
Image Cryptographic Application Design using Advanced Encryption
Standard (AES) Method
Nur Afifah
1
, Aris Fanani
1
, Yuniar Farida
1
and Putroue Keumala Intan
1
1
Department of Mathematics, Science and Technology Faculty
Sunan Ampel Islamic State University, Street Ahmad Yani 117, Surabaya, East Java
Keywords: Cryptography, Image, Advanced Encryption Standard, Attack, Encryption
Abstract: Development of technology gives significant impact on progress of all field of life, both in positive and
negative way. Among the negative impacts is crime, such as theft, burglary and others. In communication
security, information is very important. Data confidentiality is a priority so that maintaining the information
security needs an application that can encrypt the data. One of the sciences used to design a data security
application is cryptography, in which there are many methods can be used to encrypt a data. However, the
best method is Advanced Encryption Standard method (AES). There are many types of AES that can be used
but the most effective is AES-128. So, the aim of this study is to design image cryptographic application using
the AES-128 method. Process of design applications with this method is through several stages, such as
process of encryption, decryption, key generation and testing of the methods used. The attacks test is given
by cropping, blurring, and enhancing the ciphertext image. In previous studies, there has never been an attack
on the results of ciphertext, so this study will be accompanied by testing of attacks on ciphertext to determine
the resistance of the method used. From the result of encryption and decryption, it is known that this AES-
128 method was successfully applied to the image. While on the attack test, it was found that this method is
resistant to cropping attacks, but not resistant to blurring and enhancement attacks.
1 INTRODUCTION
Technology development, including computer
technology, is one of the most important aspects of
human life. Anything as complex as any problems can
be solved quickly and easily by a computer.
Technology development is closely linked to the
development of mathematics because every creation
of a new technology is always calculated
mathematically. However, by the sophistication of
technology, now almost every secret can be found
easily just by computer encoding. To obtain the data
or information, people will do anything they can, such
as breaking, stealing, or even tapping. This is very
unfortunate. Some examples of data theft cases are
even experienced by large companies, such as
linkedIn, whose password was stolen (Rahmad,
2016), Gmail data theft (Darmawan, 2010) etc.
In the field of communication, information
security is very important (Soleh, 2010) because that
theft of data or information also includes violations of
copyright. This has been regulated in Law No.28 of
2014 because the information obtained does not get
the permission from the owner or the manufacturer.
In addition, Indonesia also regulates the theft of data
in the ITE Law in article 3 of 2008.
In order to anticipate the theft of such data,
encryption is necessary to keep the confidential data
to stay safe. Cryptography is a mathematical
computation study that has relationships with
information security, such as data integrity, entity
authenticity, and data authenticity (Rahmatullah,
2016). Cryptography uses various techniques to
secure data, one of which is the Advanced Encryption
Standard (AES) method.
AES is the best choice method in encoding
(Munir, 2006). This method has been used in several
researches, such as Designing Application
Encryption and Digital Image Description Using
Rijndael Algorithms based on Java SE which produce
encrypting and shortcut technique with 100%
accuracy value (Yoga, 2014), Image Encryption and
Decryption using AES Algorithm which can encrypt
and decrypt an image (Desmukh, 2016).
Afifah, N., Fanani, A., Farida, Y. and Intan, P.
Image Cryptographic Application Design using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Method.
DOI: 10.5220/0008905500002481
In Proceedings of the Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference (BEST ICON 2018), pages 247-254
ISBN: 978-989-758-414-5
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
247

AES method has three types according to the
key length that are AES- 128, AES -192, and AES
256. Previous studies mentioned that the most
excellent AES algorithm is AES 128 (Arya, 2016).
Therefore, in this study the method used is AES 128.
2 THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 Cryptography
The term “cryptography” is derived from two Greek
words, crypto and graphia. Crypto means secret and
graphia means writing (Munir, 2006).
Terminologically, cryptography is encryption
techniques where randomized data uses an encryption
key so that it will be difficult to read by someone who
does not have a decryption key (Kromodimoeldjo,
2009).
According to historical records, cryptography
has been used in Egypt since 4000 years ago by
Egyptian kings during the war to send secret
messages to their warlords through their couriers. The
person who does this encoding is called a
cryptographer, while the person who studies science
and art in opening or deciphering a cryptographic
algorithm without having to know the key is called
cryptanalyst (Munir, 2006).
A good cryptographic algorithm is determined
by the complexity of processing data or messages to
be delivered and by fulfilling the following 4
requirements (Munir, 2006):
Confidentiality. Message (plaintext) can only be
read by authorized party.
Authentication. The sender of the message must
be identified with certainty, the intruder must be
ensured that he cannot pretend to be someone else.
Integrity. The recipient of the message must be
able to ensure that the message received is not
modified during data transmission process.
Non-repudiation. The sender of the message must
not be able to deny the message he sent.
Cryptograph basically consists of two processes,
namely the process of encryption and the decryption
process. The encryption process is the process of
encoding common messages into secret messages
called ciphertext. Ciphertext is something to be
delivered through open communication channels.
When ciphertext is received by the recipient of the
message, then the secret message is changed again
into an open message through the decryption process
so that the message can be read again by the recipient
of the message. This plaintext can be writing, photos,
or videos in the form of binary data.
Generally, based on the key similarities, the
encryption algorithm is divided into 2 types:
1. Symmetric key algorithm
In this algorithm, the key used in encryption and
decryption is the same. The AES method is
included in this algorithm.
2. Asymmetric key algorithm
This algorithm uses different keys in the
encryption and decryption process. For example,
the RSA method.
2.2 Advanced Encryption Standard
(AES)
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a
cryptographic algorithm that can be used rightly to
secure data. This AES algorithm works on data blocks
in the form of 4 x 4 matrix. Symmetrical ciphertext
blocks can encrypt (encipher) and decrypt (decipher)
information. AES algorithm uses clicking the
cryptographic keys 128, 192, and 256 bits to encrypt
and decrypt the data. Therefore, this algorithm is
known as AES-128, AES-192, and AES-256. This
algorithm also has another name that is Rijndael
algorithm. It is because this algorithm was made by
Rijndael, which is combined from Vincent Rijmen
dan John Daemen.
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is the
development of the standard DES (Data Encryption
Standard) encryption algorithm of which validity
period deemed to be over due to security. The rapid
computer speed was considered very dangerous to the
DES, so that on March 2, 2001 the new Rijndael
algorithm was established as AES (Publication,
2001).
In the process stages of this algorithm, there are
3 main processes, namely encryption, decryption, and
key expansion.
2.2.1 Key Expansion
The key expansion function takes the user supplied
16 bytes long key and utilizes the previously created
round constant matrix rcon and the substitution table
s_box to generate a 176 byte long key schedule w,
which will be used during the end and decryption
processes (Buchholz, 2001)
.
In this key generation. we initialize the initial
key as a 16 byte cipher key and then expand to
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
248
generate another key In this process, there are 3
stages, namely RotWord, SubWord, and XOR.
On RotWord shifting, every one byte is up
cyclically in the fourth column. Results from
RotWord are then substituted with the S-Box table.
Then, to get the first sub key of the first column, XOR
operation is performed with the first column of the
cipher key and the R-con. The results of the operation
then are used to get the next column by doing XOR
to the column with the corresponding cipherkey and
so on.
2.2.2 Encryption
Encryption is process of encoding the plaintext into
ciphertext. On an 8-bit processor, encryption with
Rijndael or AES can be programmed by simply
implementing the different steps. The implementation
of ShiftRows and AddRoundKey is straight forward
from the description. The implementation of
SubBytes requires a table of 256 bytes (Joan Daemen,
Vicent Rijmen, 2002).
In encryption, there are several processes, they
are:
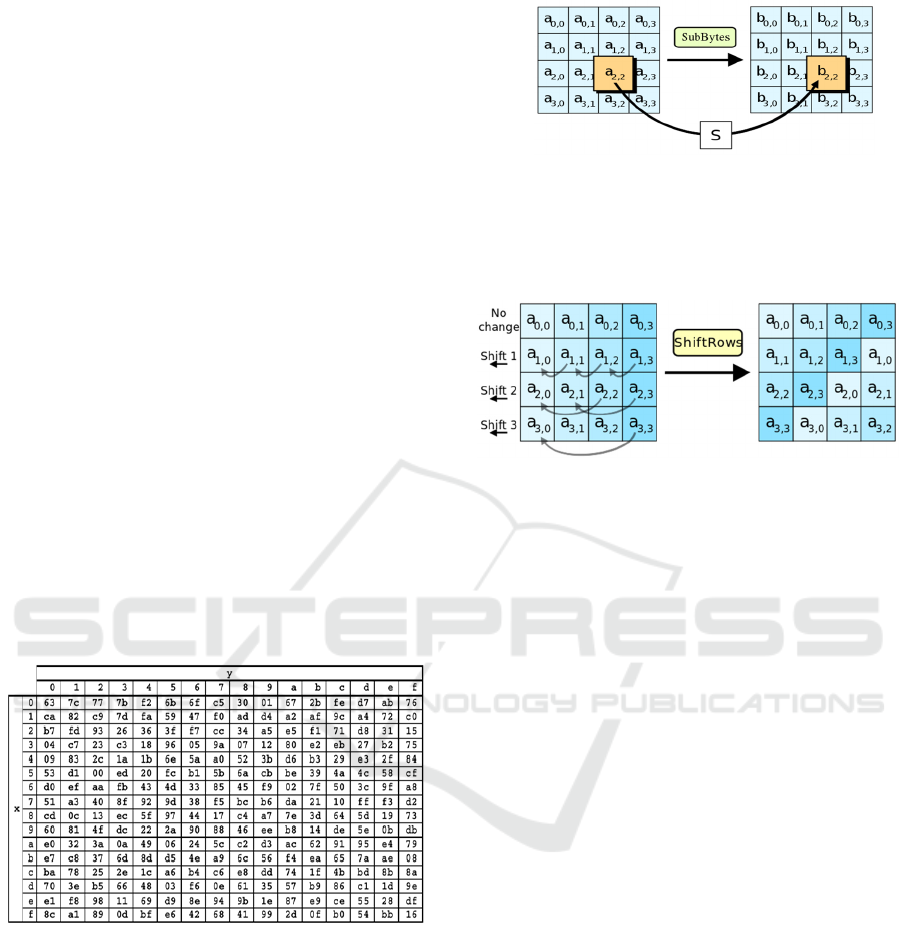
SubBytes
In this process, substitution is carried out for each
byte in the state with the S-box table set by
Vincent. The following is the S-Box table used:
Figure 1: S-box table
Substitution for each byte in the state array, for
example S [r,c] = xy, is a hexadecimal digit of
the value S [r,c]. Then, the substitution value
expressed by S [r,c] is an element in the S-Box
which is the intersection of row x and column y.
The following is transformation of SubBytes.
Figure 2: Subtituion of byte with s-box table
ShiftRows
In this process, shifting each byte is carried out in
the state as the following figure:
Figure 3: ShiftRows process
MixColumns
In the MixColumns stage, it operates every
element in one column at the state. The elements
in the column are multiplied by a fixed
polynomial
03
01
01
02
1
More details for the MixColumns transformation
can be seen in the following multiplication matrix:
′
,
′
,
′
,
′
,
02 03
01 01
01 02
03 01
01
03
01
01
02 03
01 02
,
,
,
,
2
AddRoundKey
This round key process is added to the state with
a simple bitwise XOR operations. Each round key
consists of Nb words in which each word is then
summed up with the corresponding word or
column from state. The state of addroundkey is of
the same size and obtain the next state an XOR
operation for every element. So, it becomes:
,
,
⊕
,
3
Image Cryptographic Application Design using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Method
249
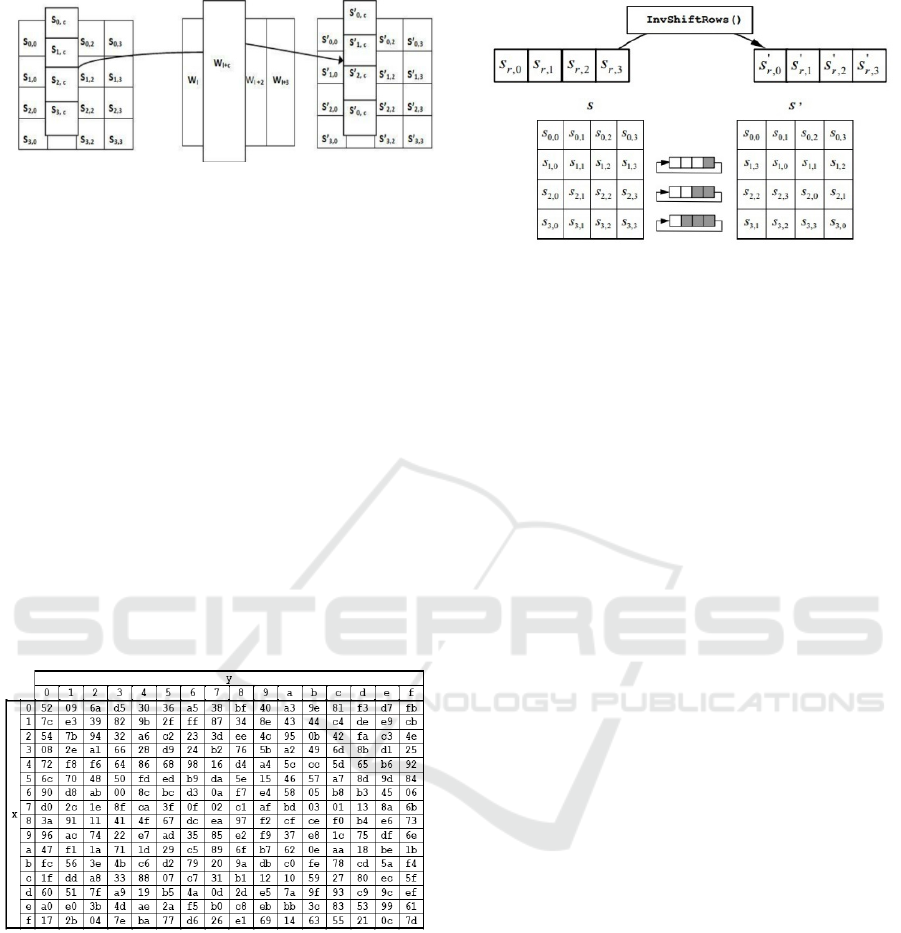
Figure 4: AddRoundKey Operation
with
is word of the corresponding key where
∗.
The AddRoundKey transfromation is
implemented first in round = 0, where the key used
is the initial key or key entered by the cryptographer
and has not experienced key expansion process.
2.2.3 Decryption
Decryption is similar in structure to encryption, but
uses the invers (Joan Daemen, Vicent Rijmen, 2002).
At this decryption stage, the process is the same as
encryption, but it uses inverse in each process. So, it
consists of:
InvSubBytes
This Inverse SubBytes process is almost the same
as process on encryption, but the subtitution is
with the Invers S-Box table
Figure 5: Inv S-box table
InvShiftRows
Inv ShiftRows is a transformation of a byte that is
the opposite of the ShiftRows transformation. If
ShiftRows transform the bit shift to the left, then
InvShiftRows transform the bit shift to the right.
Figure 6: InvShiftRows process
InvMixColumn
In the InvMixColumns process, the columns in each
state or word will be seen as polynomials for
GF2
and multiplying the modulo x
1 with
fixed polynomials a
x obtained from:
0
0
09
0
4
or in a matrix:
′
∗
5
′
,
′
,
′
,
′
,
0 0
0 09
09 0
0 0
0
0
09
0
0 0
09 0
,
,
,
,
6
InvAddRoundKey
In the transformation of Inverse AddRoundKey, it
does not have a difference with the AddRoundKey
transformation because in this transformation, only
simple addition operations are performed using
XOR bitwise operations.
2.2.4 Digitial image
Image is a multimedia component that has an
important role as a form of visual information
(Hanifah, 2012). Image has different characteristics
from data of text. Image has more information than
data of text. In other words, image data can provide
more information than text because the information
of them is presented in text form (Hanifah, 2012).
In general, Image is a two dimensional plane.
Image is a continuous function of light intensity in a
two dimensional plane symbolized by ,. In this
case, ,is a coordinate in two dimensional fields
and , is the light intensity at the point
,
(Munir, 2006).
Digital images are generally rectangular in size,
expressed by dimensions of length width.
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
250
Dimensional size is the representation of an image in
the form of a matrix of size m x n pixels, as presented
in the following functions:
,
0,0
1,0
⋮
1,0
0,1
1,2
⋮
1,1
…
…
⋮
…
0,1
1,1
⋮
1,1
3 RESEARCH METHOD
To collect data required in this study, researcher
searched data and information as appropriate
reference to support the truth of the description of the
material, theory, and discussion. Meanwhile, the data
used in this research is an image file of greyscale with
the size 32 x 32.
Design on this system uses AES 128 so that the
pixel value matrix of the image is entered in the
partition into blocks 4 x 4 and represented in
hexadecimal numbers.
The attacks tested in this study were cropping,
blurring, and enhancing. This testing attacks is used
to determine the resistance of an AES or Rijndael
method.
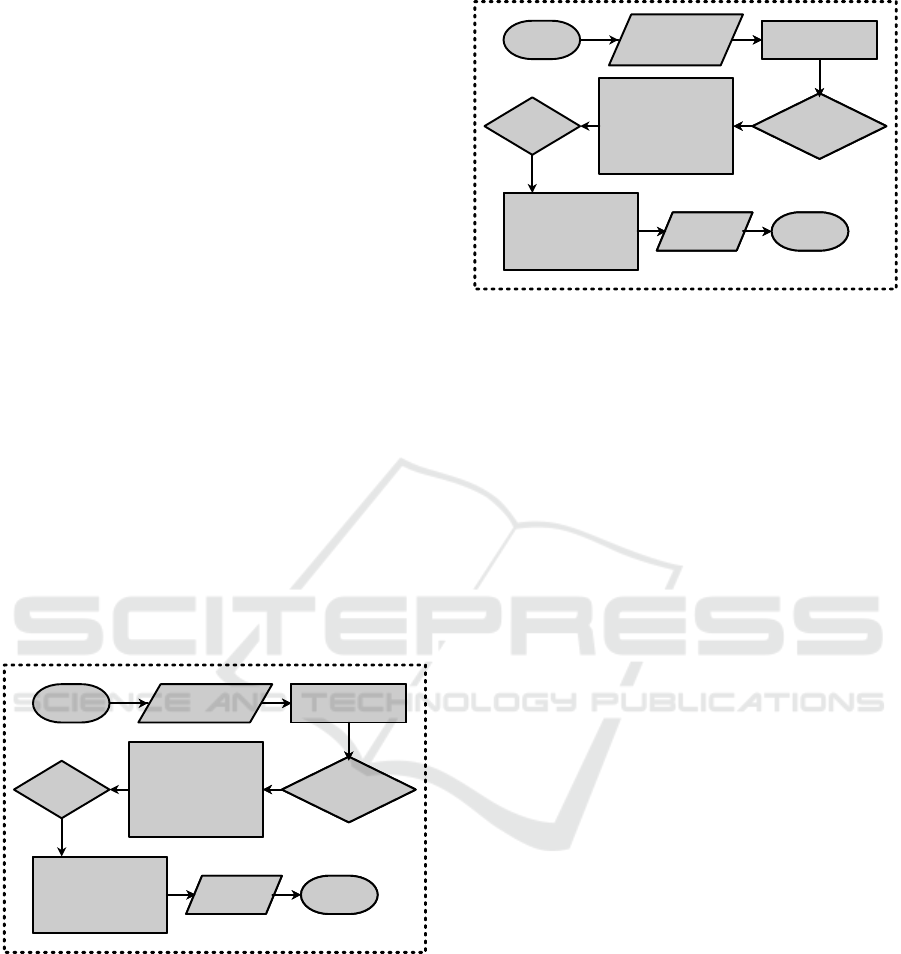
The following is a flowchart of the encryption
process:
Figure 7: Flowchart of Encryption Process
Ciphertext that has been attacked then is
decrypted for testing. The following is the flowchart
of decryption process:
Figure 8: Flowchart of Decryption Process
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The previous discussion has been briefly described
the process of encryption and encryption using AES
method. This chapter will explain about the design
and each stage. The first stage in the design of the
application is to generate the first key and then to do
the encryption and decryption stages. For more
details, it will be described in each of the following
stages:
4.1 Key Schedule
Key schedule is a process to generate keys that will
be used in the process of encryption and decryption.
As explained in the previous chapter, this key
formation consists of several stages, namely
RotWord, SubWord, XOR with R-con values, and
XOR with the previous word. In designing this
system, the cipher key is inputted by the application
maker. The cipher key entered is then converted to an
ASCII number. If the cipher is inputted more than 16
bytes, then the first 16 bytes are used, but if the cipher
entered is less than 16 bytes then the cipher will be
computed to 16 bytes with the addition of the number
0. The ASCII number of the cipher key is then
converted to hexadecimal number and represented in
matrix which size 4 x 4.
Input cipher key: "prodi matematika"
Each input entered will be converted to ASCII
number. So, the ASCII number of inputted cipher key
is:
110 172 73 99 62 176 85 60 90 145 103 115 82 168
96 79
ASCII numbers are converted into hexadecimal and
represented in the matrix of 4 x 4 so as to produce the
cipher key as follows:
AddRoundKey
1. SubBytes
2. ShiftRows
3. MixColumns
4. AddRoundKey
Round=
Round+1
Round=9
1. SubBytes
2. ShiftRows
3. AddRoundKey
Ciphertext Finish
Start Plaintext AddRoundKey
1. SubBytes
2. ShiftRows
3. MixColumns
4. AddRoundKey
Round=
Round+1
1. SubBytes
2. ShiftRows
3. AddRoundKey
Ciphertext Finish
AddRoundKey
1. SubBytes
2. ShiftRows
3. MixColumns
4. AddRoundKey
Round=
Round+1
Round=9
1. SubBytes
2. ShiftRows
3. AddRoundKey
Ciphertext Finish
Start
Ciphertext has
been attacked
InvAddRoundKey
1. InvSubBytes
2. InvShiftRows
3. InvMixColumns
4. InvAddRoundKey
Round=
Round+1
1. InvSubBytes
2. InvShiftRows
3. InvAddRoundKey
Plaintext Finish
Image Cryptographic Application Design using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Method
251

Cipher key:
6e 3e
ac b0
5a 52
91 a8
49 55
63 3c
67 60
73 4f
The next stage is RotWord. This stage is used to
generate the first column in the first sub key Wi,
then to shift each byte in the last column of the cipher
key cyclically up one time.
RotWord:
52
a8
60
4f
→
a8
60
4f
52
The results of RotWord at this stage are then
substituted with the S-Box table that has been set.
Subword:
a8
60
4f
52
→SBox→
c2
d0
84
00
The last stage to get the column key into W
is the
XOR process to the sub word result with the
corresponding R-con value. XOR process is then
done again with the column W
. At this stage,
hexadecimal numbers are changed first to binary
numbers to be able to do XOR operations. The
process is as follows:
c2
d0
84
00
⊕
01
00
00
00
⊕
6e
ac
49
63
The following is XOR operation using binary
number:
11000010
11010000
10000100
00000000
⊕
00000001
00000000
00000000
00000000
⊕
01101110
10101100
01001001
01100011
10101101
01111100
11001101
01100011
Result from binary XOR operations is
10101101
01111100
11001101
01100011
if it changes in hexadecimal, it is
7
63
.
So the result for the first sub key of the first column
is =
7
63
Furthermore, to get the first sub key to the
second to fourth column, XOR operations are carried
out between W
i
and column
. Similar step is
carried out to get the third and fourth columns in the
first key sub.
The second column of the first sub key
7
63
⊕
3
0
55
3
93
98
5
The third column of the first sub key
93
98
5
⊕
5
91
67
73
9
5
6
The fourth column of the first sub key
9
5
6
⊕
52
8
60
4
9
5
9
23
So the first sub key is
7
63
93
98
5
9
5
6
9
5
9
23
The above processes are repeated as many as 10
iterations to produce 10 sub keys used for the
encryption and decryption process.
4.2 Encryption and Decryption
The input is in the form of a greyscale image, then
represented in matrix according to the pixel size of
the image. The AES algorithm operates using blocks
cipher so that the matrix of the image will be
partitioned into blocks of size corresponding to the
type of AES used.
Design on this system uses AES 128 so that the
pixel value matrix of the image is entered in the
partition into blocks 4 x 4 and represented in
hexadecimal numbers. If the last partition of the
element does not reach 16 bytes, it will add dummy
of element 0 to 16 bytes.
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
252
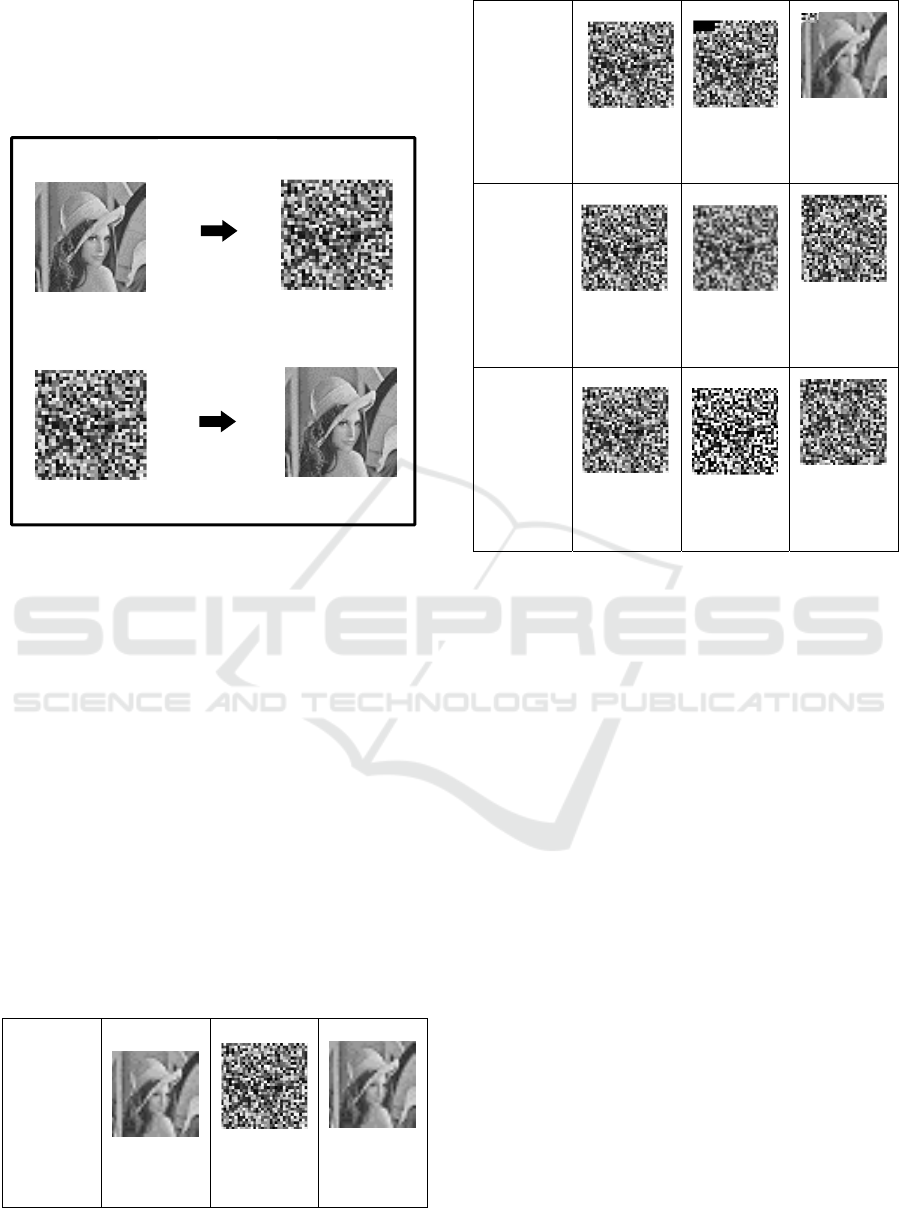

The first is to put the digital image that will be
used with the size of 32 x 32. The image that this
inputted can be any image as long as it is at the same
size with the limits set. The following is the result of
encryption and decryption of the image.
Figure 9: Flowchart of Decryption Process
From the encryption and decryption process, it
has been found that the AES method can be used to
encrypt images. The images that become ciphertext
can be returned or decrypted to the original plaintext.
4.3 Testing
Testing in this study is a test carried out on encryption
results. The encrypted image will be attacked in the
form of crop, blur, and enhancement. This attack can
do inside or outside the process using supporting
applications. Testing on the decryption process of the
ciphertext that has been attacked aims to determine
the resistance of the AES method against the attack.
The result of tests are as shown ini Figure 10:
Encryption
&
Decryption
Original
Image
Image of
Encryption
Results
Image of
Decryption
Result
Cropping
Ciphertext
Encryption
Result
Cropping of
Encryption
Image
Crop Test
Result of
Image
Decryption
Blurring
Ciphertext
Encryption
Result
Blurring of
Encryption
Image
Blur Test
Result of
Image
Decryption
Enhanceme
nt
Ciphertext
Encryption
Result
Enhancing of
Encryption
Image
Enhancement
Test Result
of Image
Decryption
Figure 10: Results of Attack Tests
From the result of attacks test on the ciphertext,
it can be seen that:
Test of cropping attacks on ciphertext can still
recognize the original plaintext. Although the
cropping area is different, the original plaintext
can still be detected clearly. This is because the
process at the decryption stage on each block has
no effect on other blocks. This cropping is only
partial so the decryption changes only on the
block affected by the cropping. For other blocks,
it is still able to properly prune the initial plaintext.
So, in this test, the Advanced Encryption Standard
(AES) method is resistant to cropping attacks.
Test of blurring attack performed on ciphertext
affects the decryption process so the result of this
testing attack can not return the original plaintext.
This is because the blurring process changes the
existing pixel values in the ciphertext image
matrix and it affects the decryption process as
well. Therefore, decryption of the ciphertext
image that has been blurred can not restore to the
original plaintext. So, the Advanced Encryption
Standard (AES) method is not resistant to blur
attacks.
Testing the ciphertext with enhancement attack
produces a different plaintext, or in other words,
plaintext can not return to the original image
because the enhancement process changes the
Encr
yp
tion
Pl
a
in
te
x
t
Decr
yp
tio
Ci
p
hertex
t
Ci
p
hertex
t
Plaint
e
x
t
Image Cryptographic Application Design using Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Method
253

pixel value of the image matrix, which is very
influential on the decryption process. In the
process of ciphertext decryption that has been
done, enhancement is not able to restore the
original plaintext. So, the Advanced Encryption
Standard (AES) method is also not resistant to
Enhancement attacks.
This research of encryption and decryption
was carried out on an image by adding attack testing.
From several attack tests that have been carried out
on ciphertext to determine the resistance of the AES
method, it was found that the determinant of the
success or failure of the decryption process of the
image file depends on the pixel value. When the pixel
value of the encrypted image is changed, the
decryption process have been successful, but it cannot
restore the plaintext image. So, the key for the success
of endurance testing is that the attack cannot change
the pixel value. Whereas the cropping process
changed only the pixel value, which is partial of the
image, so that the other pixel values remain. It makes
the encrypted image that has been cropped still
recognizable, but if the cropping of the image is very
large, then there is possibility that the decrypted
image will not be able to be recognized. Because the
blurring and enhancing process can change the pixel
value of the image, the decryption process cannot
restore the original image. It can be concluded that the
AES method is resistant to cropping attacks, but is not
resistant to blurring and enhancement attacks.
The result of the research is that advanced
encryption standard (AES) method still have
weakness. Although the attacker cannot solve or find
the key, but if they attack the ciphertext using blurring
or enhancement, it can prevent the recipient from
opening the plaintext. Result of this research is
expected to be an input to improve Advanced
Encryption Standard (AES) method.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm
was successfully applied to encrypt an image. In the
decryption process, this method can restore plaintext
as clear as before.
Attack test is given on the ciphertext by
cropping, blurring, and enhancing. It is found that this
method can recognize plaintext clearly for cropping
attacks only. However, for the other two attacks, it
cannot recognize the original plaintext. It can be
concluded that the Advanced Encryption Standard
(AES) method is a method that is resistant to cropping
attacks and is not resistant to blurring attacks and
enhancements. So, this method still has weakness that
when the attacker performs attacks, such as blurring
and enhancement of the ciphertext image, the
recipient cannot open the original plaintext.
REFERENCES
Arya, A. (2016). Effective AES Implementation . IJECET
Buchholz, J. J., 2001. Advanced Encryption Standard.
s.l.:s.n.
Darmawan, I. (2011). Gmail Hacked, US-China on the
verge of Cyber War. Jakarta: VIVA.
Deshmukh, P. (2016). An Image Encryption And
Decryption Using AES Algorithm . IJSER , 7.
Hanifah, F. (2012). Aplikasi Algoritma Rijndael Dalam
Pengamanan Citra Digital. Skripsi
Joan Daemen, Vicent Rijmen, 2002. The Design of
Rijndael. New York: Springer-Verlag Berlin
Heidelberg.
Kromodimoeljo, S. (2009). Teori Dan Aplikasi Kriptografi.
Jakarta: Spk It Consulting
Munir, R. (2006). Cryptography. Bandung: Informatika
Bandung.
Publications, F. I. (2001). Announcing the Advanced
Encrytion Standard. New York: National Institute of
Standarts and Technologys
Rahmat, A. (2016). Thief 117 LinkedIn passwords arrested
in Czech. Czech: PT. Net Mediatama Indonesia.
Rahmatullah. Design of File Cryptography Applications
Using the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
Method . 2016 . Surabaya. Journal of ITS
Soleh, M. (2010). Analysis and Implementation of
Watermarking with AES Algorithm for Giving Data on
Copyright on Audio Files . UIN Syarif Hidayatullah ,
Jakarta.
Yoga Palilianto. Design of Encryption Applications And
Digital Image Descriptions Using Java-based Rijndael
Algorithms SE .2014.
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
254
