
The Implementation of Teachers Plan in English Learning Activities
of Students with Autisms in Senior High School of School with
Special Needs Untung Tuah Samarinda
Godefridus Bali Geroda, Dedi Rahman Nur, and Arbain
English Deparment , Widya Gama Mahakam Samarinda University, K.H. Wahid Hasyim Street, Samarinda, Indonesia
Keywords: Teaching English, Foreign Language, Autism.
Abstract: Discussion on children with special need especially those with autism requires an understanding of its close
relation with an inclusive education as one of the most essential part in which these disabled students are
involved. This study aims to describe how is the implementation of teachers plan in English Learning
Activities of students with autisms in Senior High School of School with Special Need Untung Tuah. The
design of this study was case study used qualitative approach. The subjects of this study were English
Teachers. The researcher used flow model made by Miles and Huberman (1994). This study showed that the
implementation of teachers plan in English Learning Activities is divided in teacher method of teaching,
teaching media and teachers manage the classroom. Teaching method or learning model that is used by
teacher were direct instruction and problem base learning. English teacher manages their class used direct
approach to managing and directing their classrooms, others focus on building a friendly, collaborative
relationship with their students. Thus, the researcher concludes that English syllabus in this school is based
on teacher’s book which is including purposes and scope of teaching English to students with autism which
is create main competences, basic competences.
1 INTRODUCTION
Discussion on children with special need especially
those with autism requires an understanding of its
close relation with an inclusive education as one of
the most essential part in which these disabled
students are involved. Along with the other regular
students, these disabled students have equal right to
have equal education, to learn certain subjects
including English. Autism is a complex
developmental disorder that appears by age 1-3
years. Signs of autism usually appear in the first year
and the previous 3-year-old child. The exact cause of
autism is not known for sure it is not caused by a
wrong upbringing. Most recent writing focuses on
the biological and neurological abnormalities in the
brain, including imbalances, biochemical, genetic
factors and immune disorders. (Sarwindah, 2002).
One of the major characteristics of the autistic
syndrome is an important delay in language
acquisition (DMSM-IV 1994). The acquisition
process of autistic children also different with
normal children. Autistic children do not seem to
acquire language through immersion as normal
children do but need speech therapy support.
Additionally, only about half of children with autism
speak as adults and their linguistic level remains
lower than that of normal subjects (Howlin 2003).
Despite the importance of language in both the
diagnosis and the deficits of autistic people,
longitudinal studies of how language develops in
autistic children do not exist.
According to Hilyati (2013), teaching English to
the students with autism means provide them the
equal and best quality of English education.
Appropriate teaching method, developing
appropriate annual program, syllabus and lesson
plan, providing appropriate treatment for them,
designing simplified test and evaluation for them,
the goal to acquire English as Foreign Language for
these students with autism is reached. In the other
words, the purpose of these efforts is made in order
to reach the goal of learning that is to achieve
outcome through the designed process of learning.
Government policy no. 20 year 2003 on
national education system has provided different
nuances in serving education for children with
Geroda, G., Nur, D. and Arbain, .
The Implementation of Teachers Plan in English Learning Activities of Students with Autisms in Senior High School of School with Special Needs Untung Tuah Samarinda.
DOI: 10.5220/0009019500002297
In Proceedings of the Borneo International Conference on Education and Social Sciences (BICESS 2018), pages 255-262
ISBN: 978-989-758-470-1
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
255

special need. In special education, it has been
explained that special education refers to an
education for learners with disorders or learners with
exceptional intelligence conducted inclusively or an
educational unit in the elementary and middle level.
School with special need (Sekolah Luar Biasa)
Untung Tuah is one of the school that very concern
with autism students. In every year, this school
always get new students and this school also teach
English to their students even with mental disorders
or delay in language. Base on the background above,
the researcher interest to conduct research about
teaching English as foreign language (EFL) to
students with autism in Senior high school of
SekolahLuarBiasa (SLB) Untung Tuah Samarinda
2016.
2 METHODOLOGY
This research used qualitative research with case
study approach. According to Miles and Huberman
(1994), qualitative research, usually work with a
small number of people in context. Qualitative
research uses appropriateness technique to determine
the individuals. According to Gay, et al (2006),
qualitative sampling is the process of selecting a
small number of individuals for a study in such a
way that the individuals chosen will be able to help
the researcher understand to the phenomenon under
investigation. This study used purposive sampling.
So, the subject of this research were two English
teachers of the students with autism in this case, how
the teacher plan and managing their class in the
Senior high school of school with special need
(Sekolah Luar Biasa) Untung Tuah Samarinda. One
of the subject of this research was teacher’s
assistant.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
It is useful to have an understanding the condition of
the students with autism, be acquainted with their
ways of processing information’s and benefit from
previous experiences in order to conduct the method
of teaching. Based on documentation, interview and
observation, the method of teaching that used by the
English teachers in senior high school of school with
special need especially in SMASLB Untung Tuah
Samarinda are as follow:
3.1 Direct Instruction Model
Direct learning model is a learning model that is
specifically designed to support the learning process
of students with respect to the knowledge of
procedural and declarative knowledge that is well
structured and can be learned gradually, step by step.
Learning directly though centered on permanent
teachers must ensure the involvement of students, so
the environment should be created oriented tasks.
Direct learning model for training the models, active
teaching models, teaching mastery, and explicit
instruction.
It is supported by interview result. It shows
that teaching method that is used by English teachers
is Direct Instruction Model as we can see in the
result interview above:
Extract 7.
“You know, we can’t teach the students with autism
same with normal students because this student’s is
different. So, we can’t use specific teaching method to
teach them but I also use explicit instruction method
because for the students with autism teaching process
which is taught they step by step.”
TM1.12. Line 1-3.
Extract 8.
“For example, I teach them about body with song.
So I create a song such as “this is a eyes this is e lag, this
is a ears this is a hand” or something like that”
TM2.25. Line 1-2
So, we can say that teaching method that is used
by the English teacher in SLB Untung Tuah is
explicit instruction but sometime they didn’t really
use specific teaching method to teach.
3.2 Problem based Learning
Problem-based learning model (problem base
instruction) is one model of learning that will take
participants vote learners to work on authentic
problems with the intention that learners can
construct their own knowledge so as to develop self-
reliance and self-confidence and it is also used to
teach English to students with autism in SMALB
Untung Tuah Samarinda. Base on theory there are
some phase that need to pay attention by the teacher
that is adopted by SMALB Untung Tuah.
BICESS 2018 - Borneo International Conference On Education And Social
256
Table 2. Problem Base Learning Phase
Activity Teacher Behaviorism
Phase 1
Provide orientation about problems to the
student
1. Teacher discusses learning objectives
2. Teachers describe various logistical needs
3. Teacher to motivate students to get involved in problem-solving
activities
Phase 2
Organize students to learn
Teacher’s help students explain the definition and organize appropriate
task which is related with the problem.
Phase 3
Helps investigation independently and
group
Teachers push the students to get the valid information, carry out
experiments and give explanations and solutions
Phase 4
Develop and present the work of
Teachers to help students in planning and delivering artifacts and
Exhibit precise as reports, video footage and models. Teachers help
students submit / present to others
Phase 5
Analyze and evaluate the process of
overcoming the problem
Teacher helps students to reflect on their investigations and the
processes they use.
It is supported by interview result. The result of
interview shows that English teacher in SMALB
Untung Tuah Samarinda used problem base
learning.
Extract 1.
“I also Used PBL (Problem Base Learning) but
not really)
TM3. 26. Line 1
Extract 2.
“I ask my student to download the electronic
dictionary in their HP and when they ask a word that
they don’t understand, I will ask them to open their
dictionary and search the words. Or I will ask them to go
out the classroom and investigate what they interesting
in outside and search the word in their dictionary.
TM4.27. Line 1-2
So, we can conclude that, teaching method or
learning model that is use by teacher in Senior High
School of School with Special Need Untung Tuah
Samarinda were Direct instruction and problem base
learning even in teaching English to autism they
have three model of learning including cooperative
learning but it difficult to use cooperative learning
because in one class the students have different
disability.
3.3 The Relevance Teachers Aid Used
by Teacher’s
The process of teaching and learning largely
depends on the available teaching materials. Today
there are a wide range of teaching aids which can be
audio, video, books, DVDs etc. Teaching aids are
those materials that help the teachers explain better
knowledge and help the students understand. It is
like the picture of the lesson. It is especially
important in lessons or topics that are strange to the
kids. E.g. if you were teaching a group of kids in a
remote village with no civilization about types of
houses, you will need a picture or a DVD showing
the different houses and their names because most
probably these kids have never seen or heard of
such. It also happens in autism classroom. There are
many other tested teaching tools and resources that
have had a great impact in improving learning
processes for students. If you are a teacher and have
not use any of the free or paid available teaching
aids today, you will immediate see the difference in
regards to your students’ performance once you try
it.
Base on result of this research we can see that
English teacher in SLB Untung Tuah use some
teaching aids for example: electronic dictionary,
picture, video and props. It is proof by the result of
interview:
Extract 3.
“I usually use electronic dictionary, video and props
such as human body”
TA1.26.Line 1.
It is supported by observation. The observations
show that, teaching aids that is used by English
teacher in SLB Untung Tuah were electronic
dictionary, picture, video and props. They use
teaching aids to make the students easy to
understand.
Extract 4.
We use electronic dictionary, picture, video and
props to teach the students
TA2.10. Line 1.
The Implementation of Teachers Plan in English Learning Activities of Students with Autisms in Senior High School of School with Special
Needs Untung Tuah Samarinda
257

Based on the observation and documentation,
teaching media which is used by English teachers is
based on teacher’s book. In that Teacher’s book said
that in teaching English to students with autism
teaching aids is highly recommended to use because
it very helpful for the students to understand what
the teacher teaches for them. There are some types
of teaching aids that can be used to teach students
with autism and also include in teacher book that is
use by teacher.
1. Visuals: these are aids that use the actual vision
like maps, charts, objects, pictures, models, flash
cards, chalkboard, projectors, slides, bulletin
boards. Of all the chalkboard is the most used
and sometimes pictures.
2. Audio: these aids uses only the student’s sense of
hearing examples are films, television, DVDs,
film strips etc.
3. Audio – visuals: these aids combine both the
vision and hearing senses and always give a more
vivid picture examples are films. The use of
audio- visual teaching aids is known to be more
effective and aid comprehension in learners. The
type of teaching aid used will also depend largely
on the level and age of students. For kindergarten
and play pen kids rhymes, pictures and flash
cards are most appropriate, you definitely will
not use rhymes and flash cards to teach students
in tertiary institutions instead go for slides, maps
and charts.
4. Three Dimension. These aids combine some
aspect such as can be seen or touch by the
students
So, we can say that teaching aids is used in
teaching English for students with autism in SLB
Untung Tuah. It is important to bring new
technology into the classroom. Devices used are
more lightweight than books and PCs. Mobile
learning can be used to diversify the types of
learning activities students (or a blended learning
approach). Mobile learning supports the learning
process rather than being integral to it. Mobile
learning can be a useful add-on tool for students
with special needs. However, for SMS and MMS
this might be dependent on the students’ specific
disabilities or difficulties involved. Mobile learning
can be used as a ‘hook’ to re-engage disaffected
youth.
3.4 Teachers Manage Classroom
Teachers are called upon to be creative and
innovative when preparing classrooms. Managing an
all-inclusive classroom is easier if simple,
personalized teaching strategies for the special needs
student are implemented. Teaching students with
autism is a challenge, but the experience can be a
positive one for the autistic child, his teachers, and
his classmates if the proper teaching strategies are
incorporated into the daily routine. Autistic children
struggle with socialization. The See. Touch. Learn
computer-based program opens a world of wonder
for each student who is enrolled. The autistic student
can work independently and can feel a sense of pride
and accomplishment as he masters skills and learns
new concepts. The program makes it possible to
focus on the things that appeal to the student.
Effective classroom management can often be
the difference between a classroom that’s focused
and attentive and a classroom in which students
struggle to achieve their educational objectives.
Teachers face a variety of choices when it comes to
classroom management. While some teachers take a
direct approach to managing and directing their
classrooms, others focus on building a friendly,
collaborative relationship with their students.
The results show that English teacher in SLB
Untung Tuah Samarinda manage their class use
direct approach to managing and directing their
classrooms, others focus on building a friendly,
collaborative relationship with their students. So in
particular class they have two teachers to managing
and directing their classrooms, others focus on
building a friendly, collaborative relationship with
their students. One English teacher and one teacher
assistant who help English teacher to manage the
classroom.
Extract 5.
“Yes, they have two teachers for each class”
CM1. 17. Line 1
Extract 6.
“They help me to arrange the class room, to control the
students, watch over the students and some time they
write on the blackboard”
CM2. 19. Line 1
The reason why they still need teacher assistant
because English teacher need someone to watch over
the students when learning and teaching process and
also in one class they at nine student and sometime
the students barely scream without any reason. It is
proof by the result of interview above:
Extract 7.
“Because you know some times when you are teaching
the students barely scream without any reason. So I need
someone to watch over them”
CM3. 22. Line 1-2
It is supported by the result of observation. Base
on the observation, students with autism in Senior
High School of The School with Special Need
BICESS 2018 - Borneo International Conference On Education And Social
258

Untung Tuah Samarinda have two teachers in one
class. Teachers assistant job are also to arrange the
class room, to control the students, watch over the
students and some time they write on the blackboard.
English teacher also taught two classes in the same
time. She also teaches in the other school so she also
comes to the school on Tuesday which is in her
schedule. The other problem is teacher assistant the
background of study is not in education so it not
effective to manage the classroom especially students
with autism classroom.
Teachers method of teachingis useful to have an
understanding of the condition of the students with
autism, be acquainted with their ways of processing
information’s and benefit from previous experiences
in order to conduct the method of teaching. The
method of teaching that used by the English teachers
in Senior High School of School with Special Need
Untung Tuah Samarinda is different with teaching
English to normal students.
So, we can say that teaching method that is used
by the English teacher in SLB Untung Tuah is
explicit instruction but sometime they didn’t really
use specific teaching method to teach. Sometime
English teacher used song to teach their students to
get students attention or ask students to go to outside
and find out the meaning of particular thing in
outside of the class that they don’t know.
The process of teaching and learning largely
depends on the available teaching materials. Today
there are a wide range of teaching aids which can be
audio, video, books, DVDs etc. Teaching aids are
those materials that help the teachers explain better
knowledge and help the students understand. It is
like the picture of the lesson. It is especially
important in lessons or topics that are strange to the
kids. E.g. if you were teaching a group of kids in a
remote village with no civilization about types of
houses, you will need a picture or a DVD showing
the different houses and their names because most
probably these kids have never seen or heard of
such. There are many other tested teaching tools and
resources that have had a great impact in improving
learning processes for students. If you are a teacher
and have not use any of the free or paid available
teaching aids today, you will immediate see the
difference in regards to your students’ performance
once you try it.
The observations also show that, teaching aids
that is used by English teacher in SLB Untung Tuah
were electronic dictionary, picture, video and props.
They use teaching aids to make the students easy to
understand. Teaching aids is used in teaching
English for students with autism in SLB Untung
Tuah. It is important to bring new technology into
the classroom. Devices used are more lightweight
than books and PCs. Mobile learning can be used to
diversify the types of learning activities students (or
a blended learning approach). Mobile learning
supports the learning process rather than being
integral to it. Mobile learning can be a useful add-on
tool for students with special needs. However, for
SMS and MMS this might be dependent on the
students’ specific disabilities or difficulties involved.
Mobile learning can be used as a ‘hook’ to re-engage
disaffected youth.
The results show that English teacher in SLB
Untung Tuah Samarinda manage their class use
direct approach to managing and directing their
classrooms, others focus on building a friendly,
collaborative relationship with their students. So, in
particular class they have two teachers to managing
and directing their classrooms, others focus on
building a friendly, collaborative relationship with
their students. One English teacher and one teacher
assistant who help English teacher to manage the
classroom.
The reason why they still need teacher assistant
because English teacher need someone to watch over
the students when learning and teaching process and
also in one class they at nine students and sometime
the students barely scream without any reason
Teachers assistant job are to arrange the class
room, to control the students, watch over the students
and some time they write on the blackboard. The
other reason is. English teacher also taught two
classes in the same time. She also teaches in the other
school so she also comes to the school on Tuesday
which is in her schedule. The other problem is
teacher assistant the background of study is not in
education so it not effective to manage the classroom
especially students with autism classroom.
3.5 Teachers Plan Formulated Model
Education for All (Ontario Ministry of Education,
2007a), provides educators with recommendations
on a broad range of techniques to enhance the
instruction of students with special education needs,
including those with ASD. The report provides
information on the use of the principles of Universal
Design for Learning (UDL) and differentiated
instruction to plan for and respond to students with
various needs. Learning is a continuum and every
student is a unique learner. Flexible, supportive, and
adjustable classrooms and programs must be
planned and developed to meet the learning needs of
individual students. These are important
considerations in the planning of programs for
students with ASD.
The Implementation of Teachers Plan in English Learning Activities of Students with Autisms in Senior High School of School with Special
Needs Untung Tuah Samarinda
259

Figure 2. Ontario Ministry of Education, 2007
3.6 Universality and Equity
Teachers are encouraged to develop a class profile to
identify the strengths, challenges, and needs of all
students and to determine the stage that each student
has reached in his or her learning. The instructional
methods and classroom accommodations should
Students with ASD vary in their cognitive level,
communication ability, social skills, and behavioural
characteristics. They have a wide range of skills and
diverse needs. It is important for teachers to gather
information to understand the individual strengths,
needs, and interests of students to identify
appropriate curriculum expectations, required
accommodations, and effective instructional
approaches are planned to ensure that the needs of
all students are met. It can be cover in syllabus and
lesson plan that use and design by English teachers.
3.7 Flexibility and Inclusion
To ensure that all students are provided
opportunities for real learning experiences,
flexibility and options should be built into the
planning of teaching strategies, materials, and
student activities. The ability of students with ASD
to participate in or respond to a learning experience
may be affected by limitations in communication
and social skills. Consideration of the likes, dislikes,
strengths, needs, and interests of a student with ASD
can help to make materials and tasks more engaging
and provide motivation for the student to participate
in and complete the desired task or activity.
Concrete examples and hands-on activities provide
students with opportunities to learn by seeing and
doing and have been found to increase the
motivation and engagement levels of students with
ASD. For example, a student who has difficulty with
concepts in mathematics may be motivated to learn
graphing techniques by gathering data on items of
personal or special interest.
3.8 An Appropriately Designed Space
Consideration should be given to the size, space, and
arrangement of the physical and visual elements in
the learning environment to ensure that they are
conducive to student learning. Some students with
ASD are very aware of and need to know where
things belong. The organization of materials,
furniture, and resources should be carefully
considered in relation to their effect on the learning
environment of the student with ASD.
3.9 Simplicity
Teachers should ensure that the information
provided in learning situations is presented clearly
and is easily understood by the students.
Unnecessarily complex and distracting information
should be reduced as much as possible. The
communication impairments that are often present in
students with ASD may affect their ability to process
verbal information. They will often have difficulty
understanding complex, abstract language and may
misinterpret metaphors, slang terms, and
colloquialisms. Effective methods to simplify
information and make it easier for the student to
understand include using clear and concise language,
breaking instructions and tasks into smaller steps,
and using visual supports, such as written or picture
schedules. Information and materials should be
organized in such a way that important or key
component are highlighted and easily identified by
students.
BICESS 2018 - Borneo International Conference On Education And Social
260
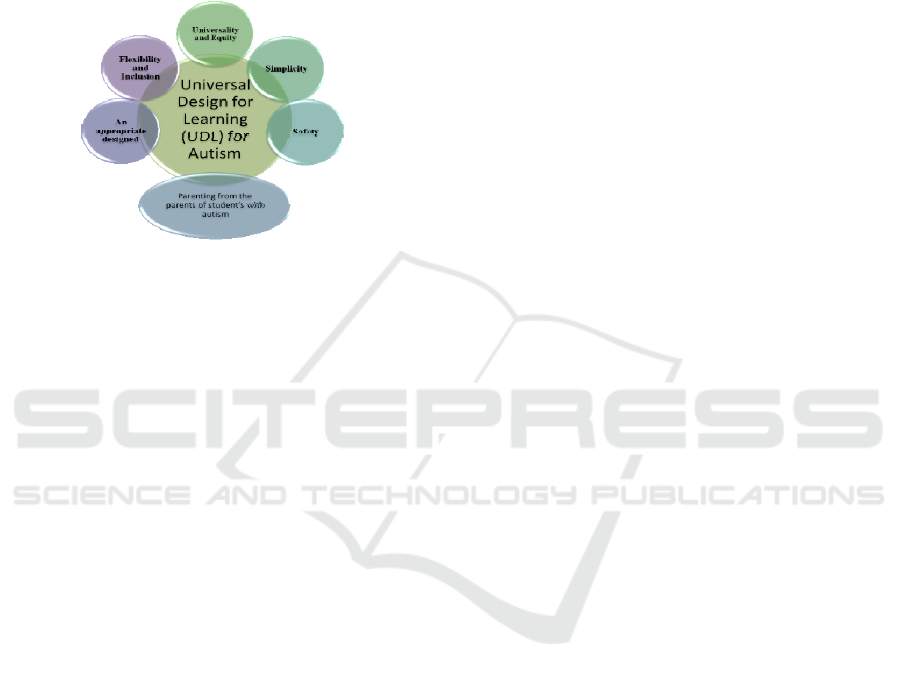
3.10 Safety
Teachers need to consider possible safety hazards
and elements with the potential to cause accidents in
the classroom. Staff should be aware of and able to
act on any safety assessments, safety plans, or safety
protocols that may apply to specific students in the
classroom.
Figure 2. Universal Design for Learning for Autism
If a student with ASD is considered to be a safety
risk in the school setting, adults involved with the
student need to have access to the information and
supports that are required to ensure a safe learning
environment. A safety assessment can help to
identify the factors that may lead to or cause
situations and provide an assessment of the potential
risks in given situations. A safety plan outlines the
appropriate responses and supports that are required
during specific situations with students.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The conclusions of this study are presented below:
1. The implementation of teachers plans in English
Learning Activities of students with autisms in
Senior High School of School with Special Need
(Sekolah Luar Biasa) Untung Tuah Samarinda is
divided in teacher method of teaching, the
relevance teachers aid used by, teachers manage
classroom. Teaching method or learning model
that is use by teacher in Senior High School of
School with Special Need Untung Tuah
Samarinda were Direct instruction and problem
base learning even in teaching English to autism
they have three model of learning including
cooperative learning but it difficult to use
cooperative learning because in one class the
students have different disability.
2. Teaching aids is used in teaching English for
students with autism in SLB Untung Tuah. It is
important to bring new technology into the
classroom
3. English teacher in SLB Untung Tuah Samarinda
manage their class use direct approach to
managing and directing their classrooms, others
focus on building a friendly, collaborative
relationship with their students. So, in particular
class they have two teachers to managing and
directing their classrooms, others focus on
building a friendly, collaborative relationship
with their students.
REFERENCES
Aarons, Maureen, & Gittens Tessa. 1999. The handbook of
Autism: A guide for parents and professionals (2nd
ed.). London:Routledge.
AlqawasmiHebaAbdelhaleem. 2012. Language
Acquisition among Autistic Children. Jordan:
Yarmouk University
Arikunto, Suharsimi.2006. ProsedurPenelitian;
SuatuPendekatanPraktik. Jakarta: PT RinekaCipta
Belch, G. E., and Belch, M. A., 2004. Advertising and
promotion: An integrated marketing communications
perspective (6th Ed.). Boston: McGra
Bogdashina, Olga. 2004). Communication issues in
Autism and Asperger syndrome: Do we speak the
same language? London: Jessica Kingsley Publishers.
Branch of the British Columbia Ministry of Education
gratefully.2010 Teaching Students with Autism: A
Guide for Educators as a basis. Victoria: Canadian
Cataloguing
BudiharsoTeguh. 2007.
PanduanLengkapPenulisanKaryaIlmiah. Yogyakarta:
GallaIlmu
Daymon, Christine., danImmy Holloway. 2002.
Metode-MetodeRisetKualitatif: dalam Public
Relations dan Marketing Communications.
Yogyakarta: PenerbitBentang..
Fraser, William I. 1981. Clinical Presentations of
Retarded Language. In Fraser, William I, and Grieve,
Robert B (Eds.). Communicating with Normal and
Retarded Children. Bristol: J. Wright
Fry, S, Laurie, H, &Ordish, R. 1989. Language
Conversation In R. Ordish (Producer), A Bit of Fry &
Laurie. London, UK: BBC Warner.
Gay L.R., Mills, GoeffeyE.,andAirasian, Peter. 2006.
Education Research: Competencies for Analysis and
Applications. New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall
Given, Lisa M. 2008. The Sage Encyclopedia of
Qualitative Research Methods. London : Sage
Publications, Inc
Hastuti, EndahDwi. 2014. Bahasa InggrisSekolah
Menengah AtasLuarBiasa. Jakarta:
KementrianPendidikan&Kebudayaan
Harley, T. A. 2010. The Psychology of Language: from
Data to Theory. New York, NY: Psychology Press
Ltd.
The Implementation of Teachers Plan in English Learning Activities of Students with Autisms in Senior High School of School with Special
Needs Untung Tuah Samarinda
261

Hatch, JA 2002, Doing qualitative research in education
settings. State University of New York, Albany
Howlin, P & Magiati, I., 2003. A pilot evaluation study of
the Picture Exchange Communication System for
children with Autistic Spectrum Disor- der. Autism:
The International Journal of Research and Practice, 7,
297–320
Jufrizal. 2010. Agent less Clause Construction in
Minangkabaunese and Language Politeness Value’
(makalahdisajikanpada The Fifth International
Seminar on Austronesian Languages and Literature).
Denpasar: Program Magister danDoktorLinguistik PPs
UniversitasUdayana.
Kasdi S &Nur M. 2008. PengajaranLangsung. Surabaya:
University Press
Leblanc, L., Richardson, W., & McIntosh, J. 2005. The
use of applied behavioral analysis in teaching children
with autism. International Journal of Special
Education, 20(1), 13-34. Retrieved from
http://eric.ed.gov/PDFS/EJ846504.pdf .
Lahey, Margaret. 1988. Language disorders and language
development. New York, London: Macmillan and
Collier Macmillan.
MacKenzie, Heather. 2008. Reaching and teaching the
child with Autism spectrum disorder using learning
preferences and strengths. London, Philadelphia:
Jessica Kingsley
Mack, N., Woodsong, C., Macqueen, K. M., Guest, G.
&Namey, E. 2005. Qualitative Research Methods: A
Data Collector’s Field Guide. Family Health
International, North Carolina, USA
Miles, M.B. & Huberman, A.M. 1994. Qualitative data
analysis: An expanded sourcebook. New York: SAGE
Publications.
Needlman, Robert. 2000. The Types and Terminology of
Autism. Retrieved from
http://www.drspock.com/article/0,1510,5473,00.html
Ormrod, J. E. 2004. Human learning. (4th ed.). Upper
Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Pope C, Mays N Popay J. 2005. Systematically Reviewing
Qualitative and Quantitative Evidence to Inform
Management and Policy-making in The Health Field.
Journal of Health Services Research and Policy; 10
(Suppl 1): 6-20
Quinn, Barbara, & Malone, Anthony. 2000. Pervasive
Developmental Disorder an Alerted Perspective.
London, Philadelphia: Jessica Kingsley Publishers.
Ritchie, Jane and Lewis, Jane. 2003. Qualitative Research
Practice: A Guide for Social Science Students and
Researchers. India: Great Britain The Cromwell Press
Ltd
Robinson, Ricki G. 2011. Autism solutions: How to Create
a Healthy and Meaningful Life for Your Child.
Ontario, Canada: Harlequin Enterprises Limited.
Sarwindah, Dwi. 2002. PsikologiAnakKhusus. Diktat
KuliahPsikologiAnakKhususSurabaya:
UniversitasNegeri.
Scott, S., &Manglitz, E. 1997. Foreign language learning
and disabilities. LD Online. Retrieved December 5,
2014, from http:// www.ldonline.org/article/6066/
Smilovitz, R. 1996. If not now, when ? Education not
schooling. Kearney: NE. Morris.
Sudaryanto. 2012. Metodedan Aneka TeknikAnalysa
Bahasa. Yogyakarta: CV.
The University of Tennessee at Chattanooga 1998.
Cooperative Learning. Retrieved April 12, 2010, from
Wardhaugh, Ronald. 1972. Introduction to Linguistics.
New York: McGraw Hill Book.
Widodo Rachmad.2009. ” Model Pembelajaran Explicit
Instruction (Rosenshina& Stevens, 1986) ”.
Willig Carla.2008. Introducing qualitative research in
psychology: adventures in theory and method.
Philadelpiah,USA: Open University Press
BICESS 2018 - Borneo International Conference On Education And Social
262
