the effectivity of audit program is
achievement of audit program objective, which audit
program is internal auditor tool to achieve internal
audit objective that is to add value and improve
organization operation to accelerate achievement of
organization objective (strategic, operations,
reporting and compliance) as an indicator to evaluate
audit design effectiveness. Therefore, this research
conclude that audit design is not effective. The
fourth result is audit implementation is effective
because all audit program has been done while audit
is conducted.
After get the result that audit design is not
effective, this research will combine all result from
evaluate internal audit role according to COBIT 5
and 3 lines of defense to know what the root of
problem that cause audit design is not effective. The
result is audit design not effective because internal
auditor not perform all role according to COBIT 5
and wrong doing role according to 3 lines of
defense, internal auditor cannot identify significant
risk, weakness control that should be audited,
determination of audit objective and subject audit for
interview (All of this process is before internal
auditor writes the audit program (designing audit)).
This result is aligned with Sawyer (2006:217)
that said one of the function of audit internal
professional is to show that the program is effective-
only emphasize to significant things and to give
evidence that significant risk and control has been
identified and evaluated.
Furthermore, Sawyer (2006:217) said that
analysis that made with help from operational
manager- can give operational objective, identified
Evaluation the Effectiveness of Audit Design and Implementation in Sub-cycle Procurement Information System: Case Study in PT. X
1109
actual or potential risk, and determine the right
control for this situation. That analysis can produce
thoughtful, relevant, effective and economics audit
program.
Therefore, this research gave 2 output to improve
effectiveness of audit design that is the internal
auditor role that conform with COBIT 5 and 3 lines
of defense framework and 7 audit program to solve
the root of problem that identified in this research.
The role of internal auditor for Department
Internal Audit and Compliance is divided into 2
major that is role in governance and role in
management. The role of internal auditor in
governance is internal auditor should act as place of
management to ask about job allocation,
responsibility and management act in monitoring IT
and internal auditor should act as place of
management to ask about operation of information
system that is use and allocation of resource,
satisfied stakeholder need and risk management on
IT. The role of internal auditor in management is
actively act as consultant in project management,
requirement management and IT operation.
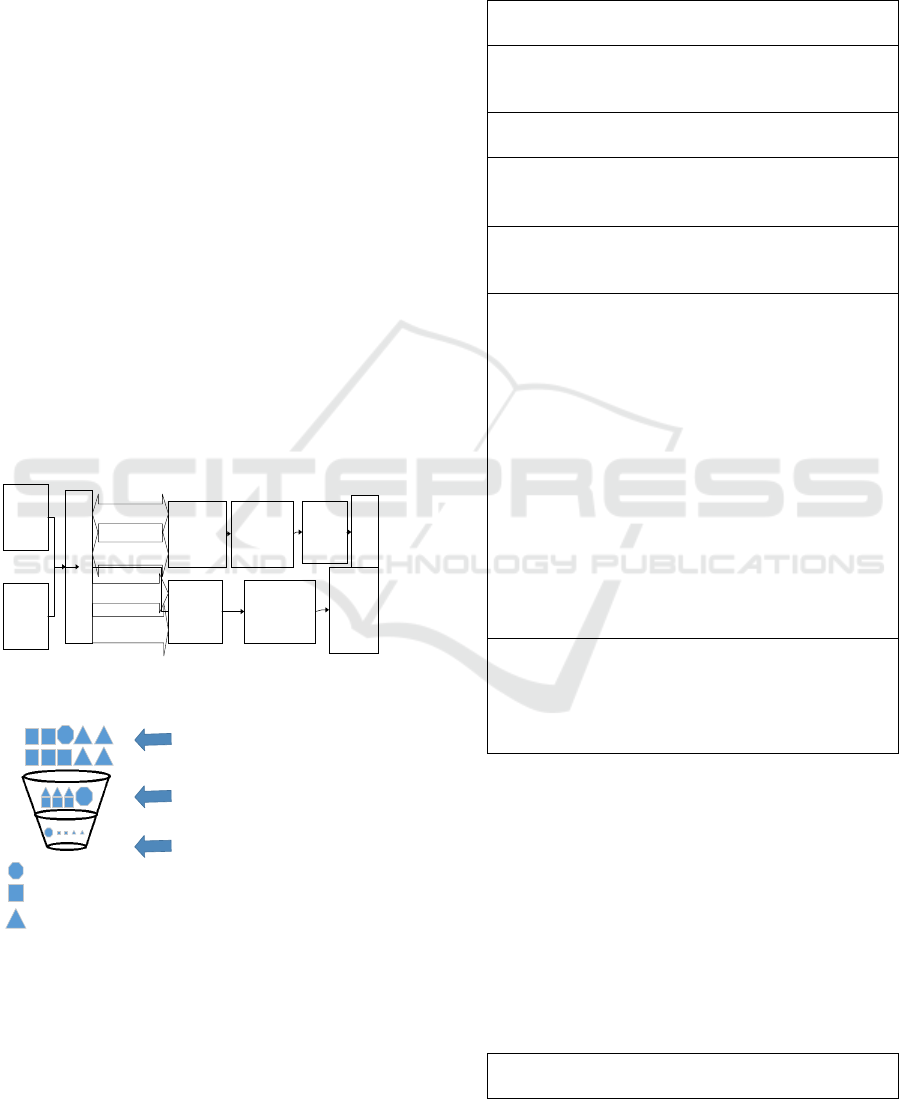
This figure below, describes the suggested
internal auditor’s role (figure 1) and the expected
effect of implementation of the role of internal
auditor that has suggested (figure 2):
COBIT 5
3 LINES OF
DEFENSE
INTERNAL AUDITOR
OPERATIONAL
MANAGEMENT
AND RISK
MANAGEMENT
AUDIT
DESIGN
(AUDIT
PROGRAM)
RISK
REDUCE
REDUCE RISK
BELOW RISK
TOLERANCE
CONSULTED
INFORMED
ACCOUNTABLE
RESPONSIBLE
BUILD INTERNAL
CONTROL AND
RISK
MANAGEMENT
EFFECTIVITY IN
DETERMINE
SIGNIFICANT
RISK
INTERNAL
CONRTOL
Figure 1: Role of Internal Auditor
= Strategic Risk
= Operational Risk
INTERNAL CONTROL THAT
BUILD BY MANAGEMENT AND
RISK MANAGEMENT
AUDIT PROGRAM BUILD BY
INTERNAL AUDITOR THAT
MORE FOCUS ON SPECIFIC
RISK AND STRATEGIC RISK
RISK APETITE DAN RISK
TOLERANCE
= Operational Risk
Figure 2: The Effect which were Expected from
Implementation the Role of Internal Auditor
The audit program in this research contain 7 audit
program that disembogue into 3 part that is:
1) Audit design for data redundancy
To solve wrong and delay in decision making
problem. There is 1 audit design (audit program) for
audit data redundancy, that is:
Table 1: Audit Design (Audit Program) for Data
Redundancy
AUDIT PROGRAM FOR DATA
REDUNDANCY
Audit Ob
j
ective:
To ensure control adequacy to mitigate data
redundanc
y
Time:
Interim 1
Risk:
1) Wrong in decision making
2) Delay in decision making
Control:
Memory capacity is allocate for each
department
Test:
1) Inspect standard operating procedure (SOP)
and compare with how end user using
worksheet
2) Take a sample of data redundancy and
identify who is updating the data redundancy
3) Inspect and compare all data redundancy (see
the data content and what the difference in
content of each data)
4) Compare all data redundancy with data that
has been attached in SAP (see the content
and compare the difference)
5) Discuss, confirm and ask to the user (data
owner and data updater) for the reason of
why data redundancy
Document:
1) Worksheet in Department Supply Chain
Management (procurement sub-cycle)
memory
2) Worksheet that has been attached in SAP
2) Audit design for database goods and services
To solve ordering goods and services that not
needed, ordering to not qualified supplier even
though supplier approved by SKK Migas, goods and
services are exclude from cost recovery calculation
by government and recorded goods that no physical
existence. There is 2 audit design (audit program)
for audit database goods and services, that is:
Table 2: Audit Design (Audit Program) for Goods
and Services Database
AUDIT PROGRAM FOR GOODS AND
SERVICES DATABASE
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1110
Audit Ob
j
ectives:
To ensure control adequacy to mitigate
purchase requisition for goods and services that
not needed.
Time:
Interim 1
Risk:
Purchase requisition for goods and services
that not needed
Control:
Access control
Test:
1) Compare all goods and services catalog with
physic of goods and services
2) Check addition or changes of catalog
parameter or catalog itself
3) Compare changes or addition of catalog
parameter or catalog itself with purchase
requisition (focus on time of occurrence)
4) Check log and see the person who makes
changes or addition on catalog parameter or
catalog itself
5) Re-performance:
a) Make a changes on catalog or catalog
parameter and makes purchase requisition
b) Make an addition on catalog or catalog
parameter and makes purchase requisition
6) Inspect all document of parameter catalog
Document:
1) Record or documentation of changes or
addition on catalog or catalog parameter
2) Record of purchase requisition time
3) Documentation of purchase requisition time
4) Log record of changes or addition on catalog
or catalog parameter
5) Log record of access to goods and services
database
Table 3: Audit Design (Audit Program) for Supplier
Database
AUDIT PROGRAM FOR SUPPLIER
DATABASE
Audit Ob
j
ective:
1) To ensure control adequacy to mitigate
purchasing goods and services that cannot
include in cost recovery calculation
2) To ensure control adequacy to mitigate
purchasing to unqualified supplier even
though the supplier approved by SKK Migas.
Time:
Interim 1
Risk:
1) Purchase goods and services that cannot
include in cost recovery calculation
2) Purchase to unqualified supplier even though
the supplier approved by SKK Migas.
Control:
1) Access
2) Authorization
Test:
1) Obtain purchase requisition (PR) and
purchase order (PO) document.
2) Compare purchase requisition (PR) and
purchase order (PO) document.
3) Check log to know who make purchase order
(PO) document
4) Inspect supplier parameter document and
compare with parameter in supplier database
5) Check log of changing in supplier database
parameter
6) Take a sample (focus on big and small
supplier) and compare supplier qualification
with parameter in database
7) Re-performance:
a) Input supplier name that you want to win
with not changing the parameter
b) Input supplier name that you want to win
with changing the parameter
Document:
1) Supplier parameter
2) List of SKK migas supplier
3) Log list of changing in database supplier
parameter
4) Supplier pra-qualification document
5) Purchase requisition (PR) document
6) Purchase order (PO) document
3) Audit design for administration role in SAP
To solve access violation problem. There is 4 audit
design (audit program) for audit administration role
in SAP, that is:
Table 4: Audit Design (Audit Program) for SAP
Support SOP
AUDIT PROGRAM FOR SAP
SUPPORT SOP
Audit Ob
j
ective:
To know the procedure of giving advice for
updatin
g
role in SAP
Time:
Interim 1
Risk:
There is a person who have 2 or more roles
in SAP
Control:
Segregation of duties
Control:
1) Inspect SOP of SAP Support in a process to
Evaluation the Effectiveness of Audit Design and Implementation in Sub-cycle Procurement Information System: Case Study in PT. X
1111
giving advice for updating role
2) Observe the evaluation mechanism in
determine the suitable role
Document:
SOP of SAP Support in giving advice for
updating role
Table 5: Audit Design (Audit Program) for SAP
Security Admin SOP
AUDIT PROGRAM FOR SAP
SECURITY ADMIN SOP
Audit Ob
j
ective:
To know the role updatin
g
process
Time:
Interim 1
Risk:
SAP Security Admin forget to revoke old
role
Control:
Se
g
re
g
ation of duties
Control:
1) Inspect SOP of SAP Security Admin in
updating role
2) Observe updating role process
Document:
SOP of SAP Security Admin in updating
role
Table 6: Audit Design (Audit Program) for
Information System and SAP Development,
Expansion and Maintenance Documentation
AUDIT PROGRAM FOR
INFORMATION SYSTEM AND SAP
DEVELOPMENT, EXPANSION AND
MAINTENANCE DOCUMENTATION
Audit Ob
j
ective:
1) To know information system access error
2) To know information system fault that can
infiltrated by parties outside the company
3) To detect and prevent the using of double
role because of the faulty of SAP Support
and SAP Security Admin
4) To know the existence of SAP Administrator
Time:
Interim 1
Risk:
Access that not conform with function and
p
osition but authorized by SAP
Control:
Access
Test:
1) Inspect development, expansion and
maintenance documentation
2) Try to access from every information system
network
3) Check the existence of SAP Administrator
function
Document:
1) Information system and SAP development
documentation
2) Information system and SAP expansion
documentation
3) Information system and SAP maintenance
documentation
Table 7: Audit Design (Audit Program) for SAP
Administrator SOP
AUDIT PROGRAM FOR SAP
ADMINISTRATOR SOP
Audit Ob
j
ective:
To ensure that SAP Administrator has gave
the control adequacy for all access in company
information system network (SAP)
Time:
Interim 2
Risk:
Access that not conform with function and
p
osition but authorized b
y
SAP
Control:
Se
g
re
g
ation of duties
Test:
1) Check SOP of SAP Administrator
2) Observe SAP Administrator Activity
3) Compare SOP with observation result of
SAP Administrator activity
Document:
SOP of SAP Administrator
4 CONCLUSIONS
According to research that has been conducted, the
conclusion is audit design is not effective but audit
implementation is effective. The problem that cause
audit design is not effective is internal auditor not
doing all role according to COBIT 5 (only
responsible and accountable but not consulted and
informed) and wrong doing role according to 3 lines
of defense (internal auditor actively involved in
make internal control system and risk management).
This problem make internal auditor cannot identify
significant risk and root of the problem in a process
to design audit (audit program).
REFERENCES
Gordon, Rachael P. (1998). The contribution of human
factors to accidents in the offshore oil industry.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1112

Reliability Egineering and System Safety 61 (95-
108)
Information System Audit and Control Association.
(2016). Information System Auditing: Tool and
Techniques Creating Audit Program
___________________________________________.
(2014). Assessment Programme
___________________________________________.
(2012). COBIT 5 Enabling Process
___________________________________________.
(2012). COBIT 5 Implementation
___________________________________________.
(2012). COBIT 5 A Business Framework for the
Governance and Management of Enterprise IT
Pickett, K.H. Spencer. (2005). Auditing the Risk
Management Process. New Jersey: John Willey &
Sons, Inc
Sawyer, Lawrence B. et al. (2006). Sawyer’s Internal
Auditing Audit Internal Sawyer (Desi Adhariani,
Penerjemah) (Edisi 5) (Buku 1). Jakarta: Salemba
Empat
______________________. (2006). Sawyer’s Internal
Auditing Audit Internal Sawyer (Desi Adhariani,
Penerjemah) (Edisi 5) (Buku 2). Jakarta: Salemba
Empat
______________________.(2006). Sawyer’s Internal
Auditing Audit Internal Sawyer (Ali Akbar,
Penerjemah) (Edisi 5) (Buku 3). Jakarta: Salemba
Empat
Sugiyono. (2017). Metode Penelitian Kombinasi (Mixed
Method). Bandung: Alfabeta
Weber, Ron. (1999). Information System Control and
Audit. New Jersey: Prentice Hall
Zhang, Shengnan & Hans Le Fever. (2013) An
Examination of Practicability of COBIT Framework
and the Proposal of a COBIT-BSC Model. Journal
of economics, Business and Management, 1 (4)
Evaluation the Effectiveness of Audit Design and Implementation in Sub-cycle Procurement Information System: Case Study in PT. X
1113
