
Relationship between the Application of Good Islamic Business
Governance and Voluntary Disclosure on Islamic Bank in Indonesia
Moh Arifin
1
, Imron Mawardi
2
, Muhammad Nafik Hadi Ryandono
2
, Sri Iswati
3
, Bahrina Almas
3
1
Islamic Economic Science, Postgraduate School, Airlangga University, Campus B. Jl. Airlangga No.4-6 Surabaya,
Indonesia
2
Departement of Islamic Economic, Faculty of Economics and Business, Airlangga University, Campus B. Jl. Airlangga
No.4 Surabaya, Indonesia
3
Postgraduate School of Universitas Airlangga, Campus B. Jl. Airlangga No.4-6 Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Islamic Bank, Good Islamic Business Governance, voluntary disclosure.
Abstract: The development of Islamic bank assets has a relatively significant growth, so that Indonesian banks create
good Islamic business governance as a benchmark for Islamic banking governance in accordance with
Islamic principles. The position of assets is reaching IDR 429.39 trillion with financing level at IDR 289.99
trillion. This has been a concern for Islamic banking not only to pursue profit but to fight for the welfare of
customers and shareholders. The purpose of this study is to obtain empirical evidence on the reciprocal
relationship between good Islamic business governance and voluntary disclosure at 7 Islamic banks in
Indonesia in the period of 2011-2017. The research methodology used is quantitative descriptive with
voluntary disclosure as dependent variable and good Islamic business governance as an independent
variable. The results show that voluntary disclosure has a positive relationship with good Islamic business
governance. The two variables will be co-integrated in the long run, which is indicated by trace statistic >
critical value of 5%. So in the long run the variables will affect each other. The maximum voluntary
disclosure is applied then the implementation of Good Islamic Business Governance will be better, so the
customer confidence will increase and the growth of Islamic bank will be more optimal.
1 INTRODUCTION
Publicly disclosing information about the company
is a form of transparency and accountability to
stakeholders. Barako, et. al, (2006) said that
companies can use financial statements to convey
company information in a qualitative and
quantitative way. According to Yuniasih, et. al,
(2012) the form and extent of information disclosure
is strongly influenced by corporate governance.
Meilani (2016), note that one of the information
disclosures provided to stakeholders is the voluntary
disclosure used by management to increase the
company's credibility. Thus, good governance can
be achieved and company performance can be
improved when transparency and disclosure quality
are highly achieved.
Bank Indonesia (2009) states that to encourage
the management of Islamic banks in Indonesia
should refer to the principles of good Islamic
business governance. So, Bank Indonesia (2009)
issued regulation no. 11/33/PBI/2009 dated
December 7
th
, 2009 regarding good Islamic business
governance and Circular Letter no. 12/13/DPbS
dated 30 April 2010 regarding the implementation of
good Islamic business governance for Islamic
commercial banks and Islamic business units.
Good corporate governance involves a set of
relationships between a company's management as
such its board, its shareholders and other
stakeholders. According to Jumansyah and Syafe'i
(2013), good corporate governance cannot be
applied entirely to Islamic business entity mainly
Islamic banking, because governance of Islamic
bank must conform with Islam.
Along with the increasing awareness of the
increasing application of Islamic values in life and
business, Bank Indonesia declared the
Arifin, M., Mawardi, I., Ryandono, M., Iswati, S. and Almas, B.
RelationshipÂ
˘
a between the Application of Good Islamic Business Governance and Voluntary Disclosure on Islamic Bank in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0007538901370141
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School (ICPS 2018), pages 137-141
ISBN: 978-989-758-348-3
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
137

implementation of good Islamic business
governance. According to Shahul (2001) that Islamic
bank as a business institution that runs based on
Islamic principles should not be directed to generate
maximum profit. According to statistical data of
Islamic bank (Financial Services Authority, 2018),
the position of Islamic bank assets reached IDR
429.36 trillion and financing value is still moving at
double-digit level of IDR 289.99 trillion. Growth is
inseparable from good governance to maintain
welfare and security for customers and shareholders.
This study can obtain empirical evidence of the
mutual relationship between good Islamic business
governance and voluntary disclosure in the annual
report of Islamic bank in Indonesia period 2011-
2017 using ganger causality.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Governance is a new form of new public
management regulation. Corporate governance is the
alignment between the interests of corporate
management with other stakeholders and integrates
the goals between management and owners,
incentives, monitoring and control (Nofianti and
Ardi, 2014). Voluntary disclosure is a phrase that the
company provides outside the applicable provisions.
Lys, et. al, (2015) said that in theory companies that
implement voluntary diclosure indicate good news
or good performance by releasing sustainable
financial statements to differentiate from
competitors.
The relationship between the disclosure of non-
financial sustainability and sustainability
performance remains controversial when researchers
use the theory of voluntary disclosure and legitimacy
theory to explain its relationship to sustainability
performance (Hummel and Schlick, 2016). Whereas
according to Hidayah (2008) said that accurate and
detailed disclosure will provide a picture of the
actual performance of the company. Large
companies are more likely to get big risks, including
Islamic bank. According to Darmadi (2013)
conventional banks or Islamic banks are also at risk
due to the complex nature of their capital structure,
where banks present many short-term claims and
relative to customer and depositors' trust.
Hypothesis: There is a one-way relationship
between good Islamic business governance and
voluntary disclosure.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1
Population
Research approach used in this study is quantitative
approach which aims to test hypothesis with
measured data and produce generalizable
conclusion. The population in this study are the
annual financial report of Bank Syariah Mandiri,
Bank Muamalat Indonesia, Bank Negara Indonesia,
Bank Rakyat Indonesia, Bank Bukopin Indonesia,
Bank Mega Syariah Indonesia, and Bank Central
Asia Syariah for the period 2011-2017 December,
namely 49 financial reports.
The sample in this study is taken by purposive
sampling, where the sample is taken if it meets the
following criteria: First, the Islamic banks that
reported the complete financial period December
2011-2017. Secondly, 7 Islamic banks have the
largest assets in December 2017. Thirdly, Islamic
banks are still operating in Indonesia during the
period of December 2011-2017 (Bank Syariah
Mandiri, Bank Muamalat Indonesia, Bank Negara
Indonesia, Bank Rakyat Indonesia, Bank Bukopin
Indonesia, Bank Mega Syariah Indonesia, Bank
Central Asia Syariah).
3.2 Definition Operational of
Variables
3.2.1 Dependent Variable
Voluntary disclosure is the delivery of information
provided voluntarily by companies beyond the
obligated disclosure established by Bank Indonesia
(Meilani, 2016). The calculation of the voluntary
disclosure index refers to the study (al Bawat, 2015)
by providing a score of "1" for the item disclosed
and gives a score of "0" for an undisclosed item of
56 indicators.
3.2.2 Independent Variable
Good Islamic business governance is an important
element in maintaining the sustainability of business
growth (Meilani, 2016). Businesses that run with a
good governance concept will survive in the long
run. According to the national committee on
governance policy (2011) states that the ability to
maintain business power is very important for all
parties so that good governance for Islamic banks
can be illustrated by the consistency of the
implementation of good Islamic business
governance. According to Jumansyah and Syafei
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
138
(2013) that good Islamic business governance
consists of 42 indicators with a score of "1" for the
indicator disclosed and gives a score of "0" for the
undisclosed indicator.
3.2.3 Types and Sources of Data
The type of data used in this study is the annual time
series data from 2011-2017 which is sourced from
various books, journals and financial reports
published by Islamic banks in Indonesia.
3.2.4 Analysis Techniques of Data
Based on the problem formulation and research
objectives, the analytical technique used in this
study is using the granger causality test analysis tool.
Causality test is a test to determine the cause of
effect in Vector Auto Regressive (VAR) system.
Granger Causality test is used to know the
dependent variable (not independent variable) can be
influenced by other variables (independent variable).
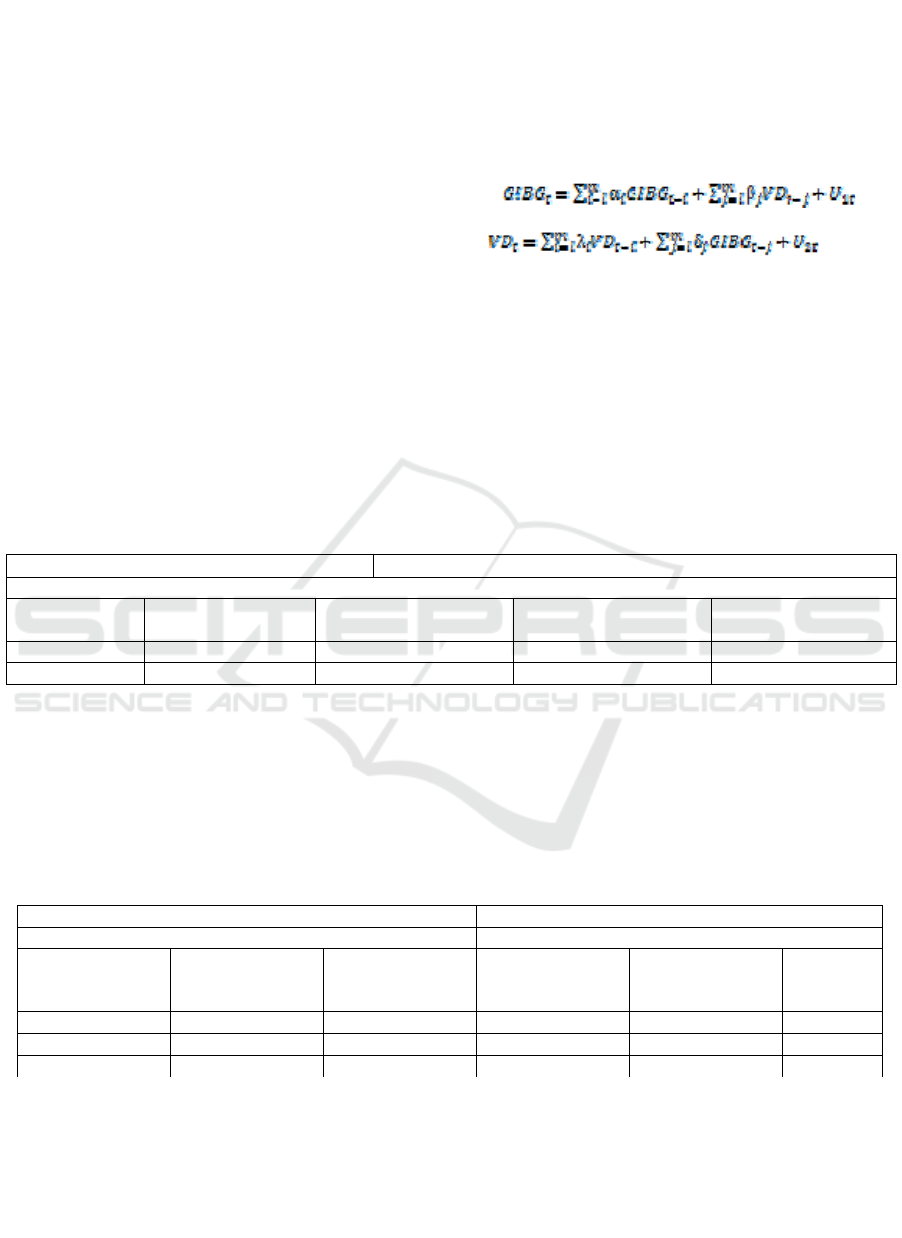
The model of granger causality can be formulated as
follows (Junaidi, 2012):
(1)
(2)
Where:
GIBG = Good Islamic Business Governance
VD = Voluntary Disclosure
Ut = Nuisance Variable
M = Number of lag
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Stationary Test (Unit Root Test)
Table 1: Stationary Test Result.
Dickey-fuller test for unit root
T-statistics and Critical Values
Interpolated dickey-fulle
r
Statistic Test 1% Critical Value 5% Critical Value 10% Critical
Value
GIBG -6.050 -3.594 -2.936 -2.602
VD -6.221 -3.594 -2.936 -2.602
Table 1 shows the stationary test result on the
degree level, where the t-statistical value for the
GIBG variable is -6.050 and VD of -6.221. The test
results show stationary data at critical values of 1%,
5%, and 10%, all variables have met the stationary
criteria because the resulting t-statistic value is more
negative than the critical value of 1%, 5%, and 10%.
4.2 Co-integration Test
Table 2 : C0-integration Test Result.
Vecrank GIBG VD, La
g
Johansen tests for co-inte
g
rations
Trent: constant La
g
s = 1
Maximum rank parms LL Eigenvalue Trace Statistic 5%
Critical
Value
0 2 -264.63211 71.7072 15.41
1 5 -241.57346 0.61740 25.5899 3.76
2 6 -228.77851 0.41323
From the results of table 4.3 can be seen in the co-
integration test using Johansen Test, obtained results
that variable GIBG and VD co-integrated in the long
term, which is indicated by trace statistic> critical
value 5%. The value of the trace statistic of the trace
test is 71.7072 greater than the critical value of
15.41, which means that in the system there is one
co-integrated equation. Trace statistic value of
25.5899 is greater than the critical value of 3.76.
This indicates that in the two variables (GIBG and
VD) in the Islamic bank in Indonesia in the period
RelationshipÂ
˘
a between the Application of Good Islamic Business Governance and Voluntary Disclosure on Islamic Bank in Indonesia
139

2011-2017 there is a long-term or co-integrated relationship.
4.3 Granger Causality-Test
Table 3 : Result of Granger Causality Test.
E
q
uation Exclude
d
Chi2 Df Prob > chi2
GIBG VD 1.4187 2 0.492
GIBG ALL 1.4187 2 0.492
VD GIBG 16.7 2 0.000
VD ALL 16.7 2 0.000
From the table above, it can be explained that which
has a granger causality relationship is a variable with
a probability value smaller than α 0.05. The variable
of good Islamic business governance (GIBG) does
not affect the voluntary disclosure (VD) variable
(0.492) and the voluntary disclosure variable (VD)
influences the good Islamic business governance
(GIBG) variable (0.000). It can be said that there is a
one-way relationship that is from VDÆGIBG that is
only the VD variable that statistically affect the
variable GIBG and not vice versa.
It can be argued that the implementation of good
Islamic business governance is highly dependent on
the growth of voluntary disclosure which
statistically has a positive relationship to good
Islamic business governance as well as good Islamic
business governance is not related to voluntary
disclosure. This is contrary to Meilani’s research
(2016) that good Islamic business governance has a
relationship with voluntary disclosure. The study
states that the contribution of Good Islamic business
governance implementation to the increase of
Voluntary Disclosure of Islamic bank in Indonesia is
11.56%, and the rest of 88.44% is influenced by
other factors beyond the application of Good Islamic
business governance. While in this study good
Islamic business governance has no influence on the
voluntary disclosure, otherwise voluntary disclosure
effect on good Islamic business governance.
The level of disclosure is strongly influenced by
the source of financing, revenue, legal system,
economic and political circumstances, level of
economic development, education and cultural level.
Costs that are needed in the disclosure are the
collection of information, management supervision
fees, auditor fees and legal counsel, and the cost of
disseminating information. The decision of the
company to make voluntary disclosure depends on
the incentives that will be obtained because there are
no rules that regulate it. Voluntary disclosure is
undertaken to reduce asymmetric information with
the aim of minimizing conflicts of interest between
management and shareholders.
If voluntary disclosure is well practiced then
good Islamic business governance will be good
because voluntary disclosure affects good Islamic
governance significantly. Based on a survey by
Mcinsey & Company (2002) many investors
consider that governance is at least as important as a
company's financial indicators. Therefore, voluntary
disclosure in Islamic banks must be optimized for
better governance so that the management of Islamic
banks increases.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The result of the measurement, it is concluded that
there is one-way relationship between voluntary
disclosure and good Islamic business governance
and vice versa there is no relation between good
Islamic business governance and voluntary
disclosure. It can be argued that the higher the
voluntary disclosure, the better the Islamic business
governance.
The variable of good Islamic business
governance (GIBG) does not affect the voluntary
disclosure (VD) variable (0.492) and the voluntary
disclosure variable (VD) influences the good Islamic
business governance (GIBG) variable (0.000). It can
be said that there is a one-way relationship that is
from VD Æ GIBG that is only the VD variable that
statistically affect the variable GIBG and not vice
versa.
REFERENCES
Albawat, Ala’ Hussein., Mohamad Yazis Ali Basah.,
2015. Corporate Governance and Voluntary
Disclosure of Interim Financial Reporting in Jordan.
Journal of Publik Administration and Governance.
ISSN 2161-7104 2015, Vol. 5, No. 2.
Albawat, Ala’ Hussein., 2015. The Relationship between
Voluntary Disclosure and Company Performances on
Interim Reports in Jordan Using the Method of
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
140

Causality Directions. International Journal of
Economic and Finance. Vol, 7, No. 7.
Indonesia, Bank., 2009. PBI No. 11/33/2009: Pelaksanaan
Good Islamic Governance Pada Bank Umum Syariah
dan Unit Usaha Syariah.
Barako, D. G, et. al. (2006). Relationship between
corporate governance attributes and voluntary
disclosures in annual reports: The Kenyan experience.
Financial Reporting, Regulation and Governance, 5.
1: 1-26.
Darmadi, Salim., 2013. Corporate governance disclosure
in the Annual Report An exploratory Study on
Indonesian Islamic Banks. Emerald Insight Journal
Humanomics. Vol. 29 No. 1.
Hidayah, E., 2008, Pengaruh Kualitas Pengungkapan
Informasi Terhadap Hubungan antara Penerapan
Corporate Governance dengan Kinerja Perusahaan di
Bursa Efek Jakarta, JAAI, Vol. 12, No. 1, Juni: 53-64.
Hummel, K., Schlick, C., (2016). The Relationship
Between Sustainability Performance and
Sustanaibility Disclosure-Reconciling Voluntary
Disclosure Theory and Legitimacy Theory. Journal of
Accounnting and Publik Policy, 35 (5), 455-476.
Jumansyah., Syafei., 2013. Analisis Penerapan Good
Governance Business Syariah dan Pencapaian
Maqashid Shariah Bank Syariah di Indonesia. Jurnal
Al-Azhar Indonesia Seri Pranata Sosial. Vol . 2, No. 1,
Maret 2013.
Juanda, Bambang., Junaidi., 2012, Ekonometrika Deret
Waktu Teori dan Aplikasi. IPB. PT Penerbit IPB Press.
Komite Nasional Kebijakan Governance. 2011. Pedoman
Umum Good Governance Business Syariah. Jakarta.
Indonesia.
Lys, T. Naughton, J., Wang, C., 2015. Signalin through
corpoate accountability reporting. Journal of
Accounting and Economic. 60. 1, 56-72.
Meilani, Sayekti Endah Retno., 2016. Penerapan Good
Governance Business Syariah dan Voluntary
Disclosure.
Shahul, H.M.I., 2001. Different Worldview Needs
Different Accounting. Paper presented at IIUM
International Conference of Accounting I, Kota Bahru,
Kelantan, Malaysia. Jurnal EKA CIDA. Vol. 1 No. 1,
Maret.
RelationshipÂ
˘
a between the Application of Good Islamic Business Governance and Voluntary Disclosure on Islamic Bank in Indonesia
141
