
Fraud Disclosure: Determinants and Implication
Enggar Diah Puspa Arum
1
and Diza Armalia Wisdianti
1
1
Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Jambi, Jambi-Indonesia
Keywords: Audit Committee, Internal Audit, Managerial Ownership, Whistleblowing System, Fraud Disclosure, Market
Reaction
Abstract: The purpose of this research is to analyze factors affecting fraud disclosure and its implication on market
reaction. Audit committee, internal audit, managerial ownership, and internal control play important role to
reach good governance that can reduce fraud. Whistleblowing system is a part of internal control and expected
to strengthen good governance. Minimizing the possibility of fraud is expected to improve the company's
reputation as reflected in market reactions. This research was analyzed by using path analysis. Target
population is banking industries listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange. Results showed that audit committee,
internal audit, and managerial ownership have a positive effect on whistleblowing system. Internal audit and
whistleblowing system have a negative effect on fraud disclosure. Audit committee and whistleblowing
system have a positive effect on market reaction, and fraud disclosure has a negative effect on market reaction.
This research provides empirical evidence that the better the governance structure the better the
whistleblowing system. The better implementation of the whistleblowing system, the less disclosure of fraud.
Furthermore, the less fraud disclosure the better the market reaction.
1 INTRODUCTION
Accounting fraud cases still occur until now,
including one of the big companies in the UK. At the
beginning of the second quarter of 2017, British
Telecom known to perform accounting fraud at one
of its business lines in Italy. Accounting fraud was
detected by a whistleblower. The modus operandi is
to perform an increase in the profits of the company
for several years through corruptive cooperation with
corporate clients and financial services. The practice
of accounting fraud has occurred since 2013 with the
motive of obtaining a bonus as a stimulus. The fraud
scandal caused losses to shareholders and investors
where British Telecom's share price plummeted when
it announced a correction of its 530 million earnings
in January 2017 (Priantara, 2017).
Accounting fraud scandals also occured on large
companies in Japan, namely Toshiba. In May 2015 it
was revealed that Toshiba did a lie through
accounting fraud, with a value of 1.22 billion US
dollars. Toshiba then was removed from the stock
index and a significant sales decline occured. (Sari,
2017).
Accounting fraud cases in Indonesia are
dominated by the banking industry. According to the
statement of the Chief Executive of the OJK Banking
Supervisor, Nelson Tampubolon, from January to the
end of the third quarter of 2016, the Financial
Services Authority (OJK) recorded 26 cases of
banking crime (OJK, 2016).
Indonesia still has a high risk of fraud and the
most detrimental fraud is fraudulent financial
reporting (ACFE, 2016). One of the most effective
ways to prevent fraud is through a whistleblowing
system mechanism where the effectiveness can be
seen from the number of frauds that have been
detected as well as the shorter time of action
compared to other methods. The Whistleblowing
System is a part of the internal control system in
preventing the practice of irregularities and fraud and
strengthening the application of good governance
practices (KNKG, Pedoman Sistem Pelaporan
Pelanggaran - SPP (Whistleblowing System - WBS),
2008) (KNKG, Pedoman Sistem Pelaporan
Pelanggaran - SPP (Whistleblowing System - WBS),
2008). An effective internal control system requires
the support of directors as the management of the
company, an audit committee that carries out overall
supervision, and an internal audit as part of its duties
and responsibilities (KNKG, Pedoman Umum Good
Corporate Governance Indonesia, 2006).
Arum, E. and Wisdianti, D.
Fraud Disclosure: Determinants and Implication.
DOI: 10.5220/0009500510011005
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 1001-1005
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
1001

The market penalizes fraud firms significantly
when the prospective fraud news is released to the
public (Christensen, Paik, & Williams, 2010).
Investors perceive fraudulent reporting to be more
prevalent in the economy or rely more on financial
statement information relative to other sources of
information, they place greater importance on
conducting their own fraud risk assessments. In turn,
investors who deem fraud risk assessment to matter
in investment decision making make greater use of
fraud red flags to avoid potentially fraudulent
investments (Brazel, Jones, Thayer, & Warne, 2015).
This study is a replication of the research of
Cahyo & Sulhani (2017) which indicated that the
audit committee had a negative effect on
whistleblowing system while the internal audit had no
effect on the whistleblowing system. Furthermore,
the whistleblowing system did not affect fraud
disclosure and fraud disclosure had a significant
negative effect on the market reaction. This study
intends to reexamine the variables that have been
studied by adding managerial ownership variables as
one element of the governance structure.
2 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 Audit Committee and Whistleblowing
System
The audit committee must have members who are
experts in the financial sector to improve the
supervision of the company. Increasing oversight of
companies has an impact on improved internal
control and reduced fraud practices (KNKG,
Pedoman Umum Good Corporate Governance
Indonesia, 2006). The Audit Committee which has
expertise in finance reduces problems in internal
control. This means that Audit Committee members
who have expertise in finance can increase the
effectiveness of internal controls (Khrisnan, 2005).
According to Lee and Fargher (2018), higher-quality
audit committee is associated with the
implementation of a stronger internal whistleblowing
system, so the first hypothesis in this study is
formulated as follows:
H
1
: The audit committee has an effect on the
whistleblowing system.
2.2 Internal Audit and Whistleblowing System
The importance of appropriate whistleblowing
policies and procedures to the effective discharge of
an organization’s corporate governance is significant.
Corporate governance is fundamental to effective risk
and control within organisations, which means that
whistleblowing policies must be at the heart of
internal auditors’ responsibilities (Cowan, 2014). In
other words, internal audit is a party that plays an
important role in implementing the whistleblowing
system (Read & Rama, 2003).
Internal audit function effectiveness influenced by
internal auditor competency (Arum, 2015). Therefore
internal audit competencies that measured by
expertise in finance will improve the implementation
of a whistleblowing system, so the second hypothesis
in this study is as follows:
H
2
: The internal audit has an effect on the
whistleblowing system.
2.3 Managerial Ownership and
Whistleblowing System
Managerial ownership can help reduce opportunistic
actions to maximize personal interests, in addition
managers will also be more careful in making
decisions that are in accordance with the interests of
the company because it is related to their interests as
owners, so that disclosure of internal control
information will be more qualified (Wardani &
Sulhani, 2017). Therefore the third hypothesis in this
study is as follows:
H
3
: The managerial ownership has an effect on the
whistleblowing system
2.4 Whistleblowing System and Fraud
Disclosure
Whistleblowing system can detect the majority of
fraud in an organization. Whistleblowing system is a
device that can be used to warn management about
fraud within the company (KNKG, Pedoman Sistem
Pelaporan Pelanggaran - SPP (Whistleblowing
System - WBS), 2008). The disclosure of fraud has
become an early detection of company management
to prevent ongoing fraud (Khan, Anuar, & Mahzan,
2014). So that the fourth hypothesis in this study is as
follows:
H
4
: The whistleblowing system has an effect on
the fraud disclosure
2.5 Fraud Disclosure and Market Reaction
According to ACFE (2016), companies that are
indicated to have fraud can reduce their business
reputation so that it can cause losses to the company.
Disclosure of fraud and the use of financial statement
information have an effect on investor perceptions in
conducting investment risk assessments (Brazel,
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1002

Jones, Thayer, & Warne, 2015). Companies that
indicated fraud cases experienced a decline in the
stock market reaction (Christensen, Paik, & Williams,
2010). So the fourth hypothesis in this study is as
follows:
H
5
: The fraud disclosure has an effect on the market
reaction.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
The type of research is quantitative research that uses
secondary data in its analysis. According to Sekaran
& Bougie (2013), secondary data is the data or
information collected from available sources.
Secondary data for this study was obtained from
annual reports of research subject. The data can be
downloaded on the relevant company website pages
as well as on the Indonesia Stock Exchange website.
While the company's stock price data was obtained
from the Indonesia Stock Exchange website.
The target population in this study were banking
companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange in
2017. All members of the target population were used
as samples in the study. Data analysis in this study
was tested by using path analysis with SPSS 22
Program.
The object of this research is the audit committee,
internal audit, managerial ownership, whistleblowing
system, fraud disclosure, and market reaction. The
audit committee variable was measured by the ratio
of the number of members who have accounting and
financial backgrounds to the total number of audit
committee members.The internal audit variable was
measured by dummy variable, if the head of the
division of internal auditors have a background in
finance experts then rated 1, and if otherwise then
rated 0. The managerial ownership variable was
measured by percentage of share ownership by the
companies manager. The fraud disclosure was
measured by the amount of fraud reported in that
period on the annual report, and the market reaction
was measured by stock returns.
Hypothesis testing is done to obtain empirical
evidence of the influence of the audit committee,
internal audit, and managerial ownership on the
whistleblowing system. Hypothesis testing is also
done to obtain evidence of the influence of the
whistleblowing system on fraud disclosure and its
implications for market reaction.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 The Effect of Audit Committee on
Whistleblowing System
Based on statistical testing, it is empirically proven
that the audit committee has a positive effect on the
whistleblowing system. This can be seen from the
direction of the regression coefficient and the
significance level of 0.045 which is smaller than 0.05
(table 1). Thus Hypothesis 1 in this study was
accepted.
The background of the financial expertise of the
audit committee has a role in improving internal
control in the implementation of the whistleblowing
system. The results of this study indicate that the audit
committee has carried out overall supervision
including internal control and the Whistleblowing
system..
4.2 The Effect of Internal Audit on
Whistleblowing System
The result of statistical test showed that internal audit
has a positive effect on the whistleblowing system.
This is indicated by the direction of the regression
coefficient showing a positive number and a
significance level of 0.027 which is smaller than 0.05
(table 1). Thus hypothesis 2 in this study was
accepted.
The head of the internal audit division with an
accounting and financial education background is
proven to be able to improve internal control in a
whistleblowing system. The internal audit division
has a large responsibility in overseeing and ensuring
that the internal control function has been running
effectively.
4.3 The Effect of Managerial Ownership on
Whistleblowing System
The result of statistical test showed that managerial
ownership has a positive effect on the whistleblowing
system. This is indicated by the direction of the
positive coefficient and the significance level
obtained is 0.036 which is smaller than 0.05 (table 1).
Managerial ownership is indicated by the number of
shares owned by the board of commissioners,
directors, and management in a company. The results
of the observations in this study indicate the
percentage and number of share ownership by
management is still few. But managerial ownership
proved to have a positive effect on the whistleblowing
system.
Fraud Disclosure: Determinants and Implication
1003
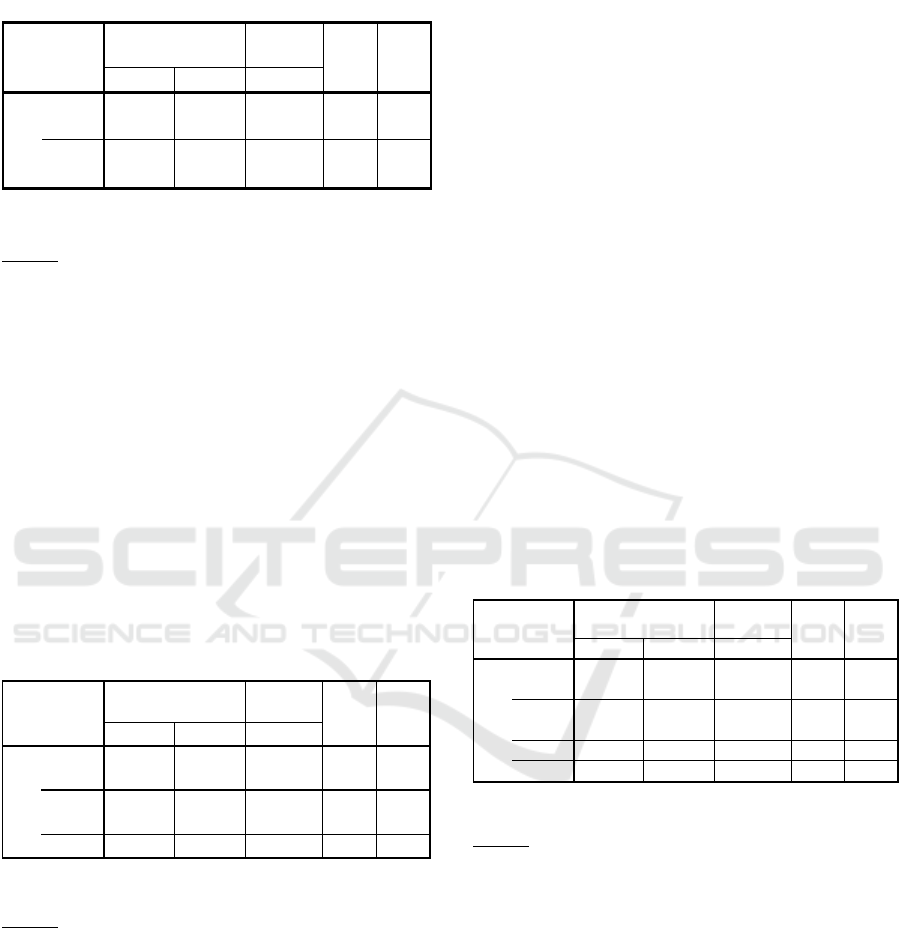
Table 1: Test Results of the Effect of Audit
Committee, Internal Audit, and Managerial
Ownership on Whistleblowing System
Source: SPSS 22 output based on research data
4.4 The Effect of Whistleblowing System on
Fraud Disclosure
Based on the results of statistical testing using SPSS,
the whistleblowing system has a negative effect on
fraud disclosure. This can be seen in the direction of
the negative regression coefficient and the level of
significance smaller than 0.05 (table 2). Thus it can
be said that hypothesis 4 in this study was accepted.
The existence of a whistleblowing system is to
prevent and reduce fraud. Based on the results of this
study it can be said that the whistleblowing system is
proven to reduce fraud disclosure.
Table 2: Test Results of the Effect of Whistleblowing
System on Fraud Disclosure
Source: SPSS 22 output based on research data
The direct effect of the audit committee on fraud
disclosure is 0.236 while the indirect effect is -0.084,
so the total effect is 0.152. The direct effect of the
internal audit on the fraud disclosure was -0.139
while the indirect effect was -0.252, so the total effect
was -0.391. Furthermore, the direct effect of
managerial ownership on fraud disclosure is 0.094
while the indirect effect is -0.081, so the total effect
is 0.013.
4.5 The Effect of Fraud Disclosure on Market
Reaction.
Based on the result of the study, fraud disclosure has
a negative effect on market reaction as measured by
stock returns. This can be seen from the direction of
the negative regression coefficient and the
significance level of 0.002 which is smaller than 0.05
(table 3). Thus it can be said that Hypothesis 5 in this
study was accepted.
Based on the research result showed that the lower
the level of fraud disclosure, the higher the stock
return, and conversely the higher the level of fraud
disclosure, the lower the stock return.
The direct effect of the audit committee on the
market reaction is 0.363 while the indirect effect is -
0.138, so the total effect is 0.225. The direct effect of
the internal audit on market raction is -0.159 while the
indirect effect is 0.081, so the total effect is -0.078.
The direct effect of managerial ownership on the
market reaction is -0.141 while the indirect effect is -
0.055, so the total effect is -0.196. Furthermore, the
direct effect of WBS on the market reaction is 0.052
while the indirect effect is 0.409, so the total effect is
0.461.
Table 3: Test Results of the Effect of Fraud
Disclosure on Market Reaction
Source: SPSS 22 output based on research data
5 CONCLUSIONS
This research examined the effect of audit committee,
internal audit, managerial ownership, and
whistleblowing system on fraud disclosure and their
implication on market reaction. The results indicated
that the better the audit committee, the better the
whistleblowing system. The better the internal audit,
the better the whistleblowing system. The better the
managerial ownership, the better the whistleblowing
system. Whistleblowing system has a negative effect
Coefficients
a
Model
Unstandardized Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t Sig. B Std. Error Beta
1 (Constant) .299 .053
5.642 .000
AC .074 .096 .120 .764 .045
IA .147 .064 .360 2.295 .027
MO .141 .179 .115 .787 .036
a. Dependent Variable: WBS
Coefficients
a
Model
Unstandardized Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t Sig. B Std. Error Beta
1 (Constant) 1.077 .179
6.005 .000
AC .483 .245 .236 1.973 .056
IA -.189 .172 -.139 -1.100 .027
MO .384 .454 .094 .845 .040
WBS -2.333 .399 -.701 -5.848 .000
a. Dependent Variable: FD
Coefficients
a
Model
Unstandardized Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t Sig. B Std. Error Beta
1 (Constant) -.027 .024
-1.137 .263
AC .066 .025 .363 2.675 .011
IA -.019 .017 -.159 -1.147 .259
MO -.051 .044 -.141 -1.162 .253
WBS .015 .053 .052 .293 .071
FD -.052 .015 -.583 -3.374 .002
a. Dependent Variable: MR
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
1004

on fraud disclosure and fraud disclosure has a
negative effect on market reaction.
This research is only conducted on banking
companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange in
2017, therefore the further research is expected to
expand observations on other type companies. This
study also only used stock returns to measure market
reaction, therefore further research is expected to use
other indicators to measure market reaction, such as
abnormal returns and cumulative abnormal returns.
Further research is also expected to examine other
variables that related to good governance to explain
their effect on fraud disclosure and market reaction.
REFERENCES
ACFE. (2016). Survai Fraud Indonesia. Jakarta: ACFE
Indonesia Chapter.
Arum, E. D. P. (2015). Determinants of Internal Audit
Function Effectiveness and Its Implication on Financial
Reporting Quality. International Journal of Economic
Research, 12(5), 1989-2000.
Brazel, J. F., Jones, K. L., Thayer, J., & Warne, R. C.
(2015). Understanding Investor Perceptions of
Financial Statement Fraud and their Use of Red Flags:
Evidence from the Field. Review of Accounting
Studies, 20(4), 1373–1406.
Cahyo, M. N., & Sulhani. (2017). Analisis Empiris
Pengaruh Karakteristik Komite Audit, Karakteristik
Internal Audit, Whistleblowing System, Pengungkapan
Kecurangan Terhadap Reaksi Pasar. Jurnal Dinamika
Akuntansi dan Bisnis, 4(2), 249-270.
Christensen, T. E., Paik, D. G., & Williams, C. (2010).
Market Efficiency and Investor Reactions to SEC Fraud
Investigations. Journal of Forensic & Investigative
Accounting, 2(3), 1-30.
Cowan, M. (2014). Whistle-blowing: Not Childs Play for
Internal Auditors. New Mexico: Thomson Reuters.
Khan, M., Anuar, B., & Mahzan, N. (2014). The
intervening effects of whistleblowing in reducing the
risk of asset misappropriation. Journal of Business and
Economics, 5(10), 1929-1939.
Khrisnan, J. (2005). Audit Committee Quality and Internal
Control: An Empirical Analysis. The Accounting
Review, 80(2), 649-675.
KNKG. (2006). Pedoman Umum Good Corporate
Governance Indonesia. Jakarta: Komite Nasional
Kebijakan Governance.
KNKG. (2008). Pedoman Sistem Pelaporan Pelanggaran-
SPP (Whistleblowing System-WBS). Jakarta: Komite
Nasional Kebijakan Governance.
Lee, G., & Fargher, N. L. (2018). The Role of Audit the
Committee in Their Oversight of Whistle-blowing.
AUDITING: A Journal of Practice & Theory, 37(1),
167-189.
OJK. (2016, November 14). Siaran Pers Otoritas Jasa
Keuangan. Retrieved from ojk.go.id: https://www.ojk.
go.id/id/berita-dan-kegiatan/siaran-pers/Documents/
Pages/Siaran-Pers-Tekan-Kasus-Tindak-Pidana-
Perbankan,-OJK-Luncurkan-Buku-Pahami-dan-
Hindari/SIARAN%20PERS%20SOSIALISASI%20TI
PIBANK.pdf
Priantara, D. (2017, June 22). Warta Ekonomi. Retrieved
from wartaekonomi.co.id: https://www.wartaekonomi.
co.id/read145257/ketika-skandal-fraud-akuntansi-
menerpa-british-telecom-dan-pwc.html
Read, W. J., & Rama, D. V. (2003). Whistle-blowing to
Internal Auditors. Managerial Auditing Journal, 18(5),
354-362.
Sari, K. (2017, September 14). Integrity. Retrieved from
integrity-indonesia.com: https://integrity-
indonesia.com/id/blog/2017/09/14/skandal-keuangan-
perusahaan-toshiba/
Sekaran, U., & Bougie, R. (2013). Research Methods for
Business: A Skill Building Approach. UK: John Wiley
& Sons.
Fraud Disclosure: Determinants and Implication
1005
