
Correlation between Student Centered Learning (SCL) and Learning
Motivation of Nursing Student at Faculty of Nursing, University of
Jember
Retno Purwandari, Aulia Bella Marinda and Mulia Hakam
Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Jember, JL. Kalimantan No. 37 Kampus Tegal Boto, Jember, Indonesia
Keywords: Learning Model, Learning Motivation, SCL, Nursing Student.
Abstract: Learning motivation is affected by several factors, one of them is learning model known as Student Center
Learning (SCL). The purpose of this study was to determine the correlation between SCL and learning
motivation of nursing student at faculty of nursing University of Jember. This research was quantitative
study with cross-sectional method. The samples used were 252 students conducted by stratified random
sampling technique. The results showed that SCL had average score 76.71. In the other hand, learning
motivation of nursing students had average score 100,19. There was a correlation between Student-Centered
Learning and learning motivation on nursing students Faculty of Nursing, University of Jember based on
Pearson correlation test, but the correlation between the two variables were weak (p-value=0.001 ; α = 0.05 ;
r = 0.281). The motivation of students in faculty of nursing is not only influenced by SCL learning model,
but many factors influence the learning motivation. This study could be used for college student to self-
evaluation to improve their learning motivation to achieve maximum results.
1 BACKGROUND
Students are learners who study at university and
cannot be separated by learning activities and doing
task (Artyani, 2015) . Learning is a process of
behavioural change that occurs as a result of
experience, involving elements of the soul and body
that must be balanced to change (Sherwood, 2010).
The success of the learning process is influenced by
several factors that come from the student's personal
self, the lecturer's effort in providing and creating
the condition of teaching, and the environment
especially the adequate facilities and infrastructure
for the growth of teaching process (Sudjana, 2010).
The main factor in the learning process is
motivation (Sobur, 2009). Motivation to learn is
something that exists in everyone who know the
urge to learn (Hardini & Puspitasari, 2012).
Motivation refers to a person's desire to learn (Potter
& Perry, 2005). Learning motivation is also
influenced by the model and the learning method
applied by the college (Indriasari, 2016). One of the
learning model that has been applied is Student
Centered Learning (SCL). SCL learning model is a
learning model with a constructivism approach
where students are actively forming their own
knowledge (Trinova, 2013). SCL is a learning model
that should be used because it has several
advantages, student have big participation in
learning, have strong motivation to follow the
learning, growing atmosphere of democratic
discussion in learning, and increase knowledge for
teachers because something experienced and
delivered not previously known by the teacher
(Ramdhani, 2009).
Based on the research entitled The Relationship
Between Student Centered Learning (SCL)
Implementation With The Achievement of Student
Learning at PSIK STIKES Achmad Yani
Yogyakarta, 47 respondents (56,0%) from 84
respondents considered that the application of SCL
learning model in STIKES Achmad Yani
categorized well. The result of bivariate analysis
using Kendall Tau test is known p-value (0.897)>
0,05 means that there is no correlation between
applying student-centered learning model with
student achievement of PSIK STIKES Jenderal
Achmad Yani Yogyakarta. The results of the
coefficient correlation, the value is r = 0.016, it
324
Purwandari, R., Marinda, A. and Hakam, M.
Correlation between Student Centered Learning (SCL) and Learning Motivation of Nursing Student at Faculty of Nursing, University of Jember.
DOI: 10.5220/0008324703240328
In Proceedings of the 9th International Nursing Conference (INC 2018), pages 324-328
ISBN: 978-989-758-336-0
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
means that the relationship between them is very
weak (Hasan, 2011).
The fundamental difference between Student
Centered Learning (SCL) and Teacher Centered
Learning (TCL) can be seen from its orientation.
The orientation of the SCL model emphasizes that
learning activities in the students are oriented
towards learning (learning oriented). While TCL
learning model strategy is more oriented to content
(content-oriented). Therefore, in the SCL teaching is
no longer a process for transferring information from
teachers to learners, but as a facilitate the process of
learning in the classroom (Rasiban, 2013).
The preliminary study conducted at nursing
faculty of University of Jember obtained a
population of 723 students from the 2013 to 2016.
Interviews conducted on 20 students from second
and fourth-degree found that most of the students’
desire will increase to follow the lecture and listen if
the lecturer delivered material with interactive.
Interview conducted on 3 lecturers found that faculty
of nursing in general have used SCL learning model,
but there is still a combination between SCL model
with TCL (Teacher Centered Learning).
2 METHODS
This research is a quantitative research with cross-
sectional approach. The sample used is nursing
students of University of Jember which is still active
status from 2014, 2015, and 2016 level. The
sampling technique used is stratified random
sampling.
Data collection using questionnaire for assess
application of learning model based on SCL, and
learning motivation. Questionnaires were made
using Likert scale. Validity and reliability test result
showed r product moment = 0,3610 and the value of
Cronbach's Alpha was 0,912.
Research ethics are, usefulness, justice,
confidentiality, and anonymity. Utilization means
this research provides benefits for students or
lecturers to know the good or bad application of
SCL learning model, in addition to knowing how the
motivation to learn students in educational
institutions where doing research. The respondent's
approval sheet, given to the respondent before
conducting the research so that the respondent knew
the purpose of the research. Justice means
researchers treat respondents fairly well before,
during and after research. Confidentiality means the
researcher does not publish all respondent
information relating to research to public except for
research purposes. Anonymity means the researcher
ensures the identity of the respondent by not
specifying the respondent's full name.
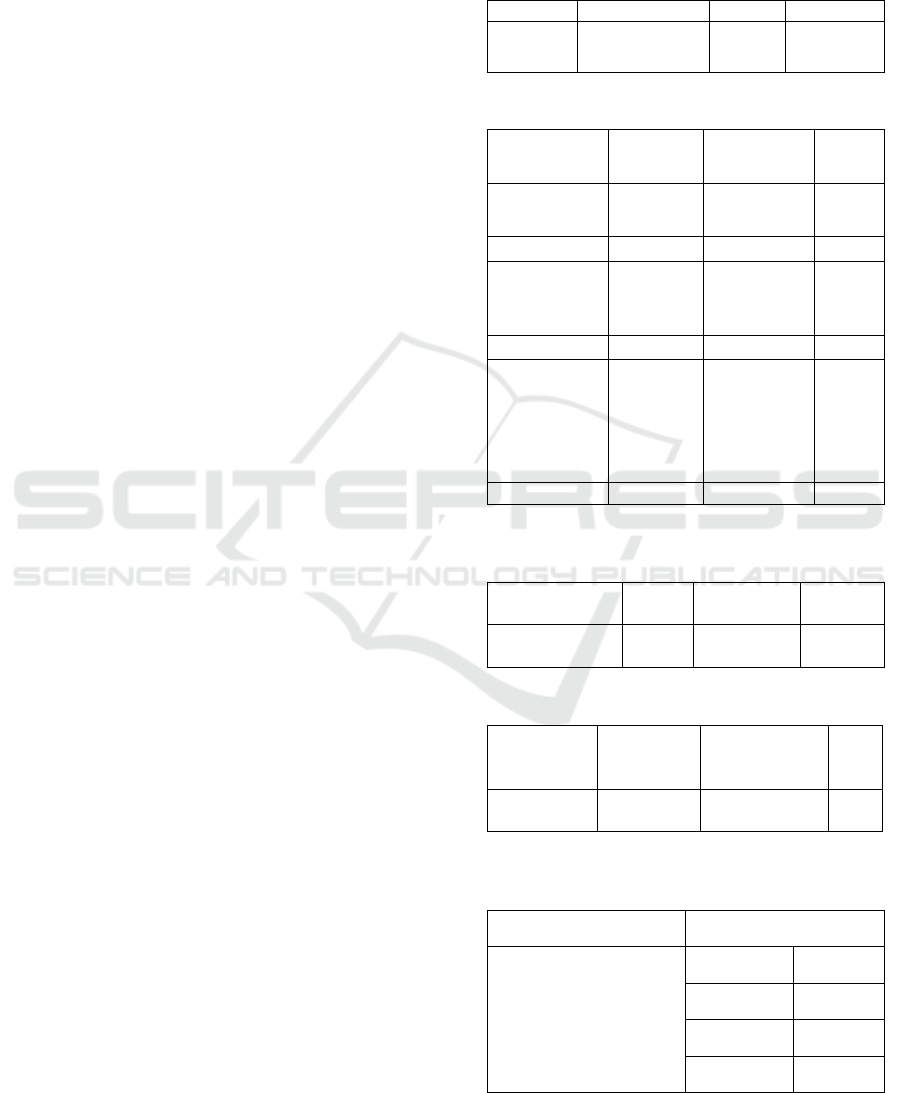
Table 1: The average of students age (n=252).
Age
Mean
SD
Min– Max
Age
(Year)
20,11
0,924
18 – 23
Table 2: Characteristic of students (n= 252).
Characteristic
Category
Frequency
(person)
%
Sex
Male
Female
54
198
21,4
78,6
Total
252
100
Degree
2014
2015
2016
46
106
100
18,3
42,1
39,7
Total
252
100
Religion
Islam
Kristen
Katolik
Hindu
Budha
247
4
0
1
0
98
1,6
0
0,4
0
Total
252
100
Table 3: The implementation of SCL in faculty of nursing
(n=252).
Variable
Mean
Standard
Deviation
Max
Implementation
of SCL
76,71
6,962
100
Table 4: The average of learning motivation (n=252).
Variable
Mean
Standard
Deviation
Max
Learning
motivation
100,19
9,317
135
Table 5: Correlation between SCL and learning motivation
(n=252).
Learning motivation
SCL
r
0,281
p-value
0,001
α
0,05
n
252
Correlation between Student Centered Learning (SCL) and Learning Motivation of Nursing Student at Faculty of Nursing, University of
Jember
325

Data collection was conducted in June to July
2017. The researcher gave google form link to each
respondents. Respondents who agreed to participate
in this study were asked to sign the consent. This
research was conducted after obtaining approval
from Faculty of Nursing (No: 2425/UN25.1.14/
LT/2017).
Univariate analysis was performed to describe
the respondent characteristic, application of learning
model based on SCL and learning motivation.
Before conducting bivariate analysis, Kolmogorov
Smirnov was used to test the normality of the data.
Based on the result of normality test, data were
analyzed by Spearman correlation test with
significance level of 0.05.
3 RESULTS
Table 1 reveals that the average age was 20.11 with
a standard deviation 0.924, the youngest age was 18
years old and 23 years old age.
Based on table 2, shows the distribution of
gender frequency result that of 252 students as much
as 54 (21.4%) students male, while female students
are as many as 198 (78.6%) students. The frequency
distribution of client characteristics based on degree
can be known by the year 2014 number 46 (18,3%)
student, 2015 number 106 (42,1%) student, and year
2016. Frequency distribution of respondent based on
religion can be known that most of student religion
is Islam 247 (98%), Christian 4 (1.6%), and Hindus
1 (0.4%).
Table 3 indicates that the application of SCL
model has mean 76,71 and standard deviation of
6,962. Table 4 shows the average value of learning
motivation was 100.19 and the standard deviation
9.317. Table 5 shows that Spearman rank correlation
test obtained a p-value of 0.001 and r-value of 0,281.
It can be concluded that Ha accepted and Ho
rejected so there is a relationship between the
implementation of SCL with student learning
motivation.
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 Implementation of SCL
The result of data analysis shows that the
implementation of SCL has reached 76,71% (from
maximum score of questionnaire score 100) with
average which is 76,71. Application of SCL
learning model, students are expected to be active as
independent participants in the learning process,
who are responsible and have the initiative to be able
to recognize their learning needs. Student-centred
learning process occurs when lecturers and students
are equally active in teaching and learning activities.
However, the lecturer retains an active role in the
teaching and learning process in the classroom, the
lecturer's role must actively assist students during
the process (Rudolfo, 2006). Lecturers are more of a
role as FEE (Facilitating, Empowering, and
Enabling) and guide on the sides than as mentors in
the centred (Hadi, 2007).
The lecturer as a facilitator, helps students access
information, organizes and transfers them to find
solutions the problems, as guides on the sides ie
lecturers as teachers who listen and direct the
discussion not only deliver material from the
beginning of learning until the end of the
deliberations, as well as designing a comfortable
learning strategy (Jogiyanto, 2009).
Student assessment on the role of lecturers in
faculty of nursing shows that the lecturers have been
acting as facilitators, motivators, giving inputs
during the teaching and learning process and
providing feedback on the results of the learning.
The material presented by the lecturers has also
achieved the target of learning. Lecturers in teaching
and learning process using media such as PPT,
handout, module, and provide structured tasks in
accordance with the competence to be achieved.
The role of nursing students in faculty of nursing
also influences the successful achievement of SCL
learning model. Learning process with SCL will be
successful if the role of lecturers and the role of
students running together in teaching and learning
activities. Students learn both individually and in
groups by digging information and knowledge
actively, besides the students are competent in
learning which means that students not only know
the contents of the course but also learn how to
know (Ramdhani, 2009). The application of SCL
can be appropriately applied in faculty of nursing ,
because the results same with previous research
(Kurdi, 2009). The results of questionnaires obtained
from the role of students and the role of lecturers,
students and lecturers already apply the role in the
model of learning based on SCL in Faculty of
Nursing, University of Jember.
4.2 Learning Motivation
The result of data analysis about nursing student
motivation in faculty of nursing got average score of
100,19, which shows that the motivation of nursing
student has reached 74.21% (from maximum score
of questionnaire score of 135). Motivation to learn is
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
326

the tendency of learners in learning activities that are
driven by the desire to achieve the best achievement
or learning outcomes (Hamdu & Agustina, 2011).
Motivation is divided into two types, intrinsic
motivation is the motivation that arises from person
in accordance with they needs, while extrinsic
motivation arise because of stimulation or
encouragement from outside or from others, such as
learning models provided by lecturers during the
learning process teaching (Sardiman, 2007).
Motivation to achieve optimal learning outcomes.
This is because each individual person has a desire
to get achievement and outperform the other
(Kristini & Mere, 2010).
Motivation to study at Faculty of nursing is
influenced by two factors which both have equal
value in determining motivation learn in influencing
motivation, that is intrinsic motivation and extrinsic
motivation. Students faculty of nursing have
maximal learning motivation if the result of learning
is as expected, beside that student struggle to face
difficulties in learning by asking to lecturer and
close friend. In addition, students also have
perseverance in learning, for example, students are
happy to follow and read the lecture materials.
However, with the many duties and submission of
boring material resulted in students less motivated
in teaching and learning process in college.
4.3 Correlation between
implementation of SCL and
Learning Motivation
The result of bivariate analysis showed that there
was a correlation between SCL with the motivation
of nursing student, Faculty of Nursing, University of
Jember. This result is similar to previous research
which showed that there was a significant
correlation between PBL learning method with
student learning motivation PSIK STIKES
Yogyakarta (Indriasari, 2016).
Motivation can be influenced by dynamic
elements in learning, is meant in the learning
instrument such as hardware and software
(Nursalam & Efendi, 2012) . Hardware is in the
form of teaching and learning tools, while software
such as curriculum, facilitator, and the methods or
models used while studying (Notoatmodjo, 2007).
Learning motivation can also be influenced by the
model and the learning method applied by the
educational institution where the student places the
education (Indriasari, 2016).
The coefficient correlation of SCL and student's
learning motivation has positive correlation , which
means the greater the value of the application of SC,
the greater value of learning motivation. Positive
perceptions formed by students on the learning
model will increase the student's motivation to
conduct learning activities, and will be active and
productive in the process of teaching and learning in
the classroom (Indriasari, 2016).
However, SCL has not been fully able to
improve student's learning motivation. Based on the
results of this study, the correlation strength between
application of SCL and learning motivation shows
weak correlation. This is in accordance with the
results of previous studies which indicate that there
is a significant relationship between PBL learning
model (Problem Based Learning) with learning
motivation of nursing students with weak correlation
strength. Motivation learning is not only influenced
by the learning model, but many factors that can
affect learning motivation (Indriasari, 2016).
There are several elements that influence the
motivation of learning, including the condition of
learners, the ability of learners, aspirations, teaching
strategies in educating learners, dynamic elements in
learning, and learning environment (Nursalam &
Efendi, 2012). There are aspects of input, process,
and output also affect student learning motivation
(Sardiman, 2007). Therefore, the motivation of
students in faculty of nursing is not only influenced
by SCL learning model, however, many factors
influence the motivation of learning, one of which is
intrinsic motivation where intrinsic motivation is
more effective in influencing one's learning
motivation.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Implementation of SCL in faculty of nursing has
average value 76,71. The motivation of nursing
students has an average score of 100.19. There is a
positive relationship with the weak correlation
strength between the application of SCL with the
motivation of nursing students in faculty of nursing.
Suggestions for educational institutions, can
upgrading SCL learning model that has been done as
well as academics can be more active role in
realizing SCL learning model in PSIK University of
Jember in order to realize optimal learning
objectives. Suggestions for further researchers that
researchers can carry out more in-depth research
related factors that affect learning motivation. The
next researcher can also do research with
experimental research design and also can use other
variable that can influence student's learning
motivation.
Correlation between Student Centered Learning (SCL) and Learning Motivation of Nursing Student at Faculty of Nursing, University of
Jember
327

REFERENCES
Artyani, M. (2015). Hubungan Antara Kepercayaan Diri
Dengan Prokrastinasi Akademik Pada Mahasiswa
Fakultas Psikologi Universitas Muhammadiyah
Surakarta. UMS. Retrieved from
http://eprints.ums.ac.id/38761/1/02.NASKAH
PUBLIKASI.pdf
Hadi, R. (2007). Dari Teacher-Centered Learning Ke
Student-Centered Learning, Perubahan Metode
Pembelajaran Di Perguruan Tinggi. JURNAL
PEMIKIRAN ALTERNATIF PENDIDIKAN, Vol. 12
No, 408–419.
Hamdu, G., & Agustina, L. (2011). PENGARUH
MOTIVASI BELAJAR SISWA TERHADAP
PESTASI BELAJAR IPA DI SEKOLAH DASAR.
Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan, Vol. 12 No.
https://doi.org/ISSN 1412-565X
Hardini, I., & Puspitasari, D. (2012). Strategi
Pembelajaran Terpadu. Yogyakarta: Familia.
Hasan, B. (2011). Hubungan Penerapan Model
Pembelajaran Student Centered Learning (SCL)
Dengan Prestasi Belajar Mahasiswa PSIK STIKES
Jenderal Achmad Yani Yogyakarta. STIKES Jenderal
Achmad Yani Yogyakarta. Retrieved from
http://repository.stikesayaniyk.ac.id/387/
Indriasari, F. . (2016). Hubungan Antara Penerapan Model
Pembelajaran Problem Based Learning Dengan
Motivasi Belajar Mahasiswa Program Studi Ilmu
Keperawatan. Jurnal Keperawatan Notokusumo, Vol 4
No 1. https://doi.org/issn: 2338-4514
Jogiyanto. (2009). Filosofi, Pendekatan, dan Penerapan
Pembelajaran Metode Kasus Untuk Dosen dan
Mahasiswa. Yogyakarta: CV. ANDI OFFSET.
Kristini, R., & Mere, F. (2010). ubungan Antara Motivasi
Belajar Dengan Prestasi Akademik Pada Mahasiswa
Prodi Keperawatan S1 Program A Angkatan I STIKES
RS. Baptis Kediri. Jurnal Penelitian Stikes RS Baptis
Kediri, Vol 3, No. https://doi.org/ISSN : 2085-0921
Kurdi, F. (2009). Penerapan Student-Centered Learning
Dari Teacher-Centered Learning Mata Ajar Ilmu
Kesehatan Pada Program Studi Penjaskes. Forum
Pendidikan, Volume 28, 108–113. Retrieved from
http://forumkependidikan.unsri.ac.id/userfiles/Artikel
Fauziah Nuraini Kurdi-UNSRI.pdf
Notoatmodjo, S. (2007). Promosi kesehatan dan ilmu
perilaku. Jakarta: Rineka CIpta.
Nursalam, & Efendi, F. (2012). Pendidikan Dalam
Keperawatan. Jakarta: Salemba Medika.
Potter, P. ., & Perry, A. . (2005). Fundamentals of
nursing: concepts, process, and practice. 4th ed.
Jakarta: EGC.
Ramdhani, N. (2009). Ruh experiential learning dalam
SCL. UGM. Retrieved from
http://neila.staff.ugm.ac.id/?pilih=lihat&id
Rasiban, L. (2013). Penerapan Student Centered Learning
(SCL) Melalui Metode Mnemonik Dengan Teknik
Asosiasi Pada Mata Kuliah Kanji Dasar. Jurnal
Penedidikan Bahasa Dan Sastra, Vol 13, No.
https://doi.org/e-ISSN 2527-8312
Rudolfo, S. (2006). Education for a multicultural world, in
jasque delors, learning: the treasure within. Retrieved
from http://unesdoc.unesco.org
Sardiman. (2007). Interaksi dan Motivasi Belajar
Mengaja. Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada.
Sherwood, L. (2010). Human physiology: from cells to
systems (7 ed). USA: Brooks/cole.
Sobur, A. (2009). Psikologi umum. Bandung: Pustaka
Setia.
Sudjana, D. (2010). Strategi belajar mengajar. Jakarta:
Rineka CIpta.
Trinova, Z. (2013). Pembelajaran berbasis student
centered learning pada materi pendidikan agama
islam. Al-Ta’lim Journal, Vol 20, No. Retrieved from
https://journal.tarbiyahiainib.ac.id/index.php/attalim/ar
ticle/download/28/36
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
328
