
Elementary Teachers’ Competencies in Planning, Creating, and using
ICT-based Learning Media
Hamdan Husein Batubara, Dessy Noor Ariani, Jarkawi, Galuh Nashrulloh Kartika Majangsari Rofam
Universitas Islam Kalimantan MAB Banjarmasin and Universitas Negeri Jakarta. Padat Karya Street, Number 51, North
Banjarmasin, Banjarmasin City, ZIP Code: 70122.
Keywords: Teacher Skill, ICT, Elementary Education
Abstract: The main purpose of this study is to explore the level of teachers’ skill in planning, creating, and using ICT-
based learning media. A descriptive quantitative research design was implemented within this study by
using survey as the instrumentation which used a set of questionnaire to measure teachers’ knowledge in
planning, creating, and using ICT-based learning media. The participants for this study are Elementary
School teachers in Banjarmasin. The results of this study were analyzed using descriptive analysis. The
finding was that the majority of the respondents had moderate level of Planning (M= 3,46, SD= 0,62,),
Creating (M= 2,51, SD= 0.73), and Using (M= 3,19, SD= 0,60). The teachers’ skill in planning correlated
with the teachers’ skill in creating (ryx = 0.96), and using (ryx = 0.89). The teachers’ skill in creating
correlated with the teachers’ skill in using (ryx = 0.87). The findings indicate the need to train teachers in
planning, creating, and using ICT-based learning media. Because of low skill of elementary teacher will
only impede the success of all ICT initiatives introduced by the ministry.
1 INTRODUCTION
The rapid changing of ICT has brought a substantial
impact on all spheres of human activities, including
education system. It has also provides a new
challenge for teachers to implement innovative
learning activities and in accordance with education
demand of 21st century. Unfortunately, some results
of researches indicated that the teachers’ level of
ICT integration is still at the low level, although in
general they admitted that ICT positively affects
their teaching practice and their students’ learning
(Umar, 2015).
ICT is basically a tool. It can be hardware (such
as computers, Radio, Telephone, projector, camera),
software (such as PowerPoint, Adobe Flash, Video,
Excel, Websites), or both. In the educational context,
it mainly refers to various resources and tools
(software) presented on the computer. Educational
ICT tools can be divided into 3 categories: Input
source, Output source and Others. The input source
consist of visualizer/ document camera, Computer/
laptop, Slate/ tablet, Student response system,
application software. The output source consist of
projector, interactive whiteboard and display;
monitor, TV etc. Others technology consist of digital
camera, switcher, digital recorder, and other
technology (Wang & Woo, 2007).
Pavla HLÁSNÁ (2017) lists several benefits of
the use of ICT on teaching and learning in primary
education:
1. Students' concentration in learning is better than
learn with teachers
2. Learning activities become more personalized
3. Learning becomes on the one hand more
independent, and on the other more provide
facilities to collaborate with others
4. Learning activities can happen anywhere and
anytime
5. Learning material is more up-to-date and can be
be tailored according to students’ immediate
needs
6. Thanks to multimedia activities, the learning
atmosphere becomes more varied and dynamic
7. Learning activities require critical thinking
8. Learning activities become more culture
conscious.
Aktaruzzaman explained the roles of ICT in
education are as follows: a) ICT encourages learning
anytime and anywhere; b) ICT helps everyone to
access learning resources; c) ICT sets up individuals
Batubara, H., Ariani, D., Jarkawi, . and Rofam, G.
Elementary Teachers’ Competencies in Planning, Creating, and using ICT-based Learning Media.
DOI: 10.5220/0009020900002297
In Proceedings of the Borneo International Conference on Education and Social Sciences (BICESS 2018), pages 347-354
ISBN: 978-989-758-470-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
347
for the workplace; d) ICT increases the quality of
education process and learning outcome; and e) ICT
turns learning environment into learner-centered of
learning (Aktaruzzaman, 2011).
Based on the description above, the use of the
ICT has many benefits for education, namely: 1)
display of multimedia in ICT can improve the
retentive memory of students, 2) teachers can easily
explain complex instructions and ensure students’
comprehension, 3) teachers are able to create
interactive and active classses and present the lesson
more enjoyable, 4) improve students attendance and
concentration, 4) removing the fear of students to
some subjects that abstract and considered difficult,
and 5) improving student achievement.
ICT Competence for teacher has been vey
important in this era. So that, Indonesia Government
has determined the ICT competencies as one of the
skills that must be mastered by the teacher
(Regulation of National Education Minister No. 16,
2007). The use of the ICT in education has
supported some characteristics of curriculum 2013.
Such as, suggesting the communication from
anywhere, to anywhere, emphasizing the importance
of cooperation and collaboration in solving
problems, increasing attention of educators (Wang &
Woo, 2007).
On the other hand, the ICT functions can not be
claimed will replace the role of the teacher. ICT is
just a tool introductory message or one of the
students' learning facilities. Therefore, teachers need
to keep active in guiding the process of learning
activities. The position of ICT in the communication
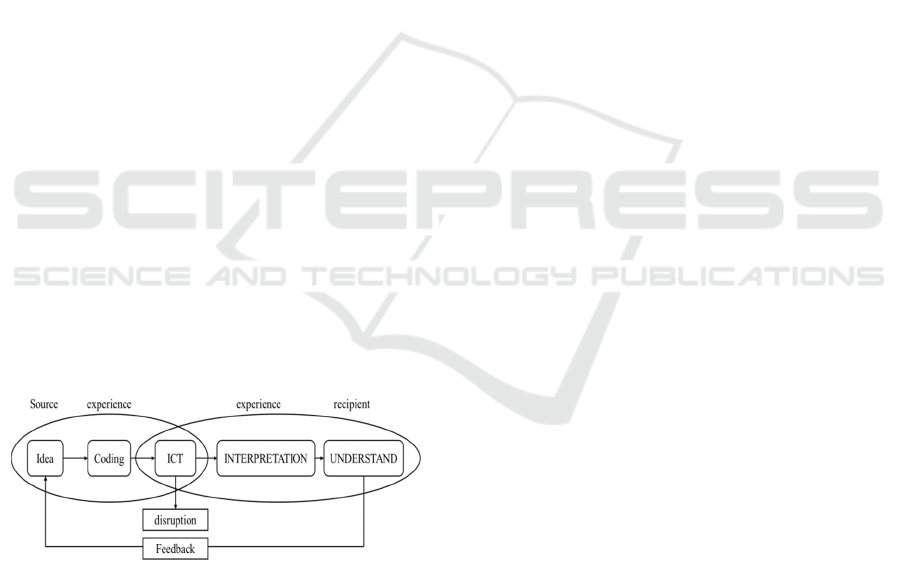
system can be described as follows (H. H. Batubara,
2015).
Picture 1. The position of ict in the communication system
The need and urgency for developing
technological literacy, although not a new idea,
emerged with greater emphasis in the early 1980’s.
With this increasing awareness and interest,
technology quickly was recognized as a powerful
vehicle for offering educators innovative ways to
enhance student learning. In the early 1990’s the
International Society for Technology in Education,
ISTE established standards defining technological
literacy for teacher education. ICTs are a potentially
powerful tool for extending educational
opportunities, both formal and non-formal, to
previously underserved constituencies – scattered
and rural populations, groups traditionally excluded
from education due to cultural or social reasons such
as ethnic minorities, girls and women, persons with
disabilities, and the elderly, as well as others who for
reasons of cost or because of time constraints are
unable to enrol on campus (Aktaruzzaman, 2011).
The systematic of ICT integration into teaching
and learning is divided into three areas, namely: (1)
design planning, (2) creating learning media, and (3)
using in teaching and learning. According to
Sukiman, the components of integrating ICT to
create lesson plan are consists of: (1) analyzing the
needs and characteristics of students, (2) formulating
standard competencies and indicators of learning
outcomes, (3) developing subjects content, (4)
formulating assessment instrument, and (5) writing
story board. The components of ICT integration in
creating learning media are consists of a teacher's
ability in : (1) operating application of graphic
design, audio, video, and animation, (2) blended
media component using the computer application,
and (3) evaluating product based on the principles of
ICT media development (Sukiman, 2012). There are
some general principles in creating ICT are: 1)
Visible: easy viewing, 2) Interesting, 3) Simple, 4)
Useful for students or users, and 5) Accurate: true
and on target, 6) Legitimate: legitimate and
reasonable, 7) Structured: well structured, and 8)
coherent (Aqib, 2013).
According to Totok A. Soefijanto, education
observer of Paramadina Public Policy Institute, the
use of ICT in Indonesia school is still about 20
percent. Even less in Elementary School (Admin,
2015). The factors that affect elementary teachers’
decision to integrate ICT in education are limited
teacher to join training in ICT integration, technical
support, pedagogical support, access to technology
resources, teachers’ skill in using multiple ICT tools
and skills (Hafez, 2013).
The result of initial study on Elementary teachers
as participant training interactive media showed that
most elementary schools already have facilities that
support the use of ICT. So, the purpose of this study
is to explore teachers’ competencies in ICT
integration in creating lesson plan, creating learning
media, and teaching and learning process, This study
is important to be done in order to know and to map
the teachers’ competence so the data can use as a
tool to increase the teachers’ competence.
BICESS 2018 - Borneo International Conference On Education And Social
348

2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Research Method
A descriptive quantitative research was employed in
this study. Additionally, this study belongs to study
of exploration that explain the phenomenon of
description between variables based on theory and
research of previous research using empirical data
(Cooper, 2003) which used survey method and using
instruments to acquire data for all variables. This
design was chosen because it is more practical when
involving respondents and the process of collection
of data is done in a short period of time.
2.2 Study Participants
The population in this study is elementary school
teachers of grades 1st to 6th. The researchers
delivered the instruments to the elementary schools
from five area in Banjarmasin (West Banjarmasin,
South Banjarmasin, East Banjarmasin, Middle
Banjarmasin, and North Banjarmasin), South
Kalimantan, Indonesia.
A cluster sampling was used in this study. The
researchers determined the sampled Elementary
Schools for each area. In this study, the researchers
conducted it within two steps. Firstly, the
researchers determined the sampled Elementary
Schools from the five areas in Banjarmasin is 62. To
determine the ideal sample size for this population,
the opinions of Gay & Diehl was used. (Gay L.RR.
and Diehl, 1992) They state that the sample should
be 10 % of population. Therefore, the sampling of
elementary schools from five areas in Banjarmasin
are 10% x 62= 6 primary schools.
Secondly, the researchers determined the sample
teachers who represented the sampled schools from
each area. The population in this study was 62
Elementary School teachers from 6 sampled
elementary schools in Banjarmasin. To determine
the ideal sample size for this population, Slovin’s
formula was used. Slovin’s formula stated that n=
N/(1+N.e2)), where n= number of samples, N= total
population, e= margin of error and therefore sample
of this study was n= 75/ (1+75(0.05)2)= 63 teachers
with e =0.05.
The researchers delivered survey to 6 randomly
selected elementary schools directly by hand to the
teachers at the schools. A total 0f 63 questionnaires
were distributed. A total of 50 over 63
questionnaires or 80 % were successfully returned to
the researcher. Thus, total of participants is 50
elementary school teachers.
2.3 Research Instruments
The instrument was survey instrument to measure
teachers’ competence in integrating ICT. It is consist
of planning, creating and using ICT in teaching. The
survey was developed based on Sukiman theory
(Sukiman, 2012). The survey items are of 5-point
Likert’s scale (from 1—strongly disagree to 5-
strongly agree). A brief demographic information
was also used to obtain the background
characteristics of the participants. A brief
demographic questionnaire was constructed to
obtain information of the participants including
gender, level of education, number of years of
experience in teaching, and status for professional
teaching.
2.4 Data Analysis
Internal reliability of the three construct was first
established through high Cronbach alphas for all
cojnstructs: Planning (∝= .784), creating (∝=.872),
and using (∝= .902). The analyses in this study was
conducted using the Statistical Package for the
Social Science software (SPSS) 19.0. Descriptive
analyses were used to describe the research data.
The descriptive analyses involved were the mean,
percentage, frequency, and standard deviation.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Profile of Participants
Table 1, Table 2, Table 3 and Table 4 below reflects
the number and percentage of teachers’ gender,
years of experience in teaching, level of education,
and status of teachers professional.
Table 1. Frequency and percentage of teachers’ gender
Gender Percentage
Male 40%
Female 60%
Table 1 above shows the number of teachers that
were involved in this study. According to gender,
this indicates that there were more female teachers
than male teachers.
Elementary Teachers’ Competencies in Planning, Creating, and using ICT-based Learning Media
349
Table 2. Frequency and percentage of teachers’ experience
in teaching
Experience in Teaching Percentage
< 10 years 86%
11-20 years 12%
>20 years 2%
Table 2 above shows that the distribution of
teachers’ years of experience in teaching. Most of
the teachers had <10 years of teaching experience
were 43 teachers or 86 %.
Table 3. Percentage of teachers’ education level
Experience in Teaching Percentage
Diploma 6%
Under Graduate 90%
Post Graduate 4%
Table 3 above shows that the distribution of
teachers’ education level. Most of the teachers were
qualified teachers as having an under graduate (S1)
with total of 45 teachers or 90 %
Table 4. Frequency and percentage of teachers’
professional status
Status Percentage
Yes 26%
No 74%
Table 4 above shows that the distribution of
teachers that have teachers’ professional certificate.
Most of 37 teachers or 74 % did not have certificate
of teacher professional.
3.2 Level of Elementary Teachers’
Competencies in Planning,
Creating, and using ICT-based
Learning Media
The following is descriptive analysis for the
research’s findings. The descriptive analysis
involved the mean, percentage, frequency, and
standard deviation the mean and standard deviation.
Table 5 shows each subscale consisting of teachers’
skill in planning, creating, using ICT-based learning
media.
Table 5. Mean, standard deviation and categorization of
planning, creating, and using ICT
Dimension Mean Std. Deviation
Planning ICT-based learning
media
3.4640 .61735
Creating ICT-based learning
media
2.5120 .73252
Using ICT-based learning
media
3.1920 .60435
Table 5 above shows mean and standard
deviation of teachers’ competence. Most of the
teachers express that the teachers’ skills in planning
is better than the teachers’ skills in using, and the
teachers’ skills in using is better than the teachers’
skills creating.
34.640
25.120
31.920
0
10.000
20.000
30.000
40.000
Pl i
Ci
Ui
Figure 2. Level of competence teacher in planning,
creating and using ICT
Based on the table 5 and figure 2 above, The
criteria divided into three groups: low, moderate,
high was described (Azwar,1986). The
categorization level criteria, frequency, and
percentage about planning, creating and using ICT
in teaching is explained as below:
3.2.1 Planning ICT-based Learning Media
The instrument survey to discribe teacher
competence in planning ICT has ten statement items
as in the table vi.
Table 6. Mean and standard deviation of teachers’
competence in planning ICT
Dimension
Level
High Moderate Low
I identify students’ need 4 44 2
I analyze standard
competence
2 45 3
I adjust kind of media
with content
4 39 7
I analyze characteristic
of lesson
5 39 6
I develop content of
media based on
curriculum regularly.
6 37 7
I consider available
resource, i.e. teachers’
competence, facilitation,
4 42 4
BICESS 2018 - Borneo International Conference On Education And Social
350
finance
I consider available time 5 36 9
I create assessment to
evaluate ICT
3 41 6
I always create story
board before creating
ICT
5 41 4
I ask expert people to
evaluate my story board
18 27 5
The table above shows that teachers knowledge
about planning ICT-based learning media is in
moderate level. Some Elementary School teachers
are confident to analize students’ need and
characteristic, standard competence, lesson
characteristic, adjust kind of media, develop content
based on curriculum, consider finance, facilitation,
and teacher competence, and create story board. But,
mean of teacher in creating assessment and asking
people to evaluate their story board have taken lower
position than the others. Items of ICT instruments in
planning ICT-based learning media is in accordance
with the theory Sukiman.
Table 7. Frequency and percentage of teachers’ competence in planning ICT
Level of Teachers’
Planning
Categorization Level Range of Value Percentage
Level of
Teachers’
Planning
Low
x<(µ-1.0
)
x < 2.85 16% Low
Moderate
(µ-1.0
)≤x≤(µ+1.0)
2.85 ≤ x ≤ 4.08 62% Moderate
High
(µ+1.0
)<x
4.08 <x 22% High
Total 100.0 Total
The table 6 above shows that the competence of
teachers in planning ICT-based learning media is at
low = 16%, moderate = 62%, and high = 22%. Mean
of that score take place at moderate level.
3.2.2 Creating ICT-based Learning Media
The instrument survey to describe teacher
competence in planning ICT has ten statement items
as in the table 8.
Table 8. Mean and standard deviation of teachers’ competence in creating ICT
Dimension
Level
High Moderate Low
I ever study creating ICT for teaching (join workshop,
course, or lectures)
13 32 5
I can operate design graphics application, such as
Photoshop, Corel draw, etc.
7 37 6
I can operate aplication of recording voice, recording
video, editing voice, and editing video (i.e. Movie Maker,
Camtasia, Ulead Video Studio, Sony Vegas, etc.)
6 40 4
I can create ICT media using MS. Power point
application.
11 34 5
I can create ICT media using software such as
Macromedia flash Professional 8, or Adobe Flash, or Auto
play
5 39 6
I create ICT independently 7 36 7
I just edit available media 6 37 7
I know the ICT development principles 5 37 8
I try media to user to be, expert media, per se, before use it 6 38 6
I fix media immediately when the media cannot work 8 37 5
The table 8 above shows that teachers’
competence about creating ICT-based learning
media is at moderate level. Some Elementary School
teachers are confident to operate ICT sofware and
hardware. Such as Photoshop, Corel Draw,
Camtasia, Editing Video, Sound Recorder,
Powerpoint, Adobe Flash, ect. Comparing between
item directed that some of teachers have low ability
in editing media, operate aplication as Corel Draw,
Elementary Teachers’ Competencies in Planning, Creating, and using ICT-based Learning Media
351

Photosop, Movie Maker, Macromedia Flash 8 and
Adobe Flash.
The teachers knowledge about principles of
creating ICT are lower than the other. Such as: (1)
Visible: easy viewing, (2) Interesting, (3) Simple,
(4) Useful for students or users, and (5) Accurate:
true and on target, (6) Legitimate: legitimate and
reasonable, (7) Structured: well structured, and (8)
coherent.
The teachers also have not tried ICT product to
users to be or expert ICT or per se before using ICT
in their class. Items of ICT instruments in creating
ICT is in accordance with the theory Aqib about
principles used in the creating and using
instructional media. So that, the teachers have to
increase their ability in mastering software and
hardware of computer.
Table 9. Frequency and percentage of teachers’ competence in creating ICT
Level of Teachers’
Planning
Categorization Level Range of
Value
Frequency
Percentag
e
Low x<(
µ
-1.0)x<1.7810 20%
Moderate
(µ-
1.0
)≤x≤(
µ
+1.0)
1.78≤x≤3.24 34 68%
Hi
g
h (
µ
+1.0)<x 3.24<x 6 12%
Total 50 100.0
The table 9 above shows that the competence of
teachers in creating ICT-based learning media is at
low = 20%, moderate = 68%, and high = 12%. Mean
of that score take place at moderate level.
3.2.3 Using ICT-based Learning Media
The instrument survey to describe teacher
competence in planning ICT has ten statement items
as in the table x.
Table 10. Mean and standard deviation of teachers’ competence in using ICT
Dimension
Level
Hi
g
h Moderate Low
The school facilitation support to integrate ICT,
such as Laptop/computer, LCD, Projector, internet,
Computer Lab, etc
441 5
M
y
School, has enou
g
h ICT media collections 14 31 5
I use ICT media (i.e. Learning CD, MS.
PowerPoint, Video, Internet, etc.) when teaching
43610
I use ICT to solve misunderstanding of subjects
content
23711
I use ICT to describe abstract subjec
t
s conten
t
17 27 6
I use ICT to simulate content 2 39 9
I use ICT to exercise 14 22 14
I use available ICT (from internet, government, etc)
when teachin
g
12 27 11
I use ICT which is created by myself in
teaching
11 26 13
I interest to create and use ICT in teachin
g
635 9
The table 10 above shows that teachers’
competence about using ICT is in moderate level.
This instrument is relevant with Aktaruzzaman
theory about the roles of ICT in education
(Aktaruzzaman, 2011). The table above shows that
the teachers’ competence in using ICT created by
themselves take lower level than the other. This is
consistent with the low competence of teachers to
operate a computer program for learning.
BICESS 2018 - Borneo International Conference On Education And Social
352
Table 11. Frequency and percentage of teachers’ using level
Level of Teachers’
Planning
Categorization Level Range of
Value
Freque
ncy
Percent
age
Low
x<(µ-1.0)
x<2.59 6 12%
Moderate
(µ-1.0)≤x≤(µ+1.0)
2.59≤x≤3.80 36 72%
High
(µ+1.0)<x
3.80<x 8 16%
Total 50 100.0
The table 10 above shows that the competence of
teachers in using ICT is at low = 12%, moderate =
72%, and high = 16%. Mean of that score take place
at moderate level. The comparison between the
teachers’ competence to plan, create and use of ICT
shows that most of teachers in elementary school
have an interest to use ICT in teaching and learning.
However, some teachers become often lazy to use
the technology. Because of that, existing technology
is just left unused. Therefore, a important program to
do ICT media development training based on the
needs, principle and backgrounds of teachers’
competencies.
3.3 Relationship between Activity
Planning, Creating, and using of
ICT-based Learning Media
The relationship between planning, creating, and
using ICT-based learning media in Elementary
school teachers can be known from the value of the
correlation coefficient as indicated in the table xii.
Table 12. The coefficient correlation among planning,
creating, and using ICT
Planning Creating Using
Planning 1 0,96 0,89
Creating 0,96 1 0,87
Table 12 shows that: (1) the level of the teacher's
skill to plan ICT-based learning media is related to
the teacher's skill to create ICT-based learning
media, namely the coefficient value is 0.96, (2) the
teacher's skill to plan ICT-based learning media is
related to the teacher's skill to use ICT-based
learning media, namely the coefficient is 0.89, and
(3) the level of teacher's skill to create ICT-based
media is related to the teacher's skill to use ICT-
based learning media, namely the coefficient is 0.87.
The way to give an interpretation of the correlation
coefficient value is by referring to the empirical
guilford rule as shown in the table xiii.
Table 13. The coefficient correlation among planning,
creating, and using ict
Level of R
YX
Interpretation of relationship
level
0,00 – < 0,20 Very weak
≥ 0,20 – <
0,40
Low or weak
≥ 0,40 – <
0,70
Moderate
≥ 0,70 – <
0,90
Strong
≥ 0,90 – ≤
1,00
Very strong
Based on the table above, it is known that the
relationship among elements studied has a positive
and very strong relationship. It means that the
teachers’ skill in planning ICT-based learning media
interact positively with their skills to create, and use
ICT-based learning media..
4 CONCLUSIONS
The teachers’ skill in planning, creating and using
ICT-based learning media requires to be more
creative. This study found some important teachers’
competencies to be improved, which is as follows:
1. The finding was that the majority of the
respondents had moderate level of Planning (M=
3,46, SD= 0,62), Creating (M= 2,51, SD= 0.73),
and Using (M= 3,19, SD= 0,60). This study
shows that the teachers’ skills in creating are
lower than planning ICT-based learning media,
and the teachers’ skills in using are lower than
planning ICT-based learning media.
2. The teachers’ skills in planning correlated with
the teachers’ skills in creating (ryx = 0.96), and
using (ryx = 0.89). The teachers’ skill in creating
correlated with the teachers’ skill in using (ryx =
0.87).
Elementary Teachers’ Competencies in Planning, Creating, and using ICT-based Learning Media
353

3. 3. The teachers’ skills that are lowest is mastery
of computer software, such as: editing video,
audio, powerpoint and macromedia flash 8.
4. The teachers’ knowledge of the principles of ICT
development is still relatively low.
5. Some factors affecting elementary teachers’
decision to not use ICT are because
uncomfortable feeling, and there are problems
with ICT devices
6. The teachers are interested to study basic and
medium software, such as powerpoint, adobe
flash, editing picture, video, sound, animation,
web and the other.
Some findings above showed that teacher need
workshop activies about planning, creating, and
using ICT-based learning media. Moreover, the
headmaster have to motivate and give a awards to
outstanding teachers. Finally, teachers have to
improve their ICT skills to advance the future of
education.
REFERENCES
Admin. 2015. Mei 26. LPMP PAPUA; Lembaga
Penjaminan Mutu Pendidikan. Retrieved from Demi
Kemajuan Pendidikan, Guru Harus Melek Teknologi:
http://lpmp-papua.web.id/berita/Demi-kemajuan-
pendidikan-guru-harus-melek-teknologi
Aktaruzzaman, R. H. S. dan C. K. C. 2011. Trends and
Issues to integrate ICT in Teaching Learning for the
Future World of Education. International Journal of
Engineering & Technology IJET-IJENS, 11(3), 114–
119.
Aqib, Z. 2013. Model-model media dan Strategi
Pembelajaraan Kontekstual (Inovatif). Jakarta: Haa
Widya.
Batubara, H. H. 2015. Pengembangan Media
Pembelajaran Interaktif pada Materi Operasi Bilangan
Bulat. MUALLIMUNA: Jurnal Madrasah Ibtidaiyah,
1(1), 1–12.
Cooper, D. R., & Schindler, P. S. 2003. Business Research
Methods. McGraw-Hill: New York.
Daryanto. 2010. Media Pembelajaran, Peranannya
sangaat Penting dalam Mencapai Tujuan
Pembelajaran. Yogyakarta: Gava Media.
Gay L.RR. and Diehl, P. 1992. Research Methods for
Busness and Management. New York: Mac Millan
Publishing Company.
Hafez, S. M. 2013. Factors Affecting Elementary
Teachers’ Decision to Integrate Information And
Communication Technologies (ICT) in an Egyptian
international school. Cairo: The American University
in Cairo.
Hlasna, P., Klímová, B., & Poulova, P. 2017. Use of
information and communication technologies in
primary education–A case study of the Czech
Republic. International Electronic Journal of
Elementary Education, 9(3), 681-692.
Mayer, R. E. 2001. Multimedia Learning. New York:
Cambridge University Press.
Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan Nasional Republik
Indonesia Nomor 16 Tahun 2007 tentang Standar
Kualifikasi Akademik dan Kompetensi Guru. Jakarta:
Menteri Pendidikan Nasional Republik Indonesia.
Sukiman. 2012. Pengembangan Media Pembelajaran.
Yogyakarta: Insan Madani.
Umar, I. N., & Hassan, A. S. A. 2015. Malaysian teachers’
levels of ICT integration and its perceived impact on
teaching and learning. Procedia-Social and Behavioral
Sciences, 197.
Wang, Q., & Woo, H. L. 2007. Systematic Planning for
ICT Integration in Topic Learning. Educational
Technology & Society, 10(1), 148–156.
BICESS 2018 - Borneo International Conference On Education And Social
354
