
Development of Portfolio based Learning Instrument for Early
Childhood
Farida Samad, Haryati, and Syarifah Kurniaty Kahar
Lecturers of Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, Universitas Khairun, Jalan Bandara Babullah Akehuda Ternate
Maluku Utara, Indonesia
Keyword: Portfolio, Early Childhood.
Abstract: The study is a research and development research which aims at developing portfolio-based learning
instrument in terms of teacher’s manual, child’s worksheet and daily lesson plan. The subject was teachers and
students at PAUD Terpadu Alkhairat Skep Ternate. The instrument of portfolio was tested to 12 students of
class B at PAUD Terpadu Alkhairat Skep Ternate. The development model used was thiagarajan model or 4D
models consisted of four stages, namely defining stage, designing stage, development stage, and dissemination
stage. The portfolio instrument was validated and revised by the expert which then produced feasible product.
The result of the study showed that the portfolio-based learning instrument was valid, practical, and effective.
The learning instrument was develop after content validation and empirical validation were conducted. Then,
they were stated as valid based on Gregory’s formulation (>75% or 0.75). The learning instrument was stated
as practical because all of the aspects of learning was in completely conducted. The learning instrument was
stated as effective because it has fulfilled the criteria of effectiveness with the result that teachers gave 80% of
positive response toward the learning instrument based.
1 INTRODUCTION
Kindergarten provides guidance through stimulus
in the form of learning. This task shows that
through learning it is expected that children have
readiness to enter further education and they are
ready to learn in a broad sense. Therefore
development is needed in the learning model to
realize the learning objectives.
Learning functions is to direct students to
design learning used as a guide in learning
implementation in order to achieve effective,
efficient, attractive, and humanistic learning. Joice,
(1992) (in Yus, A: 2008) explains the learning
model is a plan or a pattern used as a guide in
planning classroom learning or tutorials and
determining learning instrument and directing us in
designing learning for students so that its
objectives are achieved.
In learning activities there are several
innovative learning models can be used by
teachers. Innovative learning models can provide
motivation for students to learn more actively so
that they can improve achievement and one of the
innovative learning models is portfolio-based
learning. Learning carried out in kindergartens
requires varied activities. One form of learning that
fulfills the learning is portfolio-based learning which
includes all aspects of child development to the
assessment of children's work. Machado, (2002) (in
Yus, A: 2008) states that portfolio-based learning
provides a great opportunity for children to move
according to their needs (Yus, A, 2008).
Portfolio-based learning is very possible to do in
kindergarten because teachers and students always
do certain products or works, for example, inviting
children to draw, color, cut, fold, stick and so on.
Meanwhile, activities to collect products or works of
students and interpret the collection of children's
products are sometimes forgotten. Some products or
children's work collected by educators are often not
evaluated again and at the end of the semester the
product is returned to the parents.
The problems occur in portfolio-based learning
start from the creation of student worksheets by
teachers and what the teacher makes as portfolios are
available magazines while the work of other children
is not portfolio. There are still many shortcomings in
the portfolio used in kindergarten. In fact, the
portfolio has an advantage can be used to evaluate
34
Samad, F., Haryati, . and Kahar, S.
Development of Portfolio based Learning Instrument for Early Childhood.
DOI: 10.5220/0008897000340037
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning (ICTL 2018), pages 34-37
ISBN: 978-989-758-439-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

learning process of students, so teachers and
parents can know children development from time
to time. However, the success of a learning model
depends on teaching instruments used to support
the learning model. The instrument is something
that supports the implementation of learning,
therefore learning instruments must be in
accordance with the learning model. In portfolio-
based learning, learning instruments are needed
such as manuals used by teachers in implementing
learning, the role of students worksheets is used to
test children's abilities and its results can be used
as children's portfolios, and daily lesson plan are
used to support learning models in accordance with
activity portfolio based. Based on the explanation
above, the researcher wants to conduct research on
the development of portfolio-based learning
instruments in kindergarten.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
This research is research and development/R&D
method because researchers want to develop
portfolio-based learning instruments for early
childhood using the 4D development model
includes four stages of development namely
define, design, develop, and disseminate. It is
expected to get products in the form of teacher
guidebook, students worksheets, and daily lesson
plans for effective activities. It was conducted at
PAUD Terpadu Alkhairat Skep in Ternate City.
The subjects were students in group B academic
year 2018/2019, the reason is students were able to
recognize letters, were able to read the beginning,
were able to write and were able to understand the
teacher's explanation. This research was conducted
from September to October of the 2018/2019
school year. The instruments used in this study are:
(1) teacher questionnaire on portfolio learning
devices (2) learning implementation observation
sheet (3) validation results sheet.
Data has been collected using these instruments
will then be analyzed quantitatively to explain
validity and effectiveness and the practicality of
the learning devices developed. Data obtained
from the results of validation by experts were
analyzed to explain the validity of learning
devices. The results of the trial data, namely the
teacher questionnaire and student performance
value data are used for the effectiveness of the
learning learning device.
𝐶𝑜𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑛𝑡 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑖𝑑𝑖𝑡𝑦 =
𝐷
(𝐴 + 𝐵 + 𝐶 + 𝐷)
Analysis to calculate the percentage of the
number of teachers who responded to each category
listed on the teacher's response questionnaire using
the following formula:
Pr=
∑𝑅𝑠
∑𝑠
x 100%
Then determine the category of implementation of
each aspect or overall aspect of the implementation of
the learning device (Nurdin, 2007):
1.5 M 2.0 all implemented
0.5 M 1.5 partly implemented
0.0 M 0.5 not implemented
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Portfolio-based learning is student-centered learning
that is very effective in teaching and learning. This is
in accordance with the constructivism theory
according to Yager (1992), the application of
constructivism means placing students in a central
position in the overall learning. To support portfolio-
based learning, supporting instruments such as daily
lesson plan do not include all portfolio and portfolio-
based learning scenario stages so that daily lesson
plan are needed, then improper portfolio compilation
and making portfolios are only a collection of
students assignments that only cognitive and motoric
development can be seen while in the portfolio all
that is included or all aspects of development are in,
that is why photos and videos are needed to find out
the extent of language development, gross motoric,
art and several other developments, in accordance
with previous research deal with portfolio-based
learning showed that portfolios contain work and
activities of children in learning process so that
teachers and parents can see child development, this
is in accordance with Herman's theory, Gearhart and
Ascbacher (1995) states that the use of portfolios in
learning has two functions, that are used as a form of
learning assessment as well as learning techniques.
Furthermore winter (1989) also emphasizes the
use of a good portfolio must contain a number of
learning experiences and should also be supported
by documentation. Therefore it takes preparation and
assessment handbook that summarizes how the
portfolio and preparation of portfolio as well as ways
to assess the portfolio. The process of developments
instruments done through some stages such as
define, design and develop and disseminate aims to
produce learning instrument in this case teacher
handbook, students worksheet, and daily teaching
Development of Portfolio based Learning Instrument for Early Childhood
35
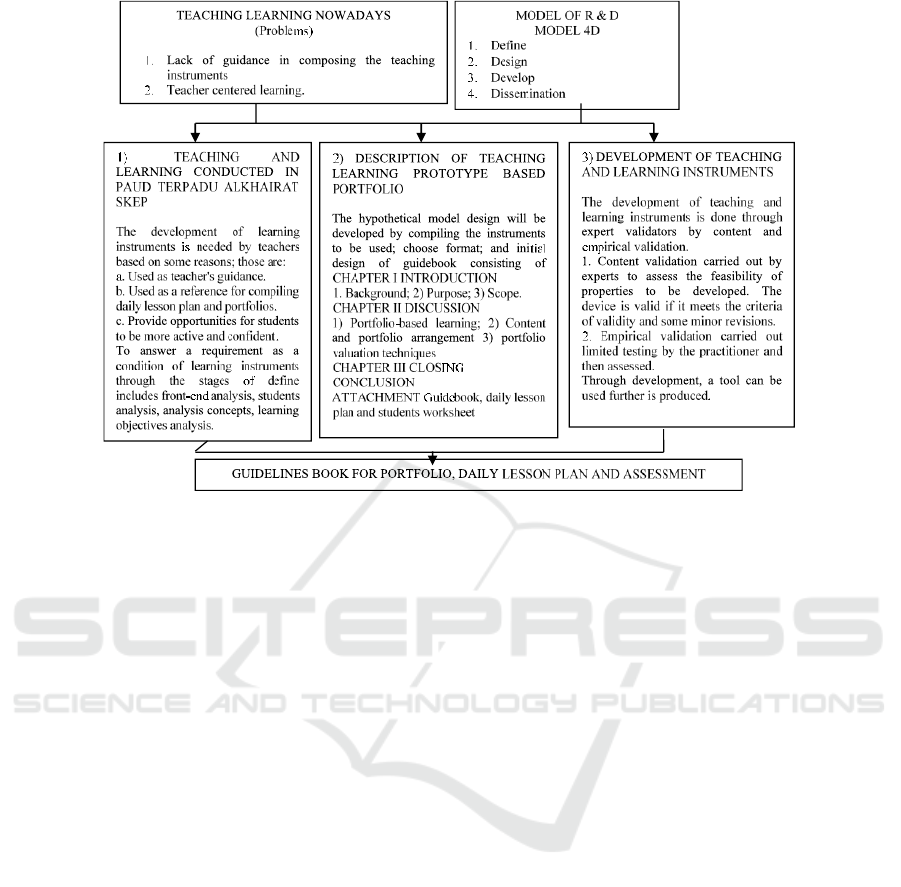
Figure 1.
plan to obtain valid and effective instruments used
in PAUD Terpadu Alkhairat Skep in Ternate.
These results prove that learning instruments
that has been revised based on input from
validators are valid and reliable to be tested. The
initial validator assessment for the teacher
guidebook and daily lesson plan based on the
results of analysis of all aspects was valid and
reliable even though there was a revision of the
preparation format.
Empirically the results of trials for practicality
criteria have met the criteria, the practicality
component of the teacher handbook and daily
lesson plan is determined by observation of two
observers on the implementation of portfolio-based
learning that have been implemented, from the
results can be considered adequate because all
components that are assessed in the instrument are
carried out entirely with a high level of reliability
so that the instruments meet the criteria of
practicality. Components that are considered to be
in the category are fully implemented because the
learning instruments used are easily understood by
students. This shows that learning instruments that
have been developed can be used in kindergarten
in accordance with the themes and sub-themes that
have been determined.
The effectiveness of learning instruments can
be seen from the questionnaire of teacher
responses that provide a positive response to the
portfolio used. These shows the effectiveness criteria
have been achieved. Thus the effectiveness criteria
of assessment for teacher also achieved because
teachers feels delighted in using portfolio so it
indicates that the teaching instruments are suitable
for use in kindergarten.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The condition of learning instrument is still not
perfect, there are still many things need to be
addressed so that portfolio-based learning is as
expected, so learning instruments such as teacher
guidebook and daily lesson plan are needed to
support the portfolio-based learning model because
of lack understanding of teacher about the
appropriate children's portfolio and how to compile
and assess the student's portfolio.
The prototype of previous instrument was not in
accordance with portfolio-based learning even
though the portfolio used in PAUD Terpadu
Alkhairat Skep in Ternate city had fulfilled some of
learning aspects but it was not perfect, therefore the
prototype instrument was developed to complement
portfolio-based learning in PAUD Terpadu Alkhairat
Skep in Ternate city through the stages of design to
form a hypothetical prototype.
Based on the results, the instrument is feasible to
use. The results of portfolio-based learning
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
36

development obtained through a 4-D model,
including: 1) the defining stage consists of five
steps, namely: initial analysis, students analysis,
task analysis, concept analysis and learning
objectives.2) design phase consisting of four steps,
namely: test preparation, media selection and
design of the format, and initial design. 3) The
development stage, namely expert assessment and
field trials, then all the initial designs are validated
by experts and they are in the valid category then
tested to find out its practicality and effectiveness,
so it is feasible to use. 4) The stage of deployment,
namely the stage that the product is distributed to
other classes or other schools to further test the
product effectiveness. However, in this study the
distribution stage was not carried out.
REFERENCES
Anonim. 2010. Direktorat Manajemen Pendidikan Dasar
Sekolah. Pelaksanaan Penilaian dalam
Implementasi KTSP di SMA. Kementerian
Pendidikan Nasional dan Direktorat Manajemen
Pendidikan Dasar Sekolah Menengah Atas.
Anonim. 2010. Direktorat Pembinaan TK dan SD.
Pedoman Pengembangan Silabus di Taman Kanak-
Kanak. Kementrian Pendidikan Nasional dan
Direktoral Jenderal Manajemen Pendidikan Dasar
dan Menengah, Direktorat Pembinaan TK dan SD.
Arter, Judhit A. 2003. Portofolio for Assessment and
Instruction. (Online) (http://www.Oxford.Org/
portofoliowahtis/ html). diakses tanggal 5 Maret
2015.
Boediono. 2002. Pelaksanaan Kurikulum Berbasis
Kompetensi. Jakarta: Badan Penelitian dan
Pengembagan Departemen Pendidikan Nasional.
Brewer, Jo Anin. 2007. Introduction to Early Childhood
Preschool Through Primary Grades Sixht Adition,
New York Pearson Education. Inc.
Dimyati&Mudjiono. 2006. Belajar Dan Pembelajaran.
Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Essa, Eva, L. 2003..Introduction to Early Childhood
Education Fourth Edition. Autralia: Thamson
Delmar Learning,
Fajar, A. 2005. Portofolio Dalam Pembelajaran IPS.
Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya.
Fadlillah, M. 2012. Desain Pembelajaran PAUD
Tinjauan Teoritik dan Praktik. Jogjakarta: Ar-ruzz
media
Farida, A. S. Implementasi Evaluasi Portofolio. (Online)
(http://staff.uny.ac.id/sites/default/files/artikel
porfolio.pdf) diakses tanggal 23 Februari 2015.
Fitri, B. 2012. Silabus PAUD nonformal (Online).
(http://Foemaherpepe.files.Wordpress.com/2012/10/
02/) diakses tanggal 22 April 2016.
Isjoni. 2010. Model Pembelajaran Anak Usia Dini.
Bandung: Alfabeta.
Mochano, Fransisko. 2002. Portofolio Based Learning,
(Online) (http://www.wsu.edu/teaching.html) diakses
pada tanggal 5 Maret 2015.
Putra, N. 2011. Research & Development. Jakarta: PT
Raja Grafindo.
Ruslan. 2009. Validitas Isi. Makassar: Buletin Pa’biritta
LPMP Sulawesi Selatan.
Sujiono, Y. N. 2010. Mengajar Dengan Portofolio.
Jakarta: Indeks.
Sugiyono. 2009. Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif, Kualitatif
dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Taniredja, Efi, Sri. 2012. Model-ModelPembelajaran
Inovatif. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Trianto. 2009. Mendesain Model Pembelajaran Inovatif-
Pogresif. Jakarta: Kencana
Winter, Richard. Learning from Experience: Principles
and Practie in Action-Research. Philadelphia: The
Falmer Press. 1989.
Yager, E Robert, 1996, STS Science/ Technology/ Society
As Perform in Science Education, New York. United
State of Amerika.
Development of Portfolio based Learning Instrument for Early Childhood
37
