Analysis of Consolidation Settlement:
A Case Study on State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Campus
Abdul Hakim
1
, Kusnul Prianto
1
1
State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel, Jl. Ahmad Yani 117, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Embankment, soil classification, Settlement, consolidation.
Abstract: Analyzing the soil settlement is very important to prevent the civil structure damages. This study revisits a
case study of an embankment in UIN Sunan Ampel Gununganyar Campus. The soil investigation was carried
out by boring holes until 60 m in depth. Moreover, both Standard Penetration Test (SPT) and Cone penetration
Test (CPT) were conducted to know the soil bearing capacity in site and to assess the consolidation parameters
on undisturbed and remolded samples. Based on the soil investigation, the grade of the soil from top layer to
3.5 m depth is soft clay with high plasticity (C-H), thus, the layer of 3.5 m to 22.5 m is fine sand that is very
loose (S-P). An embankment sand gravel with 2 m height has been placed on the top layer. The consolidation
settlement is analyzed by comparing empirical analysis and finite element software Plaxis. The result of the
consolidation settlement based on empirical analysis and Plaxis is 0.144 m in 47 days and 0.147 m in 47 days,
respectively.
1 INTRODUCTION
As crowded campus in Jl. Ahmad Yani, State Islamic
University (UIN) Sunan Ampel has planned to build
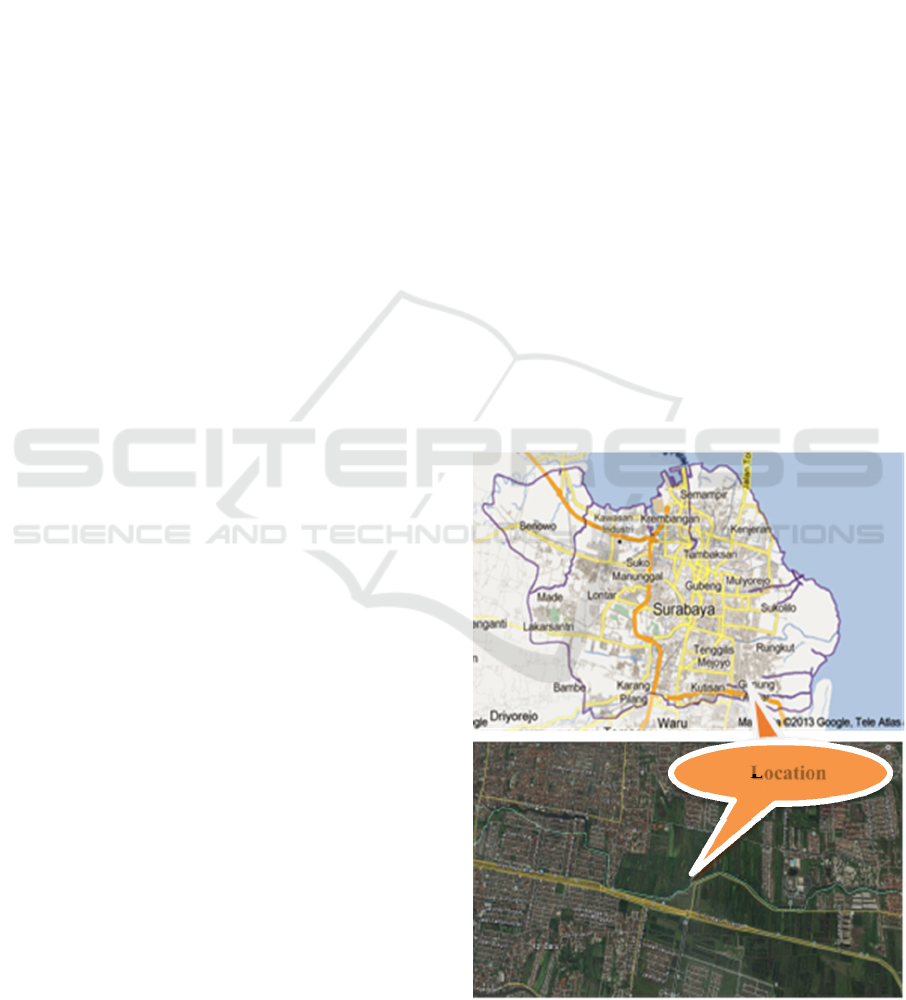
another campus in Gunung Anyar, Surabaya (Figure
1). Unfortunately, it is not only located in crowded
area but also it is laid in the area with low soil bearing
capacity, triggering the soil settlement. The soil
settlement usually causes damages to the civil
structures, e.g., academic buildings, roads, park area,
and bridge.
Standard Penetration Test (SPT) and Cone
penetration Test (CPT) were conducted in many
points of the area with 60 m in depth. The result is
that SPT value as well as CPT of top layer at depth of
3.5 m were zero. Soil classification, meanwhile,
consists of clay with high plasticity (C-H) from 1 m
to clay high plasticity (M-H) from 20.5 m to 60 m
respectively
Recently, UIN Sunan Ampel starts the land
preparation and embankment work for area of 35.000
m
2
from total area of 400.000 m
2
. The embankment
height was reach 2 metres from top layer of soft soil
or soft ground.
Figure 1: Location map of study area
Location
172
Hakim, A. and Prianto, K.
Analysis of Consolidation Settlement: A Case Study on State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Campus.
DOI: 10.5220/0008907600002481
In Proceedings of the Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference (BEST ICON 2018), pages 172-176
ISBN: 978-989-758-414-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
Top layer of soil with 3.5 m in depth is highly
plastic clay and has very soft consistency. Beneath
clay, it is very loose sand 3.5 to 19.5 m and highly
plastic silty clay with stiff consistency 19.5 m to 60
m. The settlement will happen if soil material
receives many loads. The settlement is strain change
in the depth of soil.
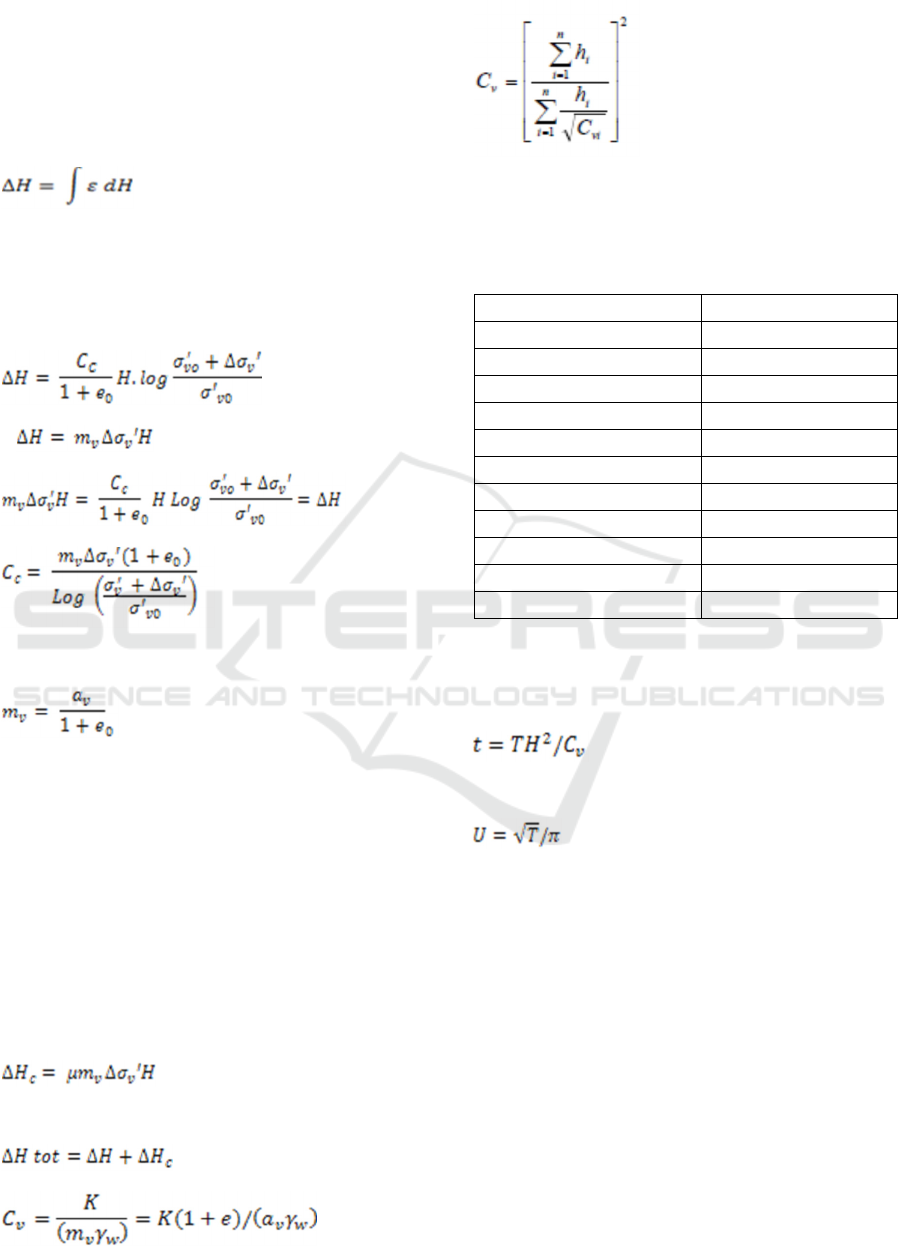
(1)
Ε = ∆H/H atau ε = σ/Es
Where:
ε = strain ∆H = Settlement
σ = Stress Es = Elasticity Modulus
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
݉
௩
= ∆e/∆p ݉
௩
= 1/E and E= ∆p/∆e
(6)
Remarks:
Cc: Compression Index
Cv: Consolidation Index
e
o: Initial void ratio
Δ
σ
v: External load
Σ
v’: Effective pressure overburden
Pc: Pre-Consolidation Pressure
Mv: Coefficient of soil volume compression
a
v: Coefficient of pressure
Horizontal settlement equation can be found
below
(7)
Where μ is affected factor of load area
(8)
(9)
(10)
The relation between degree of consolidation
(U) and time factor (T) is shown in table 1.
Table 1: The relation between consolidation degree
and time
The soil consolidation consists of time
consolidation and degree of consolidation. Time of
consolidation is
(11)
While degree of consolidation is
(12)
Where, T: time factor
t: duration of consolidation
2 RESEARCH METHOD
The study of settlement and consolidation conducted
through six steps below:
1. Finding a literature review. A literature is needed
to know about basic theory of settlement and
consolidation time.
2. Collecting Data. Data used for analysis of the
study are soil sampling from embankment and
soil beneath embankment.
3. Testing the samples. Material test was conducted
by PT. Patron Jakarta. Sampling coincided with
U T
00 0.000
10 0.008
20 0.031
30 0.071
40 0.126
50 0.197
60 0.287
70 0.403
80 0.567
90 0.848
100 ~
Analysis of Consolidation Settlement: A Case Study on State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Campus
173

site test SPT and CPT. Literature study is also
used to complete unavailable data.
4. Analyzing consolidation settlement. Analysis of
consolidation settlement uses geotechnical
method and finite element software Plaxis 8.6.
5. Calculating time of consolidations settlement.
Calculating time of consolidation uses
geotechnical method
6. Giving a recommendation for the owner. The
result of the study is expected to give a
recommendation, especially for the problem of
structures, for the owner.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The embankment for land preparation and grade layer
of soil in UIN Sunan Ampel Gununganyar Campus is
shown in Figure 2. The embankment material, sand
gravel non plastic must have coefficient of
permeability (K) less than 10
-3
m/day. The property
tests from laboratory were unit weight of 20.31
KN/m
3
and water content 12.17%. Material free from
colloid or grain-size material over 0.075 mm was
4.8%. The summary of embankment material is
shown in table 2 below:
Table 2: The property material of embankment
Soil paramete
r
Value
ϒ (KN/
m
3
) 20.31
Water content (%) 12.17
IP (%)
N
on Plastic
K (m/da
y
) < 10
-3
Passin
g
size 0.075 mm (%) 4.8
The soil classification of the embankment based
on Unified Soil is well grade Sand Gravel (G-W) and
specific gravity (Gs=2.69). The soil layer beneath
the embankment as shown by figure 2 consists of
highly plastic soft clay, loose fine sand, respectively.
The material properties of each layer are shown in
table 3.
Figure 2: Embankment soil of sand gravel
Table 3: Soil parameter beneath embankment
Parameter
Depth (m)
0 - 3.5 3.5- 22.5
Soil Classification Clay (C-H) Fine sand
NSPT 0 0
ϒsat (KN/m
3
) 14.28 17.85
ϒdray (KN/m
3
) 11.34 16.40
Cohesivity (KN/m
2
) 19.3 0
Internal Friction angle (ϕ) 7.25 32
E (KN/m
2
) - 20000
K (m/day) 1.43 x 10
-3
0.84
Poisson Ratio (μ) 0.25 0.3
Table 3 shows us that two layers of soil beneath
the embankment consist of clay, fine sand and clay
silt, respectively. The clay layer with 3.5 m in depth
has color of grey to black, while the properties of clay
are low unit weight, low bearing capacity (NSPT=0),
high cohesivity (19.3 KN/m
2
) and low permeability
(1.43 x 10
-3
m/day). Under clay layer is fine sand
layer. It has black color, high permeability (0.84
m/day) and internal friction angle (32°) but low
bearing capacity (NSPT=0).
Figure 3: Bore log soil layer
3.1 Consolidation Settlement Calculation
The calculation of consolidation settlement in this
study using equation (2) was to find the result of
primary settlement (ΔH), thus it was interpolated
degree of consolidation (U) in table 1 to gain the
consolidation settlement (Sc), therefore:
Sc = U. ΔH
The compression index (Cc), coefficient and time
of consolidation were derived from equation (4), (9)
and (10) respectively.
Table 4: Analysis of Consolidation Settlement
Layer Depth (m) eo
Cv )
(m
2
/day)
Cc
Embankment 2 0.13 NP NP
Layer 1 3.5 1.56 5.5 x10
-2
0.45
Layer 2 19 0.5 NP NP
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
174
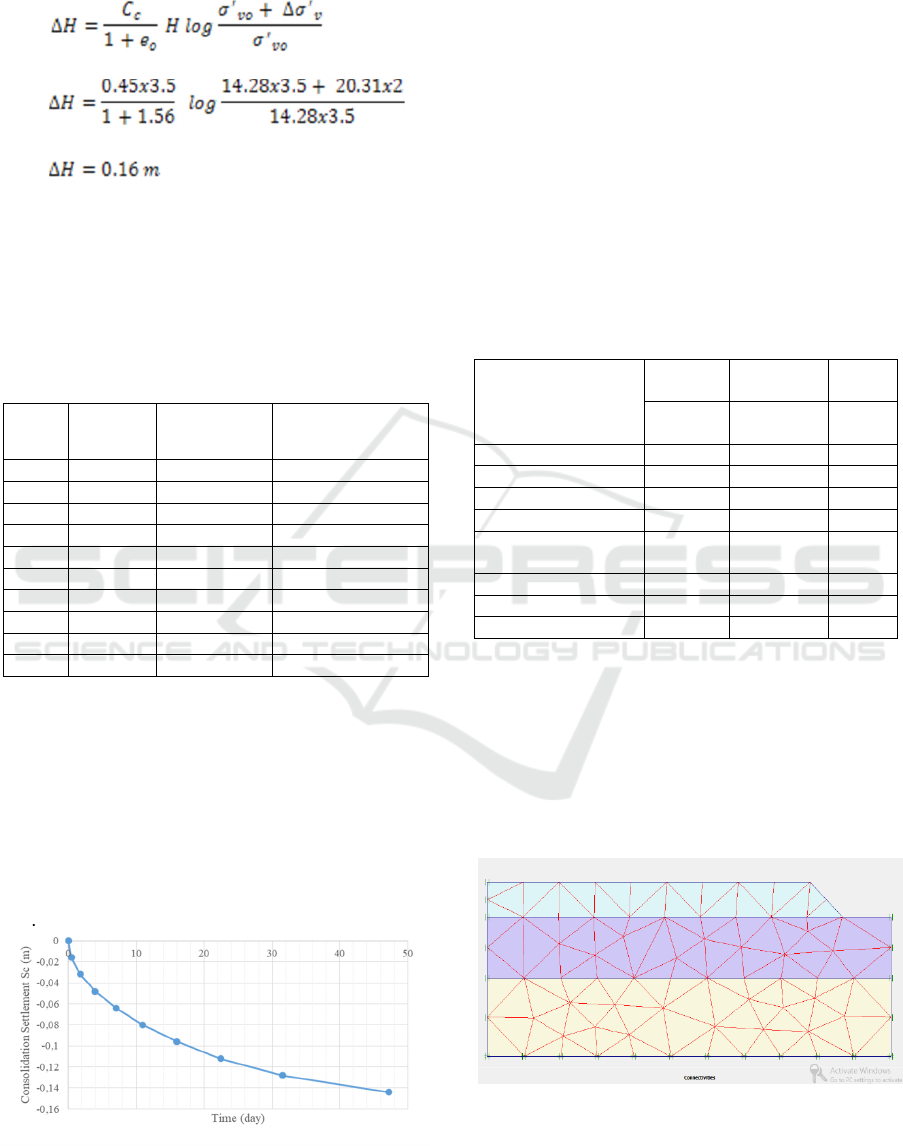
The calculation of primary of settlement is shown
below:
3.2 Consolidation Time
The calculation of consolidation time used equation
(10). The results of consolidation settlement and
consolidation time without improvement are shown
table 5.
Table 5: The relation between consolidation degree
and time for top layer in 0 to 3.5 m depth
Time
(day)
Time
Factor
(Tv)
Degree of
consolidation
(Uv)
Settlement
Consolidation (Sc)
(m)
0 0.000 00 0.00
0.45 0.008 0.1 -0.016
1.73 0.031 0.2 -0.032
3.95 0.071 0.3 -0.048
7.02 0.126 0.4 -0.064
10.93 0.197 0.5 -0.080
15.98 0.287 0.6 -0.096
22.44 0.403 0.7 -0.112
31.57 0.567 0.8 -0.128
47.22 0.848 0.9 -0.144
Table 5 explains that based on analytical
calculation, top layer of clay 0 to 3.5 m in depth will
undergo consolidation settlement (Sc) approximately
0.144 m with degree of consolidation (U) of 90%,
thus the time consolidation for pore water dissipation
of 90% degree consolidation was 47 days. The
consolidation settlement (Sc) and time consolidation
(t) experienced by UIN Sunan Ampel embankment is
also showed in figure 4.
.
Figure 4: Graph of consolidation time (t) and
consolidation settlement (Sc)
3.3 Analysis of Consolidation
Settlement using Plaxis Software
In order to convince the consolidation settlement of
embankment without any improvement on soft soil
and to compare the result of analytical calculation,
Plaxis 2D version 8.6 is used for this purpose.
3.3.1 Material Parameters
The material parameters given in table 6 were used
for analytical calculation. The embankment can be
modelled with Mohr-Coulomb model with
parameters: elasticity Modulus (E), Poisson’s ratio
(μ), internal friction angle ((ϕ), cohesivity (c), and
dilatation (ᴪ).
Table 6: Paramaeters of Uinsa Soil
Parameters
Embank
ment
Layer 1
Layer
2
Sand
Gravel
Clay (C-
H)
Fine
sand
Model MC MC MC
ϒsat (KN/m
3
) 20.31 14.28 17.85
ϒdray (KN/m
3
) 18.80 11.34 16.40
Cohesivity (KN/m
2
) 0 19.3 0
Internal Friction
angle(ϕ)
25 7.25 25
E (KN/m
2
) 10000 1000 10000
K (m/day) 0.05 1.43 x 10
-3
0.84
Poisson’s Ratio (μ) 0.3 0.25 0.3
3.3.2 Boundary Condition
The embankment was assumed symmetrical, thus
only half of embankment is determined in the finite
element analysis as shown in figure 5. The modelled
boundary in vertical direction is 25 m in depth and
horizontal direction is 25 m. The plane strain
condition and fifteen nodes are used.
Figure 5: Finite Element analysis mesh
The nodes are only allowed to move in vertical
direction and horizontal displacement can be defined
Analysis of Consolidation Settlement: A Case Study on State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Campus
175
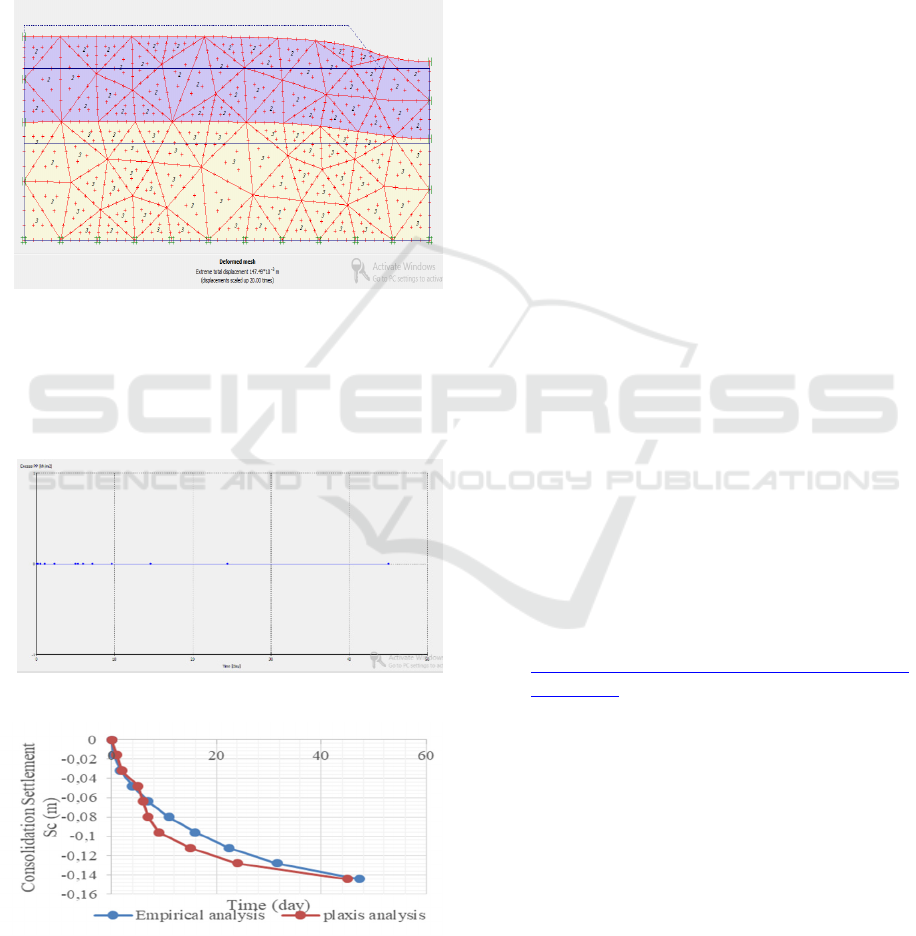
as zero. The excess pore pressure at nodes is set zero.
Meanwhile, the lateral boundaries are closed.
3.3.3 Initial Condition and Calculations
Active pore pressure was experienced by layer 1
because water flows from sand layer. Thus, the
embankment has only experienced effective stress or
there is no excess pore pressure.
.
Figure 6: Deformed Mesh of embankment finite
element
The result of output of Plaxis as shown in figure 6
is that embankment soil undergoes displacement
0.147 m. The time of consolidation, meanwhile, is 47
days as shown by graph in figure 7.
Figure 7: Deformed Mesh of the embankment finite
element.
Figure 8: Graph of consolidation time (t) and
consolidation settlement (Sc) between empirical
analysis and Plaxis
From figure 8, it can be concluded that the
consolidation settlement and time consolidation of
Sunan Ampel campus embankment are different in
empirical analysis and Plaxis program. The result of
calculation using Plaxis is lower than analytical
calculation but they almost are similar.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the discussion, it concluded that the
foundation of embankment of UIN 2
nd
Campus is soil
with low bearing capacity and vulnerable with
settlement. It was grey-black clay with high plasticity
and low consistency. To avoid structure damages, it
is necessary to know the soil characteristics by
conducting soil investigation and laboratory test. The
result of empirical analysis is that the consolidation
settlement of Sunan Ampel Campus embankment is
0.144 m and time with degree of consolidation 90%
is 47.7 days. Meanwhile, calculation using Plaxis is
0.147 m in 47 days too. While the result from
consolidation settlement and time consolidation
analysis should be used for giving some technical
recommendations for the owner.
REFERENCES
Das, Braja M, 1995, Mekanika Tanah (Prinsip-prinsip
Rekayasa Geoteknis), Terjemahan oleh Noor Endah
& Indra Surya Mochtar. Jilid I Jakarta, Erlangga.
Giatmajaya, W.I, (1993). Analisa Settlemen cara analitis
dan metode finite element pada tanah lunak dengan
software sebagai alat bantu. Jurnal Ilmiah
KurvaTeknik.
https://media.neliti.com/media/publications/144281-
ID-none.pdf.
Sohail S, Aadil N, Khan MS, 2012. Analysis of
Geotechnical and Consolidation Characteristics: A
Case Study of UET, Kla Shah Kaku Campus Lahore,
Pakistan, IACSIT International Journal of
Engineering and Technology.
Sutarman E, 2009. Concept and application of Soil
Mechanic, ANDI. Yogyakarta, 1
st
edition.
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
176
