
The Development of Learning Devices based on Local Wisdom to
Train Creative Thinking Skills of Students at SDN 21 Kota Ternate
Rusdi Hasan
1
, Mardia Hi. Rahman
2
, and Astuti Salim
2
1
Civics Education Study Program, Khairun University, Ternate City-Indonesia
2
Physics Education Study Program, Khairun University, Ternate City-Indonesia
Keywords: Learning Device, Local wisdom, and Critical thinking skills
Abstract: Learning devices based on local wisdom is one of the innovations in developing learning devices that are
expected to help teachers, especially elementary school teachers (SD) in the learning process. This research
was held because there are still teachers who have not been able to develop students' creative thinking skills
especially primary school students. This study aims to develop learning devices based on local wisdom that
can train students 'thinking skills and develop models of assessment of students' creative thinking skills.
This research is a development research carried out by referring to the 4-D development model, namely
Define, Design, Development and Disseminate. The subjects of this study were teachers and students of
grade V SD Negeri 21 Ternate in the academic year 2018/2019. Learning device quality data is collected
with validation sheets, implementation sheets, teacher and student response questionnaires, and critical
thinking skills tests. The results of the research indicate that the learning devices based on local wisdom
were able to improve students' critical thinking skills on the theme of 2 clean air for health on the sub theme
of the importance of clean air for breathing. The learning device has the characteristics of each learning
activity and subject lesson in the student's book, teacher's instruction book, or lesson plan based on the
stages of discovery learning model.
1 INTRODUCTION
Local wisdom-based learning has been proven to
develop the positive character of elementary
students (Mannan, Sopyan and Sunarno,
2015).Development of well-designed of learning
lesson plan is proven to be able to improve students'
critical thinking skills (Prihartanto, 2016). Current
learning, especially at the elementary level, is still
too focused on the teacher so that students' creative
thinking skills are not developed.As a solution,
learning using various models, approaches and
learning strategies that are in accordance with the
subject matter must be able to be done.
However, the elementary school teachers have
not been implemented the lesson plan properly.
Therefore, this research focused on the development
of lesson plan based on local wisdom to train
creative thinking skills.
Creating or forming a new idea from the results
of thinking is a creative way of thinking. Creative
thinking is an ability by individuals to find various
solutions of a problem at hand. In other words, if an
individual has the ability to think creatively, it will
make him or her has good abilities in solving or
finding answers to the problems at hand. Ginsberg &
Opper (1969) in
Kabouropoulou (2012) said that the
purpose of education is very important to build
understanding, students can verify and not easily
accept something that has been done. Many
discussions and research on creative thinking have
been done by
Emma Gregory, Mariale Hardiman,
Julia Yarmolinskaya, Luke Rinne, and Charles Limb
(2013) in his writing said that the students’ability to
think creatively will arise because it is influenced by
several factors that can be directly manipulated in
class, for example by giving students the opportunity
to ask questions. Carter & McRae, 2014; Craft, Hall,
& Costello, 2014; Sternberg & Williams, 1996,
(Mardia Hi. Rahman, 2017) said that developing
students' creative thinking skills requires a creative
teacher. A creative teacher is a teacher who is able to
actualize all the abilities to educate, train, and guide
students optimally according to the expected goals.
Furthermore Torrance and after (Hamzah and
Kimberly. Griffith, 2006) said that to make students
Hasan, R., Rahman, M. and Salim, A.
The Development of Learning Devices based on Local Wisdom to Train Creative Thinking Skills of Students at SDN 21 Kota Ternate.
DOI: 10.5220/0008900200870092
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning (ICTL 2018), pages 87-92
ISBN: 978-989-758-439-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
87

creative learning by the way students can explore,
question, experiment, manipulate, listen, and test
problems they face. Students will learn better, and
think more critically and can think creatively if they
are or study in a safe environment. Setting a safe
environment will make students feel comfortable to
express their opinions and ideas, take risks, take the
change, be creative, and care. Preliminary studies
conducted at SDN 21 Kota Ternate, found that the
learning devices developed by the teacher were still
imitating and did not develop by themselves, which
resulted in not using learning models or learning
strategies that could increase students' creative
power.
The development of learning devices carried out
in this study is the development of learning devices
based on local wisdom to practice the creative
thinking skills of elementary students. The location
of SDN 21 Ternate is near the market and crossing
port, where the local wisdom of the community
environment is still very strong, but if not cultivated
continuously it will be lost due to the development
of this region.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Creative Thinking Skill
Creative thinking is a habit of the mind that is
trained by paying attention to intuition, enlivening
the imagination, expressing new possibilities,
opening an amazing perspective, and generating
unexpected ideas (Elaine B. Johnson, 2006).
Creative thinking skills are an ability to develop and
find new ideas that are original, aesthetic and
constructive, which relate to views and concepts and
emphasize aspects of intuitive and rational thinking,
especially in using information and materials to
bring up or explain it with the original perspective of
thinkers. Liliawati and Puspita (2010) say that
creative thinking skills are cognitive skills to bring
out and develop new ideas, new ideas as the
development of previously born ideas and skills to
solve divergent problems (from various
perspectives).
Furthermore Liliawati and Puspita (2010) say
that the aspects of creative thinking skills include the
following aspects and indicators:
1) Fluency (thinking fluently) with indicators:
answering with a number of answers if there is
a question, fluently expressing his ideas, can
quickly see errors and weaknesses of an object
or situation.
2) Flexibility with indicators: providing various
interpretations of an image, story, or problem,
if given a problem usually think of various
different ways to solve it, classify things
according to different divisions (categories)
3) Originality (originality thinking) with
indicators: after reading or hearing ideas, work
to complete new ones.
4) Elaboration with indicators: looking for deeper
meanings for answers or problem solving by
carrying out detailed steps, developing or
enriching other people's ideas, trying / testing
details to see the direction to be taken.
2.2 The Local Wisdom in Learning at
Elementary School
Local wisdom is formed as a cultural superiority of
the local community as well as geographical
conditions in a broad sense. Local wisdom is a
product of the past culture that should be
continuously taken into account in life. Although it
is locally valued, the values contained are
considered to be very universal.
(http://filsafat.ugm.ac.id).
The existence of local wisdom in each region is
not without the functions, but has functions that can
enrich the atmosphere of the area. The functions of
local wisdom according to Sartini (2006) are: 1.
Serves for the conservation and preservation of
natural resources. 2. Serves for the development of
human resources. 3. Serves for the development of
culture and science. 4. Serves as advice, trust,
literature and taboos. 5. Social meaning such as the
communal integration ceremony / relatives. 6.
Meaningful social, for example at the agricultural
cycle ceremony. 7. Meaningful ethics and morals. 8.
Meaningful politics, for example the ceremony of
the ngangkuk merana and the power of the patron
client.
Preliminary study conducted by researchers at
SDN 21 Kota Ternate, It was found that most
teachers in this school did not develop learning
devices well by using various models, strategies and
learning approaches, moreover they could integrate
local wisdom in the surrounding environment. In the
observations of researchers, most teachers are more
concerned with cognitive abilities than cognitive,
affective and psychomotor abilities. This is what
encourages researchers to conduct research on the
development of learning devices based on local
wisdom. This research is intended to help teachers to
develop learning devices properly and correctly
which will result in the learning process going well.
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
88
If the learning process goes well and can enable
students to search, develop and find their own
concepts correctly, the thinking process of students
is getting better and will make students more
creative in developing their abilities.
3 METHOD
This research is a development research using the
learning device development, Thiagarajan et al,
namely 4-D model (define, design, develop,
disseminate). Learning devices to be developed are
based on local wisdom to train students' creative
thinking skills which include, The Lesson Plans
(RPP), learning models, learning approaches, and
student worksheets (LKS).
The research process can be illustrated in the
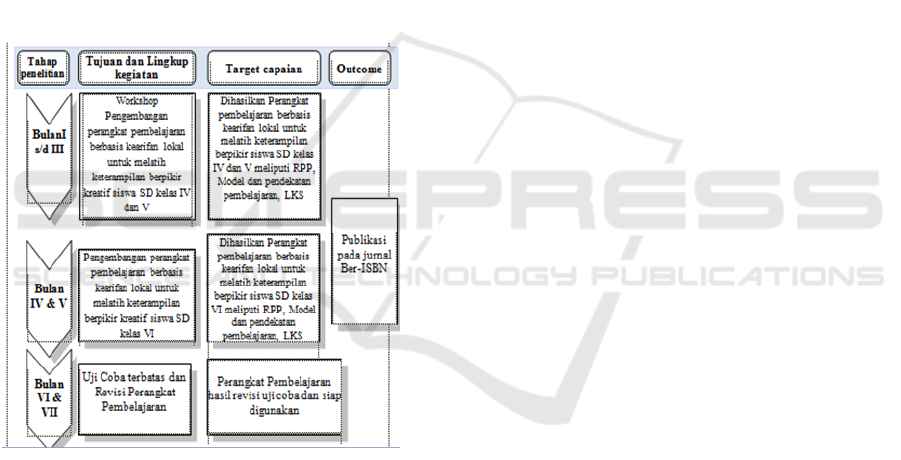
following flow chart:
Figure 1. Flowchart of research
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 The Product Development
The main product in this study is a local wisdom-
based learning device, especially at class V in odd
semester with theme 2. This device consists of
Lesson Plans (RPP) and Student Worksheets (LKS).
The first step in the development of local wisdom-
based learning devices conducted by researchers was
to analyze the curriculum and syllabus that had been
prepared which became the basis for the preparation
of Lesson Plans (RPP) and Student Worksheets
(LKS). The purpose is that the learning devices
developed (RPP and LKS) are not different from the
curriculum and syllabus.
The development of local wisdom-based learning
devices carried out is to include local elements that
exist around the school environment to be used as a
learning media and foster awareness of students
about the importance of utilizing and maintaining
the environment.
In addition to research activities to develop
learning devices based on local wisdom, the
researchers also conducted workshops to train
teachers to make their own learning devices without
imitating the results of the KKG activities. In fact,
there are still teachers who imitate other teachers’
RPP or because of the work of the KKG.
4.2 The Product Assessment
The assessment of products produced is carried out
by two people who have competence in their fields.
Product assessment uses instruments compiled by
researchers. This product assessment is intended to
get suggestions, input and criticism to complement
the products developed. The results of the
assessment by the two experts can be concluded that
the learning devices developed (RPP and LKS) are
in a very good category, namely the average
assessment of 86.36% and can be said to be feasible
to use but needs to be improved.
4.3 The Product Revisions and Final
Product
Product revisions are carried out aimed at improving
in order to obtain adequate products which is based
on the needs in the field. In this research, in addition
to obtaining quantitative data, it also obtained
qualitative data in the form of suggestions and input
on learning devices so that they can be developed
better.
These suggestions and criticisms were then
followed up by researchers to obtain quality learning
devices that were very feasible to use. Suggestions
and criticisms obtained from experts can be seen in
Table 1 below:
The Development of Learning Devices based on Local Wisdom to Train Creative Thinking Skills of Students at SDN 21 Kota Ternate
89
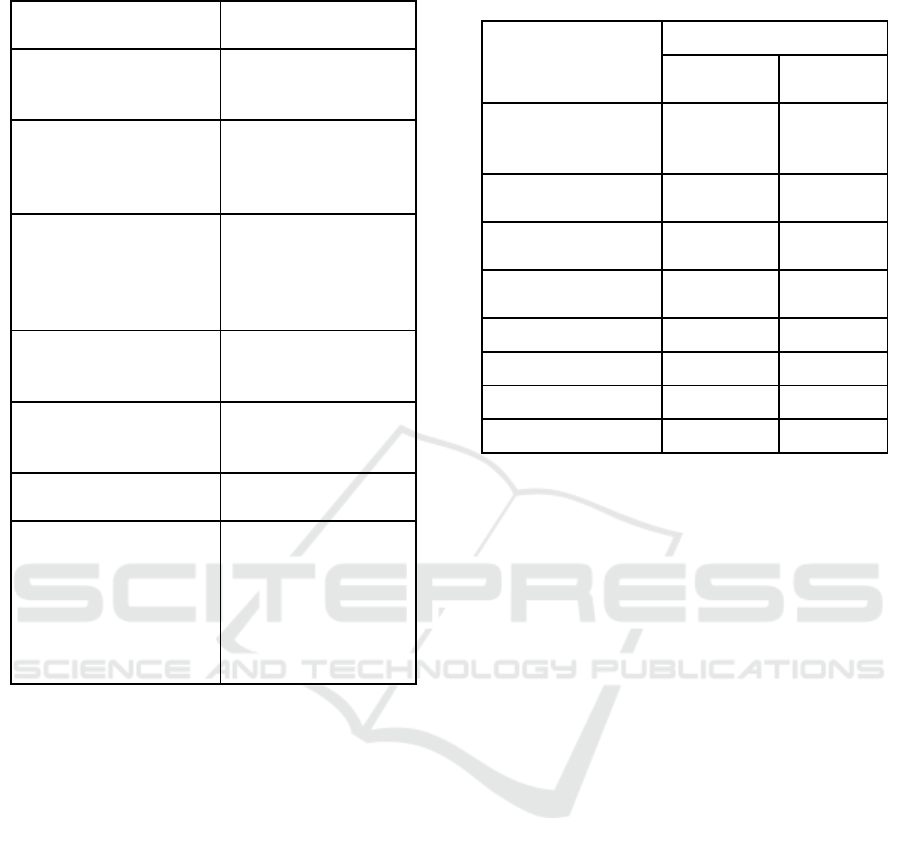
Table 1: Suggestions and Criticisms by the Experts.
Aspects
Suggestions and
criticisms
Formulation of
indicators of learning
success
It should be noted the
description of each
core competenc
y
Selection of learning
material
Learning material is
in accordance with
the teacher's book
and studen
t
b
oo
k
Organizing learning
material
Need to multiply
material from other
sources besides
student books and
teacher books
Selection of learning
resources
Use other resources
to enrich students'
knowled
g
e
Learning scenario
Scenorio learning is
adapted to the syntax
of the learnin
g
model
Assessment
Assessment rubric is
attache
d
Use of language
Note the procedure
for writing and using
languages that are in
accordance with the
enhanced Indonesian
spelling system
(EYD).
Learning devices developed in this study are
Lesson Plan (RPP) and Student Worksheets (LKS),
but the LKS developed is based on local wisdom
around the school environment that is easily utilized
to serve as a media or other learning resource. Based
on the motivation, the development research stage is
limited to development only, which was then tested
by fifth grade teachers of SDN 21 Kota Ternate.
Based on the results of the assessment by two
experts who stated that the learning device
developed was very good and feasible to use, but
there are some suggestions and criticisms for the
revision of device development. Furthermore, the
results of the assessment of the two experts can be
presented in Table 2 as follows:
Table 2: Results of Expert Appraisal of Local Wisdom
Based Learning Devices.
Aspects
Feasibility Percentage
Evaluator
1
Evaluator
2
Formulation of
indicators of
learnin
g
success
92.73 84.55
Selection of
learnin
g
material
92.73 87.27
Organizing
learnin
g
material
92.73 77.27
Selection of
learnin
g
resources
90.91 80
Learning scenario 89.09 81.82
Assessment 87.27 81.82
Use of language 90.91 80
Average 90.91 81.82
The results stated in the table can be said that
what needs to be considered for revisions is the
aspect of Organizing learning material, Learning
scenario and Assessment. The development of
devices in the aspect of organizing learning
materials is recognized that the material is still
limited, especially by using other learning
resources. The source book that is mostly used is
student books and teacher books as guidelines for
presenting material. Whereas in the aspect of the
learning scenario, there are several lesson plans
(RPP) that are considered inaccurate in the use of
learning models with the material and conditions of
students and school environment, especially in the
use of local wisdom in the environment around the
school. Furthermore, relating to the assessment, it
can be seen that at the time of the development of
learning devices based on local wisdom, it has not
been detailed in writing the assessment rubric and
scoring guidelines. From the results’ assessment of
team's evaluators, the researcher followed up by
improving the learning device developed.
The overall the results of the assessment from the
evaluators can be concluded that the RPP developed
is very good and feasible to use, because the
evaluation results of the evaluators on average are in
the very good category of 86.36%. Furthermore, the
results of the expert or evaluators can be seen in
Figure 1 below:
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
90
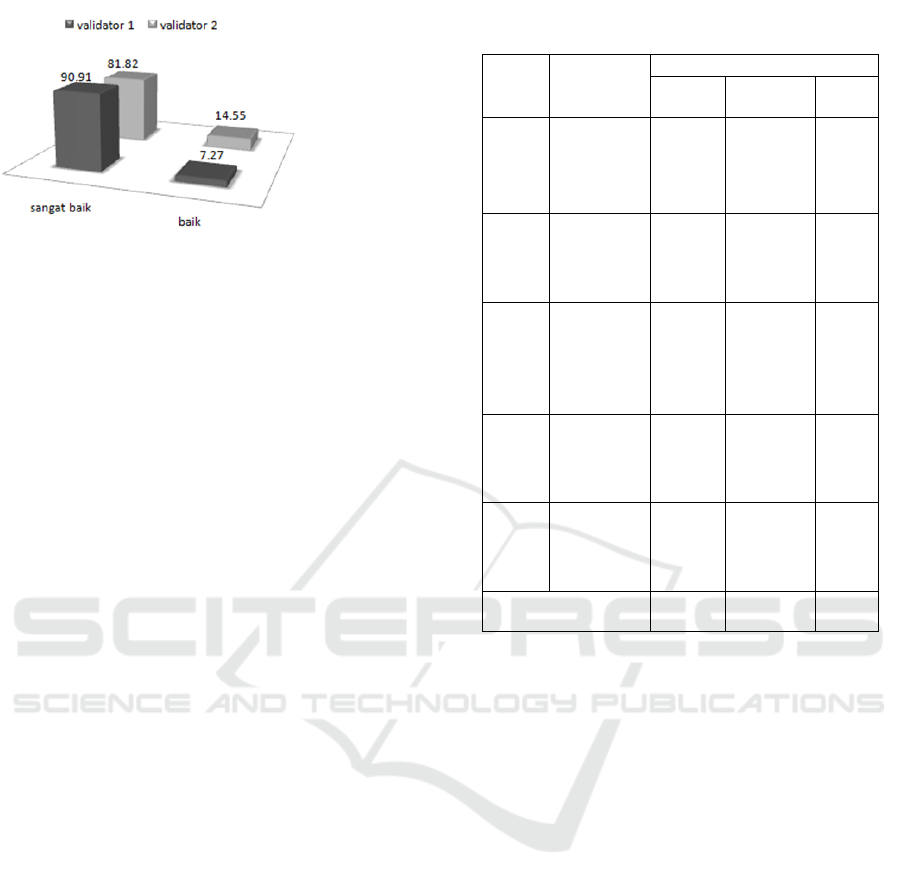
Figure 1: Form of Thematic RPP Assessment.
Learning devices that have been compiled are
then tested by fifth grade teachers of SDN 21 Kota
Ternate. When conducting a trial in the teacher's
opinion, the learning devices developed greatly to
improve students' conceptual understanding and
train students to be creative and develop their
thinking skills. The area or environment around the
school is an environment that is close to the market,
therefore the teacher can take advantage of the
environment to introduce students to the procedures
for developing business related to social studies
material, namely types of businesses, interviewing
traders about how to maintain market cleanliness,
noise, pollution and others related to clean air
science materials for health. In addition, students are
given examples of using used goods as learning
media and given project assignments to be
completed by students.
After the trial, the teacher held an evaluation to
test the students 'ability to understand the concept
being taught and asked students to do a project
assignment that is making human respiration using
local wisdom in the school environment as a form of
evaluation to determine students' creative thinking
skills. The results of student project assignments on
average are in the very good category of 95.2%.
From these results it can be said that using local
wisdom-oriented learning devices can improve
students' critical thinking skills on the theme 2 of
clean air for health on the sub-themes of the
importance of clean air for breathing. The learning
device has the characteristics of each learning
activity and Learning Materials presented in student
books, teachers’ manual, and lesson plans in
accordance with the stages of discovery learning
models and other models in accordance with the
characteristics of the material. The results of student
project assignments can be illustrated in Table 3 and
Figure 2 below:
Table 3. Project Task Results of Fifth Grade Students of
SDN 21 Kota Ternate
No.
Rated
aspect
Percentage of Scores
Good Enough Less
1 Project
task
planning
skills
94%
6%
2
Skills in
preparing
tools
100%
3
Skills for
making
work
procedures
97% 3%
4
Skill of
stringing
tools
97% 3%
5
Skills for
compiling
reports
88% 12%
Average 95.2% 4.8%
The results of the assessment of project assignments
of students on average are in the very good category,
then local wisdom-based learning devices can
improve students' creative thinking skills. The
results of the project assignments in table 3 can be
seen in the aspects of skill in compiling reports even
though they are in a very good category, but the
teacher needs to explain again about the systematic
preparation of reports in accordance with the rules of
compiling a work.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The results of the research showed that local
wisdom-oriented learning devices were able to
improve students' critical thinking skills on the
theme of clean air for health on the sub-themes of
the importance of clean air for breathing. Learning
devices have the characteristics of each learning
activity and learning materials presented in student
books, teacher manuals, and lesson plans in
accordance with the stages of discovery learning
models.
The Development of Learning Devices based on Local Wisdom to Train Creative Thinking Skills of Students at SDN 21 Kota Ternate
91

From the results of the validation by the two
experts, it can be concluded that the lesson plan used
is an average of 86.36%, the category is very good
and feasible to be used as a tool in the learning
process. Therefore, the scope of the research can be
enlarged for each grade level and not limited to the
odd semester of fifth grade. And Get to know more
about the local wisdom around us, in order to
achieve more innovative learning devices.
REFERENCES
Chandrasari, Dafik & Irfan. 2016. Pengembangan
Perangkat Pembelajaran Berbasis Constructive
Controversy Approaaches dan Conflict Resolution
Untuk Meningkatkan Kemampuan berpikir Kritis
Peserta Didik. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Pendidikan
Matematika, Universitas Madura.
Desi F. Wulandari, Ida Hamidah, Agus Setiawan, 2014.
Physics of Learning Strategy to Train Critical and
Creative Thinking Skills. International Journal of
Science and Research (IJSR. Volume 3 Issue 11.
Gregory, Emma., Hardiman, Mariale., Yarmolinskaya,
Julia., Luke, Rinne., and Limb, Charles. 2013.
Building CreativeThinkingin theClassroom: From
Research to Practice. International Journal of
Education
Research. Vol.62.
Elaine B. Johnson. 2006. Contextual Teaching and
Learning Menjadikan Kegiatan Belajar Mengajar
Mengasyikkan dan Bermakna. Bandung: MCC.
Hadzigeorgiou,Fokialis., and Kabouropoulo., 2012.
Thinking about Creativity in Science Education.
Creative Education. Vol. 3 No. 5.
Hamza dan Kimberly G. Griffith. 2006.
F
os
t
e
r
i
n
g
Problem
Solving &
Creative
Thinking i
n
the
C
l
a
ss
r
oo
m
:
Cultivating
a
Creative
M
i
nd.
National
Forum of Applied Educational Research Jounal-
Electronic. Vol 19. No. 3.
Joolingen, W.V. 1999. Cognitive Tools for Discovery
Learning. International Journal Of Artificial
Intelligence in Education (IJAIED) 10.
Liliawati dan Puspita, 2010. Efektivitas Pembelajaran
Berbasis Masalah dalam Meningkatkan Keterampilan
berpikir Kreatif Siswa. Prosiding Seminar Nasional
Fisika. Bandung.
Mannan, Sopyan dan Sunarno, 2015.
PengembanganPerangkat Pembelajaran Berbasis
Kearifan Lokal untuk Mengembangkan Karakter
Positif Siswa SD. Jurnal Inovasi dan Pembelajaran
Fisika. Vol. 2 No. 2.
Mulyasa, 2007. Standar Kompetensi dan Sertifikasi Guru.
Bandung: Remaja Rosda Karya
Nasution, S. 2008. Berbagai Pendekatan dalam Proses
Belajar dan Mengajar. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Mardia H.R, 2017. Using Discovery Learning to
Encourage Creative Thinking. International Journal of
Social Sciences & Educational Studies. Chapter 4 Vo.
4 No. 2. Ishik University.
Mayer, R.E. 2004. Should There Be a Three-Strike Rule
Againts Pure Discovery Learning The Case for
Guided Methods of Instruction. American
Psychological Association. 59(1).
Sartini. 2006. Menggali Kearifan Lokal Nusantara Sebuah
kajian Filsafati. http://filsafat.ugm.ac.id, Accessed 30
April 2017.
Shalin Hai-Jew. 2008. Scaffolding Discovery Learning
Spaces. MERLOT Journal of Online Learning and
Teaching Vol. 4, No. 4.
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
92
