
Social Media as Economics Learning Media in Higher Education: An
Empirical Study at Universitas Negeri Semarang
Ahmad Nurkhin, Fachrurrozie, Kardoyo, Ratieh Widhiastuti
Faculty of Economics, Universitas Negeri Semarang, Semarang, Indonesia
Keywords: Economics Learning; Social Media; Higher Education; Facebook; Instagram; YouTube; Twitter; What Sapp.
Abstract: Learning in higher education currently utilizes information technology, including social media. Economic
learning in higher education should make use of social media to improve the quality of learning. This study
aims at revealing the practice of social media employment for economics learning in Economic Education
Study Program of Universitas Negeri Semarang (UNNES). The quantitative descriptive analysis approach
were used in this research. The respondents of this research were faculty members and students of Economic
Education Study Program of Faculty of Economics UNNES. Interviews, questionnaires, and documentation
were employed to collect the data. The method of data analysis was descriptive analysis technique. The results
show that lecturers in Economic Education Study Program of FE UNNES have used social media in
economics learning. Lecturers and students access their social media through smart phones. Social media
often used are Facebook, Instagram, YouTube, Twitter, and Whatsapp. The utilization of social media is
intended to support lectures in class and interaction between lecturers and students. Lecturers use Instagram
accounts to facilitate students in publishing the completed tasks or work. YouTube is used as a learning
resource to gain inspiration or ideas and to publish works. Facebook is used as a media of communication
between lecturers and students. However, Twitter is the most rarely used social media in economics learning
at FE UNNES. The last result shows that faculty member and student of FE UNNES also use whatsapp for
both learning and communication.
1 INTRODUCTION
Recently, the study of the use of computers is still
focused on internet searches, e-mail and games. The
very rapid changes of technology and mobile phone
create new social media categories, which provide the
means to communicate and build relationships
(Ruleman, 2012). Recent studies have shown that
nowadays many students are accustomed to using
digital media and developing new learning styles that
certainly rely on social media and the Web. Internet-
based learners have degrees of proficiency,
competence, and adoption rates. Strategies and best
practices are then explored to address how social
media can be employed by educators to accommodate
the heterogeneity of digital learners and involve new
learning styles (Bodle, 2011). Technology creates
students' experiences in the classroom to be more
interesting and innovative, so that it possibly makes
students more interested in the learning process.
Social media is able to develop students' critical and
creative thinking skills. Social media also allows
effective engagement between students and teachers
and between students. It can even handle cross-
cultural understanding (Tadros, 2011).
Learning in college should have used information
technology (social media, internet, and others) well.
At the present time, students are the generation of
Internet literate and quite rely on social media
through their own smartphones. Learning in college
allows them to flow into a new phase. The facts about
internet and social media users in Indonesia mention
that learning should be able to anticipate the
development of the internet and learners in using
internet and social media. (Ruleman, 2012) explained
that emerging social networking technology had
become ubiquitous. Educators must pay attention to
the impact of education and how technology can be
used to provide services. (Bharucha, 2018) revealed
that a number of universities in India has employed
social media in pedagogy. They face the challenge of
how to harmonize it with the curriculum effectively.
Social media will continue to play an important role
in education sector.
322
Nurkhin, A., Fachrurrozie, ., Kardoyo, . and Widhiastuti, R.
Social Media as Economics Learning Media in Higher Education: An Empirical Study at Universitas Negeri Semarang.
DOI: 10.5220/0008411703220330
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation (ICLI 2018), pages 322-330
ISBN: 978-989-758-391-9
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

(Bharucha, 2018) stated that based on connectives
theory, social learning is related to the use of social
media technology. A learning theory that explains
how the internet has generated different and varied
opportunities to learn from the internet and from
others. Learners are given full scope to explore the
web and share what they find with networked
communities. (Ruleman, 2012) found that the faculty
member use social media for receiving RSS alerts
download music/videos, posting to a blog, social
book-marking, and online photo sharing. Facebook is
very familiar social media used by faculty member
and student. Skype is the second one.
Social media and web utilization in business and
economic learning is considered to be slow.
Technology-based learning is only used as a
supplementary of face-to-face learning or
conventional class. In many business schools, "face
to face" learning is considered to have more quality
than the on-line learning approach (Thomas and
Thomas, 2012). A blended learning approach can be
used for vocational learning. The key idea of blended
learning is to combine several learning approaches to
improve students' practical experience and as a result
it will increase their involvement (Poon, 2013). Social
media technology is part of the routine of modern
society in various ways. If students do not see value
in using virtual learning environments and learning
platforms, then the technology will be considered to
be obsolete (Garcia and Silva, 2017).
(Ford, Bowden and Beard, 2011) investigated two
social media (social bookmarking and micro
blogging) that can be used to encourage collaboration
and become very important in contemporary higher
education. A case study on the use of social media at
Bournemouth University shows how these two social
media have produced benefits. Social media is used
to improve academic excellence and encourage
efficiency in overcoming funding constraints and
demographic changes. (Garcia and Silva, 2017)
described that students consider the use of social
media to be more interesting and informative.
Students feel more comfortable when using social
media to undergo academic activities rather than
using the information system provided by the
university. The results of the study of (Bikanga Ada,
Stansfield and Baxter, 2017) determined the positive
attitude of educators and students in using mobile
devices and social media applications for learning and
teaching purposes. (Lim et al., 2014) also elaborated
that many students and instructors have begun to
explore and accept the use of SMT as a tool to engage
with their institutions and their colleagues for
teaching and learning purposes in Malaysia.
The use of social media in economics learning has
been proven through research. The results show that
the use of social media can improve the quality of
learning process and outcomes. (Stainbank and Gurr,
2016) found that time spent on the social media use
did not distract students to prepare accounting courses
in the first year. Students have a good perception of
the use of social media to provide career information.
However, it is not beneficial for teaching and learning
purposes. (Dwiharja, 2015) argued that accounting
learning can employ e-learning design. The
application that can be used is edmodo. Further
implications in Edmodo's use are in addition to
improving efficiency, as well as levelling the walls of
space and time constraints. (Erika, Yanto and Kasidi,
2018) found that there were significant differences in
learning outcomes of accounting lessons by using
social media Facebook. He provides
recommendations to teachers to be able to use social
media in learning process and provide materials and
tasks so that the students could have feedback more
immediately and make the learning process more
effective and efficient.
Based on the observations of researchers, the use
of social media is still not maximally done by young
lecturers and senior lecturers. Lecturers would rather
use traditional learning strategies (lectures and
discussions) than use information technology.
(Kardoyo et al., 2017) conducted a study dealing with
utilization of information and communication
technology (ICT) by the lecturer of Faculty of
Economics UNNES, and the results showed that there
is only little number of lecturers have employed ICT
in supporting the class. Several lecturers use blogs or
websites. Similarly, the use of e-learning is not
maximized. Other results indicate the use of
Facebook is quite intensive by lecturers. While
(Anissa et al., 2017) found EF UNNES lecturers
attempt to use Whatsapp to support classroom
learning, especially in Business English class. The
results show that there is a significant influence to
improve students' writing skill as well.
This paper tries to explore the practice of utilizing
social media for economics learning in universities,
especially in the Economic Education Study Program,
Faculty of Economics, Universitas Negeri Semarang.
It is expected to know how often and what sort of
social media used by lecturers and students.
Moreover, the researcher would like to explain the
form and types of social media used for economic
learning.
Social Media as Economics Learning Media in Higher Education: An Empirical Study at Universitas Negeri Semarang
323
1.1 Learning Strategy and Categories
of Social Media
Utilization of ICT in learning in Indonesia has a long
history. The initiative in organizing educational
television and radio broadcasts as an effort to
disseminate information to educational units that
spread across the archipelago is a manifestation of
awareness to optimize the employment of technology
in helping the learning process of the community. The
main weakness of both radio and television
broadcasting is the absence of instantaneous
interaction. Broadcast is unidirectional, from learning
resource or facilitator to the learner (Kustini and
Nurkhin, 2011). ICT-based learning is divided into
two groups, namely computer-based learning and
electronic-based learning. Computer-based learning
is learning that uses computers as a tool. Through this
type of learning, the teaching materials are presented
through computer media so that the teaching and
learning process becomes more interesting and
challenging for the students (Wena, 2009).
Some researchers use the term social media
technologies (SMTs) in order to describe the platform
more thoroughly, such as Facebook, web-based
applications, and others (Smith, 2017). The evolution
of applications and internet’s possibilities resulted in
the rising and in the improvements of technologies
that are more interactive and accessible. The variety
of social media platforms and the growth of its
popularity provide several possibilities in new forms
of this technology use (Garcia and Silva, 2017).
In general, social media technologies (SMTs) can
be grouped into seven categories: text-based, media
sharing, social networking, mobile-based
applications, virtual world and games, synchronous
communications and conferencing applications, and
mash-ups. All these platforms have different
functionalities and purposes to suit the needs of
students in this digital environment with the tools
giving students the ability to set up their own personal
learning communities within the Internet
environment which would allow them to stay
connected to the topic of their interest (Lim et al.,
2014). There are some categories of social media.
Table 1 shows the categories of social media
investigated according to (Valtonen et al., 2010).
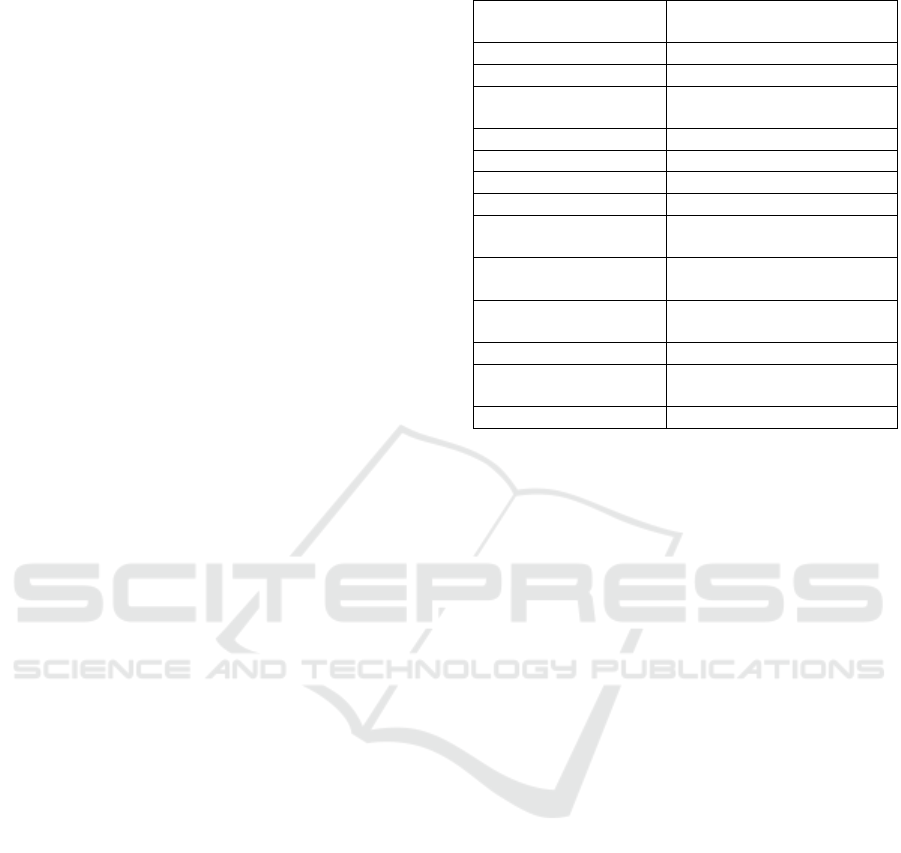
Table 1: Categories of social media investigated.
Categories of Social
Media
Social Media Technologies
Blogs
Blogger, WordPress
Wikis
Wikipedia, Wikimedia
Google Apps
Google Calendar, Google
Docs
Image sharing
Flickr, Instagram, Pinterest
Social bookmarking
Delicious
Social networking
Facebook, Google+
Social news sites
Reddit
VOIP & Instant
messaging
Skype, Google talk/chat
Do-it-yourself
networks
Ning
File sharing
Dropbox, Google Drive,
BitTorrent
Video sharing
YouTube, Vine
Location-based
applications
Foursquare, Google Maps
Microblogs
Twitter
Source; (Valtonen et al., 2010)
1.2 Social Media Utilization for
Economics Learning in Higher
Education
Utilization of social media for economics learning is
an implementation strategy of ICT-based learning,
especially electronic teaching (Kardoyo et al., 2017).
Lecturers can convey various types of materials and
other learning activities through interaction with
students by using social media. The reality shows that
students are the most active users in social media.
Lecturers must be able to take these opportunities as
well as challenges. Lecturers who are less able to play
a role in making use of information technology will
be increasingly left behind and will tend to be
uninteresting.
Utilization of mobile devices (smartphones &
tablets) in the field of learning continues to grow,
including in the higher education learning (Nurkhin,
Arief and Kardoyo, 2015). Students’ interaction with
smartphone is excessive. Many lecturers and
practitioners have been trying to develop the concept
of m-learning to take advantage of the interactive
features that exist on the smartphone. Through
mobile-based applications, students can learn and
complete the tasks from the lecturers concerned.
Through the applications, lecturers can provide
materials and practice questions and evaluation
features. (Mehdipour and Zerehkafi, 2013) explained
that mobile learning in classrooms often has students
working interdependently, in groups, or individually
to solve problems, to work on projects, to meet
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
324

individual needs, and to allow for student voice and
choice.
The next development is the utilization of social
media for learning. Social media tools give students
the ability to think critically and creatively (Tadros,
2011). SMTs enable the sharing of collaborative
activities not only in social life but also in educational
field and, now increasingly, in business contexts (Lim
et al., 2014). There is a significant relationship
between certain ways of making meaning and specific
social media use, giving the less perceptions and uses
of SMTs in learning. These findings provide for
SMTs outside of the formal curriculum (Smith,
2017).
(Lim et al., 2014) stated the successful adoption
of SMTs in HEIs will depend on many factors.
Students, academics and the institutions themselves
will all have views and practices that are not
necessarily align. Thus, innovative institutions need
to understand the critical success factors and the
barriers that restrict the implementation of SMTs
within the HEI to take advantage of the opportunities
offered by SMT’s in higher education. There are
various forms of social media utilization for learning
in college. Characteristics of social media for
undergraduate learning (Smith, 2017) are
collaborating to create documents online; sharing
information online; tracking and managing your
academic schedule; building relationships with peers;
posting / re-posting media or information found
online; creating media to share online; and
commenting on media or information found online.
2 METHOD
This research was regarded as quantitative
descriptive. This research would reveal the facts more
deeply about the practice of social media utilization
for accounting learning. The research was done
during even semester academic year 2016-2017 and
odd-even semester 2017-2018 in Economic
Education Study Program of Economics Faculty,
Universitas Negeri Semarang. Research respondents
were lecturers and students of Economic Education
Study Program.
The data collection techniques used was
interviews, questionnaires, and documentation.
Interviews and questionnaires were used to obtain
facts and perceptions of lecturers and students on the
practice of using social media for economics learning
and to expose opinions about the benefits and
constraints encountered. Questionnaire method was
used to discover the data quantitatively. The use of
social media was measured by using likert scale 5
points, ranging from very often - never, and strongly
agree - strongly disagree. Interview method was used
to confirm the respondent's answer in the
questionnaire. Documentation method was used to
observe social media that have been and are being
used by lecturers to support accounting class. Social
media observed were Facebook, Instagram,
YouTube, Twitter, and Whatsapp. The data obtained
were analysed by using descriptive analysis
technique.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Description of Respondent
(Lecturer)
Description of respondents (lecturers) in this study
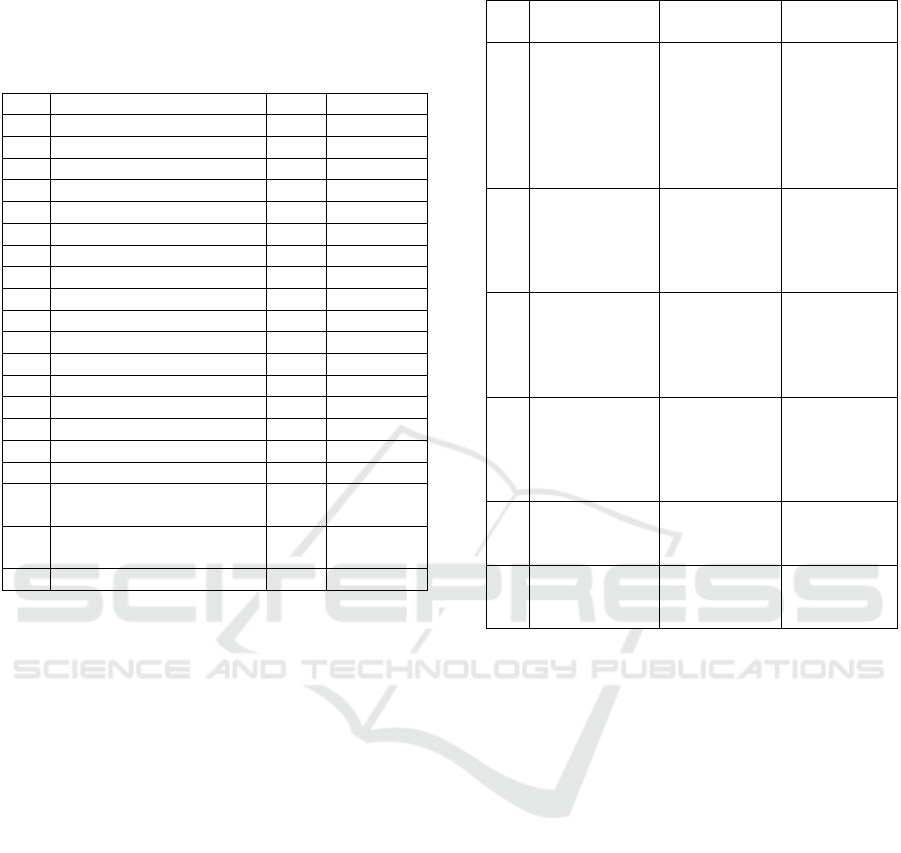
appears in Table 2. Description by gender, length of
teaching, and teaching subjects. Table 2 shows that
most respondents are woman (12 people or 57%). The
teaching duration of most lecturers is 6-10 years and
2-5 years, there are 6 people or 67%. The average
lecturer teaches the economics courses and the
education subjects (economics learning).
3.2 Utilization of Social Media for
Economics Learning
Table 3 shows the utilization of social media for
economics learning. Lecturer of Economic Education
Study Program in FE UNNES believes that social
media (Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, YouTube, and
what Sapp) can be used in economics learning in
universities. This is shown on the result score that
shows the number 4,00. Respondents' answers use a
scale of 1-5. However, not all lecturers are able to use
it.
Social media that is often accessed for economics
learning is What Sapp and YouTube. This appears at
the highest score of 4, 29 and 3, 90. Lecturers
frequently use YouTube for learning and using what
Sapp for discussion and communication. While
Twitter became a social media platform that is almost
never used for learning. The score is only 1, 29.
Lecturers quite often use Facebook and Instagram.
Scores obtained for Facebook utilization is 2, 95 and
Instagram of 2, 19. Lecturers access social media
accounts through smartphones and computers
(notebooks). YouTube is more frequently accessed
through the computer while learning in the classroom.
While other social media more accessed through
Social Media as Economics Learning Media in Higher Education: An Empirical Study at Universitas Negeri Semarang
325
smartphones. Whatsapp is instant messaging platform
that often used at anytime and anywhere. whatsapp is
easy to use and more accessible and interactive.
Table 2: Description of respondents (Lecturers).
No.
Description
Total
Percentage
1.
Gender
Woman
12
57%
Man
9
43%
Total
21
100%
2.
Teaching Experiences
Less than 2 years
0
0%
2 – 5 years
8
38%
6 – 10 years
8
38%
More than 10 years
5
24%
Total
21
100%
3.
Teaching Subject
Educational Subject
2
10%
Non-Educational Subjects
8
38%
Both
11
52%
Total
21
100%
4.
Concentration
Accounting Education
8
38%
Office Administration
Education
7
33%
Economic and
Cooperation Education
6
29%
Total
21
100%
Utilization of social media for learning include
tasks, discussions, quizzes, learning resources, and
playing YouTube videos can see in Table 4. Lecturers
used YouTube as learning resources and as
publications media of students’ work (see Figure 1).
Most lecturers use YouTube during classes in class.
YouTube presents many options, both as a source of
lecture material and for ice breaking in the classroom.
Instagram is also used for publication media of
students’ work and students’ task. Forms of YouTube
utilization can be seen in Figure 1. Instagram
utilization for learning can be seen in Figure 2. Based
on researcher observation, Facebook is not utilized
for learning for the last two semesters. Some lecturers
have taken advantage of Facebook but it has been
questionable for now. This is as highlighted by
(Ruleman, 2012; Kardoyo et al., 2017). Faculty
member and student would rather use whatsapp for
speedy communication. They can do anything like
sharing files, photos or videos. They argued that
whatsapp is a platform that is very easy to use, and it
can be used by using either smartphone or computer.
They found many features in whatsapp that are more
interactive and useful. Table 4 shows detail
description of utilization of social media for
economics learning.
Table 3: Utilization of social media for economics learning.
No
Statement
Respondent’s
answer
Explanation
social media
(Facebook,
Twitter,
Instagram, and
YouTube) can
be used for
learning
4,00
Very useable
having a
Facebook
account and
use it for
learning
2,95
Often utilize
having an
Instagram
account and
use it for
learning
2,19
Quite often
to take
advantage of
having a
Twitter
account and
use it for
learning
1,29
Almost
never take
advantage of
using
YouTube for
learning
3,90
Very often
utilize
using
Whatsapp for
learning
4,29
Very often
utilize
Table 5 also shows that lecturers found some
obstacles in using social media for learning. The
smoothness of the Internet network (access) becomes
a common problem, when they use YouTube as
learning media in the classroom. There is a lecturer
who considers the employment of social media is
very time consuming. It is because the lecturer will
open one by one student account when they are
sending assignments. Lecturers also assume that
interaction with students become meaningless when
using social media. Unfamiliar with social media is
also a constraint faced by lecturers.
Students’ response to social media use is analysed
in both good and positive categories. The students
believe that the use of social media is interesting and
fun. This is understandable because the students are
the largest users group. Students are accustomed to
social media. They are very active in using social
media than any other age group.
Based on the results of interviews with students,
Instagram is the most favourite platform used by
students. Although most students state that the reason
for using a social media is more likely to make
friends. Instagram is currently considered to be the
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
326
most attractive social media and presents more
interesting features. Beside the photo and video
uploading feature, there are also live features on
Instagram. These features become trend setter of
other social media. Instagram is also regarded as a
must-have account because there are many artists
who interact with their fans via Instagram.
Furthermore, numerous Instagram accounts used as
an online shop media and more attractive than
Facebook.
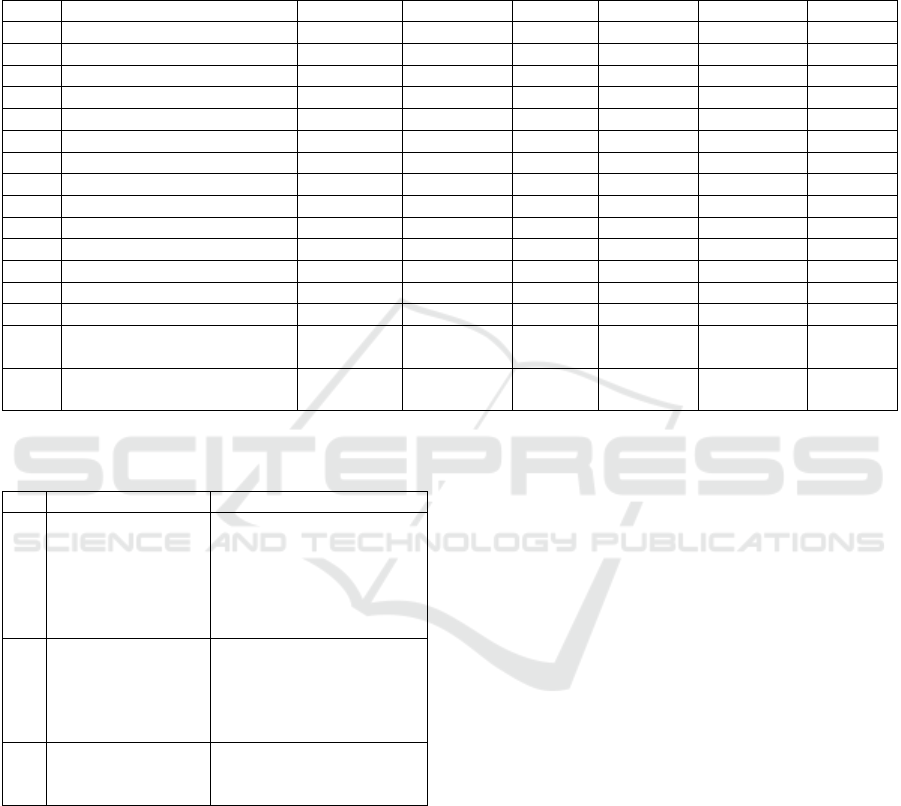
Table 4: Detail utilization of social media for economics learning.
No.
Description
Facebook
Instagram
Twitter
Youtube
Whatsapp
Overall
1.
Gender
Woman
3,11
2,22
1,11
3,78
4,00
2,84
Man
2,83
2,17
1,42
4,00
4,50
2,98
2.
Teaching Experiences
Less than 2 years
2 – 5 years
2,63
2,38
1,13
3,88
4,25
2,85
6 – 10 years
3,88
2,38
1,63
4,38
4,63
3,38
More than 10 years
2,00
1,60
1,00
3,20
3,80
2,32
3.
Teaching Subject
Educational Subject
3,00
2,00
1,00
5,00
5,00
3,20
Non-Educational Subjects
3,43
2,14
1,29
4,00
4,71
3,11
Both
2,67
2,25
1,33
3,67
3,92
2,77
4.
Concentration
Accounting Education
3,75
2,88
1,75
4,13
5,00
3,50
Office Administration
Education
1,86
1,43
1,00
3,71
3,86
2,37
Economic and Cooperation
Education
3,17
2,17
1,00
3,83
3,83
2,80
Table 5: Forms, obstacles, and student.
No
Statement
Respondent’s answer
1
Utilization form of
social media in
learning
Tasks, discussions,
quizzes, learning
resources, Playing
YouTube videos,
consultation
2
Obstacles faced in
the utilization of
social media in
learning
Less interaction, Internet
networking, time
consuming, unfamiliar
3
Student response to
the use of social
media for learning
Good and positive, very
interesting and fun, more
interactive
Other result shows that students also argue they
like to use whatsapp for interaction with lecture or
other students. Whatsapp can deliver message to
someone immediately and more simple. By using
whatsapp group, student can discuss anything or
deliver some information. The same finding is also
found by (Anissa et al., 2017).
Most of the students think that YouTube is
becoming the next and most interesting social media.
The video-based platform offers millions interesting
videos, for both lectures and other purposes.
Furthermore, only few students who have a YouTube
channel. This means that only several students upload
their work on YouTube. Students are only as users
and video viewers on YouTube.
Facebook's social media is becoming increasingly
unpopular among college students. Facebook is
considered unattractive, old-fashioned, and "the
past". Students no longer use Facebook for social
networking. They rarely open their accounts. They
think that Instagram is more fascinating although
actually sometimes Facebook has more interesting
features. This may be in accordance with the opinion
of researchers that Facebook is now more widely used
by adults. Young people do not like it. Social media
Twitter is not popular among college students. This is
the same as lecturers. The 160 characters (currently
expanded) social media platform is not interesting to
most students. Only a small number of students are
using Twitter.
Social Media as Economics Learning Media in Higher Education: An Empirical Study at Universitas Negeri Semarang
327
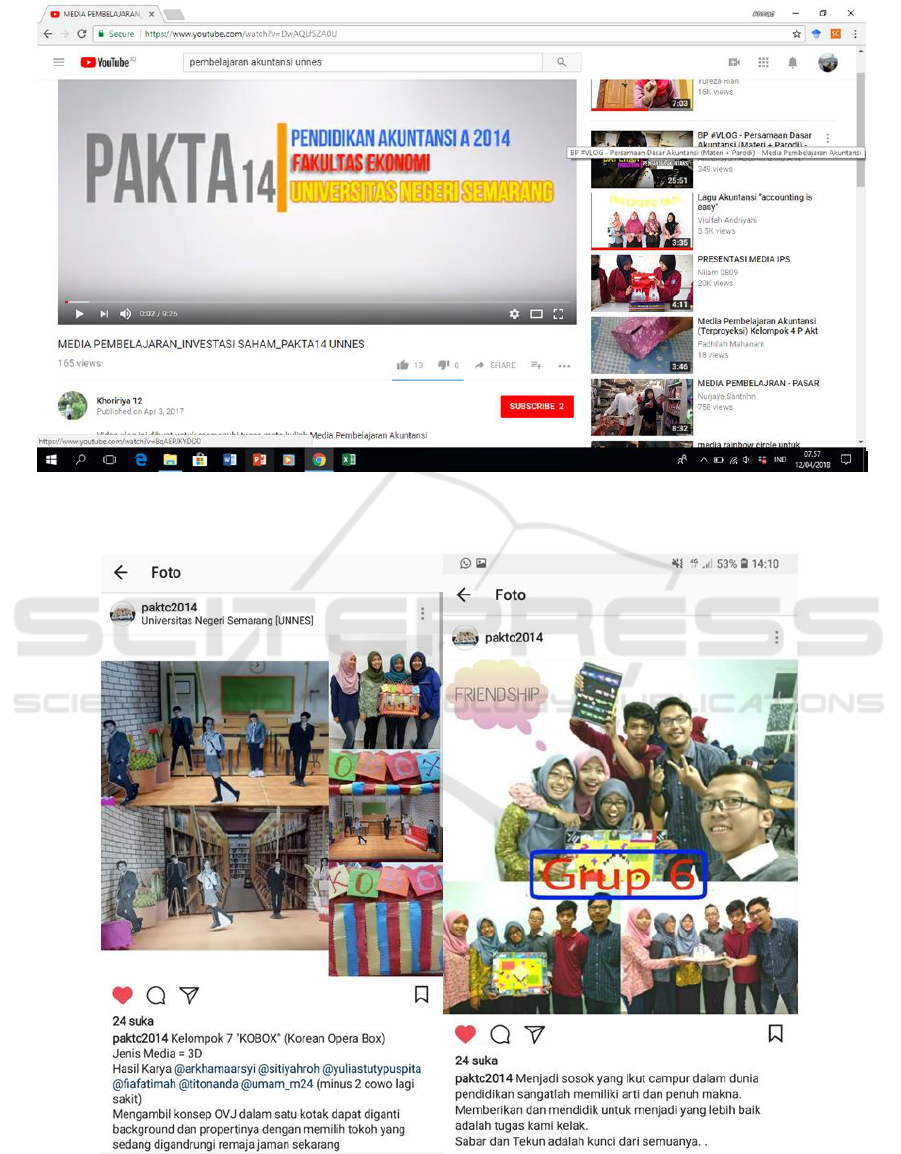
Figure 1: Utilization of YouTube for publication of student work.
Figure 2: Instagram utilization for publication of class assignments.
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
328

The results showed that some lecturers in
Economic Education Study Program of FE UNNES
have used social media for learning although have not
been optimal yet. YouTube and Instagram become
the most used platform. While Twitter become social
media that is almost never used. This condition is
nearly the same as that is experienced by students.
Lecturers are able to choose and use social media
based on access level by students. The survey also
shows that the age group of students becomes the
group that most often accesses social media than any
other group. (Garcia and Silva, 2017) pointed out that
student groups have been able to take the benefits of
using social media for their lectures.
Forms of social media utilization for learning are
still "limited". The results of this study are still in line
with the findings of (Thomas and Thomas, 2012).
Lecturers have not used social media greatly,
especially YouTube, Instagram and Facebook. The
interaction of lecturers and students is not so visible
on the results of students’ post. For example, after a
student uploads a video on YouTube, there is no
positive feedback from lecturers or other students.
Sometimes lecturers only like and share. Comments
given by lecturers will be able to provide positive
feedback for students. Especially by subscribing the
video, it will increase the spirit of students to learn
and do better in the future. Finally, the students just
fulfil the obligation of study.
The lecturer also does not have a YouTube
account or channel. The writer does not notice the
lecturer who has YouTube channel. Lecturers never
seem to upload something on YouTube. That is,
lecturers only rely on the willingness and ability of
students. Though the work of lecturers which is
uploaded will also affect the spirit and motivation of
students in producing more attractive work. Lecturers
should also be able to produce some interesting video
as a students’ source of learning and interaction
media.
The researchers also did not find intensive use of
Instagram for learning. Students only post pictures /
photos as a class assignment. For example, the task of
accounting learning media that utilizes images as a
medium of social service by providing words of
motivation or advice. There is no visible works of
lecturers in similar postings. This will cause the
students' negative perceptions of their lecturers.
Lecturers are deemed incapable of giving concrete
examples. They can only give instructions to the
students.
Inadequate utilization of social media due to the
ability of lecturers needs to improve. In fact there are
lecturers who are not accustomed to Instagram and
YouTube. The use of social media is still considered
to be time-consuming activity. Social media is an
opportunity as well as a challenge for lecturers to
develop lectures to be more attractive, open, fun and
meaningful. Students do not really care about the
enormous internet quota when accessing social
media. This is almost the same as found by
(Stainbank and Gurr, 2016) which states that social
media access time by students does not interfere the
time of study in regular classes.
4 CONCLUSION
The social media utilization for economics learning in
Economic Education Study Program of Economic
Faculty UNNES is categorized quite often. This
means that lecturers have not been able to maximize
the benefits of social media to support learning
activity in the classroom. Instagram and YouTube are
social media platforms that are often used by lecturers
and students. Whatsapp is instant messaging
application that is often used for discussion and
communication between lecturers and students. The
social media employment for learning conducted by
lecturers in Economic Education Study Program are
in the form of task, discussion, quiz, learning
resources, and playing YouTube videos. Lecturers
found some constraints in the social media
employment for learning such as the less interaction,
internet network, and time consuming, and
unfamiliar. The other result shows that the students
give positive responses. It is an opportunity as well as
a challenge for lecturers to develop further learning
strategies that use social media. Students consider
learning be more interesting and fun. Utilization of
other instant messaging platforms (telegram,
blackberry messenger, or Facebook messenger) can
be collaborated with the most popular social media
among students, namely Instagram. Lecturers can
also develop internet-based learning media through e-
learning or mobile learning.
REFERENCES
Anissa, R. N. et al. (2017) ‘What’s up with whatsapp? The
contribution of blended learning through wa group
discussion for better english writing in Indonesia’,
Advanced Science Letters, 23(8), pp. 7539–7544. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1166/asl.2017.9517.
Bharucha, J. (2018) ‘Exploring education-related use of
social media: business students perspectives in a
Social Media as Economics Learning Media in Higher Education: An Empirical Study at Universitas Negeri Semarang
329

changing India’, Education + Training, 60(2), pp. 198–
212. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/ET-07-2017-0105.
Bikanga Ada, M., Stansfield, M. and Baxter, G. (2017)
‘Using mobile learning and social media to enhance
learner feedback: Some empirical evidence’, Journal of
Applied Research in Higher Education, 9(1), pp. 70–
90. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/JARHE-07-2015-0060.
Bodle, R. (2011) ‘Social learning with social media:
Expanding and extending the communication studies
classroom’, In Teaching Arts and Science with the New
Social Media Cutting-edge Technologies in Higher
Education. Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 3, pp.
107–126. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/S2044-
9968(2011)0000003009.
Dwiharja, L. M. (2015) ‘Memanfaatkan Edmodo
Sebagaimedia Pembelajaran Akuntansi’, in In
Prosiding Seminar Nasional Pendidikan Ekonomi FE
UNY‘ Profesionalisme Pendidik dalam Dinamika
Kurikulum Pendidikan di Indonesia pada Era MEA’.
Yogyakarta: Fakultas Ekonomi UNY, pp. 332–344.
Erika, K., Yanto, T. and Kasidi, K. (2018) ‘Perbedaan Hasil
Belajar Pelajaran Akuntansi Dengan Menggunakan
Media Sosial dan Tidak Menggunakan Media Sosial’,
JurnalEcodunamika, 1(1), pp. 1–9. doi:
http://ejournal.uksw.edu/ecodunamika/article/view/15
16.
Ford, N., Bowden, M. and Beard, J. (2011) ‘Learning
together: using social media to foster collaboration in
higher education’, In Higher Education Administration
with Social Media: Including Applications in Student
Affairs, Enrollment Management, Alumni Relations,
and Career Centers Cutting-edge Technologies in
Higher Education, 2, pp. 105–126. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1108/S2044-
9968(2011)0000002009.
Garcia, L. S. and Silva, C. M. C. (2017) ‘Differences
between perceived usefulness of social media and
institutional channels by undergraduate students’,
Interactive Technology and Smart Education, 14(3), pp.
196–215. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/ITSE-01-2017-
0009.
Kardoyo, K. et al. (2017) ‘The Use of Information and
Communication Technology in Economics Teaching
and Learning’, International Journal of the Computer,
the Internet and Management, 25(1), pp. 29–32. doi:
http://www.ijcim.th.org/past_editions/2017V25N1/25n
1Page29.pdf.
Kustini, S. and Nurkhin, A. (2011) ‘Pemanfaatan Teknologi
Informasi Dan Komunikasi Dalam Pembelajaran
Akuntansi (Studi Empiris Pada Guru Smk Se Kota
Semarang).’, Dinamika Pendidikan, 6(1), pp. 84–104.
Lim, J. S. Y. et al. (2014) ‘The engagement of social media
technologies by undergraduate informatics students for
academic purpose in Malaysia’, Journal of Information,
Communication and Ethics in Society, 12(3), pp. 177–
194. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/JICES-03-2014-0016.
Mehdipour, Y. and Zerehkafi, H. (2013) ‘Mobile learning
for education: Benefits and challenges’, International
Journal of Computational Engineering Research, 3(6),
pp. 93–101.
Nurkhin, A., Arief, S. and Kardoyo, K. (2015) ‘The
Determinant Of Student’s Intention To Use Mobile
Learning’, PEOPLE: International Journal of Social
Sciences, 1(1), pp. 102–117.
Poon, J. (2013) ‘An examination of a blended learning
approach in the teaching of economics to property and
construction students’, Property Management, 3(1), pp.
39–54. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/EL-01-2017-0019.
Ruleman, A. B. (2012) ‘Social media at the university: A
demographic comparison.’, New Library World,
113(7–8), pp. 316–332. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1108/03074801211244940.
Smith, E. E. (2017) ‘Social media in undergraduate
learning : categories and characteristics’, International
Journal of Educational Technology in Higher
Education, 14(12), pp. 1–24. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-017-0049-y.
Stainbank, L. and Gurr, K. L. (2016) ‘The use of social
media platforms in a first year accounting course: An
exploratory study.’, Meditari Accountancy Research,
24(3), pp. 318–340. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1108/MEDAR-08-2015-0051.
Tadros, M. (2011) ‘A social media approach to higher
education’, In Educating Educators With Social Media
Cutting-edge Technologies in Higher Education, 1, pp.
83–105. doi: https://doi.org/10.1108/S2044-
9968(2011)0000001007.
Thomas, M. and Thomas, H. (2012) ‘Using new social
media and Web 2.0 technologies in business school
teaching and learning’, Journal of Management
Development, 31(4), pp. 358–367. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1108/02621711211219013.
Valtonen, T. et al. (2010) ‘Net generation at social
software: Challenging assumptions, clarifying
relationships and raising implications for learning’,
International Journal of Educational Research, 49(6),
pp. 210–219. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2011.03.001.
Wena, M. (2009) Strategi Pembelajaran Inovasif
Kontemporer Suatu Tinjauan Konseptual Operasional.
Cetakan ke. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
330
