
Corporate Social Responsibility is Viewed from a Contingency
Perspective
Danri Toni Siboro
1
, Audrey M. Siahaan
1
, Iskandar Muda
2
and Syafruddin Ginting
2
1
Student Postgraduate, Faculty Economic and Business, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan Indonesia
2
Lecture Faculty Economic and Business, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan Indonesia
Keywords: Stakeholder Theory, Contingency Theory, Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Abstract: Corporate Social Responsibility is a corporate social responsibility to stakeholders where the company is
part of the social environment. Corporate Social Responsibility must achieve balance or must be able to
integrate from the start of environmental economics and social issues at the same time can provide and meet
the expectations of shareholders and stakeholders. So, the company has a responsibility to the corporate
environment. Most companies do only corporate social responsibility voluntarily. Contingency theory is a
theory that adjusts leaders to the right conditions. Contingency theory argues that leader performance is
determined from his understanding of the situation in which they lead. Managers sometimes lack
understanding of the mindset rather than Corporate social responsibility. This study uses a literature study to
see how CSR is viewed from contingency theory. From the analysis, it can be concluded that CSR with
company performance occurs in differences of opinion. There are researchers who claim that the
implementation of CSR is determined by industry partnerships, the role of government, and managerial
incentives. The implementation of corporate social responsibility in the company must be freed from short-
term goals. Corporate social responsibility does not directly have an impact on improving financial
performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
The phenomenon of Corporate Social Responsibility
(CSR) is often a very phenomenon issue; among
companies in Indonesia. In Indonesia corporate
social responsibility is required by law. This is
indicated by the issuance of the Limited Liability
Company Law (UU PT) No. 40 Article 74 of 2007
and entered into force on August 16, 2007. For
companies that go public in Indonesia regulations
regarding social and environmental responsibility
are regulated by the Financial Services
Authorization in OJK Regulation No. 29 / POJK.04 /
2016 concerning annual reports Issuer or public
company. Corporate Social Responsibility Practices
in Indonesia only aim to fulfill the obligations of the
OJK, impose sanctions, a portion of funds and
business interests. The implementation of Corporate
Social Responsibility should have meaning, the
ongoing implementation, the value of the Corporate
Social Responsibility, the goal of sustainable
implementation rather than Corporate Social
Responsibility.
Companies in Indonesia only view Corporate
Social Responsibility as a tool to obtain foreign
funds that are not subject to taxes and other
regulatory obligations. The company has many
objections to the implementation of Corporate Social
Responsibility because the implementation of
Corporate Social Responsibility will impose
company budgets. The implementation of Corporate
Social Responsibility in the company is only limited
to absurd statements or principles that will not be
able to function to solve various social and business
environment problems.
Basically, Corporate Social Responsibility is an
ongoing commitment from the company's business
that acts ethically and contributes to the economic
development of the local community or the wider
community, along with improving the standard of
living of the people around them. Corporate Social
Responsibility must achieve balance or must be able
to integrate from the start of environmental
Siboro, D., Siahaan, A., Muda, I. and Ginting, S.
Corporate Social Responsibility is Viewed from a Contingency Perspective.
DOI: 10.5220/0009499109730977
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 973-977
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
973

economics and social issues at the same time can
provide and meet the expectations of shareholders
and stakeholders.
In Indonesia, a business will be seen as
implementing Corporate Social Responsibility only
for companies engaged in mining or companies
related to Natural Resources, while companies that
do not manage Natural Resources but have an
impact on Natural Resources will never be seen
implementing Corporate Social Responsibility.
Stakeholders always think of how management
in the company is effective and must be able to
understand and implement strategic and tactical
decisions. The purpose of business is to create as
much value as possible for stakeholders.
The corporate environment is part of one of the
desires of stakeholders for the survival of the
company. The theory that can fulfill the desires of
stakeholders for environmental purposes is a
contingency theory. Where this theory will make the
proposition between company activity and company
structure will be formed from the constraints of the
external environment.
Good management oversight of certain activities
and circumstances will be able to encourage the
company to achieve and the company's desires in the
future. Contingency theory can improve the
performance of entities as well as company
management. One contingency factor is the external
environment. The external environment is a source
of information and the need for information, where
information is needed in the stock market to see
whether the situation is stable or not. This
information can be obtained indefinitely. One of the
external environmental information is the corporate
social responsibility.
2 LITERATURE STUDY
Stakeholders Theory
This theory is about how management functions to
satisfy the owners and people around the company.
Company management seeks to combine
performance improvement with increased
stakeholder satisfaction. This theory puts forward
the interests of stakeholders first compared to the
interests of company management.
According to Freeman, stakeholder theory can
identify value as the main driver of the company,
and also recognizes that the value must be shared
with a group of stakeholders were not only
shareholders and company managers but also actors
in the community who might have an interest in the
company's operations. (Theodoulidis et al., 2017).
The company is part of several elements that
make up society in the social system. This condition
creates a reciprocal relationship between the
company and the stakeholders. This means that the
company must carry out its role in two directions,
namely to meet the needs of the company itself and
stakeholders.
Contingency Theory
Contingency theory is a theory of leader suitability
which means adjusting the leader to the right
conditions. This theory argues that leader
performance is determined from his understanding
of the situation in which they lead. In simple terms,
contingency theory emphasizes leadership style and
understanding the right situation by the leader.
This theory can be used to answer questions
about someone's leadership with various types of
organizations. This theory can be used to predict
someone who has worked well at one position in an
organization will be equally effective when moved
to a different position. This theory can provide
changes in the good management of top
management with lower management.
According to Donaldson, contingency theory
shows that the results of organizational effectiveness
from the characteristics of the right organization will
reflect the organizational situation. (McAdam,
Miller and McSorley, 2016). The company seeks to
improve performance by increasing conformity and
harmony with the series that has been determined by
contingency theory. Contingency theory will be very
useful when there is a shortage of existing
theoretical frameworks by emphasizing an approach
based on suitable contingencies compared to what is
best done to manage the company.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Corporate Social Responsibility is a concept in a
company where the company has responsibility to
stakeholders (such as employees, consumers,
producers, shareholders, a community and
environment) in all company operations that cover
economic, social and environmental aspects. This
Corporate Social Responsibility has a very close
relationship with sustainable development.
Sustainable development in the perspective of
corporate social responsibility must be in the form of
short-term sustainability and long-term
sustainability.
The concept of Corporate Social Responsibility
today is very popular, but uniformity has not been
found in defining the concept of Corporate Social
Responsibility. Corporate social responsibility is
also often seen as a company's business commitment
to sustainable development. To run the company's
operations, based on the point of view of corporate
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
974
social responsibility, the company should not just
look at it from an economic aspect, but also must
look at the social and environmental aspects. For
example, in gaining profits so that dividends can be
distributed, companies must also see the impact of
the emergence of these benefits and for stakeholders
what can be obtained from these benefits.
Corporate social responsibility can also be
business behavior related to business ethics. So,
companies must be responsible for the company's
social environment. In practice, a company must be
more motivated to do more corporate social
responsibility than obligations under a regulation.
There is a relevant relationship between
Corporate social responsibility in the business and
strategies naturally in the company's activities.
Corporate social responsibility and company
performance are considered the most important for
generating wealth and improving company
performancen. (Gallardo-Vázquez and Sanchez-
Hernandez, 2014).
Although many companies have realized the
importance of carrying out CSR, there are also those
who object to implementing it. Even among those
who agree that companies run CSR, there are still
differences in interpreting the level of company
involvement in carrying out CSR. In the end, the
success of CSR and the scope of CSR programs that
are carried out will be determined by the level of
awareness of business people and other relevant
stakeholders.
Corporate Social Responsibility From the
Viewpoint of Contingency Theory
The implementation of Corporate Social
Responsibility carried out by the company as a form
of accountability and concern for the environment
around the company. Many benefits obtained by the
company with the implementation of Corporate
Social Responsibility, among others, products are
increasingly preferred by consumers and companies
are attracted by investors..
Contingency theory says that there is no best
method for managing a company. Management must
be able to balance internal needs and adapt to
environmental conditions. Management must be able
to harmonize and balance internal needs with the
environment.
Most companies do corporate social
responsibility only voluntarily. This mindset guide is
the collection and interpretation of new information.
Because mindset acts as an information filter, it is
dynamic and continues to develop in response to
new information. At this time new information
appears and is not consistent with this mindset that
will make the mindset change. The following in
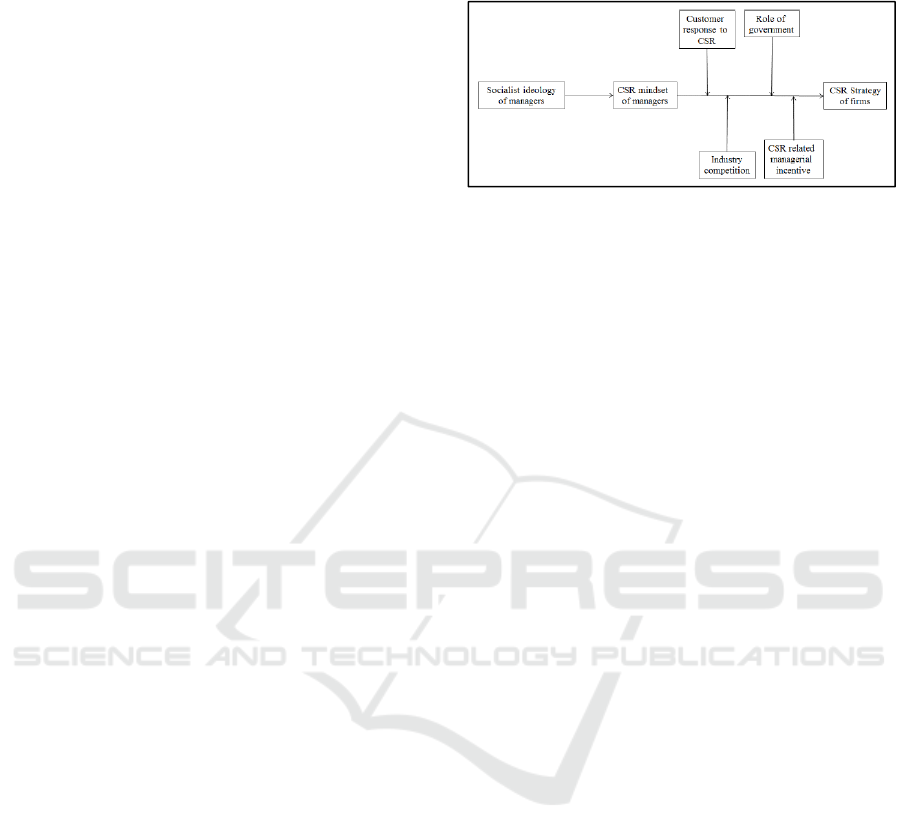
Figure 1 we can see the contingent framework
according to Jiang et al.
Figure 1: A contingent Framework of Political
Ideology, CSR mindset and CSR Stategy
Managers sometimes lack understanding of the
mindset rather than Corporate social responsibility,
so they do not consider Corporate social
responsibility less. A manager's mindset can be in
the form of the desire to maximize profits, or the
manager is considered as the representative of the
owner of the company or, more concerned with
improving the manager's personal life. Corporate
social responsibility often focuses on fulfilling
employee rights, social justice, and environmental
preservation. This is what makes the mindset of
Corporate Social Responsibility for each manager
different so that he is unable to understand the
purpose of overall corporate social responsibility.
3 METHODOLOGY
The researcher conducted a literature study to find
out how the implementation of corporate social
resposibility is seen from the perspective of a
contingency perspective. Researchers examine from
several journals related to corporate social
resposibility and contingency theory. The researcher
wants to find out whether how corporate social
resposibility is carried out by companies for the
interests of stakeholders so that a contingency
perspective is needed.
4 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
Contingency theory explains that the higher the fit
between management control predictions and other
contingent factors, the higher the level of
achievement of entity performance or vice versa.
The results of research on corporate social
responsibility with the company's performance are
very much and there are differences of opinion, there
is research that there is a positive relationship
between corporate social responsibility and company
Corporate Social Responsibility is Viewed from a Contingency Perspective
975

performance. And there are also results of research
saying that there is a negative relationship between
corporate social responsibility and company
performance. But there are also studies that say there
is no relationship between corporate social
responsibility and company performance.
Corporate social responsibility has a positive
relationship with company performance. (Wang et
al., 2015). The benefits of corporate social
responsibility will be greater in value than the costs
incurred. The commitment of a company to
implement Corporate Social Responsibility will
increase economic value.
Corporate social responsibility has a negative
relationship with company performance. (Mallin,
Farag and Ow-Yong, 2014; Chen, Feldmann and
Tang, 2015). This is because the company believes
that the social environmental costs are avoidable
costs.
Corporate social responsibility has no
relationship with company performance. (Lu et al.,
2014).
According to Jiang et al., (2015) that managerial
decision making in terms of strategy Corporate
social responsibility is influenced by political
ideology. The manager's mindset will influence the
strategy of Corporate social responsibility. The
strength of the relationship between the mindset of
Corporate social responsibility and the choice of
strategy Corporate social responsibility is moderated
by customer responses to Corporate social
responsibility, industry competition, the role of
government, and managerial incentives related to
corporate social responsibility. (Jiang et al., 2018).
In the economy in transition, manufacturing
companies are encouraged to invest more in
corporate social responsibility. According to the
managers of a company that implements corporate
social responsibility, it will create better customers
and increase the value of a company. Xie (2017)
stated that efforts to improve corporate social
responsibility can improve customer satisfaction and
recognition so that financial performance is better.
(Xie et al., 2017).
During the implementation of Corporate Social
Responsibility, all parties in the company must be
freed from short-term goals. Corporate social
responsibility does not directly have an impact on
improving financial performance.(Lu et al., 2018).
The owner and top management of the company
must consider the employee to be a tool to connect
the success of Corporate social responsibility.
Because, the company invests its money in
Corporate Social Responsibility, and the company
receives great benefits for the implementation of
Corporate Social Responsibility.. (De Roeck and
Maon, 2018).
5 CONCLUSIONS
Many company management, in allocating company
resources to improve the performance of Corporate
social responsibility. The resources owned and used
by the company do not fully translate into
productive efficiency and economic values. Every
company that moves and operates competitively will
present heterogeneity in terms of time availability.
REFERENCES
Chen, L., Feldmann, A. and Tang, O. (2015)
‘Therelationship between disclosures of
corporate social
016/J.IJPE.2015.04.004.Gallardo-Vázquez, D.
and Sanchez-Hernandez, M. I. (2014)
‘Measuring Corporate Social Responsibility
for competitive success at a regional level’,
Journal of Cleaner Production. Elsevier, 72,
pp. 14–22. doi:
10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2014.02.051.
Jiang, F. et al. (2018) ‘Mapping the relationship
among political ideology, CSR mindset, and
CSR strategy: A contingency perspective
applied to Chinese managers’, Journal of
Business Ethics, 147(2), pp. 419–444. doi:
10.1007/s10551-015-2992-7.
Lu, W. et al. (2014) ‘A decade’s debate on the nexus
between corporate social and corporate
financial performance: a critical review of
empirical studies 2002–2011’, Journal of
Cleaner Production. Elsevier, 79, pp. 195–206.
doi: 10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2014.04.072.
Lu, W. et al. (2018) ‘The paradoxical nexus between
corporate social responsibility and sustainable
financial performance: Evidence from the
international construction business’, Corporate
Social Responsibility and Environmental
Management, 25(5), pp. 844–852. doi:
10.1002/csr.1501.
Mallin, C., Farag, H. and Ow-Yong, K. (2014)
‘Corporate social responsibility and financial
performance in Islamic banks’, Journal of
Economic Behavior & Organization. North-
Holland, 103, pp. S21–S38. doi:
10.1016/J.JEBO.2014.03.001.
McAdam, R., Miller, K. and McSorley, C. (2016)
‘Towards a contingency theory perspective of
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
976

quality management in enabling strategic
alignment’, International Journal of Production
Economics. Elsevier. doi:
10.1016/J.IJPE.2016.07.003.
De Roeck, K. and Maon, F. (2018) ‘Building the
Theoretical Puzzle of Employees’ Reactions to
Corporate Social Responsibility: An
Integrative Conceptual Framework and
Research Agenda’, Journal of Business Ethics,
149(3), pp. 609–625. doi: 10.1007/s10551-
016-3081-2.
Theodoulidis, B. et al. (2017) ‘Exploring corporate
social responsibility and financial performance
through stakeholder theory in the tourism
industries’, Tourism Management. Pergamon,
62, pp. 173–188. doi:
10.1016/J.TOURMAN.2017.03.018.
Wang, D. H.-M. et al. (2015) ‘The effects of
corporate social responsibility on brand equity
and firm performance’, Journal of Business
Research. Elsevier, 68(11), pp. 2232–2236.
doi: 10.1016/J.JBUSRES.2015.06.003.
Xie, X. et al. (2017) ‘Corporate social responsibility,
customer satisfaction, and financial
performance: The moderating effect of the
institutional environment in two transition
economies’, Journal of Cleaner Production.
Elsevier Ltd, 150, pp. 26–39. doi:
10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.02.192.
Corporate Social Responsibility is Viewed from a Contingency Perspective
977
