
Topical Simvastatin as Treatment of Digital Ulcer in Systemic
Scleroderma
Tuntas Rayinda, Ika Rizki, Yohanes Widodo Wirohadidjojo
Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Gadjah Mada / RSUP Dr. Sardjito,
Yogyakarta Indonesia
Keywords: systemic scleroderma, digital ulcer, statin, topical simvastatin.
Abstract: Systemic Scleroderma (SS) is a connective tissue disease characterized by extensive fibrosis, vascular
damage, immunologic disorder, and organ involvement.
1
digital ulcer (DU) is a common clinical condition
in SS which occurred in 30% of the patients. Simvastatin, a HMG-CoA reductase competitive inhibitor, is
known to have anti-inflammatory potency and could accelerate the healing of chronic wound. We report a
case of UD in SS that improved with topical simvastatin treatment. A 61 years old woman came to the
clinic with a complaint of wounds on the tip of fingers and toes that has not healed for two weeks. The
wound initially appeared at the tip of finger, extended, and then similar wound appeared at the tip of toe.
The patient was diagnosed with systemic scleroderma since three years ago and treated with
methylprednisolone and a vasodilator agent. From physical examination, there were shallow ulcers at the
right middle toe and left thumb sized 1x1-2 cm, with irregular border and covered with necrotic tissues. DU
management in SS consisted of non-pharmacological, pharmacological, and operative methods.
Simvastatin, a statin class drug, was proven to have anti-inflammatory, immune modulatory, and wound
healing effects in several studies. The benefit of statin in wound healing process was shown by its ability to
improve vascularization in chronic wound through increased VEGF concentration which is disturbed in
abnormal wound healing process. Topical simvastatin was also proven to have antimicrobial effect which
could potentially prevent bacteria from disrupting epithelialization and wound healing process. The patient
was given normal saline compression twice daily followed by application of 0.5% simvastatin in
gentamicin ointment twice daily after saline compression. After two weeks of treatment, the ulcers on both
fingers and toes improved.
1 INTRODUCTION
Systemic scleroderma (SS) is a rare connective
tissue disorder characterized by extensive fibrosis,
vascular damage, immunologic disorder, and various
organ involvement (Barsotti et al., 2016). Two of the
most common clinical symptoms in SS are Raynaud
phenomenon (RP) and digital ulcer (DU). Digital
ulcer is defined as ischemic tissue that undergo
denudation with clear margin, loss of epidermis and
dermis, and found on the fingertips. The ulcer could
be found above bone protrusion such as proximal
phalanx, but it could also occur due to secondary
causes such as trauma. The ulcer is often very
painful and disturb hand function (Abraham, 2015;
Marvi and Chung, 2010).
Digital ulcer occurred in 30% of SS patient. In
addition, 66% of DU patients experienced more than
one episode of recurrence albeit utilization of
vasodilator (Steen et al., 2009). In March 2016-April
2017, there were 17 SS patients on maintenance
therapy in the Dermatology and Venereal Disease
Clinic of Dr. Sardjito Hospital, Yogyakarta. Four
(23.5%) of the SS patients also had DU.
Simvastatin, a plasma cholesterol lowering drug,
is a competitive inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase
and is known to have anti-inflammatory potency and
could accelerate chronic wound healing
(Stojadinovic et al., 2014). Topical simvastatin had
been reported to have efficacy in healing chronic
venous ulcer and diabetic ulcer (Asai et al., 2012;
Raposio et al., 2016).
This manuscript will report a case of DU in SS
that improved after treatment with topical
simvastatin. The discussion will focus on
simvastatin’s mechanism of action in chronic wound
Rayinda, T., Rizki, I. and Wirohadidjojo, Y.
Topical Simvastatin as Treatment of Digital Ulcer in Systemic Scleroderma.
DOI: 10.5220/0008159804650468
In Proceedings of the 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology (RCD 2018), pages 465-468
ISBN: 978-989-758-494-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
465
healing. The purpose of this manuscript is to
understand simvastatin’s mechanism of action as an
effective drug in the management of chronic ulcer in
SS patients.
2 CASE
A 61 years old woman came with the complaint of
wounds on the tips of fingers and toes that has not
healed for two weeks. The wound initially appeared
at the tip of finger, extended, and similar wound also
appeared at the tip of toe. The wound was widened
after being hit by shower handle. The wound was
painful and occasionally wet. The wound had been
treated with normal saline compression and fusidic
acid but there was no improvement.
In the past five years, the patient started to
complain stiffness in the skin and joints all over her
body. Three years later, the patient went to Dr.
Sardjito Hospital and was diagnosed with SS based
from clinical, laboratory, and histopathological
examination. The patient was treated with
maintenance therapy of methylprednisolone 8 mg/2
days, pentoxifylline 400 mg/day, nifedipine 10
mg/day, aspilet 80 mg/day, and emollient.
The patient’s general appearance and vital
signs were within normal limit. In dermatological
examination, there were dry skin with sclerotic
impression in the whole body and salt and pepper
appearance in several skin areas of the body. There
was fish mouth appearance on the face. The fingers
and toes appeared sclerotic and there were shallow
ulcers sized 1x1-2 cm, covered with necrotic tissue,
and irregular border on the right middle toe and left
thumb.
The working diagnosis of DU in SS was
confirmed by clinical examination. DU was treated
with normal saline compression twice daily,
followed by application of 0.5% simvastatin in
gentamycin ointment twice daily after saline
compression. After two weeks of treatment, there
was an improvement in both finger and toe ulcers
.
3 DISCUSSION
Fibroproliferative and microvascular endothelial cell
vasculopathy is one of the primary process in the
pathophysiology of SS. Those vascular abnormality
and dysfunction caused RP, DU, and capillary
abnormality on nail fold which are early
manifestation and key diagnosis of SS
(Postlethwaite, 2015). The change in nail fold
capillaroscopy proved that there is a severe
angiogenesis disturbance in SS patients. The loss of
blood capillary also occurs at end stage of the
disease. However, before end stage of the disease
occur, various levels of angiogenesis disturbance
manifest as various morphological changes of blood
vessels. The change in angiogenesis process will
contribute to chronic oxygen supply reduction and
ischemic tissue manifestation such as ulcers at
fingertips (Distler et al., 2002).
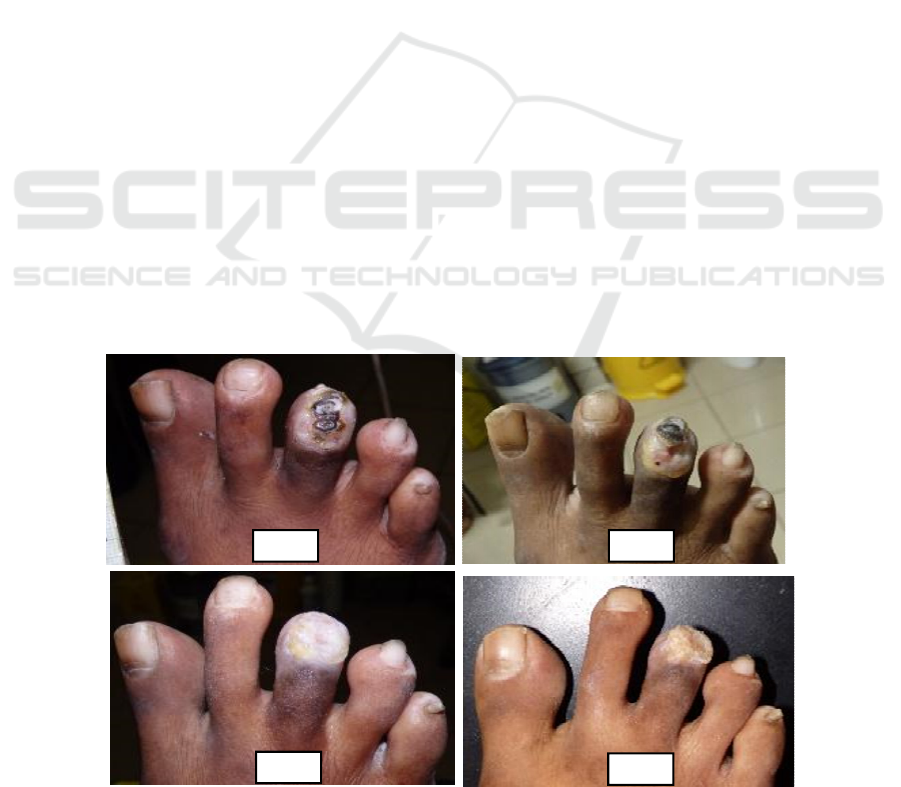
Figure 1: A). Before treatment (B). 1 week (C). 2
weeks (D). 3 weeks after application of topical simvastatin.
A B
C
D
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
466

Management of DU in SS consisted of
nonpharmacological, pharmacological, and operative
therapies. Although there are several treatment
modalities that could be used, there is no strong
evidence because of the difficulties in conducting
clinical trial (Abraham, 2015). Administration of
oral statin therapy for DU in SS patient had shown
satisfying result (A et al., 2008). In this case, we
used topical statin in ointment base for treating DU
in SS patient.
Simvastatin is one of statin class drug which is
often usedto treat hypercholesterolemia. In addition,
statin is known to have immunomodulatory,
neurotropic, and wound healing effect. Its pleotropic
effect, safety profile, and low cost made this drug a
promising alternative in SS patient. A study by
Abou-Raya et al. showed a decrease in DU number,
its degree of severity, and pain score in SS patient
who were treated with systemic statin (A et al.,
2008).
Statins are known to have anti-inflammatory
effect through several mechanisms in the
inflammatory pathway. Through inhibition of HMG-
CoA reductase in mevalonate pathway, statin would
decrease synthesis of mevalonate which then
decrease bioavailability of two important isoprenoid
intermediates, namely farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP)
and geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP) (Laufs and
Liao, 2009). With low bioavailability of the two
molecules, statin would increase vascular reactivity,
coagulation, and affect inflammatory pathway.
Important anti-inflammatory effects of statin are
decreased C-reactive protein, chemokine, adhesion
molecule, and cytokine release and to modulation of
T cell activity. Additionally, statin also act as
immunomodulator and antioxidant which protect
endothelial function by decreasing eNOS, monocyte
tissue factor, and PAI-1 expression. Statin could also
stimulate the activation of heme oxygenase and
tissue plasminogen activator (Laufs & Liao, 2009;
Vukelic et al., 2010).
In wound healing process, statin also regulate
FPP. Farnesyl pyrophosphate is known to inhibit
wound healing and epithelialization process through
glucocorticoid receptor. In vitro, decreased
endogenous FPP was proved to stimulate migration
of keratinocytes. In addition, decreased FPP, which
is glucocorticoid receptor agonist and could repress
keratin 6, was proved to stimulate epithelialization
and wound closure in Human Skin Organ Culture
Wound Model and Histology ex vivo. Through
similar mechanism, application of topical mevastatin
was proved to stimulated epithelialization ex vivo.
Therefore, decreased FPP in epidermis that was
treated with statin would be beneficial for
epithelialization process during wound healing
(Vukelic et al., 20100.
The benefit of statin in wound healing is also
shown by its ability to improve chronic wound
vascularization. Statin could reduce vasoconstriction
by decreasing angiotensin-2 response and decreasing
the concentration of preproendothelin-1 mRNA
which would decrease synthesis of endothelin-1, a
strong vasoconstrictor ( Hernandez-perera et al.,,
1998; Vukelic et al., 2010). Statin also stimulated
vascular relaxation through inhibition of Rho
geranyl-granylation which would increase the
expression of endothelial nitrite oxide synthase
(eNOS). In addition, statin could stimulate
neovascularization in ischemic tissues by increasing
the activity of endothelial progenitor cells in chronic
wound. Statin administration could also increase
VEGF concentration which was disturbed in
abnormal wound healing process. However, statin’s
effect on VEGF depends on dose and length of
administration. In high dose and long administration,
statin did not increase VEGF concentration. Statin’s
ability in improving angiogenesis became the basis
for its utilization to treat DU in SS patient as in this
case study (Hernandez-perera et al., 1998; Weis et
al., 2002; A A-R, et al., 2008; Laugs & Liao, 2009;
Vukelic et al., 2010).
Besides several abilities described above, topical
simvastatin was proved to possess antimicrobial
effect on wound. Bacteria play a role in slowing
wound healing process; hence, decreased bacteria
concentration in the wound could accelerate
epithelialization and wound healing process. Open
wounds in rats that were treated using topical
simvastatin did not show the presence of
polymicrobial infection as occurred in the group that
were not treated with simvastatin (Weis et al., 2002).
Utilization of topical simvastatin were reported
in several clinical trials in experimental animals or
human. A study on experimental animals by Asai et
al. found that statin could accelerate wound healing
process in rats with diabetes model through
angiogenesis and limphangiogenesis acceleration.
Raposio et al. reported the effect of simvastatin on
patients with chronic vascular ulcer. In the study, the
group treated with 0.5% topical simvastatin in cream
base showed faster wound healing compared to
control group, although the difference was not
statistically significant. Until now, there was no
report on utilization of topical simvastatin for
treatment of DU in SS (Weis et al., 2002;
Khoshneviszadeh et al., 2014).
Topical Simvastatin as Treatment of Digital Ulcer in Systemic Scleroderma
467

2% simvastatin gel was proved to accelerate
wound healing in experimental animal through its
anti-inflammatory effect and its influence on
granulation tissue formation and reepithelialization.
Those stereologic results from experimental animals
studies showed that simvastatin gel could increase
the number of fibroblasts, collagen, and blood
vessels formation which are important in wound
healing process (Khoshneviszadeh et al., 2014).
In this case, DU in SS showed improvement in
lesion morphology and pain scale after
administration of 0.5% topical simvastatin in
gentamicin ointment base. Until now, there is no
case report or research on topical simvastatin to treat
DU in SS. Its effect on wound healing, safety
profile, and low cost could make topical simvastatin
an alternative topical therapy for DU in SS.
4 CONCLUSION
We reported a case of DU in SS that improved after
application of topical simvastatin. Beside its anti-
inflammatory potential, simvastatin could accelerate
chronic ulcer healing through decrease in farnesyl
pyrophosphate, facilitation of vascular relaxation,
acceleration of neovascularization, and decreased
bacteria concentration. Topical simvastatin could be
used as an alternative topical pharmacological
therapy for DU in SS.
REFERENCES
A, A.-R., Abou-Raya, S., Helmii, A., 2008. Statins:
potentially useful in therapy of systemic sclerosis-
related Raynaud’s phenomenon and digital ulcers. J
Rheumatol 9, 1801–1808.
Abraham, S., 2015. Optimal management of digital ulcers
in systemic sclerosis. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 11,
939–947.
Asai, J., Takenaka, H., Hirakawa, S., 2012. Topical
Simvastatin Accelerates Wound Healing in Diabetes
by Enhancing Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis.
Am. J. Pathol. 181, 2217–2224.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.08.023
Barsotti, S., Stagnaro, C., Ascanio, A., Rossa, A. Della,
2016. Review One year in review 2016 : systemic
sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1, 3–13.
Distler, O., Rosso, A., Giacomelli, R., Cipriani, P.,
Conforti, M.L., Guiducci, S., Gay, R.E., Michel, B.A.,
Brühlmann, P., Müller-ladner, U., Gay, S., Matucci-
cerinic, M., 2002. Angiogenic and angiostatic factors
in systemic sclerosis : increased levels of vascular
endothelial growth factor are a feature of the earliest
disease stages and are associated with the absence of
fingertip ulcers. Arthritis Res. 10, 1–10.
https://doi.org/10.1186/ar596
Hernández-Perera, O., Pérez-Sala, D., Navarro-Antolín, J.,
Sánchez-Pascuala, R., Hernández, G., Díaz, C.,
Lamas, S., 1998. Effects of the 3-hydroxy-3-
methylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors, atorvastatin
and simvastatin, on the expression of endothelin-1 and
endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular
endothelial cells. Journal of Clinical Investigation 101,
2711–2719. doi:10.1172/JCI1500
Khoshneviszadeh, M., Ashkani-Esfahani, S., Namazi,
M.R., Noorafshan, A., Geramizadeh, B., Miri, R.,
2014. Topical simvastatin enhances tissue
regeneration in full-thickness skin wounds in rat
models. Iranian journal of pharmaceutical research :
IJPR 13, 263–269.
Laufs, U., Liao, J., 2009. Isoprenoid Metabolism and the
Pleiotropic Effects of Statins. Curr Atheroscler Rep 5,
372–378.
Marvi, U., Chung, L., 2010. Review Article Digital
Ischemic Loss in Systemic Sclerosis. Int. J.
Rheumatol. 2010, 1–7.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/130717
Postlethwaite, A.E., 2015. Pathogenesis of systemic
sclerosis. Frointiers Immunol. 6, 1–40.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00272
Raposio, E., Libondi, G., Grignaffini, E., Grieco, M.P.,
2016. Effects of Topic Simvastatin for the Treatment
of Chronic Vascular Cutaneous Ulcers : A Pilot Study.
J. Am. Coll. Clin. Wound Spec. 7, 13–18.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jccw.2016.06.001
Steen, V., Denton, C.P., Pope, J.E., 2009. Digital ulcers :
overt vascular disease in systemic sclerosis.
Rheumatology 8, iii19-iii24.
https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kep105
Stojadinovic, O., Lebrun, E., Pastar, I., Kirsner, R., Davis,
S.C., 2014. Statins as Potential Therapeutic Agents for
Healing Disorders. Expert Rev Dermatol 6, 1–18.
Vukelic, S., Stojadinovic, O., Pastar, I., Vouthounis, C.,
Krzyzanowska, A., Das, S., Samuels, H.H., Tomic-
Canic, M., 2010. Farnesyl pyrophosphate inhibits
epithelialization and wound healing through the
glucocorticoid receptor. Journal of Biological
Chemistry 285, 1980–1988.
doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.016741
Weis, M., Heeschen, C., Glassford, A.J., Cooke, J.P.,
2002. Statins have biphasic effects on angiogenesis.
Circulation 105, 739–745. doi:10.1161/hc0602.103393
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
468
