
The Development of Role Play Learning Model in Management
Accounting Course
Riwayadi
1
, Yulia Hendri Yeni
1
, and Denny Yohana
1
1
Faculty of Economics, Universitas Andalas, Padang, Indonesia
Keywords: Role-Play Learning Model, Student-Centered Learning.
Abstract: This research aims to evaluate the implementation of Role Play Learning Model (RPLM) in achieving the
course’s expected learning outcomes. This is an applied research using primary data collected through survey
and observation. The population consists of 182 management accounting students in the 2nd semester of
2017/2018. This research uses census sampling. Of the total respondents surveyed, 95% returned their
questionnaires. The questionnaire is developed by using five Linkert scales (5 for highly agree). The study
reveals that students agree to implement RPLM on management accounting course. RPLM can improve
students’ grades as none of them got D and E grades. The number of students who got C grade dropped from
17% to 4% while that of those who got A-, B+, B-, and C+ grades increase by 8%, 1%, 5%, and 8%
consecutively. This proves that the implementation of RPLM can (1) build a good teamwork, (2) improve the
understanding of learning materials, (3) increase the motivation of students, (4) build the self-confidence of
students, (5) make students more innovative and creative, and (6) make teaching and learning process more
interesting for the students.
1 INTRODUCTION
Job markets require high competencies that include
hard skills and soft skills. Active, creative, and
innovative learning methods should be developed to
help graduate students’ acquire high competencies.
Teacher-centred learning (TCL) approach is no
longer adequate to make students active, creative, and
innovative. Previous research found that student-
centered learning (SCL) approach is better than
teacher-centered learning (TCL) approach. Hadi
(2007) and Kurdi (2009) argue that SCL allows
students to have high motivation to achieve their
desired competencies. SCL approaches include (i)
Small Group Discussion (SGD), (ii) Role Play,
Games, and Simulation (RPGs), (iii) Case Study
(CS), (iv) Discovery Learning (DL), (v) Self-Directed
Learning (SDL), (vi) Cooperative Learning (CL),
(vii) Collaborative Learning (CbL), (viii) Contextual
Instruction (CI), (vix) Project-Based Learning
(PjBL), and (x) Problem-based learning and Inquiry
(PBL) (LPPPM Unand, 2014). In this research, role
play learning model is developed for management
accounting course. Role play is a learning method
that enables students to understand the concept [3].
The steps of Role Play Learning Model are (1) the
lecturer develops the learning scenario, (2) the
lecturer requests students to learn the scenario, (3) the
lecturer requests students to make a group to discuss
the role of each member, (4) the lecturer requests
students to make a presentation of discussion results,
and (5) The lecturer provides advisory, conclusion,
and refection (Ngalimun, 2012).
Management accounting is a compulsory course
offered in the 4
th
semester. The current learning
methods of this course are lecture and case solution
presentation. At the beginning of the semester, the
student group is established. Each group should
present the solution of the assigned case by using
power point. Student assessments include group
assessment, mid-term exam, final exam, presentation
skills, and class participation. Rubric assessment has
not been used for soft skill assessment. 51% of
management accounting students got E, D, C, C+, and
B- grades. This significant number should be
improved since job markets require the minimum
cumulative GPA of 3 (4 for the highest).
The weaknesses of the current learning method
are (i) lack of team work, since one person might only
do the group tasks, (ii) less communication skills, (iii)
less understanding of the concept between group
members, (iv) less innovation and creativity, and (v)
108
Riwayadi, ., Yeni, Y. and Yohana, D.
The Development of Role Play Learning Model in Management Accounting Course.
DOI: 10.5220/0008680801080110
In Improving Educational Quality Toward International Standard (ICED-QA 2018), pages 108-110
ISBN: 978-989-758-392-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

high possibility of plagiarism (only copy paste other
group’s case solution)
Problem definition can be formulated as follows:
is role play learning model more effective in
achieving the both the program’s expected learning
outcomes (PELOs) and management accounting
course’s expected learning outcomes (CELOs)?
The research objective is to evaluate the
effectiveness of role-playing learning model in
achieving PELOs and CELOs. The research benefit is
to provide an input for undergraduate accounting
study program and lecturers in developing the
effective learning methods in order to achieve PELOs
and CELOs.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
This is an applied research that focuses on practical
problem solving directed to answer the specific
questions for policy development, action or particular
performance (Indrianto and Supomo, 1999). This
research is the evaluation research used for the
evaluation of the effectiveness of an action, activity
or program (Indrianto and Supomo, 1999). This
research is a qualitative approach that uses data in the
form of written sentences or verbal, behavioral,
phenomena, events, knowledge, or the object of the
research (Maleong, 2006). Qualitative research is
concerned with developing the explanation of social
phenomena. It aims to help us to understand the world
in which we live and why things are the way they are
(Hancock, 2002).
The subject of this research comprises Andalas
University’s accounting students enrolled in
management accounting course. The population
consists of all Andalas Univerity’s accounting
students enrolled in management accounting course
for the second semester of 2017/2018. The research
uses census data, that is, all Andalas University’s
accounting students who are taking management
accounting course. 182 accounting students took
management accounting in the second semester of
2017/2018. The research was conducted in the second
semester of 2017/2018 for six months (January – June
2018).
The research uses primary data gathered through
questionnaire and observation. Data were collected
by using two methods: observation and survey.
Observation was conducted when the students were
presenting their video project. The observation aims
to assess the achievement of course’s expected
learning outcomes and lesson’s expected learning
outcomes that include the understanding of concepts,
communication skills, team work, innovation and
creativity, the results will then be compared to the
previous learning method. The questionnaire was
distributed to students on the final exam schedule.
Questionnaire was developed using 5 Linkert scales:
1 (highly agree), 2 (agree), 3 (neutral), 4 (not agree)
and 5 (highly not agree).
2.1 Planning
A learning plan was developed to achieve the
program’s expected learning outcomes (PELOs) that
have been formulated by the Undergraduate
Accounting Study Program. Learning plan includes
program’s expected learning outcomes (PELOs),
course’s expected learning outcomes (CELOs),
lesson’s expected learning outcomes (LELOs).
A learning plan was developed by using role play
learning model. Students will be given the group
project assignment of video creation by using role
play learning model. Each group member acts as a
manager who solves the company problem. She/he
could be a marketing manager, a production manager,
a finance manager or an accounting manager.
2.2 Implementation
The lecturer develops a case based on topics
discussed in management accounting course. The
case reflects the real condition of the companies. Each
group is given the project assignment of video
creation learning. Each group member acts
specifically as a director, division manager,
marketing manager, production manager, finance
manager, accounting manager or another manager
who solve the company’s problems. Each group
should create an interesting video which lasts 10
minutes maximum and submit it to the lecturer at least
one day before the presentation schedule. Students
are free to choose the Spot of video creation. The
Video Project Assignment will be assessed by using
the assessment rubrics.
The steps of data analysis are: (1) tabulating the
questionnaire, (2) calculating the average score of
each question by dividing total score with the total
number of respondents, and (3) drawing the
conclusion.
Besides the questionnaire, the effectiveness of the
learning method will also be assessed by looking at
the grade differences before and after the learning
method development, and also by the observation
results of the video presentation.
The Development of Role Play Learning Model in Management Accounting Course
109
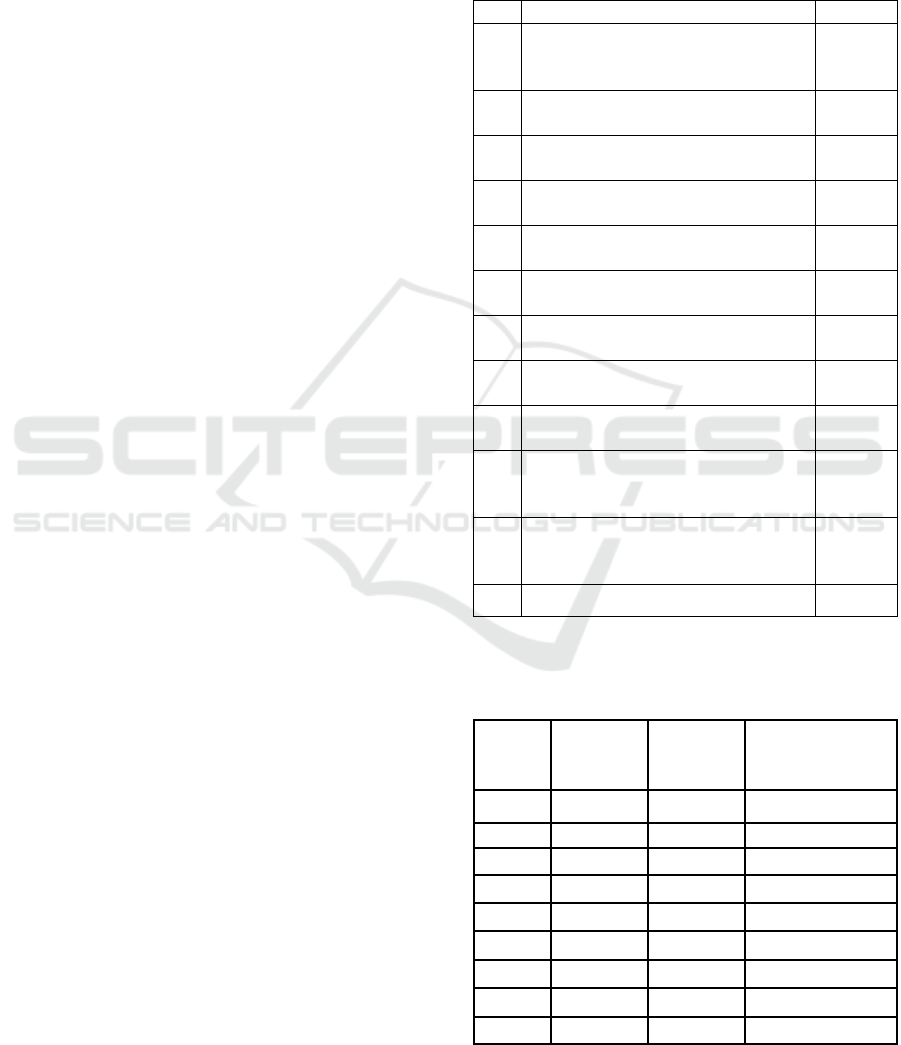
3 RESULTS AND CONCLUSION
Of the 182 questionnaires distributed, 173
questionnaires (95%) were returned and could be
processed. Students agree that role-play learning
method should be used in management accounting
course as indicated by the overall average score of
3,66. Students highly agree that Role Play Learning
Model can build good teamwork and communication
skills as indicated by the above average score of 4
(Appendix 1). After the implementation of Role Play
Learning Model, no student has had D and E grades.
The students who got C grade also dropped from 17%
to 4% or decreased by 13%. The number of students
who got A-, B+, B-, and C+ grades increase by 8%,
1%, 5%, and 8% consecutively (Appendix 2). This
proves that role-play learning model can improve
students’ grades, which will also affect students’
cumulative GPA.
It can be concluded that the implementation of
Role Play Learning Model can (a) build good
teamwork, (b) improve the understanding of the given
materials, (c) encourage student s’ motivation to
learn, (d) build students’ self-confidence, (e) make
students more innovative and creative, and f) make
lecturing activities more interesting to students.
It is suggested that firstly, role play learning
model needs to be implemented for management
accounting course and other courses and secondly,
faculty or study program needs to support the
facilities for the effectiveness of role-playing learning
model implementation.
REFERENCES
Hadi, R 2007. Dari Teacher-Centered Learning ke Student-
Centered Learning: Perubahan Metode Pembelajaran di
Perguruan Tinggi. Insania, Vol. 12, No. 3.
Hancock, Beverley. 2002. An Introduction to Qualitative
Research. Trent Focus Group. University of
Nottingham.
Indriantoro, Nur dan Supomo, Bambang. 1999. Metodologi
Penelitian Bisnis Untuk Akuntansi dan Manajemen,
Edisi Pertama,Yogyakarta: BPFE
Kurdi F.N. 2009. Penerapan Student Centered Learning
dari Teacher Centered Learnng Mata Ajar Ilmu
Kesehatan pada Program Studi Penjaskes. Forum
Kependidikan, Volume 28, Nomor 2.
Lembaga Pengembangan Pendidikan dan Penjaminan Mutu
(LP3M) Universitas Andalas. 2014. Panduan Praktis
Pelaksanaan Student Centered Learning (SCL)
Moleong, Lexy J. 2006. Metode Penelitian Kualitatif, Edisi
Revisi, Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya
Ngalimun. 2012. Strategi dan Model Pembelajaran.
Banjarmasin: Aswaja Pressindo.
APPENDIX
Survey Results
No.
Question
Average
1.
Role play learning model makes it
easier for me to understand
management accounting materials
3,51
2.
Role play learning model boosts my
learning motivation
3,34
3.
Role play learning model makes me
more innovative and creative
3,44
4.
Role play learning model gives me
more self-confidence
3,49
5.
I participate actively in to video
creation
4,13
6.
I have no difficulties in creating the
learning video
3,32
7.
Participate actively in preparing the
scenario
4,11
8.
I participate in getting the
understanding of the case and solution
4,05
9.
I give ideas in the creation of learning
video
3,94
10.
I suggest that this model should be
implemented in management
accounting
3,35
11.
I get many benefits from the
implementation role play learning
method
3,55
Average
3,66
Before and After the Implementation of Role Play Learning
Model.
Grade
2nd Smt.
2016/2017
(Before)
1st Smt.
2017/2018
(After)
Description
A
11%
11%
Unchanged
A-
8%
16%
Increased by 8%
B+
14%
15%
Increased by 1%
B
15%
14%
Decreased by 1%
B-
23%
28%
Increased by 5%
C+
4%
12%
Increased by 8%
C
17%
4%
Decreased by 13%
D
4%
0%
Decreased by 4%
E
3%
0%
Decreased by 3%
ICED-QA 2018 - International Conference On Education Development And Quality Assurance
110
